Understanding Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs): A Crucial Component of India’s Financial Landscape
In the complex web of India’s financial ecosystem, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) play a pivotal role, often serving as the lifeline for sectors and individuals underserved by traditional banks. NBFCs have evolved significantly over the years, adapting to market dynamics and filling critical gaps in financial services.
What are NBFCs?
Non-Banking Financial Companies are financial institutions that provide banking services such as loans and advances, acquisition of shares/stocks/bonds/debentures/securities issued by government or local authority or other marketable securities of a like nature, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance business, chit business but does not include any institution whose principal business is that of agriculture activity, industrial activity, purchase or sale of any goods (other than securities) or providing any services and under.
What Is An NBFC
It is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956 or Companies Act 2013 as the case may be, engaged in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of shares/stocks/bonds/debentures/securities issued by Government or local authority or other marketable securities of a like nature, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance business, chit business but does not include any institution whose principal business is that of agriculture activity, industrial activity, purchase or sale of any goods (other than securities) or providing any services and sale/purchase/construction of immovable property
In terms of Section 45-IA of the RBI Act, 1934, no Non-banking Financial company can commence or carry on business of a non-banking financial institution without a) obtaining a certificate of registration from the Bank and without having a Net Owned Funds of 25lakhs ( Two crore since April 1999). However, in terms of the powers given to the Bank, to obviate dual regulation, certain categories of NBFCs which are regulated by other Regulators are exempted from the requirement of registration with RBI
Different Types/Categories of NBFCS
i. Deposit Taking NBFC’s
ii. Non-Deposit Taking NBFC’s
iii. Non-Deposit Taking NBFC’s-systemically important
iv. Non-Deposit Taking NBFC’s- Not systemically important
NBFC’s By the kind of activity

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has implemented significant changes in the regulatory framework for Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs). The Master Direction – Reserve Bank of India (Non-Banking Financial Company – Scale Based Regulation) Directions, 2023 categorizes NBFCs into four layers, impacting their operations and compliance requirements:
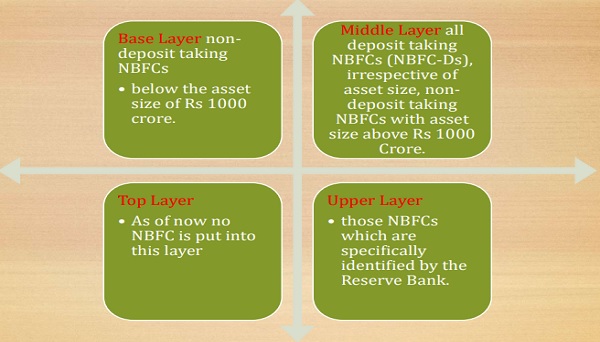
NBFC new return applicability and filing.
NBFC new return applicability and filing RBI has recently introduced XBRL returns for filing all NBFC returns CIMS portal for filing all applicable return of NBFC’s NBFC’s having assets size between Rs. 2 Crore and below Rs. 100 Crores.
- DNBS 02 ⇒ Important Financial Parameters ⇒ Quarterly
- DNBS 10 ⇒ Statutory Auditor Certificate ⇒ Quarterly
- DNBS 13 ⇒ Overseas Investment Details ⇒ Annually
NBFC’s having asset size between Rs. 100 Crore and below Rs. 500 crores.
| Important Financial Parameters | Quarterly |
| Statutory Auditor Certificate (SAC) | Annually |
| Overseas Investment Details | Quarterly |
| Certificate | Annually |
| Short Term Dynamic Liquidity (STDL) | Quarterly |
| Structural liquidity and interest rate sensitivity | Monthly |
1:- Change in NPA classifications
| MORE THAN 150 DAYS | By March 31, 2024 |
| MORE THAN 120 DAYS | By March 31, 2025 |
| MORE THAN 90 DAYS | By March 31, 2026 |
Some of the other important changes
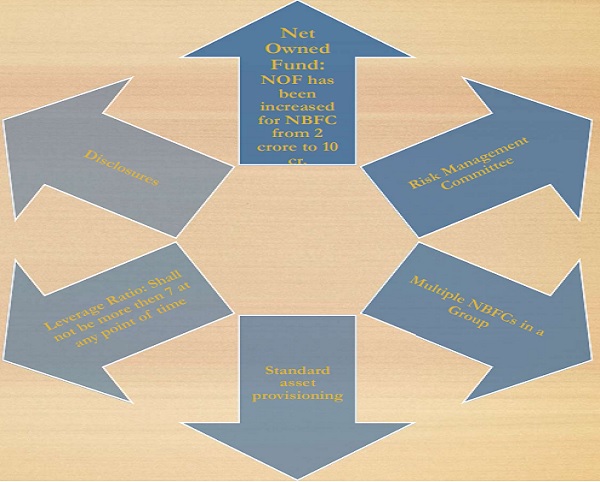
Conclusion: Understanding NBFCs is key to navigating India’s financial sector. With evolving regulatory frameworks and compliance obligations, NBFCs must stay abreast of changes to maintain operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. Stay informed to ensure seamless financial services and compliance adherence in this dynamic sector.




