Q.1 What is ‘e-invoicing’?
As per Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, notified class of registered persons shall prepare an invoice by incorporating the Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and the QR-Code generated by uploading specified particulars in FORM: GST INV-01 on Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
Such invoice containing, inter alia, the QR Code embedded with IRN (mentioning IRN separately, is optional), issued by the notified supplier to buyer is commonly referred to as ‘e-invoice’ in GST.
Please note that ‘e-invoice’ doesn’t mean generation of invoice on a Government portal or issue of invoice in pdf form.
Q.2 How is ‘e -invoicing’ different from present system (normal invoice)?
There is no much difference between the e-invoice and a normal invoice.
In the e-invoice system, the notified registered persons will continue to create their GST invoices on their own Accounting/Billing/ERP Systems, but it shall bear the QR Code embedded with IRN (mentioning IRN separately, is optional), pre-generated on IRP. In other words, the specified contents of the invoices will have to be first posted in FORM: GST INV-01 on IRP, to generate the said unique IRN with a QR Code. e-Invoice is nothing but an invoice issued to the receiver of goods/services by the supplier along with the QR Code .
A GST invoice issued by the notified supplier will be valid only with a valid IRN/QR-code.
The following flow chart indicates the process of generation of e-Invoice: –

For more detailed process, please go through https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in/
Q.NO. 3. For which businesses, e-invoicing is mandatory?
e-invoicing is mandatory for the class of Registered Persons whose aggregate turnover (based on PAN) is more than the prescribed limit (as per relevant notification) in any preceding financial year from 2017-18 onwards.
The effective date from which the e-Invoice was notified as mandatory for different class of Registered Persons is indicated hereunder:
| Class of Registered Persons (with aggregate turnover) | Effective Date | Notification No (CT) |
| Exceeding Rs. 500 Crores | 01.10.2020 | 61/2020 Dated 30.07.2020 |
| Exceeding Rs.100 Crores | 01.01.2021 | 88/2020 Dated 10.11.2020 |
| Exceeding Rs.50 Crores | 01.04.2021 | 05/2021 Dated 08.03.2021 |
| Exceeding Rs.20 Crores | 01.04.2022 | 01/2022 Dated 24.02.2022 |
Q.NO. 4. What are the legal provisions governing e -invoice?
The following Notifications provide the legal basis for e-invoice:
|
Notification No. (CT) |
Key Contents |
| 68/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019 | The following new sub-rules were inserted in the Rule 48 of CGST Rules, 2017, vide Central Goods and Services Tax (Eighth Amendment) Rules, 2019
The invoice shall be prepared by such class of registered persons as may be notified by the Government, on the recommendations of the Council, by including such particulars contained in FORM GST INV-01 after obtaining an Invoice Reference Number by uploading information contained therein on the Common Goods and Services Tax Electronic Portal in such manner and subject to such conditions and restrictions as may be specified in the notification. Every invoice issued by a person to whom sub-rule (4) applies in any manner other than the manner specified in the said sub-rule shall not be treated as an invoice. (6) The provisions of sub-rules (1) and (2) shall not apply to an invoice prepared in the manner specified in sub-rule (4). |
| 69/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019 | Notified 10 Common Goods and Services Tax Electronic Portals for the purpose of preparation of invoice in terms of Rule 48(4) CGST, 2017. |
| 70/2019- Dt. 13-12-2019 | Notified registered person, whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds one hundred crore rupees, as a class of registered person who shall prepare invoice in terms of sub-rule(4) of rule 48 of the said rules in respect of supply of goods or services or both to a registered person. This notification to come into force from 01.02. 2020.
(Notification) No: 70/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019 was superseded by Notification: 13 of 2020 Dt. 21-3-2020) |
| 2 of 2020 Dt. 1-1-2020 | Substituted Form GST INV-1 as e-invoice schema (Schema further amended vide Notification 60/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020) |
| 13 of 2020 Dt. 21-3-2020 (in supersession of (Notification) No: 70/2019 Dt. 13-12-2019 | e-invoicing to commence from the 1st October, 2020; Notified registered persons, other than those referred to in sub-rules (2), (3), (4) and (4A) of rule 54 of the said rules, whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds Rs.100 Cr., as a class of registered person who shall prepare invoice and other prescribed documents, in terms of sub-rule (4) of rule 48 of CGCT Rules, 2017, in respect of supply of goods or services or both to a registered person.
(Further amended vide Notification. No: 61/2020 Dt. 307-2020) |
| Notification 60/2020 Dt. 30-7-2020 | Central Goods and Services Tax (Ninth Amendment) Rules, 2020
New form substituted for GST INV-01 (i.e. notified revised format for e-invoice) |
| Notification. No: 61/2020 Dt. 307-2020 | Amended notification 13/2020 Dt. 21-3-2020 Special Economic Zone units also excluded from e-invoicing mandate Aggregate Turnover of registered persons (required to prepare invoice in terms of Rule 48(4)) enhanced to Rs. 500 Cr. |
| 70/2020 Dt. 30-9-2020 | The words “a financial year” in notification 13/2020 Dt. 21-3-2020 substituted with “any preceding financial year from 2017-18 onwards” Invoices for exports were also included. |
| 72/2020 Dt. 30-9-2020 | In rule 46, after clause (q), the following clause was inserted:
“(r) Quick Reference code, having embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN) in it, in case invoice has been issued in the manner prescribed under sub-rule (4) of rule 48.” In rule 48, in sub-rule (4), the following proviso was inserted: “Provided that the Commissioner may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, exempt a person or a class of registered persons from issuance of invoice under this sub-rule for a specified period, subject to such conditions and restrictions as may be specified in the said notification. In rule 138A, for sub-rule (2), below sub-rule was substituted: “(2) In case, invoice is issued in the manner prescribed under sub- rule (4) of rule 48, the Quick Reference (QR) code having an embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN) in it, may be produced electronically, for verification by the proper officer in lieu of the physical copy of such tax invoice.” |
| 73/2020 Dt. 01.10.2020 | Notified a special procedure for taxpayers for issuance of e-Invoices for the period 01.10.2020 – 31.10.2020 |
| 88/2020 Dt. 10.11.2020 | To implement e-invoicing for the taxpayers having aggregate turnover exceeding Rs. 100 Cr w.e.f: 01.01.2021 |
| 05/2021 Dt. 08.03.2021 | To implement e-invoicing for the taxpayers having aggregate turnover exceeding Rs. 50 Cr w.e.f: 01.04. 2021 |
| 23/2021 Dt. 01.06.2021 | A government department, a local authority also excluded from e-invoicing mandate. |
| 01/2022 Dt. 24.2.2022 | To implement e-invoicing for the taxpayers having aggregate turnover exceeding Rs. 20 Cr from 01.04.2022. |
Q.NO. 5. What are the advantages of e-invoice for businesses?
- e-invoice has many advantages for businesses such as:
- Smooth ITC reconciliation by Auto-reporting of invoices into GST return;
- Simultaneous generation of EWB
- Utmost reliability (no need to doubt the genuineness- eliminates fake invoices);
- Reconciliation problems are eliminated;
- Standardisation & eliminates data entry errors;
- Documents become tax compliant on real time basis;
- Reduction of processing costs;
- improve payment cycles;
- thereby greatly improving overall business efficiency and ensure Ease of doing business.
Q.NO. 6. What businesses need to do, to be e -invoice ready?
Businesses will continue to issue invoices as they are doing now. Necessary changes on account of e-invoicing requirement (i.e., to enable reporting of invoices to IRP and obtain IRN), will be made by ERP/Accounting and Billing Software providers in their respective software. They need to get the updated version having this facility
Q.NO. 7. Can we have Multiple User Creation and administrator Option for Multiple Staff?
As you are aware National Informatics Centre (NIC) has released beta of version of ‘NIC-GST e-invoice Preparing and Printing’ (NIC-GePP) excel based Tool to assist the tax payers, who are not having the ERP solution, to enter invoice in web based form and print the e-invoice with QR code, after downloading the IRN from e-invoice portal. In this, main user can create sub user accounts with respective user’s mobile number mapped to it and use with GePP-Online, GePP-Offline and Bulk generation tool.
Q.NO. 8. Will businesses now be required to generate e-invoices on the GST portal or the e-invoice portal or the IRN portal?
It is mandatory on the part of all notified registered persons to generate the IRN & QR code as detailed above, by posting the specified information in GST INV-01, on IRP; and they will continue to generate e-invoices on their internal systems, whether through ERP or their accounting / billing systems or any other application.
E-invoice – Applicability
Q.NO. 9. What documents are presently covered under e -invoicing?
A. Invoices
B. Credit Notes (CDN)
C. Debit Notes (DBN)
when issued by notified class of registered persons, to another registered recipient of goods/services (B2B) or for the purpose of Exports, are currently covered under e-invoicing system. “Bill of supply” is not covered under the e-Invoice system.
Although Credit & Debit notes are also covered, for ease of reference and understanding, the system is referred as ‘e-invoicing’.
Q.NO. 10. Is an invoice/CDN/DBN (required to be reported to IRP by notified person), valid without IRN?
As per Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, 2017 and the notification issued thereunder, a notified person shall prepare invoice by uploading specified particulars in FORM GST INV-01 on Invoice Registration Portal and after obtaining Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and QR-code.
As per Rule 48(5) CGST Rules, 2017, any invoice issued by a notified person in any manner other than the manner specified in Rule 48(4), the same shall not be treated as an invoice.
Therefore, an invoice/CDN/DBN issued by notified person becomes legally valid only with an IRN (QR-code having an embedded IRN).
Q.NO. 11. What supplies are presently covered under e-invoice?
Supplies to registered persons (B2B), Supplies to SEZs (with/without payment), Exports (with/without payment), Deemed Exports, by notified class of taxpayers are currently covered under e-invoicing.
Q.NO. 12. Can B2C (Business to Consumer) supplies also be reported by notified persons?
No. Reporting B2C invoices by notified persons is not applicable/allowed currently.
Q.NO. 13. Is e-invoicing applicable for NIL-rated or wholly-exempt supplies?
No. For supplies attracting NIL-rate or those wholly-exempt, a “bill of supply” is prescribed; but not a tax invoice. Hence, e-Invoice is not mandatory even if such supplies are by the notified registered person. However, for an invoice-cum-Bill of supply issued under Rule 46A of CGST Rules, 2017 for supply of taxable as well as exempted goods or services or both to a registered person, e-Invoice is mandatory.
Q.NO. 14. Whether the financial/commercial credit notes also need to be reported to IRP?
No. It is only the credit and debit notes issued under Section 34 of CGST Act, 2017, shall be reported on IRP and are issued with IRN/QR-code.
Q.NO. 15. Whether e-invoicing is applicable for supplies by notified persons to Government Depatment / entity?
e-invoicing by notified persons is mandated for supplies of goods or services or both to a registered person.
Thus, where the Government Department/entity doesn’t have any registration under GST (i.e. not a ‘registered person’), e-invoicing is not required.
However, where the Government department/entity is having a GSTIN (as entity supplying goods/services/ deducting TDS), the same has to be mentioned as recipient GSTIN in the e-invoice.
Q.NO. 16.Whether e-invoicing is applicable for invoices between two different GSTINs under same PAN?
Yes, e-invoicing is applicable for invoices between two different GSTINs s under same PAN. e-invoicing by notified persons is mandated for supplies of goods or services or both to any registered person, including a registered person with the same PAN. As per Section 25(4) of GST Act, 2017, “A person who has obtained or is required to obtain more than one registration, whether in one State or Union territory or more than one State or Union territory shall, in respect of each such registration, be treated as distinct persons for the purposes of this Act”.
Q.NO. 17. For high sea sales and bonded warehouse sales, whether e -invoicing is applicable?
No. These activities/transactions are neither supply of goods nor a supply of services, as per Schedule III of CGST, Act, 2017.
Q.NO. 18. Whether e-invoice is applicable for import transactions?
e-invoice is not applicable for import transaction s.
Q.NO. 19. For which entities/sectors, e-invoicing is not applicable / exempt?
E-Invoice is not applicable to the supplies made by the following registered persons:
- Special Economic Zone Units;
- Insurers;
- Banking companies or financial institutions, including a non-banking financial company (NBFC);
- Goods Transport Agency (GTA) supplying services in relation to transportation of goods by road in a goods carriage;
- Suppliers of passenger transportation service;
- Suppliers of services by way of admission to exhibition of cinematograph films in multiplex screens;
- Persons registered in terms of Rule 14 of CGST Rules, 2017, Online Information Data base and Retrieval Services (OIDAR);
- Government department and local authority.
Q.NO. 20. The exemption from e-invoicing is w.r.t the nature of supply/transaction or w.r.t the entity?
It is with respect to the entity.
Q.NO. 21. Do SEZ Developers need to issue e-invoices?
Yes, SEZ Developers need to issue e-invoices if they have the specified turnover and fulfilling other conditions of the notification.
In terms of Notification No: 61/2020-CT dt. 30.7.2020, only SEZ Units are exempted from issuing e-invoices.
Q.NO. 22. Are Free Trade & Warehousing Zones (FTWZ) exempt from e -invoicing?
Yes. As per Foreign Trade Policy, Free Trade & Warehousing Zones (FTWZ) are only a special category of Special Economic Zones, with a focus on trading and warehousing. Hence, like any other Special Economic Zone Units, Free Trade & Warehousing Zones entities are exempted from e-invoice.
Q.NO. 23. Is e-invoicing applicable for supplies by notified persons to SEZs?
Yes, e-invoicing is applicable for supplies by notified persons to SEZ developers and SEZ units, as applicable to exports by a notified registered person.
In terms of Notification No: 61/2020-CT dt. 30.7.2020, only SEZ Units are exempted from issuing e-invoices for the outward supplies.
Q.NO. 24. What is the meaning of the aggregate turnover of supplies for the purpose of e-Invoicing?
For the purpose of computation of the aggregate turnover, the value of all taxable supplies, including the value of Exports, Exempted Supplies and the Inter GSTIN Transfers, made under a single PAN based GSTIN are to be taken in to consideration.
However, the amount of Tax (CGST/SGST/UTGST/IGST/Cess) paid during any financial year is excludable.
Q.NO. 25. Whether the value of inward supplies received by a registered person on which tax is liable to be paid under reverse charge mechanism is required to be included for computation of the aggregate turnover, for the purpose of e-Invoice?
No. The value of inward supplies received by a registered person on which tax is liable to be paid under reverse charge mechanism is not required to be included for computation of the aggregate turnover, for the purpose of e-Invoice, as such supplies are from a registered person with a different PAN.
However, the value of supplies of goods/service or both to another registered person on which recipient is liable for payment of tax, shall be included for arriving at the aggregate turnover of the supplier.
Q.NO. 26. When the aggregate turnover crosses the prescribed threshold during current financial year (e.g. during 2022-23), from what date, the supplier is supposed to start e-invoicing?
If the turnover exceeds the prescribed limit in the current financial year (2022-23), then e- invoicing would be mandatory w.e.f. beginning of next financial year (2023-24), assuming that the aggregate turnover of the subject registered person had not crossed the prescribed threshold of aggregate turnover during any of the previous financial years wef: 2017-18.
Q.NO. 27. Regarding the turnover threshold, the e -invoice notification mentions ‘aggregate turnover in any preceding financial year since 2017 -18’. Considering GST was implemented since 1-7-2017, how to reckon ‘aggregate turnover’ for the FY 2017- 18?
‘Aggregate Turnover’ has to be calculated as per the definition under Section 2(6) of CGST Act, 2017. Hence, for the Financial Year 2017-18, the ‘aggregate turnover’ has to be reckoned from 1-7-2017 till the end of FY.
Q.NO. 28. There is an SEZ unit and a regular DTA unit under same legal entity (i.e. having same PAN). In one of the financial years since 2017-18, the aggregate total turnover of the legal entity is more than notified limit (considering both the GSTINs); but the turnover of DTA unit is below notified limit.
In this scenario, as SEZ unit is exempt from e -invoicing, whether e-invoicing will be applicable to DTA Unit?
Yes, it will be applicable, because the aggregate turnover of the legal entity in this case exceeds the notified limit. The requirement is based on ‘aggregate turnover’ on the common PAN.
Q.NO. 29. Is e-invoicing applicable to invoices issued by Input Service Distributor (ISD)?
No.
Q.NO. 30. Whether e-invoicing is applicable for supplies involving Reverse Charge?
If the invoice issued by notified person is in respect of supplies made by him but attracting reverse charge under Section 9(3) of CGST, Act 2017, e-invoicing is applicable.
For example, a taxpayer (say, a Firm of Advocates having aggregate turnover in a FY is more than Rs. 20 Cr.) is supplying services to a company (who will be discharging tax liability as recipient under RCM), such invoices have to be reported by the notified person to IRP.
On the other hand, where supplies are received by notified person from (i) an unregistered person [attracting reverse charge under Section 9(4)] of CGST Act, 2017, or (ii) through import of services, e-invoicing is not applicable.
Q.NO. 31. How to know a particular supplier is supposed to issue e -invoice (i.e. invoice along with IRN/QR Code)?
On fulfilment of prescribed conditions, the obligation to issue e-invoice in terms of Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, 2017, (i.e. reporting invoice details to IRP, obtaining IRN and issuing invoice with QR Code) lies with concerned taxpayer.
However, as a facilitation measure, all the taxpayers who had crossed the prescribed turnover in a financial year from 2017-18 onwards have been enabled to report invoices to IRP.
One can search the status of enablement of a GSTIN on e-invoice portal: https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in/ > Search > e-invoice status of taxpayer
This listing of GSTINs is solely based on the turnover of GSTR-3B as reported to GST System. It may contain exempt entities or those for whom e-invoicing is not applicable for some other reason. So, it may be noted that enablement status on e-invoice portal doesn’t automatically mean that the taxpayer is supposed to do e-invoicing. If e-invoicing is not applicable to a taxpayer, they need not be concerned about the enablement status and may ignore it.
Further, the turnover slab of taxpayer can also be ascertained through “Search Taxpayer” / “Know Your Supplier” Sections on GST portal also.
In case any registered person, is required to prepare invoice in terms of Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, 2017, but not enabled on the portal, he/she may request for enablement on portal: ‘Registration -> e-Invoice Enablement’.
Q.NO. 32. Where can I get the list of all taxpayers who are required to issue e-invoice?
It is difficult to make precise list of taxpayers who are required to issue e-invoice, as the fulfilment of conditions prescribed for e-invoicing (e.g. crossing of turnover threshold, exemptions, nature of supplies made etc.) is dynamic in nature.
However, the list of GSTINs which are eligible and/or actually generating IRNs is published on IRP and updated on periodic basis. Please visit:
https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in/Others/GSTINsGeneratingIRN
Further, onus is on the concerned taxpayer to check the conditions and follow the law while the recipient shall confirm this fact with his suppliers, as the list may contain the names of exempt entities also but who might have been shown as enabled for e-invoice.
Q.NO. 33. I am a buyer. For some of my suppliers, the status on IRP is shown as ‘enabled for e-invoice’. But, my supplier says that they are exempt from e -invoicing or that e- invoicing is not applicable for them (for some reason). Please clarify?
The enablement status on e-invoice portal doesn’t mean that a taxpayer is legally obligated to subscribe for e-invoicing. It is mandatory to issue e-Invoice for all registered persons having the prescribed aggregate turnover (Rs.20 Cr.) during any of the FY from 2017-18, except to the suppliers listed in the reply to Q. No: 19.
It is for the concerned taxpayers (both Buyers and Suppliers) to confirm fulfilment or otherwise of conditions as per notification/rules.
Please note that the normal invoice (other than eInvoice) issued, if any, by a notified registered person who is mandated to issue an e-Invoice, would be invalid for all purposes including for availment of ITC (Ref. Rule 48(5) of CGST, Rules, 2017).
Q.NO. 34. What happens to the invoices issued by the Tax Payer whose Aggregate Annual Turnover is more than Rs.20 crores but the same was not generated through E-invoicing portal and issued to the recipient after 01.04.2022?
The invoices of such Tax Payers, not generated by e-Invoicing system, despite having Aggregate Annual Turnover exceeding Rs.20 Crores during any of the preceding financial year wef: 2017-18, shall not be treated as an invoice in terms of the Rule 48(5) of CGST, Rules, 2017. Therefore, the recipient would not be eligible for ITC.
Q.NO. 35. What is an Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)?
Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) is the website for uploading/reporting of invoices by the notified persons.
Ten portals were notified, vide Notification No. 69/2019-CT dated: 13.12.2019, for the purpose of generation of IRN & QR-code for issue of e-Invoice in terms of Rule 48(4) of CGST, Rules, 2017.
The first Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) active and can be accessed at: https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in/
More portals will be made available in due course.
Q.NO. 36. Is e-invoicing voluntary for the entities with aggregate turnover below the prescribed limit?
No. Currently, only the notified class of persons (Registered persons having aggregate turnover exceeding Rs. 20 Crores) will be allowed/enabled to report invoices to IRP.
Q.NO. 37. Is there any time window within which a registered person need to report an invoice to IRP, i.e. is there any validation to the effect that the ‘document date’ (in the payload to IRP) has to be within a specified time window, for, reporting to IRP/generation of IRN?
No such validation is kept on the portal.
Q.NO. 38. Whether the Digital Signature of supplier is mandatory while uploading specified details in GST INV-01, on IRP? and Whether the hard copy of the e -invoice issued by due process with QR-Code embedded with IRN is required to be physically signed by the supplier/authorized signatory?
No. While uploading specified details in GST INV-01, on IRP it is not mandatory for the notified registered person to append digital signature.
Similarly, there is no need for the physical signature of the supplier or his authorized signatory on the hard copy of the e-Invoice issued by due process by incorporating the QR code embedded with IRN, as per the 5th proviso to the Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017.
Q.NO. 39. Can e-commerce operators generate e-invoices on behalf of the sellers on their platforms?
Yes. e-Commerce operators can generate e-invoices on behalf of the sellers on their platforms if such suppliers, selling through e-Commerce entity are otherwise notified persons and are supposed to report invoices under Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules, 2017.
Q.NO. 40. Whether any tool is provided to report invoices to IRP?
Yes. For entities not having their own ERP/Software solutions, they can use the free offline utility (‘bulk generation tool’) downloadable from the e-invoice portal. Through this, invoice data can be easily reported to IRP and obtain IRN/signed e-invoice.
Q.NO. 41. What are various modes for generation of e-invoice?
Multiple modes are available so that taxpayer can use the best mode to generate IRN:
A. API-based
B. Offline Utility (freely downloadable from IRP)
C. ‘NIC-GST e-invoice Preparing and Printing’ (NIC-GePP) excel based Tool – offline/online.
Q.NO. 42. What is the GePP Tool/facility under e-invoicing and who can use it?
GePP is GST e-invoice Preparing and Printing tool. It is an excel-based tool to help the notified registered persons who do not have ERP solution to enter the invoice details in a user-friendly form and print the e-invoice with IRN embedded QR code by downloading the IRN from e-invoice portal (IRP).
GST e-invoice preparing and printing tool is available on the e-invoice portal under the ‘Bulk generation tool’ option available by navigating to ‘Help tab’> ‘Tools’ on the homepage; and it can be downloaded free of cost.
Q.NO. 43. what are the Salient features of GePP tool/ facility?
GePP is an excel-based tool having the below functionalities:
- It is a very simple form in which invoice details are required to be entered one by one;
- Facilitates the creation of supplier profiles as well as creation of HSN and recipient masters for repeated use without feeding such data again, to save time;
- Helps in preparation of e-invoice JSON file and generation of IRN;
- It helps in downloading and importing the IRN embedded QR code in the tool and it enables printing of e-invoice from the tool.
Q.NO. 44. What are the advantages of the GePP tool / facility?
- GePP tool is best suitable for small notified registered persons who do not have an ERP system and issuing limited number of (about 10-12 invoices) per day;
- It helps the notified registered persons to enter data offline, to prepare as well as print the e-invoice with IRN embedded QR code;
- The user-friendly tool can be downloaded even on Mobile and can be used for generation of e-invoice with IRN embedded QR code;
- Master data of suppliers, recipients and products will help in auto-population of details for easier e-invoice generation, for repeated use without feeding such data again, to save time;
- Gepp has an option to maintain the details of payment received towards e-invoices.
In view of the above advantages, the notified registered persons who do not have their own based IT billing/accounting software systems are advised to subscribe to the GePP free download for ease of doing business
Q.NO. 45. Will it be possible for bulk uploading of invoices to IRP?
Yes. It is possible. The offline utility (‘bulk generation tool’) serves this purpose.
Further, the ERP or accounting systems used by large taxpayers can be designed in such a way that they can report invoices in bulk to IRP.
However, reporting to IRP and generation of IRN will be one after another (which will not be visible for user). For the user, it will appear like bulk upload and bulk receipt.
Q.NO. 46. As many businesses will be reporting invoice s, will there be any delay in generation of IRN by IRP? Can the portal take that much load?
IRP is only a pass through validation portal. Certain key fields will be validated on IRP. So, IRN will be generated in sub-200 millisecond duration.
The server capacity is robust enough to handle simultaneous uploads. Further, multiple IRPs will be made available to distribute the load of invoice registration.
The IRPs are dedicated portals other than the regular GST common portal (used for filing registration applications, filing returns, making payments etc.)
Q.NO. 47. Will IRP store/archive e-invoices?
No. IRP will only be a pass-through portal which performs prescribed validations on invoice data and generates IRN. It will not store or archive e-invoice data.
Q.NO. 48. In case of breakdown of internet connectivity in certain areas, will there be any relaxation in the requirement to obtain IRN?
A mechanism to provide relaxation in such contingent situations is prescribed as per proviso to Rule 48(4) of CGST Rules. It reads as: “…Commissioner may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, exempt a person or a class of registered persons from issuance of invoice under this sub-rule for a specified period, subject to such conditions and restrictions as may be specified in the said notification.”
Q.NO. 49. In the financial year 2021-2022 I am eligible for e-invoicing, whereas in April month I did not provide e-invoice as I was not aware that time i.e. April 2021. Now for the client can I provide e-invoice of April 2021 month. If I am providing e-invoice now I will give same bill number and same bill date. Is this process correct. Please suggest.
As per Rule 48(5) of the CGST Rules, 2017, the taxpayers for whom generation of IRN from the e-invoice portal is mandatory as per notification No. 13/2020-Central Tax dt. 21.03.2020, as amended, the documents without IRN will not be treated as invoice. However, for the past period, the portal is still open for generating the IRN based on demand of taxpayers.
Q.NO. 50. Whether e-invoice is applicable to notified registered persons having only the zero-rated supplies?
If the annual turnover as per Sec. 2(6) of the CGST Act, 2017, exceeds more than Rs. 20 Crores in any preceding financial year from 2017-18, e-invoice has to be generated for zero rated supplies also.
Q.NO. 51. What is e-invoice schema?
‘Schema’ simply means a structured template or format. ‘e-invoice’ schema is the standard format for electronic invoice. It is notified as ‘Form GST INV-1’.
Q.NO. 52. How to access GST INV-01 to generate IRN & QR Code?
GST INV-01 is accessible online at https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in by login (User ID & Password). Initially the supplier has to be register for obtaining User ID & Password at “Portal Login” section under Registration menu on the home page of the said portal. In case the supplier is already registered on EWB portal and has valid User ID & Password, the same are valid for accessing GST INV-01, also.
Q.NO. 53. What are the specified details/information, to be filled in the form GST INV01, for generation of IRN & QR Code?
The format of GST INV-01 comprises of the following four parts, with different particulars to be filled, as detailed hereunder: –
Part A : Details of Supplier:
- GSTIN and the name of the supplier (auto-populated).
- Address of the registered/principal place of business.
- Serial number and the date of invoice.

- The IRN & date (of generating IRN) are generated automatically.
Part B : Details of the recipient:
- GSTIN (of registered taxpayers) or UIN (for embassy or UN organization) as the case may be;
- Name of the recipient and consignee.
- Address and state code (first two digits of the GSTIN) of the consignee.
Note: The details of the consignee and recipient could be the same if the parties being billed to and the parties to whom the goods are being delivered, is the same. In certain cases, the GSTIN of both the recipient and consignee can be the same but with different addresses. And in other instances, the GSTIN of the party to whom the bill is addressed to, would differ from the one to whom it is shipped to.
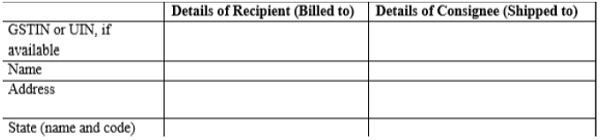
Part C: Particulars concerning the type of supply made by the taxpayer, including the type of transaction and applicability for tax provisions.
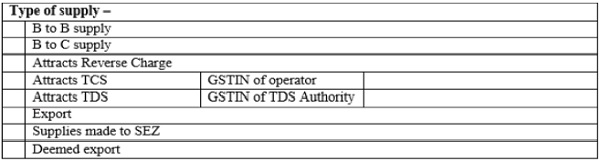
Note: As on date the e-Invoicing is not applicable to “B to C” transactions, although the form provides for the same.
Part D: Information pertaining to the Goods/ Services, being supplied:
- Description of goods/Services.
- HSN code/SAC.
- The quantity (for goods only) and unit price.
- The applicable GST rate and amount, which will be calculated based on the type of transaction (inter-state or intra-state).
- Declaration of freight, insurance, packaging & forwarding charges, as stated in the tax invoice (for goods only).
[The following Sample form of Part: D is for the goods only}
Q.NO. 54. Is there different invoice schema for different sectors/businesses, e.g. Traders, Manufacturers, Service Providers, Professionals etc.?
No. e-invoice schema is a single standard applicable to all businesses in the country.
Many optional fields are available in the schema to cater to the requirements of specific businesses and practices followed by industry and trade in India.
Q.NO. 55. What is the file format in which invoice has to be reported to IRP?
Invoice details in prescribed schema (INV-01) have to be reported to IRP in JSON format.
‘JSON’ stands for Java Script Object Notation. It can be thought of as a common language for systems/machines to communicate between each other and exchange data.
As the ERP or Accounting software will generate it, taxpayer need not worry about it. This format is also used in GST system for reporting all data to GST System.
Q.NO. 56. What are the various types of fields in e-invoice schema?
1. Data for fields marked as ‘Mandatory’ have to be provided compulsorily.
2. A mandatory field not having any value can be reported as NIL.
3. Fields marked as ‘Optional’ may or may not be filled up. Many of these are relevant for specific businesses (e.g. Batch No., Attributes etc.) and to cater to specific scenarios (e.g. export, e-way bill etc.).
4. Some sections in the format are marked as ‘Optional’. But, if this section is selected, some of the fields may be mandatory. For example, the section ‘e-way Bill Details’ is marked as optional. But, if this section is chosen, the field, ‘Mode of Transportation’ is mandatory.
Q.NO. 57. Can the supplier place their entity logo on e-invoice?
Elements of invoice which are internal to business, such as company logo/slogan etc. are not part of e-invoice format.
After reporting invoice details to IRP and receipt of IRN, at the time of issuing invoice to receiver (e.g. generating as PDF and printing as paper copy or forwarding via e-mail etc.), any further customization, i.e. insertion of company logo, additional text-like slogan etc., can be made by respective ERP/billing/accounting software providers.
Q.NO. 58. What is the maximum number of line items which can be reported in an invoice?
The limit is kept at 1000, currently. It could be enhanced based on requirement, if any, in future.
Q.NO. 59. Whether the Form GST INV-01 provides for incorporating the address and bill-to party and their PAN details?
Yes. The GST INV-01 provides for incorporating the address and bill-to party and their PAN details in the placeholders/columns provided in the schema/format.
Q.NO. 60. In the e-invoice schema, the amount under ‘other charges (item level)’ is not part of taxable value. However, some charges to be shown in invoice are leviable to GST. How to mention them?
Such other charges (includable for the levy of Tax), e.g. freight, insurance, packing & forwarding charges etc. can be added as one more line item in the invoice.
Q.NO. 61. Is it permissible to show negative values (for deducting certain amounts from the value of goods supplied Eg. underloading penalty, deductions etc.) in line items in the invoice ? How to report the such amounts which do not attract Tax in the invoice?
In the line item details, such values can be shown in ‘Item Discount Amount’. Being ‘discount’, the value is automatically treated as negative.
Q.NO. 62. The current e-invoice template provides for total discount for all the products or services. Will this be possible in the e-invoice?
Yes. There is a mechanism and placeholders to provide discounting on item level as well as total discounts on the invoice value.
Q.NO. 63. We need to show abated value in the invoice? How to report in such scenarios?
Some supplies are eligible for abatement on value. For example, in real estate, where the taxable value is 67% of the agreement value.
To report invoices in such scenarios, below workaround is suggested:
Pre_Tax_Value = Rs. 1,00,00,000/-
Taxable_Value = Rs. 67,00,000 /
GST (@ 5%) = Rs. 3,35,000/-
Other Charges (item level) = Rs. 33,00,000 (Abatement Charges)
Total_Inv_Value = Rs. 1,03,35,000
Q.NO. 64. In our business, there are scenarios where ‘amortization cost’ needs to be included invoice value (as such amount is not to be recovered from the counter party). How to report this in the invoice?
Including a separate field/column for ‘amortisation cost’ will be examined in the next revision of schema (INV-01).
As a work around, such businesses may report ‘amortised cost’, as shown in below example (where amortised cost is Rs. 2176/-):
Values at Item Level:
Pre_tax_value = Rs. 25067.52
Taxable_value = Rs. 27243.52 (Base value + Amortised cost of Rs. 2176)
Tax Rate = 28 %
IGST Value = Rs. 7628.19
Values at Invoice Level:
Discount_Amt_Invoice_Level = Rs. 2176/- (Amortised cost)
Total Invoice Value = 32695.71 (27243.52 + 7628.19 – 2176)
Q.NO. 65. In e-invoice schema, there is no placeholder for mentioning TCS (Tax Collected at Source) collected by suppliers under Income Tax Act, 1961. What to do?
At present, there is no separate field/column for TCS. Including it in format will be examined in next version.
However, as a work around, the field of “Other Charges (Invoice Level)” can be used to mention TCS where it doesn’t form part of taxable value.
It may further be noted that the Form GST INV-01 is only to report specified invoice particulars to IRP. Once IRN is obtained from the portal, the business may add any other elements not relevant to GST, while issuing invoice finally to buyer.
Q.NO. 66. In the current schema, there is no provision to report details of supplies not covered under GST, e.g. a hotel wants to give single invoice for a B2B supply where the supply includes food and beverages (leviable to GST) and Alcoholic beverages (outside GST).
For supplies which do not attract GST levy, separate invoice may be issued by such business entities.
Q.NO. 67. Will the e-invoice schema/format cater to reverse charge mechanism?
Yes. E-invoice system has a reverse charge mechanism reporting, as well.
Q.NO. 68. In INV-01 proforma, there is a field, “IGST Applicability despite Supplier and Recipient located in same State/UT”. What is the relevance/applicability of this field?
This field is meant for reporting scenarios where the supply is chargeable to IGST despite the fact that the Supplier and Recipient are located within same State/UT, as in the case of the supplies covered by the Notification No. 11/2018-Central Tax (Rate) dated 28.05.2018 levying GST on supply/trading of Priority Sector Lending Certificates (PSLCs) on reverse charge basis (i.e. the tax to be paid by the buyer bank).
The Circular No.93/12/209-GST dated 08/03/2029 issued by TRU ( CBIC ) clarifies that nature of supply of PSLC between banks may be treated as a supply of goods in the course of inter-State trade or commerce and accordingly IGST is payable.
Q.NO. 69. Will there be an option for linking multiple invoices in case of debit note/credit note?
Yes. There will be an option for linking multiple invoices to a debit / credit note as already permissible.
Q.NO. 70. In case of Credit Note and Debit Note, is there any validation w.r.t referred invoice number?
There is no linkage with any invoice required, in view of the amended provisions of GST.
Q.NO. 71. For generating IRN, whether the GSTINs of supplier and recipient should be active on GST system?
Yes. As e-invoicing is mandated for notified registered persons to other ‘registered persons’, both the GSTINs of supplier and recipient shall be active in GST System, as on the date of document (Invoice/DBN/CDN) being reported.
Q.NO. 72. In case some HSNs which are otherwise valid are not accepted by e -invoice portal, what is the remedy?
In the normal course such situation does not arise. But in case, any HSN which is otherwise legally valid but is not available / not accepted on IRP, the same may be communicated by raising a ticket on GST Self-Service Portal.
Further, it may be noted that a Search HSN facility is made available on GST System for ease of reference at : https://services.gst.gov.in/services/searchhsnsac ; and a HSN Master is also published on IRP: https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in/Others/MasterCodes, for ready reference.
Q.NO. 73. Will there be separate invoice formats required for Traders, Medical shops, Professionals and Contractors
No. The same e-invoice format will be used by all kinds of businesses. The proforma has mandatory and non-mandatory fields. Mandatory field has to be filled by all taxpayers. Non-mandatory field is for the business to choose. It covers all most all business needs and specific sectors of business may choose to use those non-mandatory field which are needed by them or their eco-system.
Q.NO. 74.How long will the e-invoice generated would be available at the Government portal?
It is reiterated that the e-invoice is not generated on the GST/NIC portal. It needs to be generated only on the supplier’s system (ERP or the accounting/ billing system / other software tools of the supplier) and can be saved for future reference. As far as data on IRP is concerned, it will be available only for 24 hours.
However, it may be noted that the IRN once generated, it is valid for 30 days for use by the supplier to issue the e-Invoice.
Q.NO. 75. Is it possible to auto-populate fields of the e-invoice form GST INV-01, based on credentials entered in order to minimize data entry errors?
No. It is not possible to auto-populate fields of the e-invoice form GST INV-01.
However, such facility can be built into the ERP or accounting/billing system of the supplier. Most of the accounting/billing software have such facility in the name of ‘item master’, ‘supplier master’, ‘buyer master’ etc. which would meet the requirement, since the invoice generation happens on the system of the supplier.
Q.NO. 76. Will it be possible to add transporter details as well?
Yes. The transporter details can be entered in form GST INV-01 at the time of generation of E-invoice.
Q.NO. 77. Will the e-invoice have columns to show invoice currency?
Yes, the seller can display the currency. Default will be INR.
Q.NO. 78. Whether the system permits the supplier/ exporter to add “Work order Number” in the format GST INV-01 ?
Such additional details for reference of the supplies like Work/purchase order or LC-number etc. can be incorporated in the invoice by the supplier while issuing the same with the IRN / QR-Code generated by posting the specified details on the IRP.
Q.NO. 79. Whether the Invoice number should be the same as Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and whether both the IRN and invoice number are mandatory on the invoice?
No. The Invoice number and the IRN are different and both are mandatory. The running serial Invoice no. (not exceeding 16 characters in one or multiple series, containing alphabets or numerals or special characters and any combination thereof, unique for a financial year ) in terms of the Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017, has to be assigned by the supplier and it is internal to the business entity. Invoice numbering pattern can differ from business to business, but it should be as per the said provision.
The IRN (e.g. 35054cc24d97033afc24f49ec4444dbab81f542c555f9d30359dc75794e06bbe), on other hand, is a unique reference number, auto-generated, on IRP, after successful submission of the GST INV-01 with the specified details. It is mandatory to print the IRN embedded in the QR-code, on the Invoice issued by the supplier. Separate mention of the IRN on the invoice, in addition to the QR-code embedded with IRN, is optional.
Q.NO. 80. Whether the IRN is to be captured in the Supplier’s ERP?
Supplier has to keep the IRN against each of its invoice. It will be advisable to keep the same in the ERP as invoice without IRN will not be a legal document.
Q.NO. 81. Can IRP reject a submitted GST INV-01? On reporting invoice details to IRP, what validations will be performed on the portal?
Yes. IRP can reject GST INV-01. In case of failure to register the invoice IRN will not be generated and the system would reflect relevant error codes, which would give an idea about reasons for rejection. The IRN Error-Code; Error- Message; Reasons for Error; and the Resolution for each of the errors can be accessed at: https://einvoice1-trial.nic.in/others/geterrorcodes/INV.
IRP will also check whether the invoice was already reported and existing in the GST System. This validation is based on the combination of Supplier’s GSTIN-Invoice Number- Type of Document-Fin.Year, which is also used for generation of IRN. In case the same document (invoice /DBN/CDN) has already been reported earlier, it will be rejected by IRP.
Q.NO. 82. Can I print an e-invoice?
Yes. The e-invoice can be printed. In fact, on successful submission of GST INV-01 with the specified details of the invoice proposed to be issued for the supplies, the IRP generates the IRN & QR-Code which are received by the suppliers on their ERP/Accounting/Billing System, for further issue of the e-invoice to cover the supplies. The e-invoice with IRN & QR-Code can be converted it into PDF for printing.
Businesses who don’t have their own ERP/Accounting Software, will be downloading and using the free offline utility (‘bulk generation tool’) to upload invoice data on e-invoice portal and obtain signed invoice (in JSON format). In this scenario also, there is a facility on e-invoice portal to generate ‘human-readable’ PDF copy of invoice, for save/print/e – mail etc..
Q.NO. 83. Do I need to print IRN on the invoice?
No. QR Code embedded with the IRN is mandatory on the invoice. Separate mention of the IRN, in addition to the QR Code embedded with the IRN , is optional.
Q.NO. 84. Do I need to print QR Code on the invoice? If so, what shall be its size and location on the invoice copy?
Yes. The QR code embedded with the IRN received from IRP , shall be extracted and printed on the invoice. This is one of the mandatory particulars of invoice under Rule 46 of CGST Rules.
However, printing of QR code on a separate paper, other than the Invoice itself, is not allowed. While the printed QR code shall be clear enough to be readable by a QR Code reader, the size and its placing on invoice is up to the preference of the notified registered person.
Q.NO. 85. What are the mandatory contents of e-invoice ?
The mandatory particulars shall be as per Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017, including QR code embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
Q.NO. 86. While receiving IRN, the IRP is also adding its “digital signature”, “Acknowledgement No.” and “Date”. Whether these details are also required to be printed while issuing invoice?
No. There is no mandate to print “digital signature of IRP”, it’s “Acknowledgement No.” and “Date” on the e-invoice copy. The “Acknowledgement No.” and “Date” given by IRP are only for reference. Being a 15-digit number, the acknowledgement number will also come handy for printing e-invoice or for generating e-way bill, instead of keying in the 64-character long IRN.
Q.NO. 87. Whether e-invoice needs to issue in duplicate/triplicate, in case e-invoice is applicable?
Where e-invoicing is applicable, there is no need of issuing invoice copies in triplicate/duplicate, as envisaged under Rule 48(6) of CGST Rules, 2017.
Q.NO. 88. Will it be possible for invoices that are registered on IRP to be downloaded and saved on handheld devices?
It depends on the ERP/Accounting/Billing Software, being used by the notified registered person (supplier). It is advisable for the supplier to properly store the signed e-invoice JSON, as received from IRP.
Q.NO. 89. Whether signed JSON file received from IRP [after generation of IRN] is required to be saved, in case a notified registered person uses offline utility to generate IRN?
IRP doesn’t store invoices and hence the facility to download e-invoice JSON from IRP is available only for limited number of days. So, the taxpayers shall take care accordingly.
The facility to download signed invoice JSON from GST System (for suppliers and recipients, over a longer period of time) will be made available in due course.
Q.NO. 90. What is the period of retention/storage/archival, in case of e -invoicing?
As per Rule 56(16) of CGST Rules, 2017, “Accounts maintained by the registered person together with all the invoices, bills of supply, credit and debit notes, and delivery challans relating to stocks, deliveries, inward supply and outward supply shall be preserved for the period as provided in section 36…” The same applies to e-invoicing also.
Q.NO. 91. Is it mandatory to print e-Invoice as provided in the portal or the notified registered persons can adopt their own format for invoice?
There is no specified format for the e-invoice. The e-invoice shall be in terms of the Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017; and it should be printed, inter alia, with the QR-code embedded with the IRN, on it.
Q.NO. 92. How to check to know whether an invoice was duly reported to IRP?
In order to know whether an e-invoice was issued after due reporting on IRP, use the “Verify QR Code” mobile app which may be downloaded from einvoice1.gst.gov.in > Help > Tools > Verify QR Code App.
One can also verify the authenticity or correctness of an e-invoice by uploading the signed JSON file or Signed QR Code (string) on e-invoice portal: einvoice1.gst.gov.in > Search > ‘Verify Signed Invoice’.
Q.NO. 93. What data is embedded in QR Code?
The QR code will consist of the following key particulars of e-invoice:
1. GSTIN of the Supplier;
2. GSTIN of the Recipient;
3. Invoice number, as assigned by Supplier;
4. Date of generation of invoice;
5. Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax);
6. Number of line items;
7. HSN Code of main item (line item having highest taxable value);
8. Unique IRN (Invoice Reference Number); and
9. Date of Generation of IRN.
Q.NO. 94. Is it possible to have more than one QR code on an invoice?
Yes. Apart from the QR code relating to IRN, the supplier is free to place any other QR Code which is required as per business needs or otherwise mandated by any other statutory requirement. In such cases, the QR Codes need to be marked clearly so that they can be distinguished easily.
Q.NO. 95. Whether, on generation of IRN, the e-invoice is sent by IRP by e-mail or otherwise, to the receiver?
No. IRP will not send the e-Invoice to the receiver, at all.
Upon receiving I R N & Q R – c o d e [ signed JSON] from the IRP, it is for the supplier to generate the e-invoice, along with QR Code embedded with IRN; and all other relevant details as prescribed under Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017; and send it to the receiver.
Q.NO. 96. How will the supplier send the e-invoice to the receiver?
The hard copy of the e-invoice, along with QR Code embedded with IRN; and all other relevant details as prescribed under Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017, can be sent to the receiver. A suggested mechanism may be to exchange the PDF of the JSON received from IRP, including QR code, as the best authenticated version of the e-invoice for business transactions.
However, a mechanism to enable system-to-system exchange of e-invoices through eco- system partners will be made available in due course.
Q.NO. 97. How do the small taxpayers (who are not mandated to issue e-Invoice) receive the e-invoices from the notified registered persons?
The taxpayers, who are not mandated to issue e-Invoice, would receive the e-invoices from the notified registered persons in the same way as it is being done now. The hard copy of the e-invoice, along with QR Code embedded with IRN; and all other relevant details as prescribed under Rule 46 of CGST Rule, 2017, can be sent to the receiver by suitable means (by post, courier etc). Alternatively, the notified registered persons can convert the signed e-invoice JSON into PDF and share the same by e-mail.
However, a mechanism to enable system-to-system exchange of e-invoices will be made available in due course.
Q.NO. 98. Where e-invoicing is applicable, whether carrying e -invoice print during transportation of goods is mandatory?
No. As per Rule 138A(2) of CGST Rules, 2017, where e-invoicing is applicable, “the Quick Reference (QR) code having an embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN) in it, may be produced electronically, for verification by the proper officer, in lieu of the physical copy of such tax invoice.” Therefore, carrying e -invoice print during transportation of goods is not mandatory.
Q.NO. 99. Can I amend details of a reported invoice for which IRN was already generated?
No. Amendments are not possible in respect of the specified details posted on GST INV-01, after the generation of IRN, on IRP.
The notified registered person has an option to cancel the IRN on IRP within 24 hours of generation of IRN, for any reason, either before issuing e-Invoice or after generation of e-Invoice. However, if the connected e-way bill is active or verified by officer during transit, cancellation of IRN will not be permitted.
In case of cancellation of IRN, GSTR-1 will also be updated with such ‘cancelled’ status.
Q.NO. 100. Can an invoice number of a cancelled IRN be used again?
No. Once an IRN is cancelled, the concerned invoice number cannot be used again to generate another e-invoice/IRN, even within the permitted cancellation window of 24 hours. If it is used again, then the same will be rejected, when it is uploaded on IRP, as IRN is a unique string based on Supplier’s GSTIN, Document Number, Type of Document & Financial Year.
Q.NO. 101. Can I partially cancel a reported invoice?
No. It has to be cancelled in toto. A partial cancellation of reported e-invoice is no t allowed. A fresh e-invoice could be issued to cover the actual supply.
Q.NO. 102. I have generated IRN for an invoice. There was a discrepancy in the invoice and supply also didn’t materialize. Hence, I had to cancel e-Invoice in my system. However, I could not cancel the IRN on IRP as the cancellation window (24 hours) had expired. What to do?
Obtaining IRN by notified registered persons is a legal requirement before issue of specified documents to recipients. Upon generation of IRN, amendments are not possible on IRP and cancellation of IRN only is permitted within a time window of 24 hours. So, the details of invoices actually issued during the tax period will have to be reported in GSTR-1. However, in case any e-invoice is cancelled, it can be deleted form the GSTR-1 before submission.
The notified registered person shall ensure that details of the fresh e-invoice issued as substitution to any cancelled e-invoice, if any, is figuring in the list of auto-populated invoices in the GSTR-1 for the relevant tax period. If not, it should be incorporated before submission of GSTR-1.
Q.NO. 103. Whether a notified registered person use the same invoice, when they failed to issue the same generated on the previous day, for supply of the same goods?
If the nature of goods remains the same and there is no change in taxable value and tax rate and only the shipment/dispatch is delayed, the same e-invoice can be used for supply of goods, along with a valid e-Way Bill. However, if the invoice is cancelled, then the same number cannot be used for the fresh invoice generated subsequently.
Q.NO. 104. When Invoice details need to be uploaded for Export Invoice, if port details needs to be changed, how to amend/correct the details ?
Once IRN was generated on IRP, the specified details in GST INV-01, including the Port Code, cannot be amended. In case there is any requirement to change the port code, the IRN could be cancelled within 24 hours and generate a fresh IRN with correct port code.
In case the discrepancy was noticed subsequently, the discrepancy in e-invoice details could be rectified while filing GSTR-1 on the GST portal.
Further, in case the GSTR-1 was already filed, the discrepancy can be rectified by using the amendment option for GSTR-1, as provided on GST portal.
Q.NO. 105. Whether e-way bill is compulsory, with the introduction of e-invoicing?
Yes. While transporting goods, wherever the e-way bill is mandatory as per the EWB-rules (Rule 138 to 138E of CGST Rules, 2017), the requirement continues to be mandatory.
Q.NO. 106. Whether the e-way bill get auto-generated?
In case both Part-A and Part-B of e-way bill are provided while reporting invoice details to IRP, e-way bill will be auto-generated.
In case Part-B details are not provided at the time of reporting specified details of invoice to IRP, the same will have to be provided by the user through ‘e-way bill’ tab in IRP log in or e-Way Bill Portal, so as to generate e-way bill.
Q.NO. 107. Why EWB is required separately when e-invoice is issued through the prescribed procedure?
Ans.: Generation of e-invoice and e-way bill are mandatory statutory requirements, as applicable under different relevant statutory provisions. Generation of e-invoice is for notified registered persons with turnover exceeding Rs.20 crore during any Financial Year since 2017-18. Generation of E-way bill is based on a different threshold limit irrespective of the fact whether the person is liable to issue e-invoice or not. Secondly e-way bill can be generated either by the supplier (or) by the recipient (or) by the transporter, while e-invoice shall be issued by the notified registered persons.
Moreover, the EWB is for the movement of the goods, subject to the conditions envisaged in the relevant CGST Rules and not relevant for the services. But the e-Invoice (and / or CDN/DBN) is mandatory for supply of Goods/Services or both by the notified registered persons, for the supply or in relation to supply.
Thus, both EWB and E-invoice are mandatory for the notified registered persons for whom the relevant provisions are applicable as per Law.
Q.NO. 108. What does it mean by simultaneous generation of EWB while issuing einvoice? Does it mean that there is no need for separate generation of EWB when e-invoice is generated?
While generating e-invoice, the relevant details like GSTIN of supplier, Document number etc. are auto populated in both Table Part –A and B of the e-way bill, to facilitate generation of EWB. Columns for entering the mandatory information for Part-B of EWB like Transporters details are also available in the e-invoice GST INV 01 and hence notified registered person, for the supplies of Goods, have the option to enter the relevant details, if available with them at the time of generation of e-invoice to simultaneously generate EWB.
In case the mandatory information for Part-B of EWB like Transporters details are not available with them at the time of generation of e -invoice the details for Part – B of EWB can be uploaded in the e way bill portal subsequent to generation of IRN/QR- code for e-invoice.
It may be noted that generation of e-invoice and e-way bill are mandatory statutory requirements, as applicable under different relevant statutory provisions.
Q.NO. 109. After generation of IRN, is there any time limit for generation of e-way bill (where applicable/desired)?
No such time limit is normally applicable presently in the system. But, the IRN itself is valid for 30 days from the date of generation. Hence, EWB cannot be generated, once IRN is not valid.
Q.NO. 110. Will the e-invoice details be pushed to GST System? Will they populate the return?
Yes. On successful reporting of invoice details to IRP, the e-invoice data (payload) including IRN, will be saved in GST System.
The GST system will auto-populate them into GSTR-1 of the supplier and GSTR-2A of respective receivers. IRN and IRN date will also be shown along with source marked as ‘e-invoice’ (except where such details were modified/re-uploaded by taxpayer).
Q.NO. 111. Whether the notified registered person has to check the details of all e-Invoice before filing GSTR-1, even if they are auto-populated ?
It may be noted that the auto-population of details from e-invoices into GSTR-1 is only a facility extended to notified registered person (taxpayer). In self-assessment, the statutory obligation to file GSTR-1 with accurate details as per documents raised during the relevant tax period lies with taxpayer.
Further, owing to validations in GSTR-1, some of the e-invoices reported may not get auto-populated in the tables of GSTR-1. However, the same may be available in the consolidated excel file downloaded from GSTR-1 dashboard (with corresponding error description). These may also be corrected and re-uploaded by the taxpayers before filing GSTR-1.
Hence, the taxpayer shall verify the data in each field, and file the same, in the light of relevant legal provisions. Other than the auto-populated e-invoices, taxpayers are further required to add details of any other supplies made during the tax period, in respective tables of GSTR-1.
Q.NO. 112. My supplier says they have generated IRN for the invoice. But, in GSTR-2A, details of IRN are not appearing against those invoices, why?
It may be possible in a situation where the details auto-populated into GSTR-1 from e- invoices vis-a-vis actual documents issued, might have changed in any respect and the same are edited/deleted/re-uploaded by the supplier while filing GSTR-1. In such cases (i.e. where the details are modified by supplier), the re-uploaded/modified details will be visible. However, the ‘Source’, ‘IRN’ and ‘IRN date’ will be reset to blank in respective tables of GSTR-1 and also the said details won’t get reflected in GSTR-2A/2B/4A/6A also.
So, non-appearance of IRN details in GSTR-1/2A alone shouldn’t be assumed to mean that such invoices were not reported to IRP.
You can, however, verify the authenticity of e-invoice by uploading the signed JSON file or Signed QR Code (string) on e-invoice portal: einvoice1.gst.gov.in > Search > ‘Verify Signed Invoice’. Alternatively, you can scan the QR Code on invoice copy, with “Verify QR Code” mobile app which may be downloaded from einvoice1.gst.gov.in > Help > Tools > Verify QR Code App
ABBREVIATION
| ABBREVIATION – | Explanation |
| IRP | Invoice Registration Portal |
| IRN | Invoice Reference Number |
| QR Code | Quick Reference Code |
| ERP | Enterprise Resource Planning |
| JSON | Java Script Object Notation |
| NIC | National Informatics Centre |
| NIC-GePP | NIC – GST e-invoice Preparing & Printing |
| GSP | GST Suvidha Provider |
| B2B | Business to Business |
| B2C | Business to Customer |
| GSTN | Goods and Service Tax Network |
| GSTIN | Goods & Services Tax Identification Number |
| NBFC | Non Banking Financial Company |
| ABBREVIATION – | Explanation |
| GTA | Goods Transport Agency |
| FTWZ | Free Trade Warehousing Zone |
| ISD | Input Service Distributor |
| TCS | Tax Collected at Source |
| TDS | Tax Deducted at Source |
| GST API | GST Application Programming Interface |
| RCM | Reverse Charge Mechanism |
| HSN | Harmonised System of Nomenclature |
| LUT | Letter of Undertaking |
| EWB | Electronic Way Bill |
| DBN | Debit Note |
| CDN | Credit Note |
Source- http://centralexcisechennai.gov.in/Chn_I_2022_File/GST%20Book%20on%20E%20invoicing.pdf




