“Bhaiyaaaaaa online sale ka kaam toh shuru karliya par kuch hisaab samajh nahi aara”
“Online sales mein toh paisa he paisa hoga,
Paisa toh hoga, but milega tab tak nahi jab tak sahi se hisaab nahi hoga”
Looking at the quantum of sales and getting happy about it while wondering where did the money go? The most common challenge faced by all the entities is that how to record all the transactions properly to get to know the actual position of the business.
Before going further in discussion of accounting aspects of online sales business we must look at potential growth of online retail sales business in India.
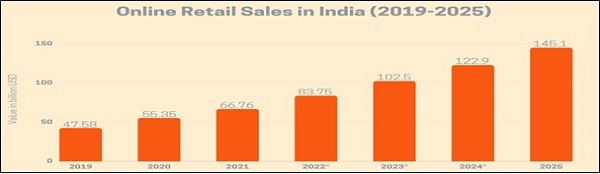
For starters, let us understand who is an E commerce operator (ECO) and an E commerce participant?
An ECO is a person who owns, operates, or manages a digital/electronic facility for the sale of goods and services. He is responsible for making payments to the e-Commerce participant on such sales. Eg: Amazon, Flipkart, Meesho, Myntra etc.
An E-commerce participant is a person who sells goods, services, or both through an electronic facility provided by an E Commerce operator. E-commerce participant must be a resident of India. Eg: Mama Earth, Boat, etc.
We will be discussing on the following areas in detail:
| 1. Data availability | 7. TDS Receivable |
| 2. Data Dumping | 8. TCS on GST |
| 3. Sales Reconciliation | 9. Security Deposit Reconciliation |
| 4. Expenses Reconciliation | 10.Claim for damages |
| 5. TDS Deduction | 11.Vendor Reconciliation |
| 6. Receipt Reconciliation |

1. Data Availability:
The ECO portal gives the e commerce participant complete detail of all the transactions that it does through that ECO, from sale to remittance, expenses deducted to TDS deducted and so on.
Various data is available on the ECO portal like:
| S. No. | Data | Details | Date of availability (generally) |
| 1 | Merchant Tax Report (MTR) | Order wise details of Sales and Sales Return | 7th of succeeding month |
| 2 | Payment Summary | Order wise details of remittance of payments by ECO | Weekly |
| 3 | Expenses Bills | Detail of expenses | 3rd of succeeding month |
For how long is the data available on the ECO?
The data is available only for a limited time on the ECO portal. For instance, the MTR sheets and payment sheets cannot be downloaded for a period older than 3 months.
So, the original data downloaded from the ECO portal should be kept and maintained in a separate folder, keeping it untouched so that in case of any grievance, it can be referred.
A copy of the above-mentioned data should be made and then used for accounting or other analysis work.
2. Data Dumping:
The most common issue is that of recording the data properly. You may have to contact your accounting software provider to assist you in this matter.
If you are doing accounting using tally software, then you will be requiring the latest version of the software and you will be required to purchase an ad-on extension from Tally which would assist in recording the bulky data properly.
This extension would allow you to import the data downloaded from the ECO portal in MS Excel format.
This would ensure completeness and accuracy of data.

Due to huge quantum of data and low system specifications of the device (Computer/Laptop) used, sometimes, errors occur in importing the data and the accountant might not be aware of this fact, does not cross check it, leading to incomplete and inaccurate data. If the accountant is aware of this fact, then too, sometimes, error of duplicity occurs as the accountant may simply import the whole data again.
Then what is the correct way of data dumping?
3. Sales Reconciliation:
Data required = MTR from ECO portal and Sales data from BOA.
The MTR report contains all the details regarding all the transactions of sales and sales return. There are two ways for recording the sales, first, by recording each entry manually from the MTR sheet into the accounting software or Data dumping method (the issues faced and correct process of recording has already been explained in Point no. 2). Generally, the second option is adopted due to heavy quantum. Ideally the sales and sales return as per MTR sheet and the BOA shall match.
| MTR | BOA | |
| Taxable value | = | Taxable Value |
| GST | = | GST |
| TCS | = | TCS |
MTR contains a lot of details like Order ID, GSTN of seller, GSTN of recipient (in case of B2B sale), Taxable value, GST amount, TCS under GST, etc. Some ECOs provide two separate sheets for B2B and B2C transactions, so beware to check both.
Author’s view: The MTR is generated by the 7th of succeeding month so it should be imported properly, maximum, by the 9th of succeeding month and details regarding GSTR 1 should be prepared accordingly.
4. Expenses Reconciliation:
Data required = Expense Bills, Debit notes for expenses and details of expenses booked in BOA.
The expenses and debit notes, if any, should be booked in the BOA with the correct expense name like Advertising, storage, commission, etc. These bills and debit notes are issued on the last date of every month. Simply, the amount of bills and debit notes should match with the expenses booked in the BOA.
Author’s view: These should be recorded maximum by 5th of every succeeding month to ensure correct and timely deduction and deposition of TDS on the same.
5. TDS Deduction:
Common mistake found in almost all the cases is that of Non deduction of TDS on the expenses charged by the ECO. Generally, auditees don’t deduct TDS on these expenses as the full amount of expense is deducted by the ECO before transferring the net proceeds from sales.
So, a query is raised by the clients that is it necessary for them to deduct TDS on such expenses?
Yes, TDS is required to be deducted on all the expenses covered under TDS as per the Income Tax Act, 1961, otherwise 30% of such expense amount would be disallowed for non-deduction u/s 40a(ia) of the above-mentioned Act, some examples are given below:
| Expense Type | Section | Rate |
| Commission | 194H | 5% |
| Storage/Warehousing | 194C | 2% |
| Advertising |
Lower Deduction Certificate (LDC) issued u/s 197 in favour of the ECO, if any, can be downloaded from the Traces portal, by entering the PAN of the ECO and relevant F.Y. under the downloads tab.
And what if they deduct TDS on these expenses, how will they recover the same from the ECO?
They must upload Form 16/16A (Declaration for deduction of TDS) on the ECO portal (quarterly basis) and then the amount will be remitted to the client’s bank account within few working days.
Author’s view: Even if the amount is not reimbursed by the ECO, it is suggested to deduct TDS to safeguard yourself from disallowance of 30% of the whole expense amount considering the cost benefit analysis.
6. Receipt reconciliation:
Data required = Payment sheet from ECO portal and receipt details in Bank from BOA.
There are two options for recording the payment by the ECO, either record all the entries as shown in the bank statement or import the payment sheet just like the MTR and it will record all the receipt transactions. Ultimately, the receipts as per ECO portal should reconcile from the amount received in bank.
It is also advised to check for transactions for which payment has not been received by reconciling the receipts report of ECO portal and bank receipts through receipt order ID (as mentioned in MTR and payment sheet)
Author’s View: It is suggested to record the receipts through Bank statement only, as recording receipts by importing payment sheet may become a tedious task as it contains a lot of other information and entries relating to expenses deducted which were already recorded through the monthly bills received, might lead to duplicity in recording of expenses, etc.
7. TDS Receivable:
Data required = Payment sheet from ECO portal, Form 26AS and BOA
The ECOs deduct TDS on every transaction u/s 194O @ 1% on the Gross amount of Sales (i.e. inclusive of GST). The details regarding this are available in the Payment sheet which should be recorded accordingly in the BOA as TDS receivable under current assets.
Although, as a general practice, everyone records this TDS receivable as mentioned in the Form 26AS.
Author’s View: TDS receivable should be recorded from Payment sheet first (weekly basis) and then must be reconciled from Form 26AS (quarterly basis) to ensure correct TDS credit.
It is not necessary that the ECO is a big company so it cannot make mistakes.
8. TCS receivable under GST:
The ECO is required to collect TCS under GST u/s 52 of the CGST Act. Just like the concept of TCS in Income Tax, where one can take credit of the amount collected in computation of tax payable, here the tax collected by the ECO shall be credited to the cash ledger of the E-commerce participant who has supplied the goods/services through the Operator. The E-commerce participant can claim credit of the tax collected and reflected in the return by the Operator in his [supplier’s] electronic cash ledger. The participant can use this amount only on the GST portal for the purpose of payments made to GST department w.r.t. tax, interest, etc.
9. Security Deposit Reconciliation:
When starting business with ECO, the T&C are set for security deposit, for which 2 options are available: One-time payment of security deposit or deducting some portion of the total remittance amount as security deposit, in every remittance cycle (generally weekly).
Author’s view: Option 1 of One-time payment of security deposit should be preferred, otherwise keeping a weekly record of the security deposit deducted on hold and balance amount remitted by ECO would have to be maintained which would be very tough and time consuming activity.
10. Claim for Damages:
In case of replacement/return of the product, sometimes another product or damaged product is received so the seller can make a claim to the ECO by having visual evidence of same through recording the opening of boxes and sharing it with ECO as a proof that the product so received was damaged/different than sold.
In case of sales return, expenses are not reversed by the ECO, rather, more expenses are charged. Some businesses have stopped doing online sales business as they were incurring more cost on sales return as compared to the profits they were earning on the sales
What should be the Treatment of such loss in the Books of Accounts of E commerce participant?
All the claims made to the ECO should be shown under current assets and income should be booked thereafter, then as the claim amount is received (which would generally be less than the total amount of claim), the balance amount not received should be debited to P&L as loss. Also, the quantity of stock lost, would have to be considered as consumed from the closing stock (normal loss) and the per unit cost would thereby increase accordingly. The amount of claim received should match with the amount released in such respect as mentioned in the Payments sheet provided by the ECO.
11. Vendor Reconciliation:
After all the above aspect of each transaction are accounted for, in a proper manner, then only, the balance of the ECO as per its portal and BOA would match.

Conclusion:
Proper accounting is the key to get the maximum benefit of the online sale business. One should expend more on the accounting rather than getting unnecessary assets.
Audit would give more qualitative results if the accounts are made in a proper manner and all the relevant documents are readily available.
Author’s view: A separate bank A/c should be maintained for doing all the transactions relating to the online business and separate BOA should be maintained to record online sales specific transactions. This would help in showing the actual profitability from the online sale business.
“Customers toh add to cart karke order karte rahenge but aap tab tak he deliver kar paaoge jab aap stock, sale, receipts, expenses, etc ka sahi se hisaab laga paaoge aur properly records maintain kar paaoge.”
Increasing the sales would not help until and unless proper records are maintained which show the actual profitability from online sale business.
About the Author:
 Mr Yash Kumat is a Senior Article Assistant and CA Jitendra Kumar is an Associate in Internal Audit Department with M/s R Sogani & Associates | Chartered Accountants, situated at C-Scheme, Jaipur, Rajasthan.
Mr Yash Kumat is a Senior Article Assistant and CA Jitendra Kumar is an Associate in Internal Audit Department with M/s R Sogani & Associates | Chartered Accountants, situated at C-Scheme, Jaipur, Rajasthan.
Disclaimer: The contents of this document are solely for informational purpose. It does not constitute professional advice or a formal recommendation. While due care has been taken in preparing this document, the existence of mistakes and omissions herein is not ruled out. The author does not accept any liabilities for any loss or damage of any kind arising out of any inaccurate or incomplete information in this document nor for any actions taken in reliance thereon. No part of this document should be distributed or copied (except for personal, non-commercial use) without express written permission. Suggestions and criticisms from all readers would be highly appreciated and acknowledged.




