CA Deepak Bansal
As we all know that Goods and Service Tax (GST) is the biggest tax reform in India post-independence. It is a tax trigger, which will lead to business transformation for all major industries.
Since, GST is going to be a reality soon, so now it’s the right time to start understanding the provisions of the GST Law. So, to start with the provisions of GST, let us first understand the Chapter I titled as Preliminary. It contains 2 sections- Section 1 talks about the Short title, extent and commencement and Section 2 contain Definitions.
Section 1: Short title, extent and commencement
Section 1 says that this act may be called the Central/ State Goods and Service Tax, 2017 and extends to the whole of India except the State of Jammu and Kashmir and shall come into force on such date as the Central Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, appoint and different dates may be appointed for different provisions of this Act.
Section 2: Definitions
Before understanding the provisions of GST Law, it’s important to first understand the meaning of various important terms used therein. These definitions are important because they suggest that meaning intended for a term to have a specific meaning that might differ in important ways from its common usage. So, let us go through some of the basic and important definitions as defined under Section 2 of the Act:-
1. Meaning of Goods and Services under GST:
- As per Section 2(52) “goods”means every kind of movable property other than money and securities but includes actionable claim, growing crops, grass and things attached to or forming part of the land which are agreed to be severed before supply or under a contract of supply;
| Comments:
Goods definition has two limbs, the first one is “Goods means every kind of movable property other than money and securities”. It is wide enough to include every kind of movable property in its ambit except money and securities. Though the term movable is not defined under Model GST Law but as per Section 3(36) of the General Clauses Act 1897 “Movable property” shall mean property of every description, except immovable property. The second limb includes in its ambit other kind of movable property viz. actionable claim which is defined under Section 2(1) of the Act, growing crops, grass and things attached to or forming part of the land. |
- As per Section 2(102) “services”means anything other than goods, money and securities but includes activities relating to the use of money or its conversion by cash or by any other mode, from one form, currency or denomination, to another form, currency or denomination for which a separate consideration is charged;
| Comments:
Definition of the services is so precise and outright to include everything that is not goods. The word ‘anything’ has enlarged the scope of services. To check whether an activity or transaction fall within the purview of services, one has to first check whether it is a good or not. If it’s not a good than certainly it will fall within the purview of the services. Money and securities are neither goods nor services but the conversion of money is covered under the ambit of services. |
II. “Outward Supply” defined:
- As per Section 2(83) “outward supply”in relation to a taxable person, means supply of goods or services or both, whether by sale, transfer, barter, exchange, licence, rental, lease or disposal or any other mode, made or agreed to be made by such person in the course or furtherance of business;
III. Different types of Supply:
- As per Section 2(47) “exempt supply”means supply of any goods or services or both which attracts nil rate of tax or which may be wholly exempt from tax under section 11 (Power to grant exemption from tax), or under section 6 of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act, and includes non-taxable supply;
- As per Section 2(108) “taxable supply”means a supply of goods or services or both which is leviable to tax under this Act;
- As per Section 2(78) “non-taxable supply” means a supply of goods or services or both which is not leviable to tax under this Act or under the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act;
IV. Composite Supply and Mixed Supply:
- As per Section 2(30) “composite supply”means a supply made by a taxable person to a recipient consisting of two or more taxable supplies of goods or services or both, or any combination thereof, which are naturally bundled and supplied in conjunction with each other in the ordinary course of business, one of which is a principal supply;
Illustration: Where goods are packed and transported with insurance, the supply of goods, packing materials, transport and insurance is a composite supply and supply of goods is a principal supply.
> As per Section 2(90) “principal supply” means the supply of goods or services which constitutes the predominant element of a composite supply and to which any other supply forming part of that composite supply is ancillary;
- As per Section 2(74) “mixed supply”means two or more individual supplies of goods or services, or any combination thereof, made in conjunction with each other by a taxable person for a single price where such supply does not constitute a composite supply;
Illustration: A supply of a package consisting of canned foods, sweets, chocolates, cakes, dry fruits, aerated drinks and fruit juices when supplied for a single price is a mixed supply. Each of these items can be supplied separately and is not dependent on any other. It shall not be a mixed supply if these items are supplied separately.
V. Aggregate Turnover means:
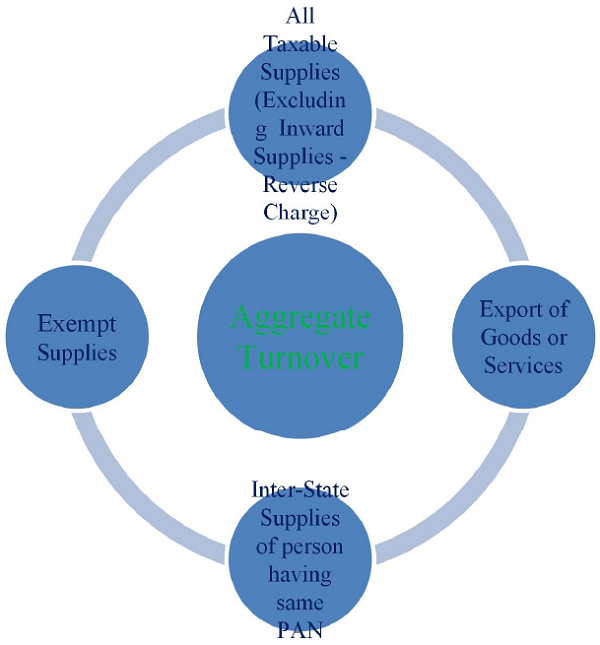
- As per Section 2(6) “aggregate turnover”means the aggregate value of:
– all taxable supplies (excluding the value of inward supplies on which tax is payable by a person on reverse charge basis),
– exempt supplies,
– exports of goods or services or both and
– inter-State supplies of persons having the same PAN (branch transfer),
– to be computed on all India basis
– but excludes central tax, state tax, union territory tax, integrated tax and cess;
- As per Section 2(112) “turnover in State”or “turnover in Union territory” means the aggregate value of all taxable supplies (excluding the value of inward supplies on which tax is payable by a person on reverse charge basis) and exempt supplies made within a State or Union territory by a taxable person, exports of goods or services or both and inter-State supplies of goods or services or both made from the State or Union territory by the said taxable person but excludes central tax, State tax, Union territory tax, integrated tax and cess;
VI. Business and Business Vertical:
- As per Section 2(17) “business” includes––
(a) any trade, commerce, manufacture, profession, vocation, adventure, wager or any other similar activity, whether or not it is for a pecuniary benefit;
(b) any activity or transaction in connection with or incidental or ancillary to sub-clause (a);
(c) any activity or transaction in the nature of sub-clause (a), whether or not there is volume, frequency, continuity or regularity of such transaction;
(d) supply or acquisition of goods including capital goods and services in connection with commencement or closure of business;
(e) provision by a club, association, society, or any such body (for a subscription or any other consideration) of the facilities or benefits to its members;
(f) admission, for a consideration, of persons to any premises;
(g) services supplied by a person as the holder of an office which has been accepted by him in the course or furtherance of his trade, profession or vocation;
(h) services provided by a race club by way of totalisator or a licence to book maker in such club
(i) any activity or transaction undertaken by the Central Government, a State Government or any local authority in which they are engaged as public authorities;
- As per Section 2(18) “business vertical”means a distinguishable component of an enterprise that is engaged in the supply of individual goods or services or a group of related goods or services which is subject to risks and returns that are different from those of the other business verticals.
Explanation.––For the purposes of this clause, factors that should be considered in determining whether goods or services are related include––
(a) the nature of the goods or services;
(b) the nature of the production processes;
(c) the type or class of customers for the goods or services;
(d) the methods used to distribute the goods or supply of services; and
(e) the nature of regulatory environment (wherever applicable), including banking, insurance, or public utilities;
VII. Concept of Supplier and Recipient:
- As per Section 2(105) “supplier”in relation to any goods or services or both, shall mean the person supplying the said goods or services or both and shall include an agent acting as such on behalf of such supplier in relation to the goods or services or both supplied;
> As per Section 2(5)“agent” means a person, including a factor, broker, commission agent, arhatia, del credere agent, an auctioneer or any other mercantile agent, by whatever name called, who carries on the business of supply or receipt of goods or services or both on behalf of another;
- As per Section 2(93) “recipient”of supply of goods or services or both, means—
(a) where a consideration is payable for the supply of goods or services or both, the person who is liable to pay that consideration;
(b) where no consideration is payable for the supply of goods, the person to whom the goods are delivered or made available, or to whom possession or use of the goods is given or made available; and
(c) where no consideration is payable for the supply of a service, the person to whom the service is rendered, and any reference to a person to whom a supply is made shall be construed as a reference to the recipient of the supply and shall include an agent acting as such on behalf of the recipient in relation to the goods or services or both supplied;
VIII. Consideration includes:
- As per Section 2(31) “consideration”in relation to the supply of goods or services or both includes––
(a) any payment made or to be made, whether in money or otherwise, in respect of, in response to, or for the inducement of, the supply of goods or services or both, whether by the recipient or by any other person but shall not include any subsidy given by the Central Government or a State Government;
(b) the monetary value of any act or forbearance, in respect of, in response to, or for the inducement of, the supply of goods or services or both, whether by the recipient or by any other person but shall not include any subsidy given by the Central Government or a State Government:
Provided that a deposit given in respect of the supply of goods or services or both shall not be considered as payment made for such supply unless the supplier applies such deposit as consideration for the said supply;
IX. Place of Business and Fixed Establishment:
- As per Section 2(85) “place of business”includes––
(a) a place from where the business is ordinarily carried on, and includes a warehouse, a godown or any other place where a taxable person stores his goods, supplies or receives goods or services or both; or
(b) a place where a taxable person maintains his books of account; or
(c) a place where a taxable person is engaged in business through an agent, by whatever name called;
As per Section 2(50) “fixed establishment” means a place (other than the registered place of business) which is characterized by a sufficient degree of permanence and suitable structure in terms of human and technical resources to supply services, or to receive and use services for its own needs;
X. Input, Capital Goods and Input Services:
- As per Section 2(59) “input”means any goods other than capital goods used or intended to be used by a supplier in the course or furtherance of business;
- As per Section 2(19) “capital goods”means goods, the value of which is capitalised in the books of account of the person claiming the input tax credit and which are used or intended to be used in the course or furtherance of business;
- As per Section 2(60) “input service”means any service used or intended to be used by a supplier in the course or furtherance of business;
XI. Input Tax, Input Tax Credit and Output Tax:
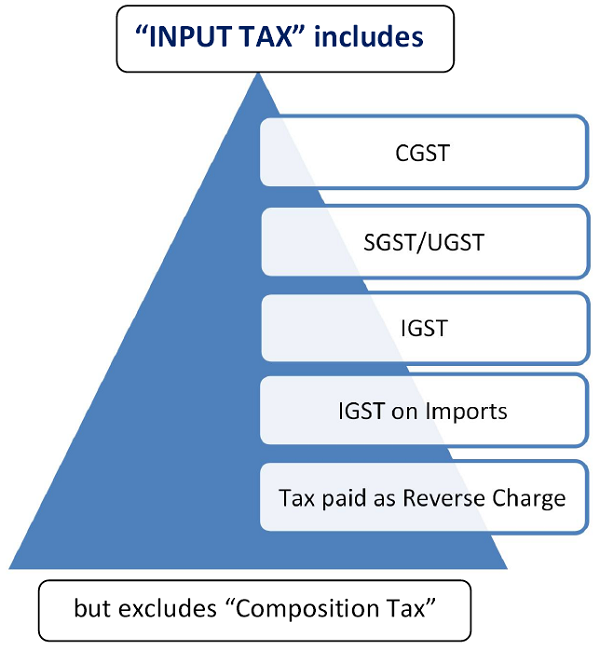
- As per Section 2(62) “input tax”in relation to a registered person, means the central tax, State tax, integrated tax or Union territory tax charged on any supply of goods or services or both made to him and includes—
(a) the integrated goods and services tax charged on import of goods; (Imports)
(b) the tax payable under the provisions of sub-sections (3) and (4) of section 9;
(c) the tax payable under the provisions of sub-section (3) and (4) of section 5 of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act;
(d) the tax payable under the provisions of sub-section (3) and sub-section (4) of section 9 of the respective State Goods and Services Tax Act or
(e) the tax payable under the provisions of sub-section (3) and sub-section (4) of section 7 of the Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Act, (Reverse Charge) but does not include the tax paid under the composition levy; (excludes Composition Tax)
- As per Section 2(63) “input tax credit”means the credit of input tax;
- As per Section 2(82) “output tax”in relation to a taxable person, means the tax chargeable under this Act on taxable supply of goods or services or both made by him or by his agent but excludes tax payable by him on reverse charge basis;
XII. Agriculturist:
- As per Section 2(7) “agriculturist”means an individual or a Hindu Undivided Family who undertakes cultivation of land—
(a) by own labour, or
(b) by the labour of family, or
(c) by servants on wages payable in cash or kind or by hired labour under personal supervision or the personal supervision of any member of the family;
XIII. Casual Taxable Person and Non-resident Taxable Person:
- As per Section 2(20) “casual taxable person” means a person who occasionally undertakes transactions involving supply of goods or services or both in the course or furtherance of business, whether as principal, agent or in any other capacity, in a State or a Union territory where he has no fixed place of business;
- As per Section 2(77) “non-resident taxable person”means any person who occasionally undertakes transactions involving supply of goods or services or both, whether as principal or agent or in any other capacity, but who has no fixed place of business or residence in India;
ISSUES:
|
XIV. Continuous Supply:
- As per Section 2(32) “continuous supply of goods”means a supply of goods which is provided, or agreed to be provided, continuously or on recurrent basis, under a contract, whether or not by means of a wire, cable, pipeline or other conduit, and for which the supplier invoices the recipient on a regular or periodic basis and includes supply of such goods as the Government may, subject to such conditions, as it may, by notification, specify;
- As per Section 2(33) “continuous supply of services” means a supply of services which is provided, or agreed to be provided, continuously or on recurrent basis, under a contract, for a period exceeding three months with periodic payment obligations and includes supply of such services as the Government may, subject to such conditions, as it may, by notification, specify;
XV. Manufacture, Job Work and Works Contract:
- As per Section 2(72)“manufacture” means processing of raw material or inputs in any manner that results in emergence of a new product having a distinct name, character and use and the term “manufacturer” shall be construed accordingly;
- As per Section 2(68) “job work”means any treatment or process undertaken by a person on goods belonging to another registered person and the expression “job worker” shall be construed accordingly;
- As per Section 2(119) “works contract”means a contract for building, construction, fabrication, completion, erection, installation, fitting out, improvement, modification, repair, maintenance, renovation, alteration or commissioning of any immovable property wherein transfer of property in goods (whether as goods or in some other form) is involved in the execution of such contract;
XVI. Location of the Recipient and Supplier in case of Services:
- As per Section 2(70) “location of the recipient of services”means,—
(a) where a supply is received at a place of business for which the registration has been obtained, the location of such place of business;
(b) where a supply is received at a place other than the place of business for which registration has been obtained (a fixed establishment elsewhere), the location of such fixed establishment;
(c) where a supply is received at more than one establishment, whether the place of business or fixed establishment, the location of the establishment most directly concerned with the receipt of the supply; and
(d) in absence of such places, the location of the usual place of residence of the recipient;
- As per Section 2(71) “location of the supplier of services”means,—
(a) where a supply is made from a place of business for which the registration has been obtained, the location of such place of business;
(b) where a supply is made from a place other than the place of business for which registration has been obtained (a fixed establishment elsewhere), the location of such fixed establishment;
(c) where a supply is made from more than one establishment, whether the place of business or fixed establishment, the location of the establishment most directly concerned with the provisions of the supply; and
(d) in absence of such places, the location of the usual place of residence of the supplier;
XVII. Who all are included in “Person “definition:
- As per Section 2(84) “person” includes—
(a) an individual;
(b) a Hindu Undivided Family;
(c) a company;
(d) a firm;
(e) a Limited Liability Partnership;
(f) an association of persons or a body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, in India or outside India;
(g) any corporation established by or under any Central Act, State Act or Provincial Act or a Government company as defined in clause (45) of section 2 of the Companies Act, 2013;
(h) any body corporate incorporated by or under the laws of a country outside India;
(i) a co-operative society registered under any law relating to co-operative societies;
(j) a local authority;
(k) Central Government or a State Government;
(l) society as defined under the Societies Registration Act, 1860;
(m) trust; and
(n) every artificial juridical person, not falling within any of the above;
- As per Section 2(107) “taxable person”means a person who is registered or liable to be registered under section 22 (Person liable for Registration) or section 24 (Compulsory registration in certain cases);
- As per Section 2(94) “registered person”means a person who is registered under section 25 (Procedure for registration) but does not include a person having a Unique Identity Number;
XVIII. Other Important Definitions:
- As per Section 2(1) “actionable claim” shall have the same meaning as assigned to it in section 3 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882;
Section 3 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882
“actionable claim” means a claim to any debt, other than a debt secured by mortgage of immovable property or by hypothecation or pledge of movable property, or to any beneficial interest in movable property not in the possession, either actual or constructive, of the claimant, which the civil courts recognize as affording grounds for relief, whether such debts or beneficial interest be existent, accruing conditional or contingent.
- As per Section 2(49) “family”means,––
(i) the spouse and children of the person, and
(ii) the parents, grand-parents, brothers and sisters of the person if they are wholly or mainly dependent on the said person;
- As per Section 2(56) “India”means the territory of India as referred to in article 1 of the Constitution, its territorial waters, seabed and sub-soil underlying such waters, continental shelf, exclusive economic zone or any other maritime zone as referred to in the Territorial Waters, Continental Shelf, Exclusive Economic Zone and other Maritime Zones Act, 1976, and the air space above its territory and territorial waters;
- As per Section 2(61) “Input Service Distributor”means an office of the supplier of goods or services or both which receives tax invoices issued under section 31 towards the receipt of input services and issues a prescribed document for the purposes of distributing the credit of central tax, State tax, integrated tax or Union territory tax paid on the said services to a supplier of taxable goods or services or both having the same Permanent Account Number as that of the said office;
- As per Section 2(73) “market value” shall mean the full amount which a recipient of a supply is required to pay in order to obtain the goods or services or both of like kind and quality at or about the same time and at the same commercial level where the recipient and the supplier are not related;
- As per Section 2(96) “removal’’in relation to goods, means—
(a) dispatch of the goods for delivery by the supplier thereof or by any other person acting on behalf of such supplier; or
(b) collection of the goods by the recipient thereof or by any other person acting on behalf of such recipient;
- As per Section 2(98) “reverse charge” means the liability to pay tax by the recipient of supply of goods or services or both instead of the supplier of such goods or services or both under sub-section (3) or sub-section (4) of section 9, or under sub-section (3) or subsection (4) of section 5 of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act;
- As per Section 2(114) “Union territory”means the territory of—
(a) the Andaman and Nicobar Islands;
(b) Lakshadweep;
(c) Dadra and Nagar Haveli;
(d) Daman and Diu
(e) Chandigarh; and
(f) other territory.
Explanation.––For the purposes of this Act, each of the territories specified
in sub-clauses (a) to (f) shall be considered to be a separate Union territory;
- As per Section 2(118) “voucher”means an instrument where there is an obligation to accept it as consideration or part consideration for a supply of goods or services or both and where the goods or services or both to be supplied or the identities of their potential suppliers are either indicated on the instrument itself or in related documentation, including the terms and conditions of use of such instrument;
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q 1. What is Goods and Services Tax (GST)?
Ans. It is a destination based tax on consumption of goods and services. It is proposed to be levied at all stages right from manufacture up to final consumption with credit of taxes paid at previous stages available as setoff. In a nutshell, only value addition will be taxed and burden of tax is to be borne by the final consumer.
Q 2. Whether actionable claims liable to GST?
Ans. As per section 2(52) of the CGST/SGST Act actionable claims are to be considered as goods. Schedule III read with Section 7 of the CGST/SGST Act lists the activities or transactions which shall be treated neither as supply of goods nor supply of services. The Schedule lists actionable claims other than lottery, betting and gambling as one of such transactions. Thus only lottery, betting and gambling shall be treated as supplies under the GST regime. All the other actionable claims shall not be supplies.
Q 3. Whether transaction in securities be taxable in GST?
Ans. Securities have been specifically excluded from the definition of goods as well as services. Thus, the transaction in securities shall not be liable to GST.
Q 4. What is aggregate turnover?
Ans. As per section 2(6) of the CGST/SGST Act “aggregate turnover” includes the aggregate value of all taxable supplies, all exempt supplies, exports of goods and/or service, and all inter-state supplies of a person having the same PAN.
The above shall be computed on all India basis and excludes taxes charged under the CGST Act, SGST Act, UTGST Act, and the IGST Act.
Aggregate turnover shall include all supplies made by the Taxable person, whether on his own account or made on behalf of all his principals.
Aggregate turnover does not include value of supplies on which tax is levied on reverse charge basis, and value of inward supplies.
The value of goods after completion of job work is not includible in the turnover of the job-worker. It will be treated as supply of goods by the principal and will accordingly be includible in the turnover of the Principal.
Q5. Who is an ISD?
Ans. ISD stands for Input Service Distributor and has been defined under Section 2(61) of the CGST/SGST Act. It is basically an office meant to receive tax invoices towards receipt of input services and further distribute the credit to supplier units (having the same PAN) proportionately.
Q6. What do you mean by “supply made in the course or furtherance of business”?
Ans. “Business” is defined under Section 2(17) include any trade, commerce, manufacture, profession, vocation etc. whether or not undertaken for a pecuniary benefit. Business also includes any activity or transaction which is incidental or ancillary to the aforementioned listed activities. In addition, any activity undertaken by the Central Govt. or a State Govt. or any local authority in which they are engaged as public authority shall also be construed as business. From the above, it may be noted that any activity undertaken included in the definition for furtherance or promoting of a business could constitute a supply under GST law.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1. Supply includes which of the following?
(a) Goods
(b) Services
(c) Goods or Services
(d) Goods or Services or both
Q2. What are the different forms of Supply of Goods?
(a) Sale
(b) Transfer
(c) Barter and Exchange
(d) All of the above
(e) a & b only
Q3. Input Tax Credit includes?
(a) CGST, SGST and UTGST
(b) CGST, SGST, UTGST and IGST
(c) CGST, SGST, UTGST, IGST and Reverse Charge Tax
(d) CGST, SGST, UTGST, IGST and Composition Tax
Q4. Who all are included in definitions of “Person”?
(a) Individual and HUF
(b) Firm and Company
(c) Limited Liability Partnership
(d) a & b only
(e) a, b & c
(Ans: Q1-(d), Q2-(d), Q3-(c), Q4-(e))




