Overview of E-way Bill
- The much talked about E-way Bill will be rolled out across the country from 1 st February 2018.
- As of now it is decided to implement the E Way Bill rules in two stages i.e. from Feb 01, 2018 for inter-state movement of goods and from June 01, 2018 for inter as well as intra state movement of goods.
- As of now the e-way bill system has already been rolled out in the States of Karnataka, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand and Kerala. Also few states have also rolled out their own version of State E Way bill such as UP, Bihar, Gujarat, Maharashtra etc.
- E-way bill is a mechanism to ensure that goods being transported comply with the GST Law and is an effective toolto track movement of goods and check tax evasion.
- The government on 01st February,2018 postponed implementation of the e-way bill requirement for movement of consignments in the goods and services tax (GST) regime after technological glitches led to disruption in trade.
- The e-way bill, an electronic documentation tracking the movement of goods, was mandatory for all inter-state movement of goods from 1 February.
- In view of difficulties faced by the trade in generating e-way bill due to initial tech glitches, it has been decided to extend the trial phase for generation of e-way bill, both for inter and intra- state movement of goods. It shall be made compulsory from a date to be announced,“ the official Twitter handle of the government on GST tweeted.
- According to a person familiar with the development, more than 1 6 states also started e-way bills for movement of goods within the state that led to a slowdown in issuance of e-way bills causing delays in truck movement. The GST e-way bill was made mandatory for all movement of goods within a state from 1 June, although these 16 states decided to implement it from 1 February.
- Businesses had two weeks trial time before the system was due for roll out in February, but policymakers chose to defer implementation to avert technical glitches causing disruption in supply chain at a time GST revenue has started stabilizing. Once implemented, e-way bill is needed for all movement of goods- within or outside a state- valued at more than Rs 50,000.
Who Should Generate E-way Bill?
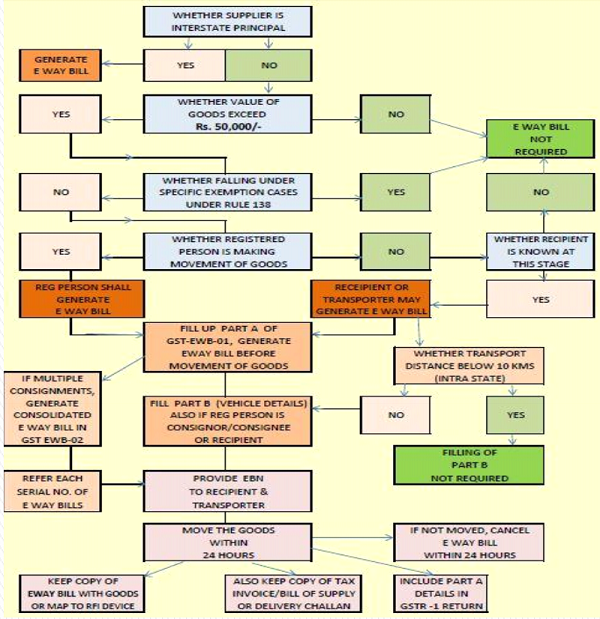
> E-way bill is to be generated by the consignor or consignee himself if the transportation is being done in own/hired conveyance or by railways by air or by Vessel.
> If the goods are handed over to a transporter for transportation by road, E-way bill is to be generated by the Transporter.
> Where neither the consignor nor consignee generates the e-way bill and the value of goods is more than Rs. 50,000/-it shall be the responsibility of the transporter to generate it.
> Further, it has been provided that where goods are sent by a principal located in one State to a job worker located in any other State, the e- way bill shall be generated by the principal irrespective of the value of the consignment
How E-way Bill is Generated
> An e-way bill contains two parts- Part A to be furnished by the person who is causing movement of goods of consignment value exceeding Rs. 50,000/- and part B (transport details) to be furnished by the person who is transporting the goods.
> Where the goods are transported by a registered person whether as consignor or recipient, the said person shall have to generate the e-way bill by furnishing information in part B on the GST common portal.
> Where the e-way bill is not generated by registered person and the goods are handed over to the transporter for transportation by road, the registered person shall furnish the information relating to the transporter in Part B of FORM GST EWB-01 on the common portal and the e-way bill shall be generated by the transporter on the said portal Person the basis of the information furnished by the registered on in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01.
> A registered person may obtain an Invoice Reference Number from the common portal by uploading, on the said portal, a tax invoice issued by him in FORM GST INV-1 and produce the same for verification by the proper officer in lieu of the tax invoice and such number shall be valid for a period of thirty days from the date of uploading
> In the above case, the registered person will not have to upload the information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 for generation of e-way bill and the same shall be auto computed by the common portal on the basis of the information furnished in FORM GST INV-1 .
KEY POINTS
| E Way Bill General Rule | Goods value > Rs. 50,000, Any movement of goods by registered person or inward supply from unregistered person |
| Special Cases | Any interstate movement irrespective of value:
–Any goods, from Principal to Job Worker –Handicraft goods from person exempted from registration |
| Who is liable to generate | Registered Person, Transporter, Principal or Person exempted from registration on case to case basis |
| For whom it is optional | Unregistered person until they are covered under special cases |
| From where to generate | www.ewaybillgst.gov.in, Android App, SMS, ASP Integration with web portal, using GST Suvidha Provider |
| Which form | EWB 01, which contains two parts:
Part A –Details of goods moved Part B –Detail of vehicle After filling both only, E Way Bill no. (EBN) can be generated |
| Validity of E Way Bill | 1 Day for first 100 Km thereafter for every 100 Km or part thereof additional 1 day |
| Documents Required to generate | –Invoice / Bill of Supply / Delivery Challan for consignment of goods
–Transport by road through transporter : Transporter ID –Transport by road through owned / hired vehicle : Vehicle number –Transport by Rail / Air / Vessel : Transport document number, date of document |
| Documents / Devices required to carry during Transit | –the invoice or bill of supply or delivery challan, as the case may be
–a copy of the e-way bill or the EBN, either physically –where notified by the Commissioner, EBN mapped to a Radio Frequency Identification Device (RFID) embedded on to the conveyance. |
| What are other forms | EWB-02 : Consolidated E Way bill (for transporter, multiple consignment in single vehicle)
EWB-03 : Summary report of Inspection by department of goods in transit EWB-04: Intimation by transporter if vehicle is detained for more than 30 minutes GST INV- 1 : For generating Invoice Reference Number (IRN) |
Validity
Consequences of Non Compliance
> If e-way bills, wherever required, are not issued in accordance with the provisions contained in Rule 138 of the CGST Rules, 2017, the same will be considered as contravention of rules.
> As per Section 122 of the CGST Act, 2017, a taxable person who transports any taxable goods without the cover of specified documents (e-way bill is one of the specified documents) shall be liable to a penalty of Rs. 10,000/- or tax sought to be evaded (wherever applicable) whichever is greater.
> As per Section 129 of CGST Act, 2017, where any person transports any goods or stores any goods while they are in transit in contravention of the provisions of this Act or the rules made there under, all such goods and conveyance used as a means of transport for carrying the said goods and documents relating to such goods and conveyance shall be liable to detention or seizure.
General Rule
> This has been provided vide Rule 138(1) which says:
> “Every registered person who causes movement of goods of consignment value exceeding fifty thousand rupees—
(i) in relation to a supply; or
(ii) for reasons other than supply; or
(iii) due to inward supply from an unregistered person,
shall, before commencement of such movement, furnish information relating to the said goods in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01, electronically, on the common portal along with such other information as may be required at the common portal and a unique number will be generated on the said portal.”
Procedure of E Way Bill
Conclusion
> The e-way bill provisions aim to remove the ills of the erstwhile way bill system prevailing under VAT in different states, which was a major contributor to the bottlenecks at the check posts.
> Moreover different states prescribed different e-way bill rules which made compliance difficult. The e-way bill provisions under GST will bring in a uniform e-way bill rule which will be applicable throughout the country.
> The physical interface will pave way for digital interface which will facilitate faster movement of goods.
> It is bound to improve the turnaround time of vehicles and help the logistics industry by increasing the average distances traveled, reducing the travel time as well as costs.
Author- CA Manish Kankani is associated with DMKH & Co.







Validity is 1 day for 100kms & another 1 day after 100kms or part thereof.