Use of Trademark in commerce:-
Trademarks started to play an important role with industrialization, and they have since become a key factor in the modern world of international trade and market-oriented economies.
Industrialization and the growth of the system of the market-oriented economy allow competing manufacturers and traders to offer consumers a variety of goods in the same category.
So, trademarks serve their owners in the advertising and selling of goods, and they serve the economy in a general sense by helping to rationalize the commercialization of goods.

What is Trademark:-
In simple word trademark is a brand name. A trademark is any sign that individualizes the goods of a given enterprise and distinguishes them from the goods of its competitors.
A trademark includes any word, name, symbol, or device, or any combination, used, or intended to be used, in commerce to identify and distinguish the goods of one manufacturer or seller from goods manufactured or sold by others, and to indicate the source of the goods.
A Trademark is a type of intellectual property consisting of a recognizable sign, design or expression which identifies products or services of a particular source from those of other. The trademark owner can be an individual, business organization or any legal entity.
For example the trademark “Adidas,” identify the shoes made by Adidas and distinguish them from shoes made by other companies (e.g. Reebok or Nike)
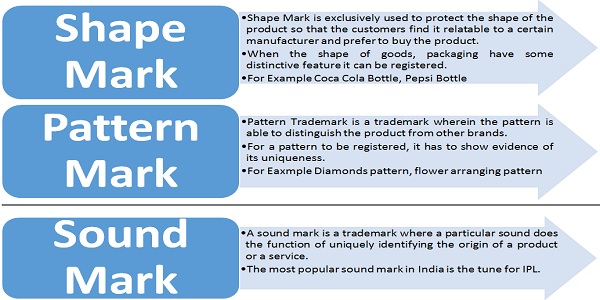
Specific Types of Trademark:-

–
Why we need for Legal Protection of Our Trademark:-
In order to fulfil their distinguishing function for consumers who wish to make their choice between different goods of the same kind on the market, trademarks must be legally protected. Otherwise competitors could use identical signs for the same or similar goods or signs so similar that the consumer would be confused as to the origin of the goods.
If the consumer eventually realizes that he has been led to buy the wrong product by a trademark confusingly similar to the one used for the product that he intended to buy, it would be difficult for him to take action against the infringer of the genuine trademark. It is therefore recognized practically everywhere that the owner of a protected trademark must have the right to prevent competitors from using identical or confusingly similar trademarks for goods identical or similar to those for which he uses his own trademark. This is the so-called exclusive right of the proprietor of the trademark.
How can a trademark be protected:-
A trademark can be protected on the basis of either use or registration. Use does still play an important role, however: first of all, in countries that have traditionally based trademark protection on use, the registration of a trademark merely confirms the trademark right that has been acquired by use. Consequently, the first user has priority in a trademark dispute, not the one who first registered the trademark.
Advantages of Registered Trademark:-
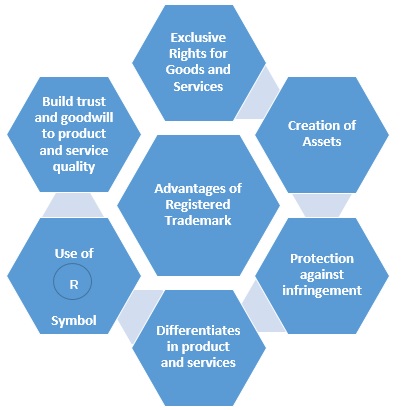
Trademark registration helps to establish an ownerships to protect brand, logo of an entity or person. It help to distinguish your goods and services from other goods and services in the market.
Who can apply for registration of a trademark?
In general, any person who intends to use a trademark or to have it used by third parties can apply for its registration. That person can be either a natural person or a legal entity, even a holding company.
Trademark Classes:-
Trademark is segregated into 45 different classes, if we concern varied goods and services there are total of 45 classes out of which 34 classes are for products and 11 are stated for services category.
Link for identification of Trademark Class- https://ipindiaonline.gov.in/tmrpublicsearch/classfication_goods_service.htm
Procedure for filing of Trademark Application:-
1. Filing of Application for Registration of Trademark–
The application for registration of the trademark can either be filed in a single- class or a multi- class totally depending on the goods and services the business pertains to. The registration application is Form TM- A which can be either filed online through the official IP India website or physically at the Trade Marks Office which depends on the jurisdiction of the trademark.
Link for filing of Trademark application in online mode- https://ipindiaonline.gov.in/trademarkefiling/user/How-To-Register.aspx
Following details and documents are required for filing of a fresh application in form TM-A:-
i. Application filed as
- Individual/Sale Proprietor
- Start Up
- Small Enterprises
- Others
ii. Class of Trademark
iii. Applicant’s Details
- Name of the Applicant i.e. Individual name or Business Name
- Address of the Applicant
- Email Id
- Phone No
- Legal Status of Applicant
iv. Category Of Mark
v .Goods and Services Descriptions
vi. Statement as to use of mark
vii. Power of Attorney, if filed through Attorney or agent
Govt. Fees for filing of application:-
The government fees for trademark registration is Rs.9000 per application per class for company. The government fees for trademark registration is Rs.4500 per application per class for individual.
If the Company / LLP / Partnership is a Start-up/Small Enterprise, then the Filing fee will be Rs.4500.00 only.
2. Allotment of Application No.:-
Once the Trademark registration application is filed with the Trademark Registrar, a trademark application allotment number is provided. After obtaining trademark application allotment number, the owner of the trademark can affix the TM symbol next to the logo.
3. Issue of Examination Report:-
After examination of the application, the registry makes an examination report of application and will decide whether the application can be accepted or not.
If accepted, the registry moved forward to advertise the trademark. In case if the examination report contains any observations, the same will be communicated to the applicant/trademark agent for submitting a reply to the examination report.
Trademark examination report shall contain the reason for objection. The applicant is required to file his reply in 30 days from the examination report. Generally, this examination report will be communicated to the trademark agent for action.
Thereafter, the applicant will be directed to file a reply to the objection within 30 days of the examination report. If the reply to the examination report found satisfactory, the Registrar shall proceed to accept the application and will advertise the same on Trademark Journal.
4. If No Objection raised by the Trademark Registrar:-
Once the trademark registration application is accepted by the Trademark Registrar, the proposed trademark is published in the Trademark Journal for public objection.
5. If No opposition raised by public:-
If no opposition raised by public than the trademark is proceeds for Registration and after that Trademark registration certificate will be issued.
6. If any opposition raised by public:-
A third party may object to the registration of a trademark in the capacity of public interest. Upon filing an objection, the status of the application will change to “Opposed”. While filing an opposition the person opposing it must include the grounds upon which he is opposing the registration of the trademark. The examiner will provide the applicant due opportunity to defend his application as per the process laid out under the Act.
7. How we can respond to Opposition:-
Once an objection is filed the applicant will be given due notice about the objection as well as the grounds of objection. The Applicant file a counter statement to the objection. This must be done within 2 months from the date of receipt of the notice of objection. If the opposition reply not filed within 2 months than the status of the application is changed to Abandoned.
i. If reply to opposition is accepted:-
After acceptance of the reply to opposition, Registrar of Trademark will forward the application for Registration and after that Trademark registration certificate will be issued.
ii. If reply to opposition is not accepted:-
If he reply in favour of the opposing party, the trademark will be removed from the Journal and the application for registration will be rejected. At this stage, the applicant may file an appeal to the Intellectual Property Appellate Board.
8. If objection is raised in Examination Report:-
In case if the examination report contains any observations, the same will be communicated to the applicant/ trademark agent for submitting a reply to the examination report within a period of 30 days.
Major reason of Objection-
The following are the two major reasons marking the application as objected by the Registrar of Trademark:
i. As per Section 9(1) of the Trade Marks Act, 1999 a trademark should be distinctive and non-descriptive. That means it should be distinct in itself and it should not be indicating the goods it stands for nor should it be common to the trade in which the Mark would do to business in.
ii. As per Section 11 (1) of the Trade Marks Act, 1999, as the mark is identical with or similar to earlier marks in respect of identical or similar description of goods and because of such identity or similarity there exists a likelihood of confusion on the part of the public. A trademark faces this objection during registration on the ground of same or similar trademark have been already registered or applied for before the registry of Trade Marks by some third party.
9. If reply to Examination Report is accepted:-
If the reply to the examination report found satisfactory, the Registrar shall proceed to accept the application and will advertise the same on Trademark Journal.
10. If reply to Examination Report is not accepted:-
If it is not accepted, the registry will mark the matter for hearing and date / time will be notified to the Trademark Agent.
11. Consequences of non-filing of Reply to examination report;-
If the reply to examination report is not filed within 30 days of notice/or by the extended time, the Trademark application shall be marked as abandoned by the Trademark Registry.
In case the application has been marked as abandoned, the applicant has to file a fresh application for the Trademark.
12. Extension of Time for Reply beyond 30 days
Applicant can file application for extension of time for filing reply in Form TM-M with requisite (₹900.00).
13. Hearing before the Registrar of Trademark
If the Reply to Trademark Examination Report is not accepted, reply filed, the trademark status will get changed to “Ready for show cause hearing” and in few months hearing notice will be issued inside which the date and time of the hearing will be mentioned.
The name of the concerned hearing officer will be mentioned on the same day of the trademark hearing. It is important to track your trademark status online in order prevent your brand name getting abandoned.
In the hearing the Registrar may also insist the applicant to file an affidavit testifying the exhibits and evidences to establish the usage of Trademark.
14. If trademark application is allowable in the hearing:-
Up on completion of hearing, if the registrar decide the trade mark application is allowable, a Letter of Acceptance (TLA order) will be issued and the trademark will be advertised in the Trade Marks Journal.
15. If trademark application is not allowable in the hearing:-
If trademark application is not allowable in the hearing the applicant may file an appeal to the Intellectual Property Appellate Board.
16. Validity of Trademark Certificate:-
The registration of a trademark is valid only for a period of 10 years. After which, it can be renewed from time to time. Trademark renewal preserves those rights which are only available to a registered mark. In case the proprietor fails to renew the trademark, then he shall lose all the protection that comes along with registration.
17. Renewal of Trademark:-
The proprietor of the trademark has to file a prescribed form for renewal before the Registrar. This application can be filed on or before 6 months from the date of expiration of the registration.
If no application for renewal has been filed, then the Registrar shall send a notice to the proprietor informing him of the upcoming renewal date. Keep in mind that no trademark can be removed if notice of renewal has not been served.
18. Consequences of failure to renewal of trademark:-
In case, no application for renewal has been filed, or in case no fee for renewal has been paid, the Registrar may remove the mark from the register. Before removing the trademark, the Registrar shall first advertise his intention to remove the mark by advertising the notice to remove in the trademark journal. Failure to renew affects not just the proprietor but also all those people who are either assigned or licensed the trademark. It also affects your legal rights, by not renewing your trademark, in effect weakens your legal position.
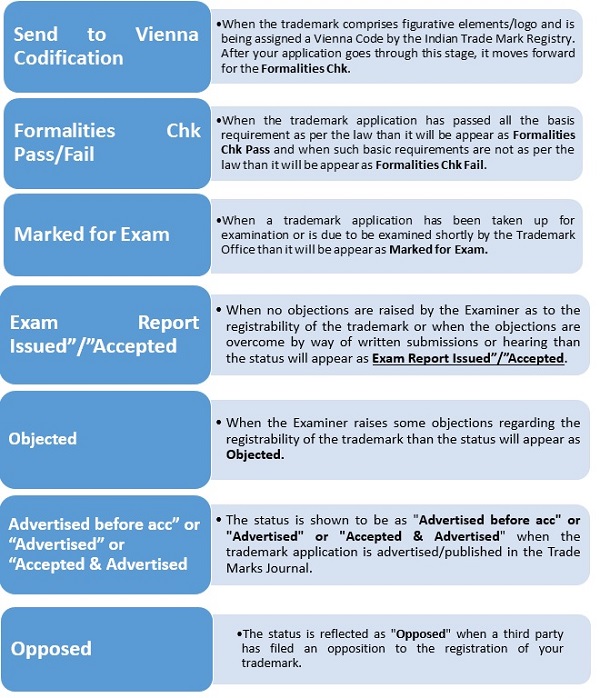
19. Meaning of different status under Trademark Registration:-