Act and Rules with respect to E-Way Bill.
CGST Act 68. Inspection of goods in movement.—
(1) The Government may require the person in charge of a conveyance carrying any consignment of goods of value exceeding such amount as may be specified to carry with him such documents and such devices as may be prescribed.
(2) The details of documents required to be carried under sub-section (1) shall be validated in such manner as may be prescribed.
(3) Where any conveyance referred to in sub-section (1) is intercepted by the proper officer at any place, he may require the person in charge of the said conveyance to produce the documents prescribed under the said sub-section and devices for verification, and the said person shall be liable to produce the documents and devices and also allow the inspection of goods.
Rules 138 to 138E of the CGST Rules lay down, in detail, the provisions relating to e-way bills.
138A. Documents and devices to be carried by a person-in-charge of a conveyance.-
(1) The person in charge of a conveyance shall carry—
(a) the invoice or bill of supply or delivery challan, as the case may be; and
(b) a copy of the e-way bill in physical form or the e-way bill number in electronic form or mapped to a Radio Frequency Identification Device embedded on to the conveyance in such manner as may be notified by the Commissioner:
Provided that nothing contained in clause (b) of this sub-rule shall apply in case of movement of goods by rail or by air or vessel:
[Provided further that in case of imported goods, the person in charge of a conveyance shall also carry a copy of the bill of entry filed by the importer of such goods and shall indicate the number and date of the bill of entry in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01.]
2. In case, invoice is issued in the manner prescribed under sub-rule(4) of rule 48,the quick Response(QR) code having an embedded invoice reference Number (IRN) in it, may be produced electronically, for verification by the proper officer in lieu of the physical copy of such tax invoice.
(3) Where the registered person uploads the invoice under sub-rule (2), the information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 shall be auto-populated by the common portal on the basis of the information furnished in FORM GST INV-1.
(4) The Commissioner may, by notification, require a class of transporters to obtain a unique Radio Frequency Identification Device and get the said device embedded on to the conveyance and map the e-way bill to the Radio Frequency Identification Device prior to the movement of goods.
(5) Notwithstanding anything contained in clause (b) of sub-rule (1), where circumstances so warrant, the Commissioner may, by notification, require the person-incharge of the conveyance to carry the following documents instead of the e-way bill
(a) tax invoice or bill of supply or bill of entry; or
(b) a delivery challan, where the goods are transported for reasons other than by way of supply.
Practical Aspects
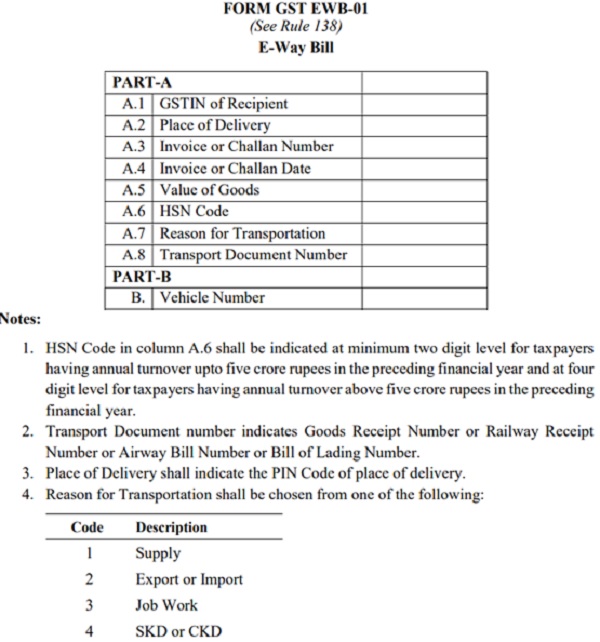
E-way bill (Form GST EWB-01) is an electronic document (available to consignor (i.e. supplier) / consignee (i.e. recipient) / transporter) generated on the common portal evidencing movement of goods of consignment value more than ₹ 50,000/-. It has two Components –
(i) Part A comprising of details of GSTIN of supplier and – recipient, place of despatch (indicated by PIN code), place of delivery (indicating PIN Code also), document (Tax invoice, Bill of Supply, Delivery Challan or Bill of Entry) number and date, value of goods, HSN code, and reasons for transportation; and
ii) Part B –comprising of transport details – transport document number (Goods Receipt Number or Railway Receipt Number or Airway Bill Number or Bill of Lading Number) and Vehicle number for road.
E-Way Bill

(Source: https://docs.ewaybillgst.gov.in/Documents/GST_EWB_01.pdf)
E-Way Bill Portal
(Source: https://ewaybillgst.gov.in/)
E-Way Bill Portal
(Source : https://ewaybillgst.gov.in/)
Exceptions to e-way bill requirement
No e-way bill is required to be generated in the following cases
a) Transport of goods as specified in Annexure to Rule 138 of the CGST Rules, 2017
b) goods being transported by a non-motorised conveyance;
c) goods being transported from the port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station to an inland container depot or a container freight station for clearance by Customs;
d) in respect of movement of goods within such areas as are notified under rule 138(14) (d) of the SGST Rules, 2017 of the concerned State; and
e) Consignment value less than Rs. 50,000/
Who should Generate an e-way Bill?
Registered Person – e-way bill must be generated when there is a movement of goods of more than ₹ 50,000 in value to or from a registered person. A Registered person or the transporter may opt to generate and carry e-way bill even if the value of goods is less than ₹ 50,000.
Unregistered Persons – Unregistered persons are also required to generate e-way Bill. However, where a supply is made by an unregistered person to a registered person, the receiver will have to ensure all the compliances are met as if they were the supplier.
Transporter – Transporters carrying goods by road, air, rail, etc. also need to generate e-way Bill if the supplier has not generated an e-way Bill. Unregistered transporters will be issued Transporter ID on enrolling on the e-way bill portal after which e-way bills can be generated.
(Source: https://keralataxes.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/1_EWB_basics.pdf)
References:
1. https://keralataxes.gov.in/2018/03/31/e-waybill/
2. https://icmai.in/upload/Students/Syllabus2022/Inter_Stdy_Mtrl/P7_B.pdf.
3. https://www.cbic.gov.in/resources//htdocs-cbec/gst/E%20Way%20Bill%20Provisions%20in%20GST_Web.pdf





