As per Section 2(68) of the CGST Act, 2017, Job-work means any treatment or process undertaken by a person on goods belonging to another person whether registered or not. Thus, goods supplied by the person for any treatment to be done upon the goods falls under job-work. It’s clear from the meaning that the goods are not sold to the person but is bailed to that job-worker, which is to be returned by him within the specified time under the act; and hence, the ownership of the goods remains that of the principal and not the job-worker.
The person on whose goods job-work is performed is called “Principal”. Goods can be sent either by the Principal to Job-Worker or by the primary supplier of goods to directly job-worker on behalf of the principal. Job-workers are given various concessions under GST, along with the principals also; but compliances are led on the principal to be fulfilled. Responsibility of sending the goods and bringing it back to/from the job-worker is casted on the principal and not job-worker and also the maintenance of proper account books for goods sent to job-work lies with the principal. GST specifies separate provisions for such kind of supply.
Page Contents
- Difference between Agent & Job-worker
- Procedure for Job-Work
- Registration of job-worker under GST
- Document of Record for Job-work under GST
- Retuning Norms for Job-work under GST
- What if goods not returned within the specified time under GST?
- What to do under GST After Job-work is finished?
- Supply of waste and scrap generated during the job work
- Input-Tax Credit availability to Principal
- Filing of Form GST ITC-04
Difference between Agent & Job-worker
Sometimes, job-worker may be misinterpreted as Agent, but there exists much difference between the two.
| Agent | Job-Worker |
| Carries on the business of the principal on behalf of the principal. | Doesn’t carry the business of the principal on principal’s behalf |
| Doesn’t process the goods further or perform any treatment. | Process the goods further or perform treatment as per the principal’s directions. |
| Sale of goods by the agent is also included in the turnover of the principal. | The treatment and processes performed on the goods is included in the turnover of the Job-worker. |
Procedure for Job-Work
Principal sends the goods to the job-worker for further processing or any other treatment to be performed; while sending the goods. Job-worker is required to do the necessary processes as mentioned under the agreement and return the same within the specified time period; on failure of which, other applicable provision may be levied.
Registration of job-worker under GST
As per clause 3 of Schedule II to CGST Act 2017, any treatment or process applied to another person goods are to be treated as supply of services; thus, job-work being work done by a person on some other person’s goods, the same shall be treated as supply of service.
As per Registration norms, any person who is engaged in supply of service whose aggregate turnover exceeds ₹20,00,000 during the financial year is mandatorily required to get registered under GST irrespective of the fact whether the same is inter state or intra state.
Document of Record for Job-work under GST
As goods are moving out of the business, the supplier too has to make record of it but as it’s not a sale thus no tax invoice can be generated, as a result of this, under Rule 55(1) of CGST Act, Challan is to be issued by the supplier furnishing all the details regarding the goods including
- Date (of challan and transportation) and the number of delivery challan
- Name, address and GSTIN of the consigner, if registered.
- If registered: Name, address and GSTIN or Unique Identity Number of the consignee. If unregistered then name, address, and place of supply.
- HSN code for the goods
- Description of goods
- Quantity of goods supplied (Optional, If the exact quantity being supplied is not known)
- The taxable value of supply
- GST tax rate and tax amount divided for CGST, SGST, IGST, and GST Cess – where the transportation is for supply to the consignee
- Place of supply, in case of inter-state movement of goods
- Signature
Details to be included in the Challan generated for job-work is provided under Rule 55 of Invoice Rules. Challan thus here works as document of record for the goods sent to job-worker for the purpose. Principal is required to show the challans so issued in its Form GSTR1 along with Form GST ITC-04.
If the goods are not received back by the principal within the specified time from the job-worker, movement of goods is deemed as sale being made to job-worker from the date on which the goods are sent by principal or on the date it received by the job-worker when directly sent from the supplier of goods; hence deeming the challan so generated earlier be treated as invoice for the same.
Retuning Norms for Job-work under GST
Goods sent for Job-work is required to be returned within the specified time as stated in Act. It is stated as under:
| Particulars | Time limit to Return |
| Input Goods | 1 year |
| Capital Goods | 3 years |
| Tools, Fixtures, Jigs, Moulds, and Dies | Not applicable |
What if goods not returned within the specified time under GST?
If the goods sent on job-work is not returned, it would be deemed as sale of goods and time of supply would be, the date of supply or date of receipt, if supplied by principal or supplier of the goods respectively; and principal would be liable to the GST on deemed supply and it would be required to be paid along with the interest as applicable, and be shown in principal’s GSTR1 in the period when the period of 1 or 3 years ends. And, if it’s supplied after the stipulated time period, then job-worker would be liable to pay GST if he is liable for registration in accordance with the provisions contained in the CGST 11 Act read with the rules made thereunder. It may be noted that if the job worker is not registered, GST would be payable by the principal on reverse charge basis in terms of the provisions contained in section 9(4) of the CGST Act.
| Cases | Implications |
| Goods sent by principal and returned in time | No adverse implication, will be treated as usual Job-Work. |
| Goods sent directly by supplier of goods and returned in time | No adverse implication, will be treated as usual Job-Work. |
| Goods sent by principal or directly from the supplier of goods to job-worker and returned after specified time | The goods sent on Job-work will be treated as Deemed Supply; time of supply will be on the date of receipt of goods by job-worker; the job worker would be liable to pay GST if registered else principal on reverse charge basis. |
| Goods sent by principal and not returned | The same will be treated as Deemed Sale, time of supply will be the date on which it sent out to job-worker. |
| Goods sent directly by supplier and not returned | The same will be treated as Deemed Sale, time of supply will be the date of receipt of goods by job-worker. |
What to do under GST After Job-work is finished?
After completion of the job-work, the same is to be returned or it can be directly sent to the customer on the standing instruction as received from the principal; But, if the goods are directly sent to the customer from the job-worker, Principal is required to mandatorily provide premise of job-worker as Principal’s Additional Place of Business (PoB); this declaration of Additional PoB is not required if job-worker is a registered person under GST.
Supply of waste and scrap generated during the job work
Sub – section (5) of Section 143 of the CGST Act provides that the waste and scrap generated during the job work may be supplied/sold by the registered job worker directly from his place of business or by the principal in case the job worker is not registered.
Input-Tax Credit availability to Principal
For the goods supplied by the Principal to the job-worker directly from the supplier of goods, then principal is not restrained from taking ITC on such goods, for the reason that goods aren’t received by Principal yet (Receiving the goods at the premise of the registered person is a must to claim the ITC); its deemed as if the goods have been received by the principal and hence, principal is eligible for claiming ITC for the input tax paid on purchase of such goods that are sent for job-work directly by the supplier or the principal, irrespectively. Following conditions are to be fulfilled for claiming ITC: –
| Conditions to claim ITC | |
| 1. | Goods should be sent to job-worker by principal or directly from supplier. |
| 2. | Goods shall be received back from job-work or sent or other job-worker or directly supplied to customer within the specified time limit. |
| 3. | ITC-04 is to be filed by the Principal half-yearly or annualy, as applicable. |
Filing of Form GST ITC-04
- Due date: –
With effect from 1st October 2021, it is a half-yearly and yearly form as follows:
(1) Those with an annual aggregate turnover of more than Rs.5 crore – Half-yearly from April-September- due on 25th October and October-March due on 25th April.
(2) Those with an annual aggregate turnover of up to Rs.5 crore – Yearly from FY 2021-22 due on 25th April.
(ITC-04 was a quarterly form until September 2021. It had to be furnished on or before the 25th day of the month succeeding the quarter. For example, for the Jul-Sept quarter, the due date is 25th October 2021.)
- Form details is to be filed in two parts: –
1. Goods sent to job-worker
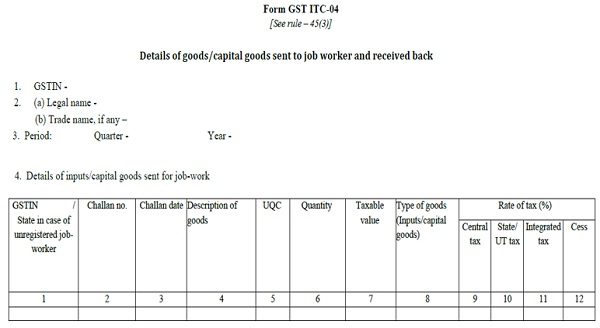
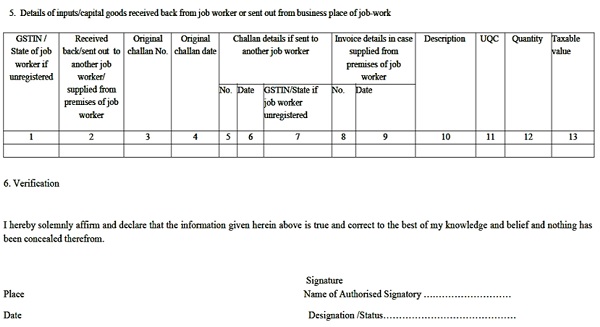
2. Goods received back from the job-worker






The correct definition under section 2(68) states :- Any treatment or process undertaken by a person on goods belonging to another registered person”. Therefore, a job-worker is the person (registered or unregistered) who is processing or treating the goods of another registered person and the owner of the goods is called the Principal in this respect.
Whereas you have mentioned that Job-work means any treatment or process undertaken by a person on goods belonging to another person whether registered or not.
As per act the principal must be another registered person than a job worker . If principal is unregistered as per GST Act then movement of goods and transaction can’t be covered under job work .