CA. Ganesh V shandage

Article explains about GST Registration of Education Institutions which includes Liability to register, Presumptive taxation and Exemption from registration. It further includes Tax Rate on Supply of goods or services by Education Institutions, Type of tax, Payment of tax under RCM, Taxable value. All issue of Invoices and Voucher related to Education Institutions which includes Tax invoice, Bill of supply, Invoice cum Bill of supply, Self-invoicing, Receipt voucher (Advance), Refund voucher and Payment voucher. Articles explains provisions related to Input Tax Credit by Education Institutions. Provisions related to Accounts and Audit which includes Books of Accounts, Electronic ledgers, Filing of Regular Returns, GST Annual Return, GST Audit and Journal entries with FAQs on all issues related to GST on Education Institutions.
Page Contents
A. Background
Education is not defined in the GST law, but as per Supreme Court ruling in “Lok Shikshan Trust v/s CIT”, education is a process of training and development knowledge, skill and character of students by normal schooling.
By constitution, Government has an obligation to provide free and compulsory elementary education to every child in the country. Education is viewed more as a social activity than business activity and hence taxing the same under indirect tax regime has always been a very sensitive and socially impactful issue. The GST law tries to ensure a fine balance hereby core education services provided and received by Educational Institutions are exempt from tax and other educational services are envisaged to be taxed at the rate of 18%.
It is important to note however that, all the services aside from education services as referred above, as provided by educational institutions are not exempt from tax. There are few supplies of goods or services which may be exigible to tax either under forward charge or reverse charge mechanism (RCM). For example educational institutions may be liable to pay GST on following illustrative list of goods or services –
→ Renting immovable property for commercial use under forward charge
→ Sponsorship revenues received from non-corporate entities under RCM
→ Receiving security services from non-corporate entities under RCM
→ Sale of capital assets
→ Conducting trainings, seminars, workshops, and the likes for other than students, faculty and staff.
B. Registration
1. Liability to register
a. In case the aggregate turnover (Gross collections) of a person exceeds the threshold limit of Rs. 20 Lakhs in any financial year, then it is mandatory to apply for registration under GST law.
b. In case such person is engaged in inter-state supply of goods or service, the threshold limit as mentioned would disregarded and such person would be required to apply for registration irrespective of the threshold limit as mentioned above.
c. In every state from which the person makes taxable supplies is liable to get himself registered in each of such states subject to crossing threshold limit as mentioned above.
2. Presumptive taxation
a. A registered person whose aggregate turnover during last financial year is up to Rs. 50 Lakhs and who is not engaged in inter-state supply of goods or service (other than restaurant service), can opt the presumptive scheme of taxation under GST.
b. In this scheme the registered person would be liable to pay GST at the rate 6% on the aggregate turnover up to Rs. 50 Lakhs and thereafter liable to pay GST at normal rates.
c. A registered person who has opted presumptive scheme is not allowed to avail input tax credit against the inputs, input service and input capital goods procurements.
d. As long as aggregate turnover of such person does not exceed Rs. 50 Lakhs in any of the financial years, the person can continue to pay taxes under this scheme every subsequent financial years. However once the aggregate turnover of such person exceeds Rs. 50 Lakhs in any financial year, in the subsequent financial year he shall not be liable to opt for this scheme and is therefore required to pay taxes as normal taxpayer.
3. Other points to note
a. New registration to be applied through GSTN portal with valid e-mail id and phone number.
b. After submission of online application form in GSTN portal, the GST registration number would be auto generated within 3 working days unless it is out sorted due to any exceptional reasons, wherein the officer would send a notice and seek clarification to his satisfaction from the applicant before issuing final GST registration number.
4. Exemption from registration
In case the person is engaged exclusively in the supply of exempted goods or service (Example – Education Service by Educational Institution), then irrespective of the total value of his aggregate turnover, he is exempted from the requirement of taking compulsory registration under GST.
C. Tax
1. Rate of Tax
i) The rate of tax for persons under presumptive tax shall be 6% without the ITC.
ii) Following are specific rates of taxes applicable for persons under normal registration –
| Chapter/ Section/ Heading |
Description of Service | Rate |
| 9992 | Education service (Other than by ‘educational institutions’) | 18% |
| 9992 | Services provided –
(a) by an ‘educational institution’ to its students, faculty and staff; (aa) by an educational institution by way of conduct of entrance examination against (b) to an educational institution, by way of, – (i) transportation of students, faculty and staff; (ii) catering, including any mid-day meals scheme sponsored by the Central Government, State Government or Union territory; (iii) security or cleaning or house-keeping services performed in such educational institution; (iv) services relating to admission to, or conduct of examination by, such institution; (v) supply of online educational journals or Provided that nothing contained in sub-items (i), (ii) and (iii) of item (b) shall apply to an Provided further that nothing contained in sub-item (v) of item (b) shall apply to an institution providing services by way of,- (i) pre-school education and education up to higher secondary school or equivalent; or (ii) education as a part of an approved vocational education course. |
NIL (S. No. 66 of Notification
12/2017) |
| 9992 | Bundled service comprising fees received towards hostel facilities and education | NIL |
| NA | Donations received | NOT A SUPPLY |
| 99 | Charitable activities rendered by an entity
registered under section 12AA of Income tax Act. |
NIL |
| 99 | Sponsorship service provided to persons other than company and partnership firms | 18% |
| 9972 | Renting of immovable property to related persons or otherwise | 18% |
The term ‘Education institution’ is defined as an institution providing services by way of –
(i) Pre-school education and education up to higher secondary school or equivalent;
(ii) Education as a part of curriculum for obtaining a qualification recognized by any law for the time being in force;
(iii) Education as a part of an approved vocational education course.
The point (i) gives the blanket exemption to every person who is providing education and training services to students from pre-school up to higher secondary school (up to PUC II or 12th Class) or its equivalent. It may be noted that the persons providing such services may be Govt approved or suppliers from private sector providing such services without any such approvals. This measure has been taken by the Govt to ensure basic education up to higher secondary school is fully out of tax net and reduce its cost of education to that extent.
Further, one more relaxation given by Govt to these institutions is the exemption on few of the auxiliary services that these institutions consume namely –
> Transportation services for students, staff and faculty
> Catering services and Govt sponsored Mid-day meal facility
> Security service
> Cleaning and housekeeping services
Thus these institutions aside from enjoying the benefit of exemption on its outward supply of service to its students, staff and faculty, these institutions also have the special privilege of receiving tax free specified input services as enumerated above.
The point (ii) covers all education institutions providing services by way education as a part of curriculum for obtaining a qualification recognised by any law for the time being force. This is an area where doubt were persisted in the earlier Service tax regime wherein the same was suitably addressed to refer such education services only when such service is delivered as a part of curriculum that has been prescribed for obtaining the qualification recognized by any law for the time being in force. The point (ii) above covers conduct of degree courses by colleges, universities or institutions which lead to grant of qualifications recognized by Indian law such as UGC Act or AICTE Act. Consequently training given by private coaching institutes would not be covered as such training does not lead to grant of a recognized qualification.
Also in case of auxiliary inbound education services as referred as referred at point (i) are provided to educational institutions providing degree or higher education, the same would not be exempt from GST. For instance, the inbound services of transportation of students to colleges in case of educational institutions providing qualification recognized by law for the time being in force shall be liable to GST.
The point (iii) covers courses run by Industrial Training Center affiliated to National council for vocational training or State council for vocational training; These also cover the Modular employable skill course approved by the National council of vocational training and being run by a registered person with Director general of training, Ministry of Skill development and Entrepreneurship.
2. Type of tax
In case taxable education services are being performed, the place of supply = Location of actual performance of service. Hence irrespective of address or state of the student, faculty and staff, the SGSG and CGST would be liable to be in case such training, teaching, etc. is conducted in the state from which the GST registration has been obtained. In case such taxable services are performed outside the state from which the GST registration has been taken, the type of taxes to be applied is IGST.
3. Payment of tax under RCM
a. Pay tax under reverse charge mechanism on following specified services received by educational institutions.
| S No. | Service description | Rate of tax |
| 1 | Goods transport service | 18% |
| 2 | Security services received from a person other than Company | 18% |
b. Pay tax under reverse charge mechanism on purchase of goods or services from unregistered dealers. For the time being until 30.09.2019 this tax has been kept under abeyance.
c. Pay IGST and custom duty of import of goods or services or both.
D. Taxable value
a. Where educational services are liable to GST, the Transaction Value of such supplies shall be the Taxable Value in GST and accordingly taxes are to be levied on such Taxable Value at the applicable rates as per tariff. Where the service recipient is related and the price to be charges to him is not the sole consideration, then the valuation rules as prescribed in GST Rules are to be applied to arrive at the taxable value of such services.
As per valuation the rules, the value of goods or services where the supplier and the recipient are related shall be the open market value of such supply or the value of supply of goods or service of like kind and quality.
For supplies the Taxable invoice is to be issued.
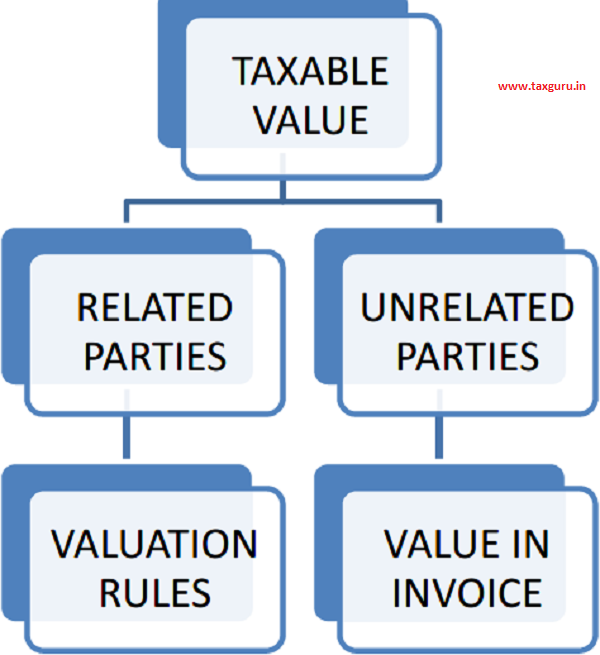
b. For exempted educational services, the supplier is required to issue Bill of supply containing only the transaction value of such supply without charging GST components in it.
E. Issue of invoices & Vouchers
1. Tax invoice
Where the supplies are liable to tax, the supplier is required to issue tax invoice containing all the particulars (as required under GST rules) at the earliest of following –
> Date of issue of tax invoice by the supplier, if the invoice is issued within 30 days of provision of service
OR
> Date of provision of service, if the invoice is not issued within 30 days of provision of service,
The tax invoice form has 17 required particulars which should be mandatorily present on the face of the invoice. Aside from that, the tax invoice should clearly reflect the breakup of tax types being levied in the tax invoice namely CGST, SGST, IGST and Cess.
Where the recipient of supply is not a registered person AND that recipient of supply does not require such invoice, the supplier may issue a single consolidated tax invoice for such supplies at the end each day in respect of all such supplies.
2. Bill of supply
Where the supplies are completely exempted from tax, the Bill of Supply is to be raised in respect all such supplies individually containing all the particulars as required under GST rules. However, the supplier is exempted from issuing individual Bill of Supplies where the recipient of supply is not a registered person and he does not require Bill of supply and in lieu thereof the supplier is required to issue an a single Consolidated Bill for Supplies at the end of each day in respect of all such supplies.
3. Invoice cum Bill of supply
Where supply includes both taxable and exempted supply to an unregistered person, the supplier should issue a combined Invoice cum Bill of supply comprising both the supplies included in the combined invoice.
4. Self-invoicing
Where the registered person is liable to pay tax under reverse charge basis, then such person on receipt of goods or service or on the receipt of payment, whichever is earlier is required to issue Self invoice containing all the particulars as required by GST rules and discharge the tax accordingly.
5. Receipt voucher (Advance)
Where registered person accepts any advance for Services to be provided in future, such person shall issue a Advance receipt voucher to the prospective service recipient containing taxable value and applicable GST where the advance is received against taxable supply of service to be provided.
6. Refund voucher
Where registered person after acceptance of advance for services wishes to return the same either fully or partially, then he would be required to issue an Refund voucher containing required particulars.
7. Payment voucher
Where the registered person is required to pay tax under reverse charge mechanism on specified supplies received, he would be required to issue Payment voucher to the supplier on performing outbound payment against the procurements either fully or partially.
F. Input tax credit
1. General provisions
a. Every registered person shall be entitled to take credit of input tax (ITC) charged on any supply to him of any goods of services or both used or intended to be used in the course or furtherance of business.
b. ITC available only in case the inputs or input services are used or intended to be used in the course or furtherance of business and on meeting following cumulative conditions –
i. Possession of purchase invoice
ii. Actual receipt of goods or service
iii. Payment made to vendor within 180 days from invoice date
iv. Timely filing of monthly return
v. Tax on supply actually paid to Govt by the vendor
At present the practice prevalent in the industry is that the taxable persons claim and avail ITC in the online portal of GST with or without meeting all the above cumulative conditions. However from the Govt’s perspective, all such ITC benefits are subject to verification and final confirmation of the credit being taken. In the meantime, such credits are to be treated as only provisional credits only.
c. ITC not available on the following (Sec. 17(5) of CGST Act) and these items are also termed as Blocked credit items or Negative list items :
i. motor vehicles for passenger transportation with seating capacity up to 13 (inclusive of driver), exceptwhen such motor vehicles are used for making following taxable supplies:
1. for further supply of such motor vehicles
2. for transportation of passengers
3. Imparting driving training to pupils
Also the costs namely general insurance premium, servicing, repair and maintenance so far related to aforesaid motor vehicle against which ITC is blocked.
ii. following supplies:
i. Food & Beverages, Outdoor catering etc. except where they are used for making an outward taxable supply of same category of goods or services
ii. membership of a club, health and fitness centre
iii. leasing, renting or hiring of motor vehicles, life insurance and health insurance
iv. travel benefits extended to employees on vacation such as leave or home travel concession
In case it is obligatory for the employer under any law for the time being in force to provide the above services to its employees, then the ITC on procurement of such services shall be allowed.
iii. works contract services for construction of Immovable property(other than plant and machinery) or purchase of goods or services for construction of immovable property (other than plant and machinery) on own account.
iv. goods or services or both used for personal consumption
v. goods lost, stolen, destroyed, written off or disposed of by way of gift or free samples.
vi. any taxes paid under fraud or dispute.
d. Where taxable person has combination of both exempt and taxable supplies, then proportionate of total ITC as that relates to the exempt supply has to be reversed in every tax period and take benefit of the balance ITC amount for clearing against output tax liability.
G. Accounts and Audit
1. Books of Accounts
Under GST law, every registered person is required to maintain following books of accounts and records either in manual or electronic form at his registered principal place of business –
a. Inward and outward supply of goods and services
b. Stock of goods
c. Input tax credit availed
d. Output tax payable and paid
e. Other particulars as may be prescribed
The above set of books of accounts and records are to be kept and maintained for at least 72 months from the end of due date of filing annual return GSTR9 for year pertaining to such books of accounts and records.
In case registered person fails to account for the goods or services as required, the proper officer shall determine appropriate tax and issue a demand as if such unaccounted goods or services are outward supplies of such registered person.
2. Electronic ledgers
Apart from the books of accounts and records as required to be kept and maintained by the registered person as referred above, the Govt on the GST portal also maintains 3 of registered persons ledgers namely –
a. Electronic cash ledger in form GST PMT-05. This ledger keeps a track record of all the cash deposits made and withdrawals made for payment of taxes, charge, etc.
b. Electronic credit ledger in form GST MT-02. This ledger keeps a track record of all the ITC components availed, utilized, reversed, etc.
c. Electronic liability ledger in form GST PMT-01. This ledger would have all the details relating to demands and settlements of taxes and charges raised by the Govt.
3. Filing of Regular Returns
Currently every registered person is required to file monthly return GSTR1 for reporting outward supplies only and return GSTR3B for reporting summarized details of all the transactions that have occurred in that month which could comprise of outward supply, inward purchases, input tax credit, advances received, debit or credit notes issued, etc.
Filing of return GSTR3B culminates with settlement of tax liability either though utilization of ITC balance or through Cash ledger payment.
4. GST Annual Return
Every registered person is required to file Annual Return for every financial year electronically in form GSR9 by normal regular registered person and in form GSTR9A by registered person paying tax under composition scheme. The annual return is required to be filed by 31st December following the end of financial year.
In case of failure to file annual return in form GSTR9 on or before the due date, minimum late fees of Rs. 200 for per day during which such failure continues shall be payable by the the registered person subject to a maximum of a 0.50% of turnover in the state.
5. GST Audit
Every registered person whose annual turnover during a financial year exceeds Rs. 2 crore is required to get his accounts audited by a CA or CMA in practice and required to electronically file a copy of the audited accounts and reconciliation statement in form GSTR 9C. The timeline for submission of these documents is also 31st December following the end of financial year.
In case of failure to file audited accounts and reconciliation statement in form GSTR9C on or before the due date, the registered person may be subjected to a penalty of up to Rs. 50,000.
6. Journal entries
| PARTICULARS | JOURNAL ENTRY | |||
| OUTWARD SUPPLY | ||||
| Local B2B Supply
|
Dr. Sundry Debtors
Cr. B2B Sales revenue Cr. Output tax SGST Cr. Output tax CGST |
118
|
100 9 9 |
|
| Local B2B Supply
|
Dr. Sundry Debtors
Cr. B2C Sales revenue Cr. Output tax SGST Cr. Output tax CGST |
118
|
100 9 9 |
|
| Inter State Supply
|
Dr. Sundry Debtors
Cr. Inter-State Sales revenue Cr. Output tax IGST |
118
|
100 18 |
|
| Advance received – 1
|
Dr. Cash or Bank
Dr. Advance tax received Cr. Client / Customer A/c Cr. Output tax S/C/I/GST Dr. Output tax S/C/I/GST Cr. Cash or Bank |
11.8
1.8
1.8
|
11.8 1.8
1.8 |
|
| Raising of invoice – 2 | Dr. Client / Customer A/c
Cr. Sales revenue Cr. Output tax S/C/I/GST |
118 | 100
18 |
|
|
|
Dr. Output tax S/C/I/GST
Cr. Advance tax received Cr. Cash or Bank |
118
|
1.8 16.2 |
|
| Payment received – 3
|
Dr. Cash or Bank
Cr. Client / Customer A/c |
106.2
|
106.2 |
|
| INWARD SUPPLY | ||||
| Purchase from
registered dealer – Local
|
Dr. Purchases
Dr. Input – SGST Dr. Input – CGST Cr. Sundry creditors |
118
9 9
|
118 |
|
| Purchase from
registered dealer – Inter state |
Dr. Purchases
Dr. Input – IGST Cr. Sundry creditors |
118
18
|
118 |
|
| Purchase under Reverse
charge mechanism
|
Dr. Purchases
Dr. Input – S/C/IGST Cr. Sundry creditors Cr. Output tax S/C/I/GST |
100
18
|
100 18 |
|
| Purchase from
composition dealer |
Dr. Purchases
Cr. Sundry creditors |
100
|
100 |
|
| EXPENSES & PURCHASES OF CAPITAL GOODS | ||||
| Indirect expenses
incurred
|
Dr. Expenses
Dr. Input – SGST Dr. Input – CGST Cr. Sundry creditors or Cash or Bank |
100
9 9
|
118
|
|
| Asset purchase
|
Dr. Furniture
Dr. Input – S/C/IGST Cr. Sundry creditors or Cash or Bank |
100
18
|
18
|
|
| TRANSFER OF OUTPUT TAX TO LIABILITY LEDGER (Month end) | ||||
|
|
Dr. Output tax SGST
Dr. Output tax CGST Dr. Output tax IGST Cr. Liability Ledger SGST Cr. Liability Ledger CGST Cr. Liability Ledger IGST |
9
9 18
|
9 9 18 |
|
| TRANSFER OF INPUT TAX TO INPUT TAX CREDIT LEDGER (Month end) | ||||
|
|
Dr. Input tax credit – SGST
Dr. Input tax credit – CGST Dr. Input tax credit – IGST Cr. Input – SGST Cr. Input – CGST Cr. Input – IGST |
9
9 18
|
9 9 18 |
|
| ON DEPOSIT OF CASH IN TO ELECTRONIC CASH LEDGER | ||||
| Cash payment
|
Dr. Electronic cash ledger – SGST
Dr. Electronic cash ledger – CGST Dr. Electronic cash ledger – IGST Dr. Electronic cash ledger – Fees Cr. Bank |
20
30 40
|
90 |
|
| OFFSET OF TAX LIABILITY WITH INPUT TAX CREDIT AND CASH BALANCE | ||||
| Offset with Input tax
credit
|
Dr. Liability Ledger SGST
Dr. Liability Ledger CGST Dr. Liability Ledger IGST Cr. Input tax credit – SGST Cr. Input tax credit – CGST Cr. Input tax credit – IGST |
9
9 18
|
9 9 18 |
|
| Offset with cash balance
|
Dr. Liability Ledger SGST
Dr. Liability Ledger CGST Dr. Liability Ledger IGST Cr. Electronic cash ledger – SGST Cr. Electronic cash ledger – CGST Cr. Electronic cash ledger – IGST |
9
9 18
|
9 9 18 |
|
H. Frequently Asked Questions
| Q. 1 | Which ‘Education Institutions’ are eligible for GST exemption on the Services that they provide to their Students, Staff and Faculty? |
| Answer | ‘Education Institutions’ providing following services are eligible for GST exemption on the Services that they provide to their Students, Staff and Faculty –
a. Providing service by way of pre-school education and education up to HSC (Up to PUC II or 12th Std). b. Providing education service as a part of a curriculum for obtaining a qualification recognized by any law for the time being in force in India c. Providing education service as part of an approved vocational course |
| Q. 2 | What is the rate of GST on education service by ‘Education Institutions’? |
| Answer | NIL Rates if the services are provided to its students, staff and faculty. In case such services are provided to none of the recipients mentioned earlier, the GST rate of 18% would be applicable. |
| Q. 3 | Private education institutions providing coaching and training for students of degree recognized by law in India, whether such education institutions are liable to pay GST ? If yes, at what rate? |
| Answer | Yes they are liable to pay GST at the rate of 18%. Only the conduct of degree courses by colleges, universities or institutions which lead to grant of qualification or degree as recognized by law in India are only exempt. It is important to understand that in order to secure eligibility for the exemption the service should be delivered as part of a formal curriculum for example of a university to which colleges are affiliated. |
| Q. 4 | Is supply of food or drink in a mess or canteen by ‘Education Institution’ |
| liable to pay GST ? | |
| Answer | In case ‘Education Institution’ does not outsource the canteen facility for its students, staff and faculty, then such supply is exempt with tax rate of NIL applicable. In case the canteen facility is outsourced, then the canteen contractor would be liable to pay GST at the rate of 5% on the supply to ‘Education Institution’ (subject to no Input tax credit is availed). However on the forward charge of canteen facility received from canteen contractor by ‘Education Institution’ to its students, staff and faculty there is no GST applicable and is exempt with NIL rate. |
| Q. 5 | Whether individual person providing examination service to ‘Education Institutions’ attract GST ? |
| Answer | No. The GST rate is NIL for any person providing services in relation to admission to or conduct of examination by such ‘Education Institutions’. This
type of service include examination supervisor, invigilators, paper |
| Q. 6 | What is the GST implication on providing bundled services comprising education service, hostel and mess facility by an ‘Education Institution’ to its students. |
| Answer | Notwithstanding whether the services are bundled or not bundled, as long as those services are provided by ‘Education Institution’ to its students, all those services are exempt from tax. |
| Q. 7 | What is the GST implication on income generated by an ‘Education Institution’ as delegate fees from hosting a Seminar/Conference/Workshop for persons other than its Students, Staff and Faculty? |
| Answer | Yes taxable at the rate of 18%. |
| Q. 8 | Whether GST payable on the fees charged by Education Institutions on the prospective employers for participating in the campus placement event? |
| Answer | Yes taxable at the rate of 18% |
| Q. 9 | Which Services received by an Education Institution up to HSC are Exempted? |
| Answer | Only the following specific input services received by Education Institutions providing services by way of pre-school education and education up to HSC (PUC II or 12th Std) are exempt from GST –
Transportation services for students, staff and faculty Catering services and Govt sponsored Mid-day meal facility Security service Cleaning and housekeeping services Note: Conversely the above listed input services are liable to GST in case of Education Institutions other than the Education Institutions providing services by way of pre-school education and education up to HSC (PUC II or 12th Std.). |
I. Conclusion
Education is the backbone to the development of a country. It gives the person human dignity who develops himself. Article 21A of the Indian constitution makes education as fundamental right of all children of the age of 6 to 14 where Govt shall provide free and compulsory education to all such children. GST law recognizes this and has rightly reciprocated by providing exemption of tax on the Services provided both by Govt and Private education institutions right from pre-school up to HSC. Few basic auxiliary inbound services procured by such education institutions have also been kept outside the ambit of GST. Other services not covered by exemptions as discussed in this write up are levied GST at the rate of 18% with full Input tax credit. The Govt has done its might for ensuing that the education services up to HSC are fully exempt from GST.
*** END OF WRITE UP ***
For any clarifications, you may please either write to me on ganesh.shandage@gmail.com or speak to me on 9975016580.





CWA is changed to CMA or Cost Accountant.
QUERY ON Q 4 OF FAQ. IF A PRIVATE LIMITED COMPANY DEALING IN FOOD AND HOSPITALITY SERVICES 1. SUPPLY FOOD IN A SCHOOL DIRECTLY TO TEACHERS AND STAFF IN SCHOOL CANTEEN. PAYMENT MADE BY SCHOOL. 2. SUPPLY FOOD IN A SCHOOL DIRECTLY TO STUDENTS IN CANTEEN. PAYMENT MADE BY CHILDREN. WHAT IS GST LIABILITY IN BOTH CASES.
Refer specifically to the contents under –
“H. Frequently Asked Questions”
OFFHAND (to share personal thoughts):
OFFHAND
For a glimpse of the contents , and an appreciation, upfront, of the glaring lack of logic or sound reasoning to back up/ project the prima facie official viewpoints, look through , -https://taxguru.in/…/gst-education-institutions-detailed-an…
Some of the Ans. given to the effect that certain activities would attract GST levy,- there could be no denying, – seek to make inroads into the time- tested and sufficiently settled propositions of law. in respect of the income-tax regime.
For an insight, and incisive undertstanding in proper light, , any practising CA, engaged by EDU. institutions for financial and tax Audit might have to prudently equip self, upfont, through a close study of the EXperts’ commentary and a plethora of decided court cases – SAY- Palhivala’s leading TEXT Book on Income Tax Act.
It goes without having to add that the liberal and very wide interprtation of the underlying scheme of / the governing provisions of the IT Act are to be considered to be of no less relevance to the GST Act; notwithstanding that there has been an impressiion impudently given, on the wrong premise that for levy of GST , diagonally opposite views could be taken ?!
• KEY Points: It needs to be made a conscious note of that the ISSUES the subject matter entails are undoubtedly brimming with complexity of its kind / singular nature, Premised so, it might be in the fitness of things, for seasoned law pundits ( infield practice,-particularly those associated with the apex body- the ICAI, and proactively participating in such matters of common interest ) – if mind and time permit, to embark on an in-depth deliberation and add value, to be of positive help/ useful guidance, so as to serve the COMMON GOOD !
OPEN to EDIT / Inviting eminent experts to share independent but wellfounded views , if any materially at vatiance on the above indicated aspects.!