Introduction
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a system where one person determines the tax and pay the tax by self-assessment. When the tax is paid by doing self-assessment, there is likely to be a chance that the tax may be short paid without any malice intention or there may be also a chance that the assessees may pay the tax short intentionally or knowingly. Under such circumstances, there are some provisions which are followed by the authority to recover those taxes which are short paid by assesses intentionally or without intention.
GST is levied on any taxable outward supplies by a person. The complete responsibility of calculation, chargeability, and payment of tax has been assigned to the person making outward supplies. It is a self-assessment tax without any interference from the department. However, it may happen that a person has short paid or not paid taxes or claimed excess or wrongful input tax credit not necessarily with the intention of fraud but otherwise.
Under Chapter XV from Section 73 to Section 84 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, The provisions relating to Demand and Recovery under Goods and Services Tax (GST) has been discussed. The process of recovery of GST starts with the issuance of the show-cause notice and end up in the Adjudication proceedings.
Central Goods and Services Tax (GST) Act, 2017, authorizes the proper offices to demand and determine the amounts:
1. A tax which is not paid (Section 73 and Section 74)
2. A tax which is short paid (Section 73 and Section 74)
3. A tax which is erroneously refunded (Section 73 and Section 74)
4. Wrongly availed Input Tax Credit (Section 73 and Section 74)
5. Wrongly utilized Input Tax Credit (Section 73 and Section 74)
6. A tax which is collected but not paid (Section 76)
7. A tax which is collected beneath the wrong head (Section 77)
8. Initiation of Recovery Proceedings Under GST (Sec 78)
Demand and Recovery under GST:
Demand means the wish or desire of a consumer to get or acquire goods or services. When there will be more demands, the market will flourish. It is an action that leads to the growth of the economy. The government imposes a tax on every goods and service. Every person is liable to pay the tax to the Government when they purchase the goods. When a person fails to oblige with his duty, the Government has to recover the tax from the defaulter. Tax is the basic source for the Government to run the economy of the country failing in which causes the economic imbalances. The government adopts strict measures to recover the tax from the defaulters.

Demand Order in Genuine Cases (Sec 73)
GST being a new tax, it may happen that any person has made the erroneous claim of blocked ITC or considered a taxable supply an exempt supply or paid tax at a lesser rate due to no knowledge of the change in tax rates. These are few scenarios where a person generally makes mistakes under a genuine belief and without any reason of fraud, wilful misstatement or suppression of facts to evade tax.
In cases where it appears to the Proper Officer that any person has:
→ Not paid tax
→ Short paid any tax
→ Erroneously received refund
→ Input Tax Credit (ITC) wrongly availed or utilized
In all such cases, the officer shall issue a show-cause notice (SCN) on the person as to provide reasons why tax should not be paid by him along with interest applicable under section 50(1). The process and time limit of issuing demand notice and order can be better understood below
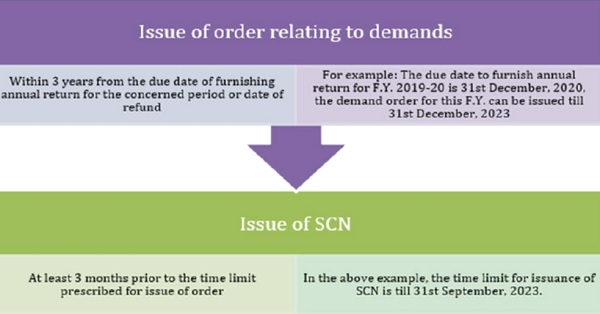
- Notice for other tax periods: If an SCN has been issued for a particular period, then there is no requirement to issue separate notices for another tax period not covered in the SCN provided a statement containing the relevant details is furnished to the person and the grounds of belief are same as of tax periods covered in SCN.
- What shall be the penalty: The penalty provision under various situations can be better understood as detailed below:
a. If a person deposits the amount of tax along with interest before service of notice and informs the proper officer in writing of such payment No penalty shall be levied and no demand notice shall be issued
b. In the above case, if the amount deposited is short of the actually payable Demand notice shall is issued for the balance payable amount
c. If any person pays the tax along with interest within 30 days of issue of demand notice No penalty
The Board has vide Circular No. 76/50/2018-GST dated 31st December 2018 has clarified that there shall be no penalty under section 73(11) as discussed in point ‘e’ on delayed filing of GSTR 3B. However, a general penalty under section 125 shall be levied since the tax has been paid late.
d. If a person pays amount payable after a period of 30 days from the issue of notice 10% of the tax amount due or Rs. 10,000/- whichever is higher
e. If a person has collected tax but not paid within 30 days 10% of the tax amount due or Rs. 10,000/- whichever is higher
The Board has vide Circular No. 76/50/2018-GST dated 31st December 2018 has clarified that there shall be no penalty under section 73(11) as discussed in point ‘e’ on delayed filing of GSTR 3B. However, a general penalty under section 125 shall be levied since the tax has been paid late.
Demand In Case of Fraudulent Tax Evasion (Sec 74)
Where a person indulges in any transaction with intent to cause tax evasion, then an extended time limit is provided to the authorities for initiating demand proceedings and higher penalties against such persons are specified under the GST law.
If it appears to the Proper officer that any person by reason of fraud, or any wilful-misstatement or suppression of facts to evade tax has –
→ Not paid tax
→ Short paid any tax
→ Erroneously received refund
→ Input Tax Credit (ITC) wrongly availed or utilized
Then, the proper officer shall issue demand notice requiring a person to show cause as to why he should not pay the amount specified in the notice along with interest payable applicable under section 50(1). The process and time limit of issuing demand notice and order in this situation are as follows:

- Notice for other tax periods: Similar to the provision in section 73, an officer can start demand proceedings by furnishing a statement of tax particulars for earlier tax periods without the issuance of a separate SCN.
- What shall be the penalty: The penalties in cases of fraud, wilful misstatement, and suppression of facts can be levied up to 100% of the tax amount. The various scenarios are as follows:
| Particulars | Penalty amount |
| If a person deposits an amount of tax along with interest before service of notice and informs the proper officer in writing of such payment | 15% of tax payable |
| In the above case, if the amount deposited is short of the actually payable | Demand notice shall be issued for the balance payable amount along with penalty on same |
| If any person pays the tax along with interest within 30 days of issue of demand notice | 25% of tax payable |
| If any person pays the tax along with interest within 30 days of communication of demand order | 50% of tax payable |
| In all other cases | 100% of the tax amount due or Rs. 10,000/-whichever is higher |
General Provisions Relating Determination Of Tax (Sec 75)
- Where the service of notice or issuance of order is stayed by an order of a court or Appellate Tribunal, the period of such stay shall be excluded from the time period of 3 and 5 years
- Where any Appellate Authority or Appellate Tribunal or court decides that charges of fraud or any wilful-misstatement or suppression of facts to evade tax are not sustainable, then tax shall be determined deeming the notice is issued under section 73
- If an appeal is filed by the revenue to the Appellate Tribunal or the High Court or the Supreme Court against such decision of the Appellate Authority or the Appellate Tribunal or the High Court and the said appeal is pending then the period of the decision by the authorities and decision of appeal shall be excluded in the calculation of time period for issue of demand order under section 73 and section 74.
- Any order to be issued based on the direction of the Appellate Authority or Appellate Tribunal or a court shall be issued within 2 years from the date of communication of such direction
- An opportunity of hearing shall be granted whenever requested in writing. The hearings can be adjourned a maximum of 3 times during the proceedings on the basis of sufficient cause shown.
- The order issued by the proper officer shall have relevant facts and the basis of decision. Also, the amount of tax, interest, and penalty demanded in the order shall not be more than the amount demanded in notice.
- Where the Appellate Authority or Appellate Tribunal or court modifies the amount of tax determined by the proper officer, the amount of interest and penalty shall stand modified accordingly.
- The interest shall be payable under section 50(1) on the tax amount even if not specified in the demand order.
- Where any penalty is imposed under section 73 or 74, no penalty shall be levied under other sections of the act for the same act or omission.
Demand In Case Tax is Collected But Not Paid To Government (Sec 76)
- A demand notice shall be issued to a person who has collected tax but not paid to the government.
- The amount shall be determined after considering the representation made by the person. The amount payable shall include interest on tax to be calculated from the date of collection till the date it is paid to the government.
- In case any amount is already deposited by the assesse, such amount shall be adjusted against the amount payable and balance if any shall be credited to either fund or to person from whom tax is collected.
- An opportunity of hearing shall be provided to the person if a request is made in writing.
- The order shall be passed within 1 year from the date of issue of notice. Any period of stay by the authorities shall be excluded in the calculation of 1 year. The order shall set out the relevant facts and the basis of his decision.
- The person, who has borne the incidence of the amount, may apply for the refund of the same in accordance with the provisions of section 54.
When amount payable is not paid, the proper officer shall, by himself or through another officer proceed to recover in the following modes:
- Deduct/ recover the amount so payable from any money owing/ goods detained belonging to the person liable
- Recover from another person from whom money is due to the person liable by issuing a notice in writing. This notice can be amended or revoked or extended for time at any time by the officer.
- distrain any movable or immovable property belonging to or under the control of such person, and detain the same until the amount payable is paid
- prepare and sign a certificate specifying the amount due and send it to the Collector of the district who shall proceed to recover the same
- File an application to the appropriate Magistrate who shall recover the amount as if it were a fine imposed
Section 77 of CGST Act 2017: Tax Wrongfully Collected and paid to Central Government or State Government
(1) A registered person who has paid the Central tax and State tax or, as the case may be, the Central tax and the Union territory tax on a transaction considered by him to be an intra-State supply, but which is subsequently held to be an inter-State supply, shall be refunded the amount of taxes so paid in such manner and subject to such conditions as may be prescribed.
(2) A registered person who has paid integrated tax on a transaction considered by him to be an inter-State supply, but which is subsequently held to be an intra-State supply, shall not be required to pay any interest on the amount of central tax and State tax or, as the case may be, the Central tax and the Union territory tax payable
Initiation Of Recovery Proceedings Under GST (Sec 78)
Any amount that is payable pursuant by an order shall be paid within 3 months from the date of order. If the amount payable is not paid within the required period of time then recovery proceedings shall be initiated against such person under the GST law.
The officer can reduce the time period of 3 months for payment of tax for specific cases if he considers it necessary in the interest of revenue. The reasons for the reduction of the time period shall be recorded in writing and communicated to the person from whom amount is payable
Modes Of Recovery
Where any amount payable by a person to the Government is not paid, then the proper officer shall proceed to recover the amount by one or more of the following modes –
- Recovery by deduction from any money owed (Rule 143): The proper officer may proceed himself or order any other specified officer to deduct the amount from any amount that is due to such person (For example refund due to a person)
- Recovery by the sale of goods under the control of proper officer (Rule 144): The proper officer may detain and proceed to sell of goods belonging to the person in default if the amount payable remains unpaid. Procedure to be followed for selling goods belonging to the person in default are as below:
→ The officer shall prepare an inventory and estimate the market value of such goods and will sell only so much as to recover the amount payable along with the cost of selling and administrative expenses. -* The said goods shall be sold through a process of auction, including e-auction and shall be transferred to the person making the highest bid. -*The proper officer may specify the amount of pre-bid deposit to be furnished to make the bidders eligible to participate in the auction, which may be returned to the unsuccessful bidders, forfeited in case the successful bidder fails to make the payment of the full amount, as the case may be.
- Recovery from a third- person (Rule 145): The proper officer shall issue a notice requiring any person from whose amount is due or any other person who holds money for or on account to the person in default to pay the payable amount within the time specified in the notice. The time limit can be revoked, amended, or extended by the officer on a case to case basis. The person can prove to the officer that there is no money due by him to the person in default or that he does not hold any money on or behalf of the person in default.
If a person who to who notice is issued fails to make the payment, then the said person shall be deemed to be a ‘Defaulter in respect of such payable amount’.
RECOVERY: MODES OF RECOVERY OF CONFIRMED DUES- Section 79
- Deduction from the amounts due to the taxable person
- Instruct other specified officer to deduct the dues from the amount which such officer is liable to pay to the taxable person
- By detaining or selling any goods (belonging to taxable person) under his control or under the control of other specified officer
- By issuing notice to Bank, post office, insurance company or customer or such other person who hold the money of the person liable to pay or due to such person to remit the money to Government account
MODES OF RECOVERY OF CONFIRMED DUES
- Payment to the taxable person by such person even after receipt of notice-such person is liable personally to the extent of such amount due
- Seizing of property based on the authorization from competent authority. Sale of such property if dues and or the cost of distress and keeping of property is not paid within 30 days of seizure.
- Send a certificate specifying the amount due to the District Collector to enable him to recover the same as arrears of land revenue.
- File an application with appropriate Magistrate, who shall proceed to recover the amount specified as if it is a fine imposed by him.
- SGST officer may recover CGST and vice versa
PAYMENT OF DUES IN INSTALLMENT – SECTION 80
- On application the Commissioner / Chief Commissioner may allow payment of dues in installments
- Reasons to be recorded for granting such facility
- Maximum installments shall be 24 monthly installments – interest would be applicable
- Self assessed tax due as per return (which is not paid) is not eligible for installment facility
- Default in one installment- balance dues could be recovered immediately without further notice
LIABILITY TO PAY IN CERTAIN CASES
- Transfer of business [Sec. 85] Both the Taxable person (transferor) as well as transferee are jointly and severally liable.
- Tax could be determined before or after transfer
- Agent & Principal [Sec.86] Agent as well as principal, both are jointly and severally liable
- Company in liquidation [88] Any tax due whether determined before, after or during course of liquidation of the company, if cannot be recovered from the company, then every person who was director of the company at the relevant time shall be jointly and severally liable
- Directors of Pvt. company [89] Where tax dues of the Pvt. company cannot be recovered from the company, then every person who was director of the company at the relevant time shall be jointly and severally liable
Transfer of property to be void in certain cases [Section 81]
- -after any amount becoming due under GST provisions
- -Transfers property with an intention to defraud
- -Such transfer would be void
- -Exceptions
- Tax to be first charge on property [Section 82]
Provisional attachment to protect revenue in certain cases[Section 83]
During assessment (non filers, un registered person), demand proceedings or search proceeding. (Pranit Hem Desai vs. Additional Director General, SCA No 9392 of 2019)
Continuation and validation of certain recovery proceedings [Section 84]
- Transfer of business [Sec. 85] Both the Taxable person (transferor)
as well as transferee are jointly and severally liable. - Tax could be determined before or after transfer
- Agent & Principal [Sec.86] Agent as well as principal, both are
jointly and severally liable - Company in liquidation [88] Any tax due whether determined
before, after or during course of liquidation of the company, if cannot be recovered from the company, then every person who was director of the company at the relevant time shall be jointly and severally liable - Directors of Pvt. company [89] Where tax dues of the Pvt. company cannot be recovered from the company, then every person who was director of the company at the relevant time shall be jointly and severally liable
- Partners of the firm [90] Partners of the dissolved firmFirm as well as partners are jointly and severally liable Every person who was partners at relevant time is jointly and severally liable
- Guardians, Trustees [91] Where business is carried on by a person on behalf of a minor , in case of any tax dues, the same may be recovered from the minor
NOTICES UNDER SEC. 73 OR 74
- A notice can be issued by the Department under Section 73 or Section 74, along with a summary, issued electronically in Form DRC- 01.
- Where such notice has been issued for any period, the proper officer may issue a statement specifying the details of the amount payable in Form DRC-02.
Voluntary payment before issuance of SCN
Under Section 73 Tax + Interest Intimate the Department about voluntary payment in Form DRC-03. The proper officer shall issue an acknowledgement, accepting the payment made by the said person in FORM GST DRC–04, and if satisfied, no notice will be issued.
Under Section 74 Tax + Interest + Penalty @ 15% of tax
Payment within 30 days of issue of SCN
Under Section 73 Tax + Interest Intimate the Department about voluntary payment in Form DRC-03. If the Authority is satisfied with the reply, it will drop the proceedings by the issue an order in Form DRC-05, or else Notice of a personal hearing will be issued.
Payment within 30 days of issue of SCN
Under Section 73 Tax + Interest Intimate the Department about
voluntary payment in Form DRC-03. If the Authority is satisfied with the reply, it will drop the proceedings by the issue an order in Form DRC-05, or else Notice of a personal hearing will be issued.
Under Section 74 Tax + Interest + Penalty @ 25% of tax
Payment after 30 days of issue of SCN but within the stipulated time mentioned in SCN
Under Section 73 Tax + Interest + Penalty @ 10% of tax or Rs. 10,000 whichever is higher Reply to the SCN in Form DRC-06 and submit documents. If the Authority is satisfied with the reply, it will drop the proceedings by the issue of Form DRC-05, or else Notice of a personal hearing will be issued.
Under Section 74 Tax + Interest + Penalty @ 50% of tax
HOW TO VIEW A NOTICE ON THE GST PORTAL?
- Step 1: Log in to the GST Portal.
- Step 2: Click on Services>User Services>View Additional Notices/Orders>Case Details.
- Step 3: Once the taxpayer clicks on View additional notices, he can see all the
Notices/Orders issued by the Department. Click View to see the Case Details.

HOW TO REPLY TO A NOTICE ON THE GST PORTAL (DRC-06)?
- Step 1: Click on ‘Replies’ on the Case Details page.
- Step 2: Click on ‘Add Reply’ tab and select ‘Reply’.
- Step 3: The status of the reply is ‘Pending for reply by the taxpayer’ in the below screenshot. But, once the taxpayer adds the reply it will change.
HOW TO REPLY TO A NOTICE ON THE GST PORTAL (DRC-06)?
- Step 4: Reply page is displayed:

HOW TO REPLY TO A NOTICE ON THE GST PORTAL (DRC-06)?
Step 6: Click Preview to view the reply. If satisfied, click on ‘File’.
Step 7: ‘Submit Application’ page will be displayed. A taxpayer can choose to file with DSC or EVC.
- a. File with DSC: Browse the certificate and click on the button ‘sign’.
- b. File with EVC: An OTP will be sent to the registered mobile number and email ID. On validation of OTP, a success message will be received along with ARN.
Step 8: Notices and Orders page will be displayed. Click on the link to download the filed reply and then click ‘Ok’

Step 9: The Case Details page will be displayed but now the status of reply will change to ‘Reply furnished, pending for order by tax ’
HOW TO VIEW AN ORDER ISSUED BY TAX OFFICIAL?
Step 1: Click on the ‘Orders’ tab in the case details page.
Step 2: All the orders issued against the taxpayer will be displayed.
ADJUDICATION PROCEDURE- Section 75
| Personal Hearing | To be granted:
√ When assessee makes a specific request for the same √ Where the proper officer contemplates an adverse decision against the assessee |
| Can assessee seek adjournment of hearing |
Yes – If there is a sufficient reason Maximum of 3 adjournments are allowed. |
| Order of the officer | √ Shall set out facts
√ Shall give basis for his decision |
| Interest | √ whether or not specifically stated in the order, interest on the demand confirmed shall be payable.
√ where there is a modification of amount demanded by the appellate authorities, corresponding interest is payable |
ADJUDICATION PROCEDURE
| Conclusion adjudication proceedings of |
√ Where order is passed
√ Where no order is passed within 3 years or 5 years as the case may be |
| Period to be excluded
|
Period during which any order is pending before Courts on the same issue then such period shall be excluded in computation of 3 years or 5 years where the SCN has been issued within time. |
| Proceedings against co-noticee |
Where the proceedings against main noticee is concluded, proceedings against co-noticee is also deemed to be concluded |
| Penalty
|
If penalty imposed under Section 73 or 74 then no penalty under any other provisions of the Act can be imposed for same act on the same person. |
ADJUDICATION PROCEDURE – Certain Issues
Orders cannot travel beyond scope of show cause notice
Order shall be a reasoned order – Cryptic orders does not stand test of law
Follow judicial discipline. Whether corrigendum could be issued to an order?
Review of the order by the authority who has passed the order?
SERVICE OF NOTICE – Section 169
Courier / through messenger to address of tax payer/ manager/ agent/advocate/ tax practitioner/person regularly employed / family member residing with the tax payer/ By registered post acknowledgment due to last known address
Email to the email id provided during registration,Publishing on common portal [GSTN]
Publishing in news paper None of the above possible — Affixing the notice at some conspicuous place last known place of businessIf none of the above is possible – affixing on notice board of the office. Deemed to be served on the date on which it is tendered or published or affixed.
If sent through Registered post/speed post – then deemed to have been received by addressee, at the expiry of normal time taken to deliver unless contrary is proved.
ADJUDICATION PROCEDURE – Certain Issues
Orders cannot travel beyond scope of show cause notice
Order shall be a reasoned order – Cryptic orders does not stand test of law
Follow judicial discipline
Whether corrigendum could be issued to an order?
Review of the order by the authority who has passed the order?
JUDICIAL DECISIONS RELATING TO SCN AND ITS SERVICE MODES, DEMAND,INSPECTION, DOCUMENTS, RECOVERY, ETC.
CCE Vs. Mehta & Co. MANU/SC/0107/2011 and UOI. Vs. Madhumilan Syntex Pvt. Ltd. & Anr. MANU/SC/0550/1988
Issue of SCN is a condition precedent to raising an enforceable demand CCE, Bangalore vs. Brindavan Beverages (P) Ltd: MANU/SC/2645/2007
- The show cause notice is the foundation on which the department has to build up its case. If the allegations in the show cause notice are not specific and are on the contrary vague, lack details and/or unintelligible that is sufficient to hold that the noticee was not given proper opportunity to meet the allegations indicated in the show cause notice.
Super Fashion Fasteners Pvt. Ltd. vs. CCE : MANU/CN/0199/2018
Having considered the rival contentions and on perusal of records, we find that the individual liability of duty alleged in the show cause notice and proposed to be recovered individually from M/s. Super and M/s. Omega has been arrived at on the basis of presumption that the clandestine activity was in the ratio of the consumption of electricity. Such a proposition is absurd and the quantification of individual liability is totally presumptive in nature. Therefore, we do not go into other arguments on merit and hold that the show cause notice is totally presumptive and relying on the ruling of Hon’ble Supreme Court in the case of Commissioner of Central Excise, Bangalore v. Brindavan Beverages Pvt. Ltd. (supra), we set aside the impugned order-in- original and allow all the appeals
Kaur & Singh vs. C.C.E., New Delhi 1997 (4) ELT 289 (SC)
- SCN must communicate to the addressee the specific allegation/charge and the basis for the demand of tax. The party to whom SCN is issued must be made aware of the allegations against it and that this is a requirement of natural justice.
Lord Chloro Alkali vs. Special Director Enforcement Directorate MANU/DE/2692/2017
16. Further, it is a settled principal of law that “Affirmati Non Neganti Incumbit Probatio”, that is, “the burden of proof is upon him who affirms – not on him who denies”.
Bhagwan Jagannath Markad and Ors v. State of Maharashtra MANU/SC/1171/2016
“18. It is accepted principle of criminal jurisprudence that the burden of proof is always on the prosecution and the accused is presumed to be innocent unless proved guilty. The prosecution has to prove its case beyond reasonable doubt and the accused is entitled to the benefit of the reasonable doubt.”
Vikas Gumber Vs. Commissioner of Customs MANU/DE/4998/2009
Departmental authorities are under obligation to release such documents as are not relied upon by them within a reasonable time.
Selvi Paper Mills Ltd Vs. CCE MANU/CC/0085/2012
Considering the fact that the appellants were not supplied with the un-relied upon documents, in that situation, the adjudicating authority is directed to supply the remaining documents which were seized and not relied upon to them appellants, so that the appellants shall be able to reconcile their records and thereafter the adjudicating authority will do the fresh adjudication. In view of this observation, the matter is remanded to the adjudicating authority with the direction to supply the non-relied upon documents to the appellants and thereafter fix a date for final hearing of the matter.
Basudev Garg Vs. Commissioner of custom-2017 (48) STR 427- Delhi High Court Cross-examination is the right.
CCE, Meerut vs. Parmarth Iron Pvt. Ltd. [MANU/UP/2113/2010 : 2010 (260) ELT 514 (Alld.)
Apex Court in [2015 (321) ELT A210] and Delhi High Court in the case of Shakti Zarda Factory (I) Ltd. [MANU/DE/1665/2004 : 2015 (321) ELT 438] and Saakeen Alloys Pvt. Ltd. [MANU/GJ/0467/2014]
- Retracted statement is not admissible in evidence in absence of independent reliable evidence to corroborate the same.
Balaji Vegetables Vs. CCE 1999 (108) ELT 802; Saphai Saw Mills Vs. CCE 1999 (109) ELT 197.
- Even if the party has agreed to pay the duty during investigation stage, yet the adjudication of SCN (i.e. service of SCN, receiving reply to SCN, grant of reasonable opportunity of personal hearing and passing of adjudication order is must
AR Plastic Vs. CCE 2004( 171 ELT 413 and also Veera Spinning Mills Vs. CCE 2001(131)
- Despite the fact that the duty has been deposited (either with protest or without protest), SCN is a must
Prabhat Forging Vs. CCE 2002(139) ELT 720
- No demand can be confirmed either upon Director or on partners unless SCN has been served upon them by the Department Pfizer Ltd GVs. CCE 2001(131) ELT 251 (Tri)
- Similarly no tax and penalty can be confirmed on employee unless he had been served with SCN setting out his role in the commission of offence or evasion of duty
Nityanand Nirmal Vs. CCE 1999(109) ELT 522 followed in CCE Vs. Sompura Ceramics 2001(130) ELT 195 (Tri).
In case of partnership firm, SCN must be served upon the firm and the service of notice only upon the partner is not a good service and shall not be deemed to be service upon partnership firm.
Steel Ingots Vs. UJOI 1988 (360 ELT 529(MP): Ennore Steel Vs. UOI 1990(47) ELT 363 Madras
- A letter issued by Supdt/AC asking the party to pay Tax/Duty is not a valid notice and is in violation of principal of natural justice J K Synthetics Vs. UOI 2009(234) ELT 417 (Delhi HC) and CCE Vs. Merchant Impex 2012( 276)ELT 458 Karnataka DB
- Every communication cannot be equated with SCN unless the communication contains all the necessary ingredients, as stated above in this para , of SCN
Metal Forgings Vs. UOI 2003( 146) ELT 241 SC
- A communication sent by the Department either in the form of directions or suggestion or advice shall not be construed as SCN as SCN requires clear, specific unambiguous charge, alleged violation of law or rules, clear and specific demand of duty/tax/penalty and grounds for levy of penalty and above all, if the extended period is invoked, then the reasons/grounds for invocation of extended period
Godrej Soap Vs. CCE 2004(174) ELT 35 (Three Member Bench)
- SCN issued by a person who is not authorized to do so, SCN is void in totality and good part of the SCN, cannot be severed from the bad part.
(a) Sanghi Textiles Processors v. UOI 1993 (65) ELT 357; (b) Methodex Systems v. UOI MANU/MP/0486/2000;(c) Balakrishna Dass and Sons v. CC, New Delhi MANU/CE/4102/2001; and (d) PGO Processors Pvt. Ltd. v. CCE 2000 (122) ELT 25.
Santogen silk mills v CCE – 2003(157) ELT 208-CESTAT Mumbai & PGO Processors P. LTD v CE – 2000(122) ELT 26- Rajasthan High Court
- merely making the relied upon documents available for inspection is not sufficient and copies of the relied upon documents have to be furnished:
Nexcus Computers Pvt Ltd Vs. CCE (2008) 9 STR 34 Chennai Tribunal)
Extended period cannot be invoked where the department itself is not clear about the facts.
Gujarat Ambuja Exports Ltd. Vs. UOI (2012) 26 STR 165 (Gujarat HC)
Extended period cannot be invoked where the department was aware about the facts as the assessee provided the requisite information.
Infinity Infotech Parks Ltd. Vs. UOI & Others 2012 – TIOL – 987 (Delhi High Court)
Mere failure to declare would not amount to wilful suppression since for wilful suppression the positive act from the side of the assessee shall be found.






Comprehensive and useful document, Sir!!