General Exemptions & Deductions available for salaried employees for FY 2018-19 i.e. AY 2019-20 includes House Rent Allowance, Interest on Home Loan, Standard Deduction and Chapter VI-A deductions which includes- Section 80C, Section 80CCC – Pension Funds, Section 80CCD – National Pension Scheme (NPS), Section 80CCE, Section 80D – Medical Insurance, Section 80DD – Maintenance of dependant disabled, Section 80DDB – Medical treatment of Specified Ailments, Section 80E – Interest on Loan taken for Higher Education, Section 80EE – Interest on Loan – For acquisition of Self-occupied house property, Section 80G – Donations, Section 80GG – Rent paid, Section 80TTA – Interest on Savings Account, Section TTB – Interest earned by Senior Citizens and Section 80U – Deduction for Disabled Individuals. Article also explains about Rebate u/s 87A.
Page Contents
- A. House Rent Allowance – Sec 10(13A)
- B. Interest on Housing Loan – Sec 24b
- C. Standard Deduction
- D. Chapter VI-A Deductions
- 1. Section 80C
- 2. Section 80CCC – Pension Funds
- 3. Section 80CCD – National Pension Scheme (NPS)
- 4. Section 80CCE
- 5. Section 80D – Medical Insurance
- 6. Section 80DD – Maintenance of dependant disabled
- 7. Section 80DDB – Medical treatment of Specified Ailments
- 8. Section 80E – Interest on Loan taken for Higher Education
- 9. Section 80EE – Interest on Loan – For acquisition of Self-occupied house property
- 10. Section 80G – Donations
- 11. Section 80GG – Rent paid
- 12. Section 80TTA – Interest on Savings Account
- 13. Section TTB – Interest earned by Senior Citizens
- 14. Section 80U – Deduction for Disabled Individuals
- E. Rebate u/s 87A
A. House Rent Allowance – Sec 10(13A)
HRA is for expenses related to rented accommodation.
Salaried employees, who live in rented houses, can claim House Rent Allowance (HRA).

The exemption available is least of the following:
- Actual HRA Received
- 50% of Salary in metro cities or 40% of Salary in non-metro cities
- Actual Rent paid in excess of 10% of Salary (Rent – 10% Salary)
– Salary = Basic salary + Dearness Allowance (DA)
– Metro cities are Mumbai, Calcutta, Delhi and Madras.
– It is mandatory for employee to report PAN of the landlord to the employer if rent paid is more than Rs.1,00,000.
– A person can avail the simultaneous benefit of HRA and deduction for ‘Interest paid’ and ‘Principal repayment’ of home loan.
– If HRA is not received from employer, deduction under section 80GG can be claimed subject to certain conditions.
B. Interest on Housing Loan – Sec 24b
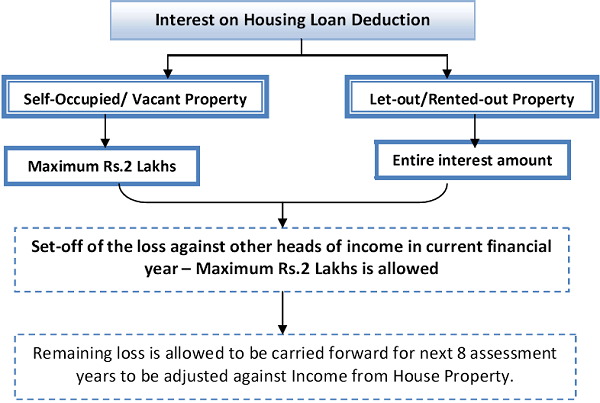
- The entire interest on home loan is allowed as deduction in case of rented out property.
- However, the deduction of interest is restricted to Rs.2 Lakhs in case of self-occupied The same restriction applies in case the house is vacant.
- The deduction is limited to Rs.30,000/- if any of the following conditions are not met:
> The home loan must be for purchase or construction of a property.
> The loan must be taken on or after 1st April 1999.
> The purchase or construction must be completed within 5 years from the end of the financial year in which the loan was taken.
- The interest paid during the construction period called “Pre-construction interest” can be claimed as deduction in 5 equal instalments from the financial year in which the construction is completed.
- In case of Joint home loan and ownership, each co-owner can claim deduction on interest paid separately in proportion of their ownership share.
C. Standard Deduction
- Budget 2018 re-introduced the benefit of standard deduction from the salary.
- The deduction of Rs.40,000/- was introduced in lieu of medical reimbursement and transport allowance.
- Earlier, medical reimbursement received by the employee was exempt up to a maximum of Rs.15,000/- and transport allowance was exempt up to Rs.1,600/- per month i.e., 19,200 per annum. Thus, an additional benefit of Rs.5,800 (40,000-15,000-19,200) can be claimed as exemption on account of standard deduction.
D. Chapter VI-A Deductions
1. Section 80C
The maximum permissible deduction is Rs.1,50,000/- (Subject to overall limit of Rs. 1,50,000 under Section 80CCE)
Following are few of the specified modes of investment for claiming 80C deduction:
| The following payments/ contributions made by an Individual/ HUF are allowed as deductions.
The payment can be made for:
– Such Individual – Individual’s Spouse – Any Child of Individual
– Any member of the HUF |
Other payments/contributions made by an Individual for which deduction is allowed are as under:
|
|
> Life Insurance Premium > Deferred Annuity (No option cash payment in lieu of annuity) > Deferred Annuity in case of Government servant (Maximum 20% of Salary) > Public Provident Fund Account (PPF) > Unit Linked Insurance plan of LIC Mutual Fund |
> Employees’ Provident Fund Scheme (EPF)
> Sukanya Samriddhi Account Scheme > National Savings Certificates (VIII Issue) > Home Loan Account Scheme/ National Housing Banks (Tax Saving) Term Deposit Scheme, 2008 > Tuition Fees (Excluding development fees, donations etc) for any 2 children > Stamp duty and Registration charges for a home > Principal re-payment of Housing Loan > Notified annuity plan of LIC or other insurer > Equity Linked Savings Scheme, 2005 > Any pension fund set up by any mutual fund/ UTI Retirement Benefit Pension Fund > Term Deposit not less than 5 years with a > NABARD bonds > Senior Citizen Savings Scheme > 5 year term deposit with Post Office |
2. Section 80CCC – Pension Funds
- Contribution to certain specified Pension Funds of LIC/other insurer (Subject to certain conditions)
- The maximum permissible deduction is Rs.1,50,000/- (Subject to overall limit of Rs. 1,50,000 under Section 80CCE)
- This benefit can be claimed by only Individual and not HUF
3. Section 80CCD – National Pension Scheme (NPS)
- Section 80CCD relates to the deductions available to individuals against contributions made to the National Pension Scheme (NPS) or the Atal Pension Yojana (APY)
- Contributions made by the employers towards the NPS, also come under this section
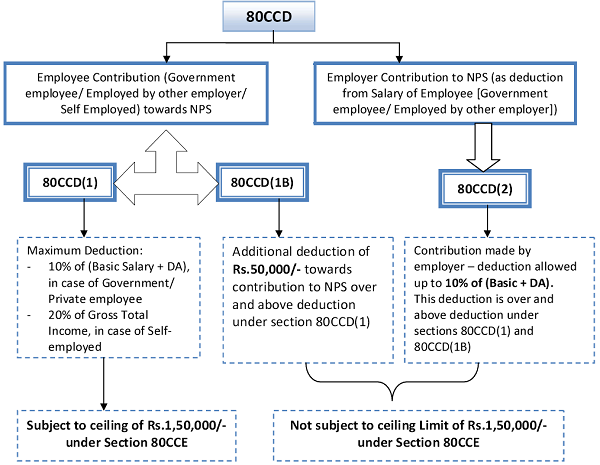
4. Section 80CCE
The aggregate amount of deductions under section 80C, section 80CCC and section 80CCD shall not, in any case, exceed Rs. 1,50,000/-
5. Section 80D – Medical Insurance
- 80D deduction can be claimed by Individual or HUF
- The insurance premium can be made
– In case of Individual – Self & Family (Family includes- Spouse, Dependant Children and Parents)
– In case of HUF – Any member thereof
- Deduction is allowed for the following payments made:
– Health insurance premium paid on the health of Self & Family in case of Individual or any member of HUF in case of HUF
– Contribution made to Central Government Health Scheme or Contributory Health Service Scheme of the Department of Atomic Energy
– Deduction to the extent of Rs.5,000/- is allowed in respect of preventive health check-up of self & family. However, the deduction is within the overall limit of sec 80D
|
Maximum Deduction allowed under Section 80D |
|||
| Self, Spouse and Dependant Children |
Parents | Total | |
| Medical Insurance – Premium to be paid in any mode, other than cash | |||
| All Individuals aged < 60 years | 25,000 | 25,000 | 50,000 |
| Either of the Parents or Both/ Any member of HUF aged >= 60 years | 25,000 | 50,000 | 75,000 |
| Any member including Parents aged >= 60 years | 50,000 | 50,000 | 1,00,000 |
| Total | 25,000/50,000 | 25,000/50,000 | |
| Preventive Health Check-up (Included in the limit of 25,000/50,000) – Maximum Rs.5,000/- | |||
| Medical Expenditure (Included in the limit of 25,000/50,000) – Maximum Rs.50,000/- The conditions for claiming medical expenditure
– Deduction available for Self/Spouse/Parents – Aged >= 60 years – Person to be Resident in India – No payment made towards Medical Insurance of such person |
|||
- In case, where mediclaim premium is paid in lumpsum for more than one year, then the deduction allowable for the relevant previous year would be equal to appropriate fraction of such lumpsum payment
- Deduction is allowed towards premium paid towards
– Children – Only if they are Dependant
– Parents – Dependant or Not
6. Section 80DD – Maintenance of dependant disabled
- An Individual or HUF can claim the deduction for amount incurred towards
– Medical treatment (including nursing), training and rehabilitation of disabled dependant
– Paid or deposited with the scheme of LIC or other insurer for the maintenance of disabled dependant
| Type of Disability | % of Disability | Deduction available |
| General Disability | 40% | Rs.75,000/- |
| Severe Disability | 80% | Rs. 1,25,000/- |
- Dependent means
– In case of Individual – Spouse, children, parents, brothers or sisters of individual
> Wholly or mainly dependant on such individual
> Not claimed deduction under section 80U in his income
– In case of HUF – Any member of HUF
> Wholly or mainly dependant on such HUF
> Not claimed deduction under section 80U in his income
- Deduction under Section 80DD is not dependant on the amount of expenses incurred. Hence, even if the actual expenses on above mentioned disabled dependent relative is less than amount mentioned, full deduction can be claimed under Section 80DD
7. Section 80DDB – Medical treatment of Specified Ailments
- An Individual or HUF can claim the deduction for amount incurred towards
– Medical treatment of a dependant who is suffering from a specified diseases (such as AIDS, cancer, neurological diseases etc)
- Dependent means
– In case of Individual – Spouse, children, parents, brothers or sisters of individual
> Wholly or mainly dependant on such individual for support and maintenance
– In case of HUF – Any member of HUF wholly or mainly dependant on such HUF for support and maintenance
- The maximum amount of deduction that can be claimed is as under
| Age of the Person | Maximum Deduction |
| Age < 60 years | Rs.40,000/- or actual expenses whichever is less |
| Age>=60 years | Rs.1,00,000/- or actual expenses whichever is less |
- In case the dependant is insured and some payment is also received from an insurer or reimbursed from an employer, such insurance or reimbursement received shall stand reduced from the deduction
8. Section 80E – Interest on Loan taken for Higher Education
- The amount paid out of income chargeable to tax towards interest on loan taken for pursuing his higher education or higher education of his relative
- The loan must be taken from financial institution or approved charitable institution
- Relative means – Spouse, Children or Student for whom the individual is the legal guardian
- The deduction of interest paid can be claimed during the Initial assessment year in which the assessee starts paying the interest and 7 immediately succeeding assessment years or until the interest is paid in full, whichever is earlier
9. Section 80EE – Interest on Loan – For acquisition of Self-occupied house property
- Sec 80EE provides additional deduction in respect of interest on loan taken for acquisition of residential house property from any financial institution
- The maximum deduction allowable is Rs.50,000/-
- This deduction is over and above deduction of Rs.2,00,000/- available under section 24 for self-occupied property

- The deduction under sec 80EE would be available till the repayment of loan continues
10. Section 80G – Donations
- Any person making donation to prescribed funds or institutes can claim deduction
- The contributions made through cash, cheque or draft can only be claimed as deduction. In-kind contributions cannot be claimed
- Cash donations in excess Rs.2,000/- will not be eligible for deduction
- Exemption limit
– Eligible donation without any limit
– Eligible donation with limit of 10% of Adjusted Gross Total Income
> There are funds/institutes in which 100% contribution is allowed as deduction, whereas in some other funds/institutes deduction allowed is only 50% of contribution
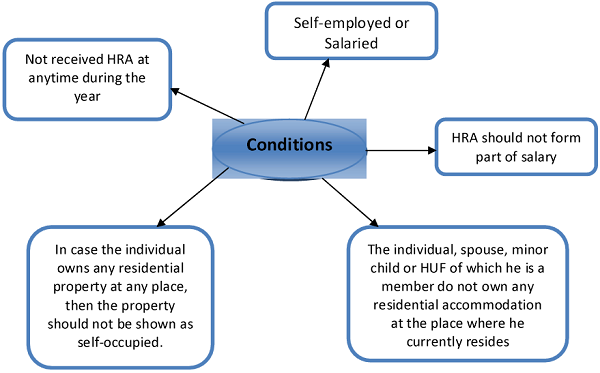
11. Section 80GG – Rent paid
- An individual who is not receiving HRA from the employer and paying rent for accommodation occupied for own residence can claim deduction u/s 80GG
- The least of the following can be claimed as deduction
> Rs.5,000/- per month
> 25% of Total Income
> Rent paid in excess of 10% of Total Income
Total Income = Gross total income – (LTCG, STCG u/s 111A, Sec 80C to 80U deductions other than 80GG and income u/s 115A)
12. Section 80TTA – Interest on Savings Account
- Interest earned from savings account with
– Bank
– Co-operative society engaged in banking business,
– Post office
will be allowed as deduction
- Interest from fixed deposits, recurring deposits or any time deposits is not eligible for deduction
- The maximum deduction allowed is Rs.10,000/-
- Total interest from all the bank should be considered
13. Section TTB – Interest earned by Senior Citizens
- A Resident individual aged >= 60 years earning interest income can claim this deduction
- The interest earned from following sources is eligible for deduction
– Interest on bank deposits – Savings or Fixed
– Interest on deposits with Co-operative society engaged in banking business
– Interest on Post office deposits
- The maximum deduction allowed is Rs.50,000/-
- This deduction is not available for HUF or Non-Residents
- If the deposit is held by the senior citizen on behalf of Firm, AOP, BOI, then the deduction is not available to such senior citizen
|
Difference between 80TTA & 80TTB |
||
| Particulars | 80TTA | 80TTB |
| Applicability | Individuals & HUF other than Resident Senior Citizens |
Resident Senior Citizens |
| Income | Interest on Savings Accounts | Interest on all Deposits |
| Maximum Deductions | Rs. 10,000/- | Rs.50,000/- |
14. Section 80U – Deduction for Disabled Individuals
- A resident individual who, at any time during the previous year, is certified by the medical authority to be a person with disability, can claim the benefit u/s 80U
| Type of Disability | % of Disability | Deduction available |
| General Disability | 40% | Rs.75,000/- |
| Severe Disability | 80% | Rs. 1,25,000/- |
- 80DD is the deduction for disability of dependants of Individual, whereas 80U is the deduction for disability of Individual himself
E. Rebate u/s 87A
- A Resident Individual having a Total Income <= Rs.3,50,000/-, then rebate can be claimed
- The rebate that can be claimed is lower of tax payable or Rs.2,500/-
- The rebate is applied to tax before Education Cess





My dependent father has medical insurance under National insurance co. Suddenly he has suffered from Cardiac arrest & treatment & operation like Angioplasty with stenting done in Nursing Home. The total expenditure comes Rs.350000, but Medical insurance provides Rs.149000 (including Bonus), Now, for extra payment which is done by debit card, can I claim deduction from Income tax under Sec 80 D /80DDB or any other section?
It is quiet informative. I need carification. Invested in ICICI pension fund without life cover. I have not claimed exemption under 80ccc while paying premiums. Pl let me know if I surrender is there any tax liabilty. I heard that, the taxation is limted to the value= Surrender Fund vaue – Total premium paid.
Pl clarify
I am 63 years old wish to claim Medicat expenditure of rs.50000/- as per sec 80D. I do not have mediclaim Insurance and expenditure includes of self & spouse who is 53 yrs. Please advice.
Deductions for Salaried Person
Well explained and easy for reference. Thanks
informative