GOODS AND SERVICE TAX COUNCIL
Issue-22, January 2021
Announcements Related to GST in Union Budget 2021-22
 On 1 February, 2021 the Hon’ble Finance Minister, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman presented the first ever paperless budget in the history. She rested the budget proposals on six pillars of: (i) Health and Wellbeing (ii) Physical & Financial Capital, and Infrastructure (iii) Inclusive Development for Aspirational India (iv) Reinvigorating Human Capital (v) Innovation and R&D (vi) Minimum Government and Maximum Governance.
On 1 February, 2021 the Hon’ble Finance Minister, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman presented the first ever paperless budget in the history. She rested the budget proposals on six pillars of: (i) Health and Wellbeing (ii) Physical & Financial Capital, and Infrastructure (iii) Inclusive Development for Aspirational India (iv) Reinvigorating Human Capital (v) Innovation and R&D (vi) Minimum Government and Maximum Governance.
In the indirect tax proposals, the following measures taken to simplify GST were highlighted: (i) nil return through SMS, (ii) quarterly return and monthly payment for small taxpayers (QRMP Scheme), (iii) electronic invoice system, (iv) validated input tax statement, (v) pre-filled editable GST return, and (vi) staggering of returns filing.
The capacity of GSTN system has been enhanced. The Government has also deployed deep analytics and Artificial Intelligence to identify tax evaders and fake billers and launched special drives against them. The results speak for themselves as record collections have been made in the last few months.
In statement I, Consolidated Fund of India – Revenue account- Receipts, the GST revised estimates and budget estimates were presented as follows:
| GST Revenue | BE 2020-21 |
RE 2020-21 |
BE 2021-22 |
| CGST | 580000 | 431000 | 530000 |
| UTGST | 3000 | 2719.49 | 3327.13 |
| IGST | ….. | ….. | ….. |
| Comp. Cess | 110500 | 84100 | 100000 |
Rs. in Crore
Note: CGST figures after settlement
Budget Highlights
Legislative Changes in CGST Act, 2017 and IGST Act, 2017 as per Finance Bill 2020-21
The Finance Bill proposes certain changes in the CGST Act and the IGST Act on the basis of recommendations made by the GST Council.
These includes measures for:
(i) facilitating taxpayers, such as remove the mandatory requirement of getting annual accounts audited and reconciliation statement, filing of the annual return on self-certification basis and charging interest on net cash liability with effect from the 1st July, 2017.
(ii) improving compliance, such as availment of input tax credit only when the details have been furnished by the supplier in the statement of outward supplies, validity of provisional attachment for a period, zero-rating on payment of IGST only in specified cases and linking it to the receipt of foreign remittances.
(iii) making certain other changes relating to seizure and confiscation, filing of appeal only on payment of a sum equal to twenty-five per cent of penalty imposed.
Source: Budget Speech pp 61 & 62
Amendments proposed in the CGST Act, 2017
To improve trade facilitation, revenue augmentation and legal gap correction, the following amendments are proposed in the CGST Act, 2017 and IGST Act, 2017 through Finance Bill 2020-21:
| Clause | Amendment |
| 99 | A new clause (aa) in sub-section (1) of Section 7 of the CGST Act is being inserted, retrospectively with effect from the 1st July, 2017, so as to ensure levy of tax on activities or transactions involving supply of goods or services by any person, other than an individual, to its members or constituents or vice-versa, for cash, deferred payment or other valuable consideration. |
| 100 | A new clause (aa) to sub-section (2) of the section 16 of the CGST Act is being inserted to provide that input tax credit on invoice or debit note may be availed only when the details of such invoice or debit note have been furnished by the supplier in the statement of outward supplies and such details have been communicated to the recipient of such invoice or debit note |
| 101 | Sub-section (5) of section 35 of the CGST Act is being omitted so as to remove the mandatory requirement of getting annual accounts audited and reconciliation statement submitted by specified professional. |
| 102 | Section 44 of the CGST Act is being substituted so as to remove the mandatory requirement of furnishing a reconciliation statement duly audited by specified professional and to provide for filing of the annual return on self-certification basis. It further provides for the Commissioner to exempt a class of taxpayers from the requirement of filing the annual return |
| 103 | Section 50 of the CGST Act is being amended, retrospectively, to substitute the proviso to sub-section (1) so as to charge interest on net cash liability with effect from the 1st July, 2017. |
| 104 | Section 74 of the CGST Act is being amended so as make seizure and confiscation of goods and conveyances in transit a separate proceeding from recovery of tax |
| 105 | An explanation to sub-section (12) of section 75 of the CGST Act is being inserted to clarify that “self-assessed tax” shall include the tax payable in respect of outward supplies, the details of which have been furnished under section 37, but not included in the return furnished under section 39. |
| 106 | Section 83 of the CGST Act is being amended so as to provide that provisional attachment shall remain valid for the entire period starting from the initiation of any proceeding under Chapter XII, Chapter XIV or Chapter XV till the expiry of a period of one year from the date of order made thereunder. |
| 107 | A proviso to sub-section (6) of section 107 of the CGST Act is being inserted to provide that no appeal shall be filed against an order made under sub-section (3) of section 129, unless a sum equal to twenty-five per cent. of penalty has been paid by the appellant. |
| 108 | Section 129 of the CGST Act is being amended to delink the proceedings under that section relating to detention, seizure and release of goods and conveyances in transit, from the proceedings under section 130 relating to confiscation of goods or conveyances and levy of penalty. |
| 109 | Section 130 of the CGST Act is being amended to delink the proceedings under that section relating to confiscation of goods or conveyances and levy of penalty from the proceedings under section 129 relating to detention, seizure and release of goods and conveyances in transit. |
| 110 | Section 151 of the CGST Act is being substituted to empower the jurisdictional commissioner to call for information from any person relating to any matter dealt with in connection with the Act. |
| 111 | Section 152 of the CGST Act is being amended so as to provide that no information obtained under sections 150 and 151 shall be used for the purposes of any proceedings under the Act without giving an opportunity of being heard to the person concerned. |
| 112 | Section 168 of the CGST Act is being amended to enable the jurisdictional commissioner to exercise powers under section 151 to call for information. |
| 113 | Consequent to the amendment in section 7 of the CGST Act paragraph 7 of Schedule II to the CGST Act is being omitted retrospectively, with effect from the 1st July, 2017. |
Amendments proposed in the IGST Act, 2017
| Clause | Amendment |
| 114 | Section 16 of the IGST Act is being amended so as to:
(i) zero rate the supply of goods or services to a Special Economic Zone developer or a Special Economic Zone unit only when the said supply is for authorised operations; (ii) restrict the zero-rated supply on payment of integrated tax only to a notified class of taxpayers or notified supplies of goods or services; and (iii) link the foreign exchange remittance in case of export of goods with refund.. |
Source: Memorandum of Explaining the Provisions of Finance Bill 2021
Notifications & Circulars
CGST (Amendment) Rules, 2021
A new sub-rule 6 is inserted to Rule 59 of the CGST Rules, 2017, restricting or blocking the filing of GSTR-1 as follows:
(a) For monthly filing of GSTR-1, where GSTR-3B filing for the preceding two months has not been filed, then furnishing the details of outward supplies in GSTR-1 for the current month shall not be allowed.
(b) For quarterly filing of GSTR-1, where GSTR-3B filing for the preceding tax period has not been filed, then he cannot use IFF nor file GSTR-1 for the current quarter.
(c) A registered person who is restricted from using the amount available in electronic credit ledger to discharge his tax liability in excess of 99% under Rule 86B, cannot use the IFF or file GSTR-1 if the preceding tax period’s GSTR-3B has not been filed.
Source: Notification No. 1/2021-CT dated 12.01.2021
Jurisdiction of Commissioner Appeals for Delhi and Mumbai amended
CBIC amends Jurisdiction of Principal Chief Commissioner/Chief Commissioner of Central Tax in terms of specified Commissioner (Appeals) and Additional Commissioner (Appeals) for Delhi & Mumbai.
Source: Notification No. 2/2021-CT dated 12.01.2021
GST Portal Updates
♦ IFF for Taxpayers under QRMP Scheme
Invoice Furnishing Facility (IFF) facility has been provided to taxpayers under QRMP Scheme (Quarterly filers of Form GSTR-1 and also of Form GSTR-3B returns), as per sub-rule (2) of Rule-59 of the CGST Rules, 2017. Taxpayers who have opted for quarterly filing frequency under the scheme can file their details of outward supplies (B2B invoices only) for first two months of a quarter (M1 and M2 respectively of a Quarter) in IFF.
Updated on 06.01.2021
♦ Aadhaar Authentication / e-KYC for Existing Taxpayers
Functionality for Aadhaar Authentication and e-KYC where Aadhaar is not available, has been deployed on GST Common Portal w.e.f. 6th January, 2021, for existing taxpayers. All taxpayers registered as Regular Taxpayers (including Casual Taxable person, SEZ Units/Developers), ISD and Composition taxpayers can do their Aadhaar Authentication or e-KYC on GST Portal. This is not applicable for Government Departments, Public Sector Undertakings, Local Authorities and Statutory Bodies.
Updated on 07.01.2021
♦ Auto-population of e-invoice details into GSTR-1
E-invoice facility was made applicable for certain notified taxpayers from 1.10.2020. It has also been extended to taxpayers with the aggregate turnover of above 100 Cr. from 1.1.2021. Details from the reported e-invoices are being auto-populated in respective tables of GSTR-1. A detailed advisory regarding methodology of auto-population of e-invoice details into GSTR-1 has already been published on GSTR-1 dashboard.
It was observed that while pulling the e-invoice data for the month of December, 2020 into GSTR-1, details of some invoices were not populated into GSTR-1. This inadvertent gap is being rectified on priority and details of those invoices will be pushed into GSTR-1 shortly. However, taxpayers should not wait for the same and are advised to proceed with the preparation and filing of GSTR-1 for the month of December, 2020 onwards, based on actual data as per their records.
The taxpayers may modify/delete only those documents where the details auto-populated from e-invoices are not as per the actual documents issued. Otherwise, the details of e-invoices auto-populated in GSTR-1 can be edited/deleted by the taxpayer. However, in such cases, the ‘Source’, ‘IRN’ and ‘IRN date’ fields will be reset to blank in respective tables of GSTR-1 and accordingly won’t get reflected in GSTR-2A/2B/4A/6A also. Such edited documents will be treated as if they were not auto-populated but uploaded separately by the taxpayer.
Other than the details auto-populated from e-invoices, taxpayers are required to add details of any other supplies made in respective tables of GSTR-1. An additional facility of consolidated excel download of all documents auto-populated from e-invoices is available in GSTR-1 dashboard. This file includes details of cancelled documents also. However, any subsequent modifications made to the auto-populated documents (in GSTR-1 tables) would not be reflected in this excel file.
Updated on 11.01.2021
♦ Due dates for filing of Form GSTR-3B for December, 2020
As per Rule 61(6) of the CGST Rules, 2017, the taxpayers had to file GSTR-3B returns for the tax period of December, 2020 in staggered manner as under:
| Turnover in the previous FY | Principal place of business (State/UTs) |
Due date for filing GSTR-3B for Dec. 2020 |
| More than Rs 5 Crore |
All States and UTs | 20th January, 2021 |
| Upto Rs 5 Crore | States of Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, the Union territories of Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep | 22nd January, 2021 |
| Upto Rs 5 Crore
|
States of Himachal Pradesh, Pannjab, Uttarakand, Haryana Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Sikkim,Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya, Assam, West Bengal, Jharkhand and Odisha, the Union territories of Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Chandigarh and Delhi | 24th January, 2021
|
Updated on 13.01.2021
Best Practices by Stat
Kerala GST Department issues informer management instructions
The Kerala State Goods and Services Tax department has issued informer management instructions for grant of reward to informers and government servants. In this regard, detailed guidelines and principles have been issued to manage the informer details in the offices concerned. Source: Kerala GST Department, Circular No. 01/2021 dated 06.01.2021
Karnataka GST Department issued GST Audit Manual
The Karnataka State GST Department has issued instructions on procedure of GST Audit outlining the principles and policies of audit to ensure that the audit of taxpayers is carried out in uniform, effective and comprehensive manner.
Source: Karnataka GST Audit Manual, dated 01.01.2021.
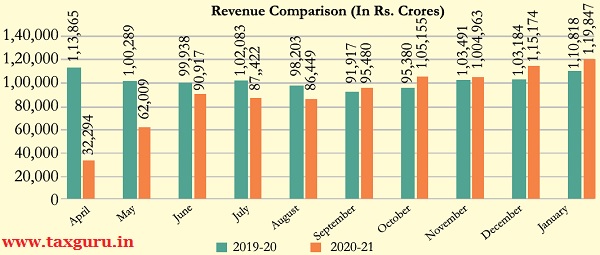
GST Revenue for January 2021
The gross GST revenue collected in the month of January 2021 is Rs. 1,19,847 crore of which CGST is Rs. 21,923 crore, SGST is Rs. 29,014 crore, IGST is Rs. 60,288 crore (including Rs. 27,424 crore collected on import of goods) and Cess is Rs. 8,622 crore (including Rs. 883crore collected on import of goods). The total revenue earned by Central Government and the State Governments after regular settlement in the month of January 2021 is Rs. 46,454 crore for CGST and Rs. 48,385 crore for the SGST.
In line with the trend of recovery in the GST revenues over past five months, the revenues for the month of January 2021 are 8% higher than the GST revenues in the same month last year, which in itself was more than Rs. 1.1 lakh crore. During the month, revenues from import of goods are 16% higher and the revenues from domestic transaction (including import of services) are 6% higher than the revenues from these sources during the same month last year.
Collection of GST revenues above Rs. 1 lakh crore over a stretch of last four months reflect a steep increasing trend over this period which are clear indicators of a rapid economic recovery post pandemic. Closer monitoring against fake-billing, deep data analytics using data from multiple sources including GST, Income-tax and Customs IT systems; coupled with effective tax administration have also contributed to the steady increase in tax revenue over last few months. The average YoY growth in GST revenue over the first four months in the second half of the financial year has been 8% as compared to (-) 24% during the first half of the year. The chart below shows trends in monthly gross GST revenues during the current year.
Source: PIB Press Release dated 31 .01.2021
DISCLAIMER: This newsletter is in-house efforts of the GST Council Secretariat. The Contents of this newsletter do not represent the views of GST Council and are for reference purpose only.