It is felt that in many cases, neither the employers nor their employees are aware about the includability of the value of various perquisites in the total income of the employees. In some cases, employers and employees are not aware as to how to correctly value the perquisites. Efforts have been made to address all such issues to assist a large number of salaried tax payers in computing their tax liability correctly and in correct Valuation of Perquisites.
Article explains / contains What is Perquisites, Taxation of Perquisites, Valuation of Perquisite, Value of certain other fringe benefits, Definition of Specified Employee, Meaning of an Allowance and Example on salary.

1. PERQUISITES
“Perquisite” may be defined as any casual emolument or benefit attached to an office or position in addition to salary or wages.
“Perquisite” is defined in the section 17(2) of the Income tax Act as including:
(i) Value of rent-free/accommodation provided by the employer.
(ii) Value of any concession in the matter of rent respecting any accommodation provided to the assessee by his employer.
(iii) Any sum paid by employer in respect of an obligation which was actually payable by the assessee.
(iv) Value of any benefit/amenity granted free or at concessional rate to specified employees etc.
(v) The value of any specified security or sweat equity shares allotted or transferred, directly or indirectly, by the employer, or former employer, free of cost or at concessional rate to the assesssee.
(vi) Any sum payable by the employer, whether directly or through a fund other than a recognized provident fund or an approved superannuation fund to effect an assurance on the life of the assessee or to effect a contract for an annuity.
(vii) The amount of any contribution to an approved superannuation fund by the employer in respect of the assessee, to the extent it exceeds one lakh rupees; and
(viii) The value of any other fringe benefit or amenity as may be prescribed.
Basically the perquisites are divided in two parts i.e. monetary perquisites and non monetary perquisites. Monetary perquisites are taxable for all employees and non monetary perquisites are taxable in the hands of specified employees – ref. sec.17(2)(iii)
2. TAXATION OF PERQUISITES
2.1 Perquisites may be defined as any casual emolument or benefit attached to an office or position in addition to salary or wages. It also denotes something that benefits a person by going into his own pocket. It does not, however, cover mere reimbursement of necessary disbursements. Perquisites can be divided in the following 3 categories:
1. Perquisites taxable in all cases
2. Perquisites not taxable
3. Perquisites which are taxable only in the hands of specified Employees.
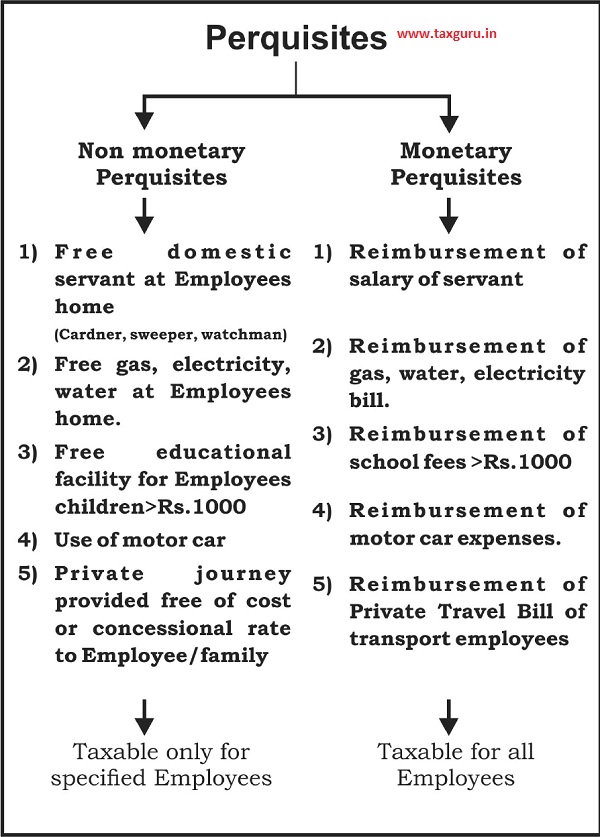
2.2 PERQUISITES TAXABLE IN THE HANDS OF THE EMPLOYEE AS A PART OF SALARY INCOME
i) Value of rent free accommodation
ii) Value of any benefit/amenity granted free or at concessional rate to specified employee
iii) Any sum paid by employer in respect of an obligation, which was actually payable by the employee.
iv) Any sum payable by the employer, directly or through a fund for assurance on life of the employee or to effect contract for an annuity.
v) Free motor car facility for personal use of employee
vi) Perquisite arising out of supply of gas, electric energy or water:
vii) Free/Concessional Educational Facility
viii) Free/Concessional journeys provided by an undertaking engaged in carriage of passengers or goods.
ix) Provision for sweeper, gardener, watchman or personal attendant.
x) Value of certain other fringe benefits.
3. VALUATION OF PERQUISITES
As a general rule, the taxable value of perquisites in the hands of the employees is its cost to the employer. However, specific rules for valuation of certain perquisites have been laid down in Rule 3 of the I.T. Rules. These are briefly given below:
3.1 VALUATION OF UNFURNISHED RESIDENTIAL ACCOMMODATION PROVIDED BY THE EMPLOYER:-
(a) Union or State Government Employees- The value of perquisite is the license fee as determined by the Govt. as reduced by the rent actually paid by the employee.
(b) Non-Govt. Employees- The value of perquisite is an amount equal to 15% of the salary in cities having population more than 25 lakh, 10% of salary in cities where population as per 2001 census is exceeding 10 lakh but not exceeding 25 lakh and 7.5% of salary in areas where population as per 2001 census is 10 lakh or below. In case the accommodation provided is not owned by the employer, but is taken on lease or rent, then the value of the perquisite would be the actual amount of lease rent paid/payable by the employer or 15% of salary, whichever is lower. In both of above cases, the value of the perquisite would be reduced by the rent, if any, actually paid by the employee.
3.2 Value of Furnished Accommodation- The value would be the value of unfurnished accommodation as computed above, increased by 10% per annum of the cost of furniture (including TV/radio/ refrigerator/ AC/other gadgets). In case such furniture is hired from a third party, the value of unfurnished accommodation would be increased by the hire charges paid/payable by the employer. However, any payment recovered from the employee towards the above would be reduced from this amount.
3.3 Value of hotel accommodation provided by the employer- The value of perquisite arising out of the above would be 24% of salary or the actual charges paid or payable to the hotel, whichever is lower. The above would be reduced by any rent actually paid or payable by the employee.
It may be noted that no perquisite would arise, if;
- The employee is provided such accommodation on transfer from one place to another for a period of 15 days or less.
- The employee is provided such accommodation at a mining/ oil exploration/ project execution/ Dam/ Power generation/ off- shore site located in remote area or being of temporary nature having plinth area < 800sq. ft and not less than 8 kms away from municipality or cantonment limits.
3.4 Perquisite of motor car provided by the employer–
a) Nil, if the motor car is used by the employee wholly and exclusively in the performance of his official duties.
b) Actual expenditure incurred by the employer on the running and maintenance of motor car, including remuneration to chauffeur as increased by the amount representing normal wear and tear of the motor car and as reduced by any amount charged from the employee for such use (in case the motor car is exclusively for private or personal purposes of the employee or any member of his household).
c) Rs. 1800/- (plus Rs. 900/-, if chauffeur is also provided) per month (in case the motor car is used partly in performance of duties and partly for private or personal purposes of the employee or any member of his household if the expenses on maintenance and running of motor car are met or reimbursed by the employer). However, the value of perquisite will be Rs. 2400/- (plus Rs. 900/-, if chauffeur is also provided) per month if the cubic capacity if engine of the motor car exceeds 1.6 litres.
d) Rs. 600/- (plus Rs. 900/-, if chauffeur is also provided) per month (in case the motor car is used partly in performance of duties and partly for private or personal purposes of the employee or any member of his household if the expenses on maintenance and running of motor car for such private or personal use are fully met by the employee). However, the value of perquisite will be Rs. 900/- (plus Rs. 900/-, if chauffeur is also provided) per month if the cubic capacity of engine of the motor car exceeds 1.6 litres.
If the motor car or any other automotive conveyance is owned by the employee but the actual running and maintenance charges are met or reimbursed by the employer, the method of valuation of perquisite value is different. (See Rule 3(2)).
THE SUMMARIZED TABLE IS AS UNDER:-
| S.
No.
|
Circumstances | Engine Capacity upto 1600 cc
|
Engine Capacity above 1600 cc |
| 1 | Where the motor car is owned or hired by the employer | ||
| (a) is used wholly and exclusively in the performance of his offcial duties; | Fully Exempt. Provided that specified documents are maintained by the employer. | ||
| (b) is used exclusively for the private or personal purposes of the employee or any member of his household and the running and maintenance expenses are met or reimbursed by the employer; | Actual amount of expenditure incurred by the employer on the running and maintenance of motor car during the relevant previous year including remuneration, if any, paid by the employer to the chauffeur as increased by the amount representing normal wear and tear* of the motor car and as reduced by any amount charged from the employee for such use. | ||
| (c) is used partly in the performance of duties and partly for private or personal purposes of his own or any member of his household and – | |||
| (i) the expenses on maintenance and running are met or reimbursed by the employer; | Rs. 1,800 (plus Rs. 900, if chauffeur is also provided to run the motor car) | Rs. 2,400 (plus Rs. 900, if chauffeur is also provided to run the motor car) | |
| (ii) the expenses on running and maintenance for private or personal use are fully met by the assessee | Rs. 600 (plus Rs. 900, if chauffeur is also provided by the employer to run the motor car) | Rs. 900 (plus Rs. 900, if chauffeur is also provided to run the motor car) | |
| Where the employee owns a motor car but the actual running and maintenance charges (including remuneration of the chauffeur, if any) are met or reimbursed to him by the employer | |||
| (i) such reimbursement is for the use of the vehicle wholly and exclusively for offcial purposes; | |||
| (ii) such reimbursement is for the use of the vehicle partly for offcial purposes and partly for personal or private purposes of the employee or any member of his household. | Subject to maintaining specified documents by employer, the actual amount of expenditure incurred by the employer as reduced Rs. 1800 (plus Rs. 900, if chauffeur is also provided by the employer to run the motor car) | Subject to maintain ing specified documents by employer, the actual amount of expenditure incurred by the employer as reduced by Rs. 2400 (plus Rs. 900, if chauffeur is also provided to run the motor car)
|
|
| 3 | Where the employee owns any other automotive conveyance but the actual running and maintenance charges are met or reimbursed to him by the employer | ||
| (i) such reimbursement is for the use of the vehicle wholly and exclusively for official purposes;
|
Fully Exempt Provided that specified documents are maintained by the employer. | Not applicable
|
|
| (ii) such reimbursement is for the use of vehicle partly for official purposes and partly for personal or private purposes of the employee. | Subject to maintaining specified documents by employer, the actual amount of expenditure incurred by the employer as reduced by the amount of Rs. 900. | ||
* The normal wear and tear of a motor-car shall be taken at 10 per cent per annum of the actual cost of the motor-car or cars.
3.5 Perquisite arising out of supply of gas, electric energy or water: This shall be determined as the amount paid by the employer to the agency supplying the same. If the supply is from the employer’s own resources, the value of the perquisite would be the manufacturing cost per unit incurred by the employer. However, any payment received from the employee towards the above would be reduced from the amount [Rule 3(4)]
3.6 Free/Concessional Educational Facility: Value of the perquisite would be the expenditure incurred by the employer. If the education institution is maintained & owned by the employer, the value would be nil if the value of the benefit per child is below Rs. 1000/- P.M. or else the reasonable cost of such education in a similar institution in or near the locality. [Rule 3(5)].
| Facility extended to Children | Value of perquisite if provided in the school owned by the employer | Value of perquisite if provided in any other school |
| Cost of such education in similar school less Rs. 1,000 per month per child (irrespective of numbers of children) less amount recovered from employee | Amount incurred less amount recovered from employee (an exemption of Rs. 1,000 per month per child is allowed) | |
| Other family member
|
Cost of such education in similar school less amount recovered from employee
|
Cost of such education incurred
|
Other Educational Facilities
|
||
3.7 Free/Concessional journeys provided by an undertaking engaged in carriage of passengers or goods: Value of perquisite would be the value at which such amenity is offered to general public as reduced by any amount, if recovered from the employee. However, these provisions are not applicable to the employees of an airline or the railways.
3.8 Provision for sweeper, gardener, watchman or personal attendant: The value of benefit resulting from provision of any of these shall be the actual cost borne by the employer in this respect as reduced by any amount paid by the employee for such services. (Cost to the employer in respect to the above will be salary paid/ payable). [Rule 3(3)].
4. VALUE OF CERTAIN OTHER FRINGE BENEFITS
(a) Interest free/concessional loans– The value of the perquisite shall be the excess of interest payable at the prescribed interest rate over, interest, if any, actually paid by the employee or any member of his household. The prescribed interest rate would be the rate charged by State Bank of India as on the 1st Day of the relevant Previous Year in respect of loans of the same type and for same purpose advanced by it to general public. Perquisite is to be calculated on the basis of the maximum outstanding monthly balance method. However, loans upto Rs. 20,000/-, loans for medical treatment specified in Rule 3A are exempt provided the same are not reimbursed under medical insurance.
(b) Value of free meals- The perquisite value in respect of free food and non-alcoholic beverages provided by the employer, to an employee shall be the expenditure incurred by the employer as reduced by the amount paid or recovered from the employee for such benefit or amenity. However, no perquisite value will be taken if food and non-alcoholic beverages are provided during working hours and certain conditions specified under Rule 3(7)(iii) are satisfied.
(c) Value of gift or voucher or token– The perquisite value in respect of any gift, or voucher, or taken in lieu of which such gift may be received by the employee or member of his household from the employer, shall be the sum equal to the amount of such gift, voucher or token. However, no perquisite value will be taken if the value of such gift, voucher or taken is below Rs. 5000- in the aggregate during the previous years.
(d) Credit card provided by the employer– The perquisite value in respect of expenses incurred by the employee or any of his household members, which are charged to a credit card provided by the employer, which are paid or reimbursed by such employer to an employee shall be taken to be such amount paid or reimbursed by the employer. However, no perquisite value will be taken if the expenses are incurred wholly and exclusively for official purposes and certain conditions mentioned in Rule 3(7)(v) are satisfied.
(e) Club membership provided by the employer– The perquisite value in respect of amount paid or reimbursed to an employee by an employer, against the expenses incurred in a club by such employee or any of his household members shall be taken to be such amount incurred or reimbursed by the employer as reduced by any amount paid or recovered from the employee on such account. However, no perquisite value will be taken if the expenditure is incurred wholly and exclusively for business purposes and certain conditions mentioned in Rule 3(7)(vi) are satisfied.
4.1 The value of any other benefit or amenity provided by the employer shall be determined on the basis of cost to the employer under an arms’ length transaction as reduced by the employee’s contribution.
4.2 The fair market value of any specified security or sweat equity share, being an equity share in a company, on the date on which the option is exercised by the employee, shall be determined as follows:-
(a) In a case where, on the date of exercising of the option, the share in the company is listed on a recognized stock exchange, the fair market value shall be the average of the opening price and closing price of the share on the date on the said stock exchange.
(b) In a case where, on the date of exercising of the option, the share in the company is not listed on a recognized stock exchange, the fair market value shall be such value of the share in the company as determined by a merchant banker on the specified date.
(c) The fair market value of any specified security, not being an equity share in a company, on the date on which the option is exercised by the employee, shall be such value as determined by a merchant banker on the specified date.
4.3 Use of Movable Assets [Section 17(2)(viii) read with Rule 3(7)(vii) ]
Taxable value of perquisites shall be
1) For use of Laptops and Computers – Nil
2) For movable asset other than Laptops, computers and Motor Car – 10% of original cost of the asset (if asset is owned by the employer) or actual hire charges incurred by the employer (if asset is taken on rent) less amount recovered from employee.
4.4 Transfer of Movable Assets[ Section 17(2) (viii) read with Rule 3(7)(viii) ]
Taxable value of perquisites shall be:
a. Computers, Laptop and Electronics items: Actual cost of asset less depreciation at 50% (using reducing balance method) for each completed year of usage by employer less amount recovered from the employee
b. Motor Car: Actual cost of asset less depreciation at 20% (using reducing balance method) for each completed year of usage by employer less amount recovered from the employee
c. Other movable assets: Actual cost of asset less depreciation at 10% (on SLM basis) for each completed year of usage by employer less amount recovered from the employee.
4.5 Medical facilities in India [Proviso to section 17(2)]
a. Expense incurred or reimbursed by the employer for the medical treatment of the employee or his family (spouse and children, dependent – parents, brothers and sisters) in any of the following hospital is not chargeable to tax in the hands of the employee:-
i) Hospital maintained by the employer.
ii) Hospital maintained by the Government or Local Authority or any other hospital approved by Government for the treatment of its employees.
iii) Hospital approved by the Principal Chief Commissioner or Chief Commissioner having regard to the prescribed guidelines for treatment of the prescribed diseases.
b. Medical insurance premium paid or reimbursed by the employer is not chargeable to tax.
c. Any other expenditure incurred or reimbursed by the employer for providing medical facility in India is not chargeable to tax up to Rs. 15,000 in aggregate per assessment year.
4.6 Medical facilities outside India [Proviso to section 17(2) ]
Any expenditure incurred or reimbursed by the employer for medical treatment of the employee or his family member outside India is exempt to the extent of following (subject to certain conditions):
a. Expenses on medical treatment – exempt to the extent permitted by RBI.
b. Expenses on stay abroad for patient and one attendant – exempt to the extent permitted by RBI.
c. Expenditure incurred on travelling of patient and one attendant- exempt, if Gross Total Income (before including the travel expenditure) of the employee, does not exceed Rs. 2,00,000/-.
4.7 Leave Travel Concession (LTC/LTA) [Section 10(5) read with rule 2B ]
The exemption shall be limited to fare for going anywhere in India along with family twice in a block of four years:
- Where journey is performed by Air – Exemption up to Air fare of economy class in the National Carrier by the shortest route
- Where journey is performed by Rail – Exemption up to air-conditioned first class rail fare by the shortest route
- If places of origin of journey and destination are connected by rail but the journey is performed by any other mode of transport – Exemption up to air-conditioned first class rail fare by the shortest route.
- Where the places of origin of journey and destination are not connected by rail:
– Where a recognized public transport system exists – Exemption up to first Class or deluxe class fare by the shortest route
– Where no recognized public transport system exists – Exemption up to air conditioned first class rail fare by shortest route.
Notes:
1. Two journeys in a block of 4 calendar years is exempt
2. Taxable only in case of Specified Employees [See Explanations]
5. DEFINITION OF SPECIFIED EMPLOYEE
The following employees are deemed as specified employees:
1) A director-employee
2) An employee who has substantial interest (i.e. beneficial owner of equity shares carrying 20% or more voting power) in the employer-company
3) An employee whose monetary income* under the salary exceeds Rs.50,000.
* Monetary Income means Income chargeable under the salary but excluding perquisite value of all non-monetary perquisites.
6. MEANING OF AN ALLOWANCE
An allowance is the financial benefit given to the employee by the employer over and above the regular salary. These benefits are provided to cover particular expenses whether personal or for discharge of his duties for example Conveyance Allowance is paid to foot expenses incurred for commuting to workplace. Some of these allowances are taxable under the head salary. A few of them again could be partly taxable and few others are non-taxable or fully exempt from taxes.
Here is a glance at allowances that are taxable, partly taxable or non-taxable:
6.1 Taxable Allowances:
1. Dearness Allowance: Dearness Allowance (DA) is an allowance paid to employees as a cost of living adjustment allowance paid to the employees to cope with inflation. DA paid to employees is fully taxable with salary. The IT Act mandates that tax liability for DA along with salary must be declared in the filed return.
2. Entertainment Allowance: Government employees are allowed the deduction of lowest of the following amounts – one-fifth of basic salary, actual amount received as allowance or Rs. 5,000. This is an allowance provided to employees to reimburse the expenses incurred on the hospitality of customers. However, Government employees can claim exemption in the manner provided in section 16 (ii). All other employees have to pay tax on it.
3. Overtime Allowance: Employers may provide an overtime allowance to employees working over and above the regular work hours. This is called overtime and any allowance received for this is fully taxable.
4. City Compensatory Allowance: City Compensatory Allowance is paid to employees in an urban centre which may be highly expensive and to cope with the inflated living costs in the cities. This allowance is fully taxable.
5. Interim Allowance: When an employer gives any Interim Allowance in lieu of final allowance, this becomes fully taxable.
6. Project Allowance: When an employer provides an allowance to employees to meet project expenses, this is also fully taxable.
7. Tiffin/Meals Allowance: Sometimes employers may provide Tiffin/Meals Allowance to the employees. This is fully taxable.
8. Cash Allowance: When the employer provides a cash allowance like marriage allowance, bereavement allowance or holiday allowance, it becomes fully taxable.
9. Non-Practicing Allowance: When physicians are attached to Clinical Centers of the various Laboratories/Institutes, any non-practicing allowance paid to them become fully taxable.
10. Warden Allowance: When an employer pays an allowance to an employee working as a Warden i.e. Keeper in an educational Institute, the allowance received is fully taxable.
11. Servant Allowance: When an employer pays an employee to engage services of a servant, such an allowance is taxable.
12. Fixed Medical Allowance: This is an allowance paid by the employer to the employee at fixed rates irrespective of any treatment taken by the employee.
6.2 Partly Taxable:
1. House Rent Allowance (HRA): When an employer pays an allowance for the employees accommodation it is called House Rent Allowance. Tax exemption under section 10 (13A) can be claimed on whichever amount is lower of the three:
i) HRA as per actual received by the employee
ii) Rent actually paid less 10% of Basic Salary
iii) In Metros i.e Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai or Kolkata, as much as 50% of basic salary or else 40% of it if the accommodation is in a non-metro.
Any amount of House Rent Allowance received after claiming such deduction is taxable.
2. Special Allowance: A special allowance
paid to employees is covered under section 10(14)(i) and does not fall within the purview of a perquisite. It is essentially for performance of a duty is not taxable to the extent to which it has been actually incurred.
3. Children education allowance: Exempt upto Rs. 100/- per month per child for a maximum of two children. Similarly, hostel subsidy of Rs. 300/- per month per child for a maximum of two children is exempt.
4. Transport Allowance: 800/- ( Rs.1600/- for blind or orthopedically handicapped with disability of lower limbs) per month exempt for the purpose of commuting between residence and place of duty. (Rule 2BB)
6.3 Non-Taxable:
Some of the allowances, usually paid to Government servants, judges and employees of UNO are not taxable. These are:
1. Allowances paid to Govt. servants abroad: When servants of Government of India are paid an allowance while serving abroad, such income is fully exempt from taxes.
2. Sumptuary allowances: Sumptuary allowances paid to judges of HC and SC are not taxed.
3. Allowance paid by UNO: Allowances received by employees of UNO are fully exempt from tax.
4. Compensatory allowance paid to judges: When a judge receives compensatory allowance, it is not taxable.
7. SOME EXAMPLE OF SALARY
Some simple illustrative examples of valuation of perquisites are given below with regard to the provisions as they stand w.e.f 1/4/2015:
1) Mr. X and Ms. Y are employees of/in Company A (i.e. an employer other than the Central Government or any State Government). Company A has total of 10 employees including Mr.X and Ms. Y.
Mr. X is provided with furnished accommodation in a city with a population exceeding 10 lakhs but not exceeding 25 Lakhs as per the 2001 census. The accommodation provided to Mr. X is owned by the employer and has an estimated fair market value Rs. 25 lakhs. The furniture and fixture provided with the accommodation is also owned by the employer and was bought at a cost of Rs.1 lakh. Mr. X pays a nominal amount of Rs.500 per month for the furnished accommodation. Mr. X has a salary of RS.80,000/- per month exclusive of the value of perquisites. He is also provided with a sweeper who receives a salary of Rs.2000 per month for services to Mrs.X. Mr.X pays nothing to the employer for his benefit. Mr. X is provided by the employer with a car and driver only for travel to and from residence to the place of work.
Ms. Y is provided with an unfurnished accommodation in the same city as Mr. X. This accommodation is not owned by the employer but taken on a lease of Rs.6000 per month. She does not pay the employer any amount for the use of the accommodation. Ms.Y also has a salary of Rs.80,000/- per month exclusive of the value of perquisites. Ms. Y has her gas bills paid by the employer. They amount to Rs.100 per month and Ms.Y pays nothing to the employer for the benefit. Ms. Y is also provided with a laptop computer that costs Rs.1 lakh.
The employer also make an expenditure of Rs.1 lakh per year for providing health cub facilities to it 10 employees. Mr.X uses these facilities regularly but Ms. Y rarely uses these facilities.
The valuation of perquisites for Mr.X and Ms. Y are given below:
| Mr.X | Ms.y |
| Value of furnished accommodation owned by employer:
10% of salary – Rs.96000/-per year Plus value of furniture & fixture: 10% of cost per annum – Rs.10000/- per year |
Value of unfurnished accommodation taken on lease rent:
Actual amount of lease rent paid/payable by the employer (Rs.72,000 per year) or 15% of the salary (Rs.1,44,000 per year), Whichever is lower: |
| Less amount paid:-
RS.6,000/- Therefore value of this perquisites is |
Therefore, value of this perquisite is Rs.72,000/- per year. |
| Value of benefit of sweeper- Rs.24,000/- per year. |
Provision of gas Rs.1200/- per year. |
| The provision of the car and driver only for travel to and from residence to the place of work is not taxable in hands of employee. |
Provision of movable asset in the case of a laptop is exempt. |
Note 1 The value of taxable perquisites as given above shall be included in the salary income of Mr. X and Ms. Y respectively. This in turn, would be a part of the total income of Mr. X and Ms. Y. It would be liable to income tax at the prevailing rates in the hands of the employees, namely Mr. X and Ms. Y.
Note 2 The provision of health club facilities is exempt from tax. As in the above example use of health club, sports and similar facilities provided uniformly to all employees
2) Mr. A and Mr. B are government
employees. Mr. A resides in an unfurnished accommodation provided by the government that has a license fees of Rs.500/- per month as per government rules. He pays Rs.500/- per month as license fee to the government. He receives transport allowance of Rs.800/- per month for commuting to and from his residence to place of work. Mr. B is provided with a furnished accommodation by the government. The license fee for the accommodation is Rs.500/- per month as per government rules. He pays Rs.500/- per month as license fees to the government. The furniture and fixtures provided with the accommodation is also owned by the employer and was bought at a cost of Rs.20,000/-. Mr. B pays Rs.50/- per month for the furniture fixture provided. He also receives the benefit of a car and a driver for commuting to and from his residence to place of work.
The valuation of perquisites for Mr. A and Mr. B are given below:-
| Mr. A | Mr. B |
| Value of unfurnished | Value of unfurnished |
| accommodation | accommodation: |
| License fee as | License fee as |
| determined by | determined by |
| government- | government:- |
| Rs. 6,000/- per year | Rs. 6000/- per year |
| Less amount paid- | Plus value of furniture |
| Rs. 6,000/- per year | and fixtures: |
| Therefore, value of | 10% of cost per |
| this perquisite is Nil. | annum- Rs. 2000/-per year |
| Less amount paid Rs.6000/- per year license fee and Rs.600/- per year for furniture & fixtures. Therefore, value of this perquisite is Rs.1400/- per year. |
|
| Transport allowance up to Rs.1600/- per month for commuting to and from his residence to place of work is exempt. |
The provision of the car and driver only for travel to and from residence to the place of work is exempt. |
DISCLAIMER:
This booklet should not be construed as an exhaustive statement of the Law. In case of doubt, reference should always be made to the relevant provisions of the Direct tax Laws and Rules and where necessary, notifications issued from time to time




