E-Way Bill is an Electronic Way bill for movement of goods to be generated on the e-Way Bill Portal. The provisions governing E-way bill are provided in Rule 138 of CGST Rules, 2017.
Below are the various provisions of E-way Bill in simplified language to help the audience in understanding the nitty-gritties of the EWB provisions.
Every registered person -> causes movement of goods -> consignment value > Rs. 50,000/-
| Registered Person | Movement of Goods | Consignment Value |
|
Supplier/ Recipient |
– in relation to a supply – for reasons other than supply – Inward supply from an URP |
Value as per Section 15 declared in Invoice/ Bill of Supply/ Delivery Challan (+) CGST/ SGST/ UTGST/ IGST (+) Cess (-) Value of exempt supply (-) Value of any services |
Shall,
Before commencement of movement -> fill Part A of Form GST EWB-01 electronically on common portal -> a Unique number will be generated.
Alternatively, a transporter on authorization received from the Registered Person may furnish the information in Part A of Form GST EWB-01.
> Unique number is generated after furnishing the information in Part-A which shall be valid for 15 days for furnishing the information in Part-B.
> If goods are transported by Road -> EWB will be generated only after furnishing the info in Part-B of Form GST EWB-01 -> commencement of movement can be done after filing info in Part-B
> If goods are transported by Rail*/ Air/ Vessel -> info in Part-B can be furnished either before or after the commencement of movement of goods
* If the goods are transported through Rail, the railways should not deliver the goods unless the EWB required is not furnished at the time of delivery.
> E-way bill shall not be valid unless the information in Part-B is not furnished. Part-B is not required to be filled if the goods are transported within the state and:
- Where the distance between the place of business of consignor and the place of business of transporter is upto 50 KMs
- Where the distance between the place of business of consignee and the place of business of transporter is upto 50 KMs
Points to remember
- Where the goods are supplied by URP to RP, then the movement shall be said to be caused by such RP.
- E-way bill once generated cannot be modified and only remedy is to cancel the e-way bill and generate a new e-way bill with correct information.
- Carrying physical copy of EWB is not mandatory and only EWB number/ Soft copy will be considered as sufficient compliance.
E-Way bill in case of E-commerce operator/ courier agency
On authorization from the consignor, e-commerce operator/ courier agency may generate the E-way bill in Form GST EWB-01.
Conditions where EWB is required even if consignment value is less than Rs. 50,000/-
- Where there is inter-state movement of goods from Principal to Job Worker, E-way bill shall be generated irrespective of the value of consignment
- Where there is inter-state movement of Handicraft goods by the person who is exempted from obtaining registration , E-way bill shall be generated irrespective of the value of consignment
Generation of e-way bill even if not required
- A Registered Person/ Transporter may at his option generate the e-way bill even if the consignment value does not exceed Rs. 50,000/-
- Where the movement of goods is caused by an URP to another URP, then he may at his option generate the e-way bill in the manner as specified.
Change of Conveyance
Where goods are transferred from one conveyance to another, then the consignor/ consignee or transporter shall update the details of conveyance in Part-B before commencing further movement of goods.
Assigning E-way bill to other transporter
- The consignor/consignee or transporter may assign the e-way bill number to another transporter for updating the information in Part-B for further movement of the consignment.
- Once the information in Part-B has been updated, the consignor/ consignee shall not be allowed to further assign the E-way bill to another transporter but the new transporter can further assign the e-way bill to another transporter.
Consolidated E-way bill
- The transporter may furnish the details of all the valid E-way bills in Form GST EWB-02 prior to commencement of movement of goods if multiple consignments are intended to be transported in single conveyance.
- Where the goods are intended to be transported inter-state through Road and where the consignor/ consignee has not generated a E-way bill and the aggregate value of the consignments to be carried in the conveyance exceeds Rs. 50,000/-, the transporter shall generate e-way bill in Form EWB-01 or EWB-02 on the basis of information available in the invoice/ bill of supply/ delivery challan before commencement of movement of goods.
Cancellation of E-way Bill
- Where the e-way bill has been generated but goods are either not transported or are not transported as per the furnished details, the e-way bill may be cancelled electronically within 24 hours of generation of e-way bill.
- Provided the e-way bill cannot be cancelled once it has been verified in transit.
Validity of E-way Bill
| S.No. | Distance (Approx.) | E-way bill validity period |
| 1. | Upto 100 Km. | One day in cases other than Over Dimensional Cargo or Multi Modal Shipment in which at least one leg involves transport by ship |
| 2. | For every 100 Km. or part thereof thereafter | One additional day in cases other than Over Dimensional Cargo or Multi Modal Shipment in which at least one leg involves transport by ship |
| 3. | Upto 20 Km. | One day in case of Over Dimensional Cargo or Multi Modal Shipment in which at least one leg involves transport by ship |
| 4. | For every 20 Km. or part thereof thereafter | One additional day in case of Over Dimensional Cargo or Multi Modal Shipment in which at least one leg involves transport by ship |
- If the goods cannot be transported within the validity period, the transporter may extend the validity by updating the details in Part-B only under the circumstances of exceptional nature like:
- Vehicle breakdown
- Natural Calamity
- Law and order issue
- Transshipment delay etc.
- The validity of the e-way bill can be extended within 4 hours before or after the time of its expiry.
Determination of validity of e-way bill
It can be explained with the help of following example:
1. Suppose an e-way bill is generated at 00:10 hrs. on 3rd Then 1st day would end on 12:00 midnight of 4th-5th October. Similarly second day will end on 12:00 midnight of 5th– 6th October.
2. Suppose an e-way bill is generated at 23:45 hrs. on 3rd October. Then 1st day would end on 12:00 midnight of 4th-5th October. Similarly second day will end on 12:00 midnight of 5th– 6th October.
Acceptance/ Rejection of e-way bill
The consignor/ consignee shall communicate his acceptance/ rejection of the consignment covered by the e-way bill within 72 hours of the details being made available. If the acceptance/ rejection not communicated within the prescribed time then it will be deemed as accepted by the consignor/ consignee.
Situations where e-way bill is not required
- Goods specified in Annexure below
| S.No. | Description of Goods |
| 1. | LPG for supply to household and non-domestic exempted category customers |
| 2. | Kerosene oil sold under PDS |
| 3. | Postal baggage transported by Department of Posts |
| 4. | Natural or cultured pearls and precious or semi-precious stones, precious metals and metals clad with precious metals |
| 5. | Jewellery, Goldsmiths’ and silversmiths’ wares and other articles |
| 6. | Currency |
| 7. | Used personal and household effects |
| 8. | Unworked and Worked Coral |
- Transportation by non-motorised conveyance
- Transport from customs port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station to an ICD or container freight station for clearance by Customs
- Transport of goods notified in the schedule appended to Notification No. 2/2017 – Central Tax (Rate) dated 28th June 2017 except de-oiled cake.
- Transport of alcohol for human consumption, petroleum crude, HSD, Petrol, Natural Gas or Aviation turbine fuel
- Transport of goods treated as no supply under Schedule III if the Act
- Transit cargo from or to Nepal or Bhutan
- Transport of exempted goods
- Defense formation under Ministry of Defenses as consignor/ consignee
- Where consignor of goods is CG/ SG/ Local Authority for transport of goods by Rail
- Transportation of empty cargo containers
- Where goods are moved from place of business of consignor to a weighment bridge and the distance between both is not more than 20 Kms and the movement is accompanied by a Delivery Challan
- Empty cylinders for packing of LPG for reasons other than supply.
Requirement of e-way bill if goods are moved by consumer himself
E-way bill is required even if the goods are purchased and moved by consumer himself to the destination if the consignment value > Rs. 50,000/-. The consumer can ask the taxpayer/ supplier to generate the e-way bill or the consumer can enroll as citizen on the common portal and generate the e-way bill himself.
Information to be furnished in e-way bill
Part A
- GSTIN of supplier
- Place of Dispatch alongwith PIN code
- GSTIN of recipient
- Place of Delivery alongwith PIN code
- Document Number – Invocie/ Bill of Supply/ Delivery Challan
- Document Date
- Value of Goods
- HSN Code – upto 2 digits if taxpayer’s annual turnover in the preceding FY is upto 5 crores and upto 4 digits if more than 5 crores
- Reason for transportation – Supply, Export/ Import, Job Work, SKD/ CKD/ Sales Return, Exhibition/ Fares, Own Use
Part B
- Vehicle Registration Number for Road
- Transport Document No/ Defense Vehicle No/ Temporary Vehicle Reg No/ Nepal or Bhutan Vehicle Reg. No.
Bill to Ship to Model
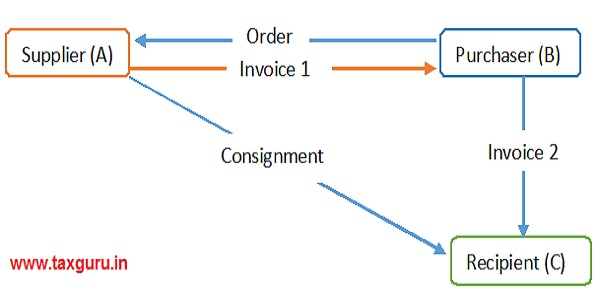
Only one EWB is required to be generated which can be generated by either ‘A’ or ‘B’
| Fields of Part-A of EWB-01 | If EWB is generated by ‘A’ | If EWB is generated by ‘B’ |
| Bill From | Details of ‘A’ | Details of ‘B’ |
| Dispatch From | Place of Business of ‘a’ | Place of Business of ‘A’ |
| Bill To | Details of ‘B’ | Details of ‘C’ |
| Ship To | Details of ‘C’ | Details of ‘C’ |
| Invoice Details | Details as per Invoice -1 | Details as per Invoice -2 |
Goods moved under Batches/ Lots
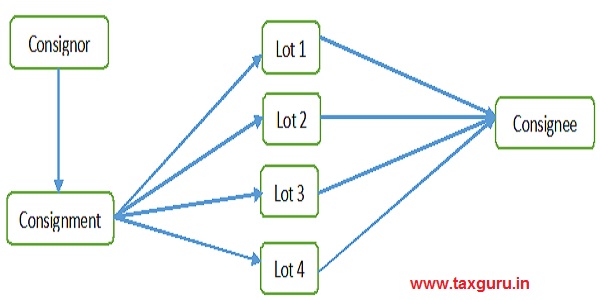
Single Tax Invoice with complete quantity -> Every lot to be accompanied with Copy of Invoice, Delivery Challan and EWB prepared as per Delivery Challan -> Last lot to be accompanied with Original Invoice, Delivery Challan and EWB with details of last lot -> CKD/ SKD/ Lots sub-supply to be selected while generating the EWBs
Non-compliance of EWB Rules
- Moving goods without generating EWB attracts a penalty of 10,000/- or the tax sought to be evaded, whichever is higher.
- Vehicle and Goods can be detained and seized and will be released only after:
- paying penalty equal to 100% of tax payable, if the owner of goods comes forward
- paying penalty equal to 50% of the value of goods, if the owner of the goods doesn’t come forward





