The basic features of the return mechanism in GST includes electronic filing of returns, uploading of invoice level information, auto-population of information relating to input tax credit from returns of supplier to that of recipient, invoice level information matching and auto-reversal of input tax credit in case of mismatch. The returns mechanism is designed to assist the taxpayer to file returns and avail ITC.
Under GST, a regular taxpayer needs to furnish monthly returns and one annual return. There are separate returns for a taxpayer registered under the composition scheme, non-resident taxpayer, taxpayer registered as an Input Service Distributor, a person liable to deduct or collect the tax (TDS/TCS), a person granted Unique Identification Number. It is important to note that a taxpayer is NOT required to file all the types of returns. In fact, taxpayers are required to file returns depending on the activities they undertake. The GST Council has however recommended to ease the compliance requirements for small tax payers by allowing taxpayers with annual aggregate turnover up to Rs. 1.5 Crore to file details of outward supplies in FORM GSTR-1 on a quarterly basis and on monthly basis by taxpayers with annual aggregate turnover greater than Rs. 1.5 Crore. Further, GST Council has recommended to postpone the date of filing of Forms GSTR-2 and GSTR-3 for all normal tax payers, irrespective of turnover, till further announcements are made in this regard.
All the returns are to be filed online. Returns can be filed using any of the following methods:
1. GSTN portal(gst.gov.in )
2. Offline utilities provided by GSTN
3. GST Suvidha Providers (GSPs). If a tax payer is already using the services of an ERP providers such as Tally, SAP, Oracle etc, there is a high likelihood that these ERP providers would provide inbuilt solutions in the existing ERP systems.
Following table lists the various types of returns under GST Law.
| Return | Description | Who Files? | Standard Date for fil-ing |
| GSTR – 1* | Statement of Outward sup- plies of Goods or Services | Normal Reg- istered Person | 10th of the next month |
| GSTR – 2* | Statement of Inward sup-plies of Goods or services | Normal Reg- istered person | 15th of the next month |
| GSTR – 3* | Return for a normal tax-payer | Normal Reg- istered Person | 20th of the next month |
| GSTR – 3B | Simple Monthly Return for the period Jul 2017 to March 2018 | Normal Reg- istered Person | 20th of the next month |
| GSTR-4 | Quarterly Re- turn | Taxable Per-son opting for Composition Levy | 18th of the month suc-ceeding the quarter |
| GSTR-5 | Monthly re-turn for a non-resident taxpayer | Non-resident taxpayer | 20th of the month suc-ceeding tax period & within 7 days after expiry of registration |
| GSTR – 5A | Monthly re-turn for a per-son supply-ing OIDAR services from a place out-side India to a non-taxable online recipi-ent | Supplier of OIDAR Ser- vices | 20th of the next month |
| GSTR-6 | Monthly re-turn for an Input Service Distributor (ISD) | Input Service Distributor | 13th of the next month |
| GSTR-7 | Monthly return for authorities deducting tax at source | Tax Deductor | 10th of the next month |
| GSTR-8 | Monthly statement for E-Commerce Operator depicting supplies effecting through it. | E-Commerce Operator | 10th of the next month |
| GSTR-9 | Annual Return | Registered Person other than an ISD, TDS/TCS Taxpayer, casual taxable person and Non-resident taxpayer. | 31st December of next Financial Year |
| GSTR – 9A | Simplified Annual Return under Composition Scheme | Taxable Person opting for Composition Levy | 31st December of next Financial Year |
| GSTR-10 | Final Return | Taxable per-son whose registration has been sur-rendered or cancelled. |
Within three months of the date of can-cellation or date of order of cancella-tion, which-ever is later. |
| GSTR-11 | Details of inward supplies to be furnished by a person having UIN | Persons who have been issued a Unique Identity-tity Number(UIN) | 28th of the next month |
* Registered persons having aggregate turnover of up to 1.5 Crore rupees in the preceding financial year or the current financial year shall furnish GSTR-1 on a quarterly basis. Other Registered persons having aggregate turnover of more than 1.5 Crore rupees shall furnish these returns on a monthly basis. Filing of GSTR-2 and GSTR-3 has been postponed till a further announcement in this regard is made.
Calendar for Return filing
The due dates for filing various GST returns may vary from the Standard dates mentioned in the table above. Various notifications are issued from time to time in this regard and as per the notifications issued till 29/12/2017.
| Return | Category of Taxpayer | Time Period | Due Date |
| GSTR-3B | All taxpayers to file along with payment of tax |
Every month till March 2018 |
20th of the succeeding month |
| GSTR-1 | Taxpayers with annual aggregate turnover up to Rs 1.5 Crore to file on Quarterly basis | July – Sep 2017 | 10th Jan 2018 |
| Oct – Dec 2017 | 15th Feb 2018 | ||
| Jan – Mar 2018 | 30th April 2018 | ||
| Taxpayers with annual aggregate turnover of more than Rs 1.5 Crore to file on Monthly basis | July – Oct 2017 | 10th Jan 2018 | |
| Nov 2017 | 10th Jan 2018 | ||
| Dec 2017 | 10th Feb 2018 | ||
| Jan 2018 | 10th Mar 2018 | ||
| Feb 2018 | 10th April 2018 | ||
| Mar 2018 | 10th May 2018 | ||
| GSTR-4 | Taxpayers who have opted for Composition scheme to file every quarter | Jul-Sep 2017 | 24th Dec 2017 |
| GSTR-5 | Non Resident Taxable Person to file every month | Jul-Dec 2017 | 31st Jan 2018 |
| GSTR-5A | Taxpayers supplying OIDAR services from a place outside India to a non-taxable online recipient | Jul-Dec 2017 | 31st Jan 2018 |
| GSTR-6 | Input Service Distributor | Jul 2017 | 31st Dec 2017 |
Note: Due dates have not been notified for GSTR-2 and GSTR-3 for any of the months. That is, a taxpayer need not file GSTR-2 and GSTR-3 for any of the months from July 2017 until a notification is issued in this regard mentioning the due dates. Till such time, Form GSTR-3B is required to be filed by tax payers instead of Form GSTR-3.
Revision of Returns:
The mechanism of filing of revised returns for any correction of errors/omissions has been done away with. The rectification of errors/omissions is allowed in the return for subsequent month(s). However, no rectification is allowed after furnishing of the return for the month of September following the end of the financial year to which such details pertain, or furnishing of the relevant annual return, whichever is earlier.
Interest on Late GST Payment
An interest of 18 percent is levied on the late payment of taxes under the GST regime. The interest would be levied for the days for which tax was not paid after the due date.
Penalty for non-filing of GST Returns
In case a taxpayer does not file his/her return within the due dates, he/she shall have to pay a late fee of Rs. 200/- i.e. Rs.100/- for CGST and Rs.100/- for SGST per day (up to a maximum of Rs. 5,000/-) from the due date to the date when the returns are actually filed.
Note: In case of GSTR-3B,
- For the months July to September, 2017, the late fee payable for failure to furnish the return has been waived completely.
- From the month of October 2017 onwards, the GST Council has recommended that the amount of late fee payable by a taxpayer whose tax liability for that month is ‘NIL’ is Rs. 20/- per day (Rs. 10/- per day each under CGST & SGST Acts). However, if the tax liability for that month is not ‘NIL’, the amount of late fee is Rs 50/- per day (Rs. 25/- per day each under CGST & SGST Acts)
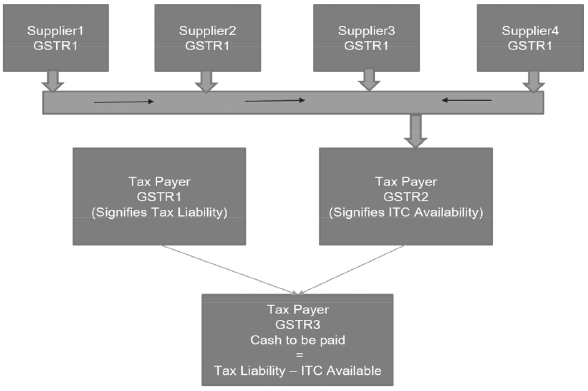
An overview of GSTR-1, GSTR-2 and GSTR-3
The population of these returns is explained by the following graphic:
NOTE:
1. Taxpayer’s GSTR2 is auto-populated from the Suppliers’ GSTR-1s
2. Taxpayer’s GSTR3 is significantly auto-populated from his/her’s GSTR1 and GSTR2
ReturnFilingMilestones:
ITC Matching and Auto-Reversal:
1. It is a mechanism to prevent revenue leakage and to facilitate availment of eligible and rightful ITC by taxpayers .
2. The process of ITC Matching begins after the due date for filing of the return (20th). This is carried out by GSTN.
3. The details of every inward supply furnished by the taxable person (i.e. the “recipient” of goods and/or services) in form GSTR-2 shall be matched with the corresponding details of outward supply furnished by the corresponding taxable person (i.e. the “supplier” of goods and / or services) in his valid return. A return may be considered to be a valid return only when the appropriate GST has been paid in full by the taxable person as shown in such return for a given tax period.
4. In case the details match, then the ITC claimed by the recipient in his valid returns shall be considered as finally accepted and such acceptance shall be communicated to the recipient. Failure to file valid return by the supplier may lead to denial of ITC in the hands of the recipient.
5. In case the ITC claimed by the recipient is in excess of the tax declared by the supplier or where the details of outward supply are not declared by the supplier in his valid returns, the discrepancy shall be communicated to both the supplier and the recipient. Similarly, in case, there is duplication of claim of ITC, the same shall be communicated to the recipient.
6. The recipient will be asked to rectify the discrepancy of excess claim of ITC and in case the Supplier has not rectified the discrepancy communicated in his valid returns for the month in which discrepancy is communicated then such excess ITC as claimed by the recipient shall be added to the output tax liability of the recipient in the succeeding month.
7. Similarly, duplication of ITC claimed by the recipient shall be added to the output tax liability of the recipient in the month in which such duplication is communicated.
8. The recipient shall be liable to pay interest on the excess or duplicate ITC added back to the output tax liability of the recipient from the date of availing of ITC till the corresponding additions are made in their returns.
9. Re-claim of ITC refers to taking back the ITC reversed in the Electronic Credit Ledger of the recipient by way of reducing the output tax liability. Such re-claim can be made by the recipient only in case the supplier declares the details of invoice and/or Debit Notes in his valid return within the prescribed timeframe. In such case, the interest paid by the recipient shall be refunded to him by way of crediting the amount to his Electronic Cash Ledger.
Note: It may be noted that the return process is being examined by a Committee of officers and has not been finalised so far.





A very nice and comprehensive Article on the subject.
knowledge enhancing article, thank you so much