The importance of Corporate Social Responsibility (hereafter referred as CSR) was much more defined in the new Company Law of 2013 in comparison to the erstwhile Companies Act where there was no specified provision for the same. With the enactment of the Companies Act 2013 by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs Government of India, the introduction of Corporate Social Responsibility as a mandatory provision by imposing a statutory obligation on specified Companies to take up CSR projects towards social welfare activities.
By introduction of this new law India is the only country to regulate and mandate the CSR activities for some selected group of Companies as registered under the said act. The primary motive behind the introduction of CSR was to push the nation towards achievement of sustainable development goals and public private partnership in transforming India.
The Corporate Social Responsibility concept in India is governed by Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 and Rules made thereunder wherein the criteria has been provided for assessing the CSR eligibility of a company, Implementation and accordingly to effectively report their CSR Policies. India having one of the most exhaustive CSR mechanism and implementation strategy has started its journey to set a benchmark in attaining sustainability goals and stakeholder activism in nation building.
The Government of India by introduction of the Companies (Corporate Social Responsibility Policy) Amendment Rules, 2021 (“Rules”) on January 22, 2021, thus giving effect to the changes introduced in CSR by the Companies Amendment Acts and rules of 2019 and 2020. The Amendment Rules 2021 shall come into force on the date of their publication in the Official Gazette i.e. January 22, 2021 unless explicitly provided elsewhere in this notification.
Further, various amendments made in the rules such as pertaining to the CSR regime, including allowing corporates to undertake multi-year projects and making registration compulsory for agencies implementing CSR activities on behalf of companies. Also, companies have been permitted to set off the excess amount spent under the ambit of CSR up to three succeeding financial years and they have also been allowed to create or acquire capital assets through CSR in the name of beneficiaries or a public authority or registered trust, among others. Non-compliance with CSR provisions has been decriminalised by shifting such offences to penalty regime, while companies whose CSR spending obligation stands below Rupees Fifty Lakhs shall be exempted from constituting a CSR committee.
KEY AMENDMENTS IN CSR RULES VIDE NOTIFICATION DATED JANUARY 22, 2021:
| Sr No. | Rule No. | Particulars | Amendment |
| 1. | 2(1)(d) | Definition of “CSR” & List of Activities Not Includible In CSR | Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)” means the activities undertaken by a Company in accordance with its statutory obligation in pursuance to section 135 of the Companies Act 2013 in accordance with the provisions contained in these rules, but shall not include the following, namely: –
(i) activities undertaken in the normal course of its business Provided that any company which undertakes any business activity in relation to development of new vaccine, drugs and medical devices in their normal course of business may undertake research and development activity of new vaccine, drugs and medical devices related to COVID-19 for financial years 2020-21, 2021-22, 2022-23 subject to the conditions that- such research and development activities shall be carried out in collaboration with any of the institutes or organisations mentioned in item (ix) of Schedule VII to the Act; (a) The Annual Report on CSR Shall separately disclose such activities; (ii) any activity undertaken by the company outside India, provided that training of Indian sports personnel representing any State or Union territory at national level or India at international level shall be an exception; (iii) contribution of any amount directly or indirectly to any political party under section 182 of the Act; (iv) activities benefiting employees of the company as defined in clause (k) of section 2 of the Code on Wages, 2019 (29 of 2019); (v) activities support ed by the companies on sponsorship basis for deriving marketing benefits for its products or services; (vi) activities carried out for fulfilment of any other statutory obligations under any law in force in India; |
| 2. | 4(1) | CSR Implementation through Eligible entities | The CSR liabilities can be undertaken through the following eligible entities: –
(a) A company as incorporated under section 8 of the Companies Act, or a registered public trust or a registered society, registered under section 12A and 80 G of the Income Tax Act, 1961 established by the company, either singly or along with any other company, or (b) A company as incorporated under section 8 of the Companies Act, established by the Central Government or State Government; or (c) Any entity established under an Act of Parliament or a State legislature; or (d) A company established under section 8 of the Act, or a registered public trust or a registered society, registered under section 12A and 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961, and having an established track record of at least three years in undertaking similar activities. |
| 3. | 4(2) | Registration by the Entity undertakes CSR activity | Every entity who intends to undertake any CSR activity, shall register itself with the Central Government by filing the form CSR-1 electronically with the Registrar of Companies, with effect from the April 01, 2021.
Form CSR-1 shall be signed and submitted electronically by the entity and shall be verified digitally by a Chartered Accountant in practice or a Company Secretary in practice or a Cost Accountant in practice. On the submission of the Form CSR-1 on the portal, a unique CSR Registration Number shall be generated by the system automatically The provisions of this sub-rule of the Companies Amendment Rules shall not affect the CSR projects or programs approved prior to the 01st day of April 2021. |
| 4. | 4(3) | International Organizations | A company may engage international organizations for designing, monitoring, and evaluation of the CSR projects or programs as per its CSR policy as well as for the capacity building of their personnel for CSR. |
| 5. | 4(4) | Collaboration with other companies | A company may also collaborate with other companies for undertaking projects or programs or CSR activities in such a manner that the CSR committees of such respective companies as to whether they are in a position to report separately on such projects or programs in accordance with these rules. |
| 6. | 4(5) | Utilization of Fund | The Board of a company shall satisfy itself that the funds disbursed to the entities for CSR have been utilized for the purposes and in the manner as approved by it and the Chief Financial Officer or the person responsible for financial management shall certify to the effect. |
| 7. | 4(6) | Monitoring of Ongoing Projects | In case of the ongoing project, the Board of a Company shall monitor the implementation of the project with reference to the approved timelines and year-wise allocation and shall be competent to make such requisite modifications, if any for smooth and effective implementation of the project within the overall permissible limit.
Any amount remaining unspent in accordance to any ongoing project, undertaken by a company in pursuance of its CSR Policy shall be transferred by the company in the unspent CSR Account. |
| 8. | 5(2) | Annual Plan | The CSR committee shall formulate & recommend an annual plan to the Board.
The annual plan by the CSR committee shall include (a) The list of CSR projects or programs that are approved to be undertaken in areas or subjects specified in Schedule VII of the Act. (b) The manner of execution of such projects or programs. (c) The modalities of utilization of funds and implementation schedules for the projects or programs. (d) Monitoring and reporting mechanism for the projects or programs. (e) The details of need and impact assessment, if any, for the projects undertaken by the company. The Board of the company may alter the plan at any time during the financial year, as per the recommendation of the CSR committee based on the reasonable justification to that effect. |
| 9. | 7(1) | Administrative Overheads | The board shall ensure that the administrative overheads shall not exceed five percent of the total CSR expenditure of the company for the financial year.
Administrative overheads mean the expenses incurred by the company for general management and administration of CSR functions in the company [Rule 2(b)] Administrative overhead shall not include the expenses directly incurred for the designing, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of a particular CSR project or program. |
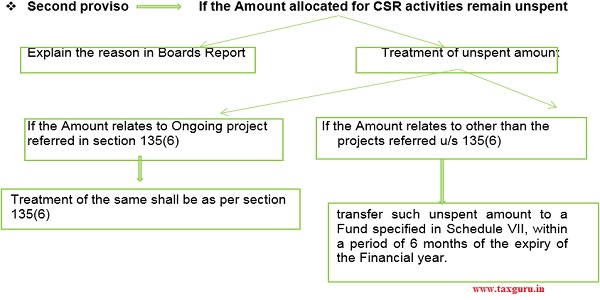
| 10. | 7(2) | Surplus Arises out of CSR Activities | Any surplus arising out of the CSR activities shall not form part of the business profit of a company and shall be ploughed back into the same project or shall be transferred to the Unspent CSR Account and spent in pursuance of CSR policy and annual action plan of the company or transfer such surplus amount to a Fund specified in Schedule VII, within a period of six months of the expiry of the financial year. |
| 11. | 8 | CSR Reporting | he Board’s Report of a company covered under these rules pertaining to any financial year shall include an annual report on CSR containing particulars specified in Annexure I or Annexure II, as applicable.
In case of a foreign company, the balance sheet filed section 381(1)(b) of the Act, shall contain an annual report on CSR containing particulars specified in Annexure I or Annexure II, as applicable |
| 12. | 8(3) | Impact Assessment | Every company having an average CSR obligation of ten crore rupees or more in the three immediately preceding financial years, shall undertake impact assessment, through an independent agency, of their CSR projects having outlays of one crore rupees or more, and which have been completed not less than one year before undertaking the impact study.
The impact assessment reports shall be placed before the Board and shall be annexed to the annual report on CSR. A Company undertaking impact assessment may book the expenditure towards Corporate Social Responsibility for that financial year, which shall not exceed five percent of the total CSR expenditure. |
| 13. | 9 | Transfer of Unspent CSR Amount | The unspent CSR amount, if any shall be transferred by the company to any fund included in Schedule VII of the Act until a fund is specified in Schedule VII for the purpose of transferring unspent CSR amount.
The Board of Directors of the Company shall mandatorily disclose the composition of the CSR Committee, and CSR Policy and Projects approved by the Board on their website, if any, for public access. |
AMENDMENTS IN CSR PROVISION THROUGH THE (CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY POLICY) AMENDMENT RULES, 2021
♦ Section 135(5): The Board of every company referred to in sub-section (1), shall ensure that the company spends, in every financial year, at least two per cent. of the average net profits of the company made during the three immediately preceding financial years or where the company has not completed the period of three financial years since its incorporation, during such immediately preceding financial years, in pursuance of its Corporate Social Responsibility Policy.
Provided also that if the company spends an amount in excess of the requirements provided under this sub-section, such company may set off such excess amount against the requirement to spend under this sub-section for such number of succeeding financial years and in such manner, as may be prescribed.
CONCLUSION
It is evident from the amendments that now the companies would not be in a position to take the advantage for not spending the CSR amounts by putting cliché explanations in the annual report. The amendments have introduced penalty provisions for not complying with the CSR regulations, thus it has moved to comply or penalty from comply or explain. Also, as per CARO-2020, the auditor is also required to comment on the CSR provisions specifically pertaining to the unspent amount and whether it has been transferred.
SOURCE
https://taxguru.in/company-law/companies-csr-policy-amen.html
DISCLAIMER
The entire contents of this article have been prepared on the basis of relevant provisions and as per the information existing at the time of the preparation. Although care has been taken to ensure the accuracy, completeness and reliability of the information provided, we assume no responsibility therefore. Users of this information are expected to refer to the relevant existing provisions of applicable Laws. We assume no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information. In no event shall we shall be liable for any direct, indirect, special or incidental damage resulting from, arising out of or in connection with the use of the information. This is only a knowledge sharing initiative and author does not intend to solicit any business or profession.

| Mehul Solanki | Saurabh Vaze |
| Research Associate | Jaya Sharma & Associates |
| Jaya Sharma & Associates | bodha@jsa-cs.com |
| bodha@jsa-cs.com |





