A Road map on ESOP Implementation and Proxy Firms views
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) notified the SEBI (Share Based Employee Benefits and Sweat Equity) Regulations, 2021 (New SEBI ESOP Regulations) on 13 August 2021. The new SEBI-Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP) regulations govern all sweat equity shares and share-based employee benefit schemes dealing in securities, including employee stock options, employee share purchase, stock appreciation rights, general employee benefits and retirement benefits (share-based benefit schemes).
A Flowchart for process of implementation of ESOP:
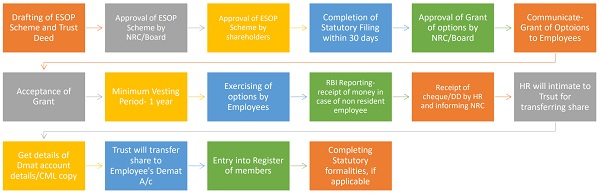
Road Map for ESOP Implementation (checklist)
|
S.N. |
Particulars | Action | Responsibility | Remarks |
| 1 | Drafting of ESOP Scheme | Scheme should be as per SEBI (SBEB & SE) Regulation 2021. | Secretarial + HR | For contents and details refer Schedule I of ESOP regulations |
| 2 | Execute Trust deed or amendments to Trust deed | Draft New / supplementary or amended Trust deed proposing the new name of trustees | Legal + HR | |
| 3 | Draft Resolutions | Prepare draft resolutions for NRC / Board and Shareholders approval | Secretarial | – |
| 4 | Notice for the NRC / Board meeting | Send to all the directors at least seven days before the meeting | Secretarial | Refer SS-1 |
| 5 | Intimation to Stock Exchange | at least 5 working days before the board Meeting | Secretarial | Reg. 29 of LODR |
| 6 | Approval of Board for ESOP Scheme | Fix time and date and approve for calling the general meeting (through Postal Ballot) | BOD / NRC | |
| 7 | Approval of Trust deed | If in compliance of schedule I | BOD / NRC | |
| 8 | Appoint Scrutinizer and Constitute NRC at Board meeting | Approval for NRC constitution under regulation 19 of SEBI LODR 2015 and approved appointment of Scrutinizer | BOD | |
| 9 | Intimation to Stock Exchange for Outcome of the Board Meeting | Within 30 minutes of the conclusion of the Board meeting. | Secretarial | Reg. 30 of LODR |
| 10 | Send the draft minutes of the board meeting | To all the directors within fifteen days of its conclusion | Secretarial | Refer SS-1 |
| 11 | File MGT-14 | To ROC within 30 days from the date of BM | Secretarial | |
| 12 | Execution of Trust Deed | Execution of Original or supplementary or amended Trust Deed | Legal | |
| 13 | Postal Ballot – e voting notice | To all the directors, auditors, shareholders and secretarial auditors simultaneously to stock exchange | Secretarial | Follow timeline of 21/30 days accordingly |
| 14 | Newspaper Advertisement | Publish advertisement in Newspaper for Postal Ballot and to stock exchange for advertisement | Secretarial | Reg 30 of LODR |
| 15 | Pass the special resolution through postal Ballot | For the issuance of shares under the ESOP to the Eligible employees | Shareholders | |
| 16 | Scrutinizer Report | Submit the Scrutinizer Report to Stock Exchange within 2 working days | Secretarial | Reg 44 of LODR |
| 17 | MGT-14 for Postal Ballot | Within thirty days of passing the special resolution | Secretarial | Sec 117 of C.A. 2013 |
| 18 | Trust Deed to Stock Exchange for implementation of ESOP Scheme | submit within reasonable time after passing of special resolution by Postal ballot | Secretarial | |
| 19 | Updation of trustees / new trustees with Banker | Intimate bankers about Trustees / new Trustees (saving accounts) | Finance / Treasury | |
| 20 | Change in Trustees, if any | Follow procedure for change of name of Trustees in Demat accounts | Secretarial | |
| 21 | Transfer of shares, if any | Transfer of shares from old Trustees to New Trustees | Secretarial | |
| 22 | MGT-4/5/6, if any | Within 30 days of transfer of shares to New Trustee | Secretarial | |
| 23 | Convey NRC Meeting | Send to all the members of NRC at least seven days before the meeting | Secretarial | |
| 24 | Prepare list of Eligible Employees and determine exercise price in NRC Meeting | Send options to the eligible employees of the company for purchasing shares under ESOP | Secretarial + HR | |
| 25 | Intimate Stock exchange regarding grant made | As soon as reasonably possible and not later than 24 hours for grant of options | Secretarial | |
| 26 | Form-ESOP in case of NRI employees | Within 30 days of Grant with RBI as per FDI policy, 2016 | Secretarial | |
| 27 | Intimate to RBI for receipt of payment from NRI | on e-biz portal within 30 days of receipt to RBI through AD | Secretarial | |
| 28 | Acceptance of Options | Within 30 days from the date of NRC meeting | Employees | |
| 29 | Vesting of Options | There shall be a minimum period of one year between the grant of options and vesting of option | Employees | |
| 30 | Prepare a list of options to be exercised by the employees. | After receiving acceptance letter | HR | |
| 31 | Exercise of options | Exercise of options by the employees | Employees | |
| 32 | Intimation to Trust | HR will intimate to Trust for Transferring shares to eligible employees (Beneficiary) | Secretarial + HR | |
| 33 | ESOP Shares to Employees Dmat Account | Trust will transfer shares to employees after verification of Demat, who have accepted options and fullfil the conditions of ESOP | Trust | |
| 34 | Intimate Stock exchange | As soon as reasonably possible and not later than 24 hours for transfer/allotment of shares | Secretarial | |
| 35 | File Form-FCTRS- in case of NRI | Within 60 days of allotment with RBI | Secretarial | |
| 36 | Updation of Insider trading portal | Updation of acquisition of shares by respective employee on Insider Trading portal | Secretarial | |
| 37 | Submit Form C of Insider Trading with Stock exchange | within 2+2 days of execution/approval by NSDL/CDSL, in case the allotment along with the previous allotment in the same quarter exceeds Rs.10 lakhs | Secretarial | Not required if companies complied with system driven disclosure |
| 38 | Update ESOP Register | Maintain ESOP register and make necessary entry | Secretarial | |
| 39 | Disclosures | Disclosure in the Balance Sheet | Finance | |
| 40 | Disclosure in the profit and loss account | Finance | ||
| 41 | Disclosures in Directors’ Report under SEBI (Share Based Employee Benefits and Sweat Equity) Regulations, 2021 | Secretarial |
“Proxy Advisory Firms’ views and expectations on ESOP”
It seems that Proxy firms are actively involved in the activity of activism of shareholders accordingly in a webinar it found that below considerable point should be taken into account while implementing ESOP:
- Institutional shareholding is on rise and proxy firms represent the investors; hence it is important to have buy-in of proxy shareholders. ESOP resolutions are special resolutions where 75% of votes in favour are required.
- Rejection of resolutions can be embarrassing for companies. Rejection may also lead to negative news and cause uncertainty or delay in launch of scheme.
Hence this aspect needs to be addressed prudently.
- Rejection of resolutions by proxy shareholders can give wrong message to employees which could be perceived as unfair.
- As per surveys, this has been the largest single area where proxy firms have given adverse vote. One of the firms have rejected 75% of ESOP resolutions, which is quite alarming.
- Proxy firms are still not seen as stakeholders, neither their views form part of ESOP discussion at management / board level. Since institutional investors seek professional advice on how they should evaluate resolutions and vote, they are considered a major stakeholder that companies need to take care of.
As proxy firms are representative of investor shareholders, they are keen to evaluate following aspects of scheme:
- Whether the plan creates a long-term value both for employees and shareholders? Anything of short-term nature is not favourably looked at.
- Whether distribution of grants is broad based or only given to specific people and what is the quantum of grant? Another parameter for evaluation is
whether vesting is linked to performance conditions. - It is generally observed that proxy firms are presuming legal compliances and they generally don’t deep dive into compliance aspect.
- Proxy firms usually are not in favour of terms that are at discretion of the NRC or Board as there is potential to be misused.
It is observed that there are differences in perspective and preferences of the Company and the proxy firms on certain design elements of ESOP scheme. Few of the critical ones are captured below:
| Sr. | Particulars | Differences in Perspective | |
| 1. | Loan to trust by the Company | Companies usually prefer using the trust route for ESOP. Since trust doesn’t have its own source of funds, loan to trust from company becomes imperative | It is observed that Proxy firms have voted against those resolutions which had loan provision for trust. |
| 2. | Source of shares | Companies prefer secondary shares option as they are anti-dilutive and there is no change in existing shareholders which also works to advantage of shareholders. | Proxy firms are not in favour of secondary shares and have voted against those resolutions that had mentioned source as secondary shares. |
| 3. | Clarity on vesting conditions | Since ESOP is a long-term instrument, it not feasible for companies to define performance conditions over a period of 4-5 years due to the dynamic economic environment. Hence companies find it difficult to “hard code” the performance conditions and other terms in resolutions. | Proxy firms need a clear disclosure and less of discretion. They expect to have performance linkage and are hesitant to vote for resolutions that gives discretion to NRC/Board to define terms later. They see it as an open-ended authority which has potential to be misused. |
| 4. | Coverage and concentration of grants | Companies prefer grants to be higher. Usually, senior management gets over 70% of the allocation and global practice is to “grant more to few”, in order to retain talent. The view is that employees find it difficult understand long term aspect of ESOP and junior employees find it difficult to align with company performance. | Proxy firms have reservation against heavy concentration of grants with senior management. They perceive that it is likely to influence management actions/decision towards gaining short term benefits (and not focus on long term gains) which may not be in the interest of shareholders. |
| 5. | Accounting cost | With IND AS becoming effective, every option has cost and it needs to be expensed. Since companies feel it’s a no cash cost and there is no liability to it, there is no pay out. | Proxy firms are hesitant to accept notional cost rational. |
| 6. | Discounts | Discount ensures lower dilution. Employees are nonfinancial investors and do not have higher risk appetite. | Discounts dilute shareholders value. Discount provides safety net to employees which is not available to shareholders. |
Ways to address the friction points:
1. Plan design:
- Business case for secondary shares and loan to trust needs to be showcased by companies. It is observed that in most cases trust implementing stock option become cash surplus after 3-4 years and can pay off loans.
- Companies could look at separate plans that can be structured for senior management and other employees – e.g. ESOP and ESPS. Each will have its
own design element to achieve the objectives and proxy firms will find it easier to analyse those. - It is observed that tax credits for companies are not adequately highlighted and its helpful if ROI on every variant is explained to proxy shareholders.
2. Proactive steps that companies may undertake:
- Interact with proxy firms and key institutional investor to seek their buy-in, instead of taking their votes for granted. This proactive approach helps both parties.
- It’s helpful to have an attitude of “convince or get convinced” to be on the same page. Proxy firms are appreciative of companies’ viewpoints, and they have been transparent in providing their reservations. In certain cases, proxy shareholders have also given their suggestion to companies, which has been helpful in getting their consents.





