TAX SAVINGS INVESTMENTS AND WEALTH MANAGEMENT
Why to save taxes..??
-Do you feel that you are paying too much tax?
-Have you ever thought of saving tax?
-Planning your taxes properly can help you save a lot of money.
-Income Tax laws appear so complex that people are scared to deal with their taxes. Why won’t they be scared? After all, the man with the greatest mind, Einstein himself called taxes the hardest thing to understand. Such people let their employers drain plenty of money as TDS from their salary.
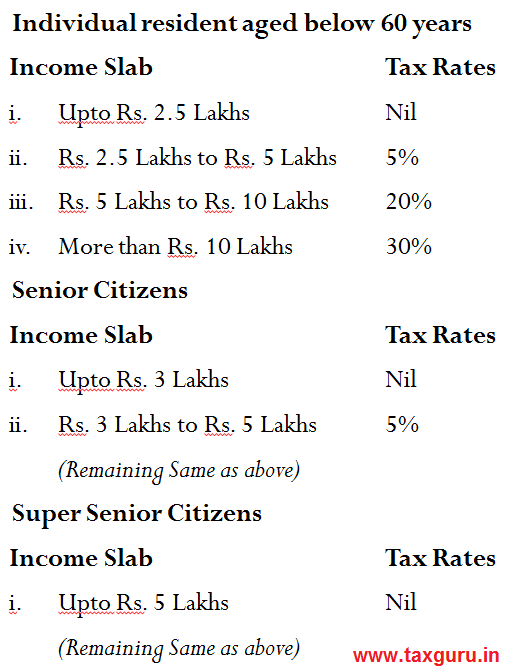
Income Tax Slab
- Zero tax on taxable income up to Rs 5 lakh:
A) Individuals having taxable income up to Rs 5 lakh in a financial year will be able to avail full tax rebate and thereby will not be required to pay any tax on this income. The tax-rebate available under Section 87A has been increased to Rs 12, 500 from FY 2019-20 onwards.
B) Remember, after claiming all the tax-saving deductions, if your taxable income still exceeds Rs 5 lakh, then you will be liable to pay income tax as per the existing rates.
Standard Deduction
> The standard deduction from salary from Rs 40,000 to Rs 50,000, an increase of Rs 10,000.
> In lieu of transport allowance and medical reimbursement. This deduction is available to all the salaried class and pensioners.
> The deduction is claimed at the time of filing your income tax return
Surcharge on Income Tax
The new rate of surcharge for Individual, HUF, AOP, BOI and AJP shall be –
- 10% (for income of Rs. 50 lakhs to Rs. 1 crore),
- 15% (for income of Rs. 1 crore to Rs. 2 crores),
- 25% (for income of Rs. 2 crores to Rs. 5 crores), and
- 37% (for income exceeding 5 crores).
Budget – New Tax Rates
Tips to Invest and save tax
- Decide about how much amount you want to invest to sax tax.
- Research about all different types of tax savings instruments.
- Compare the features of all saving products and match them to personal investing goals.
- Calculate the returns from investments before investing in any product.
- At times, facing loss can be very beneficial when you plan your tax savings.
- Be ready with you credit report and status.
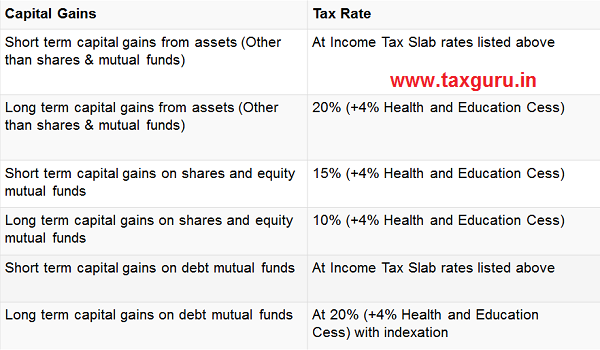
Capital Gain Tax Rate
Tax saving expenses
- Tuition Fees – Deduction under this section is available for tuition fees paid on two children’s education. The deduction is available for Full Time courses only. In our opinion no deduction is available for part time or distance learning courses. Fees for Private tuition/Coaching Classes not eligible for deduction u/s. 80C.
- House rent – HRA or 80GG
80GG: Deduction available is the minimum of:
Rent paid minus 10% of total income
Rs 5000/- per month
25% of total income
- Tax exemption on HRA is least of the following:
1) Actual HRA received
2) Actual rent paid reduced by 10% of Basic salary+DA
3) 50% of basic salary + DA if the taxpayer is living in a metro city
4) 40% of basic salary + DA if the taxpayer is living in a non-metro city
- Repayment of housing loan
- Repayment of Interest on education loan u/s 80E for 8 years
1) Loan should be from Financial Institution.
2) The loan should be taken to pursue higher studies. It does not matter whether such education loan is taken for higher studies in India or outside India. Higher studies include all the fields of study pursued after passing the senior secondary examination or its equivalent exam. It includes both the Vocational courses as well as the regular courses.
- Travel Expenses – LTA
1) Exemption of Fare Only and not total cost of holiday.
2) Travel within India only allowed.
3) Exemption on Actual Travel Expense.
4) Family’ for the purposes of exemption includes spouse and children and wholly or mainly dependent parents, brothers and sisters.
5) Exemption is not available for more than two children of an individual born after October 01, 1998.
6) Exemption only in respect of two journeys performed in a block of four calendar years. (2018-21)
7) Only one LTA can be brought forward and claimed in the first year of the next block.
8) Can I Claim LTA Twice in a Year? – No. Assessee can claim the LTA benefit just once in a year.
9) LTA in case of Switch of JOB – If assessee switch jobs, assessee can get the LTA not only from your present organisation but also from your former employer, if the concession is lying unutilised.
10) Amount Exempted under LTA Rules
> Journey performed by Air – Economy Air fair of National carrier by the shortest route or the amount spent which ever is less will be exempt
> Journey performed by Rail – A.C. first class rail fare by shortest route or amount spent which ever is less will be exempt.
> Place of origin and destination place of journey connected by rail but journey performed by other mode of transport – A.C. first class rail fare by shortest route or amount spent which ever is less.
> Place of origin & destination not connected by rail(partly/fully) but connected by other recognised Public transport system – First class or deluxe class fare by shortest route or amount spent which ever is less.
> Place of origin & destination not connected by rail(partly/fully) and not connected by other recognised Public transport system also – AC first class rail fare by shortest route (as the journey had been performed by rail) or the amount actually spent ,which ever is less.
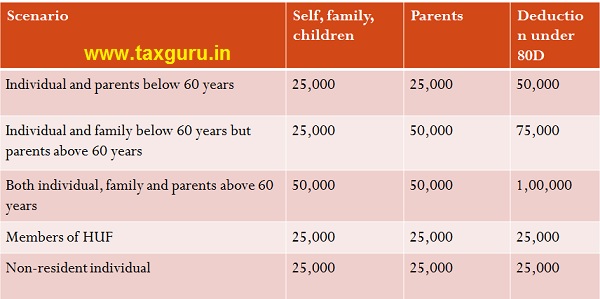
- Section 80D: Mediclaim
ELSS: Equity Linked Saving Scheme
- ELSS are diversified equity mutual funds with two differentiating features – one, investment amount in them qualifies for tax benefit under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961, up to a limit of Rs 1.5 lakh a year and secondly, the amount invested has a lock-in period of 3 years.
- The returns in ELSS are not fixed and neither assured but is dependent on the performance of equity markets.
- One may opt for dividend – for regular income, although not assured or growth option – saving for long term need.
- Long-term capital gains on redemption is nil upto Rs. 1 Lakh.
- The dividends in an equity scheme are tax-free. (Proposed to be taxed under Budget)
- Investing in ELSS yields tax-free income both for the dividend and the growth unit holders.
- Investing in ELSS not only helps you save for a long term goal but also helps you save tax and generate tax-exempt income.
Public Provident Fund
- Deposits can be made in lump-sum or in 12 instalments.
- Joint account cannot be opened.
- Account can be opened by cash/ Cheque and In case of Cheque, the date of realization of Cheque in Govt. account shall be date of opening of account.
- Nomination facility is available at the time of opening and also after opening of account. Account can be transferred from one post office to another.
- The subscriber can open another account in the name of minors but subject to maximum investment limit by adding balance in all accounts.
- Maturity period is 15 years
- Premature closure is not allowed before 15 years.
- Deposits qualify for deduction from income under Sec. 80C of IT Act.
- Interest is completely tax-free.
- Withdrawal is permissible every year from 7th financial year from the year of opening account. Max 50% of deposits.
- Loan facility available from 3rd financial year. Max 25% of deposit.
- No attachment under court decree order.
- The PPF account can be opened in a Post Office which is Double handed and above.
- Rate of Interest @ 7.9% compounded annually.
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY)
- The account can be opened by the natural or legal guardian in the name of a girl child from the birth of the girl child till she attains the age of 10 years
- A depositor can open and operate only one account in the name of a girl child under the scheme rules
- Natural or legal guardian of a girl child can be allowed to open the account for two girl children only. The third account in the name of the girl child can be opened in the event of birth of twin girls, as second birth or if the first birth itself results into three girl children
- Attractive interest rate of 8.5% (not fixed). Interest rate is regulated by Ministry of Finance from time to time
- Minimum Rs. 1,000 can be invested in one financial year
- Maximum investment of Rs. 1,50,000 can be made in one financial year
- Deposits in an account can be made till completion of 14 years, from the date of opening of the account
- The account shall mature on completion of 21 years from the date of opening of the account, provided that where the marriage of the account holder takes place before completion of such period of 21 years, the operation of the account shall not be permitted beyond the date of her marriage
- Tax Exemption
Investment in Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana scheme is exempted from Income Tax under section 80C. The scheme offers Tax Benefit under Triple E regimen i.e. Principal, interest and outflow all are tax exempted
- Withdrawal Facility
To meet the financial requirements of the account holder for the purpose of higher education and marriage, account holder can avail partial withdrawal facility after attaining 18 years of age
Kisan Vikas Patra (KVP)
- Any Indian Citizen above 18 years of age can invest.
- Interest rate 7.7% compounded annually (Taxable)
- Tenure – 9 years and 10 months (100% return on maturity)
- No maximum limit on the amount of investment but doesn’t qualify for any deduction under Income Tax Act.
- Loan against KVP certificate is available.
- Available in denominations of Rs. 100, Rs. 500, Rs. 1000, Rs. 5000, Rs. 10000 and Rs. 50000 for investment.
- Lock in Period – 30 months.
- Premature withdrawal – after 118 months
National Saving Certificate (NSC)
- Fixed Income @ 8% compounded annually but payable on maturity.
- Investment qualifies for deduction under section 80C.
- Amount of Investment – Minimum investment is Rs. 1000. No maximum limit of investment.
- Maturity Period – 5 years and 10 years.
- Loan Collateral.
- Interest earned in last year is taxable.
- Nomination facility if available.
Life Insurance Premium
- Policy should be taken on own life, or life of spouse or any child. The child includes married daughter, dependent child, adopted child, step child and adult child.
- Deduction is allowed only when the premium is actually paid in the year.
- Maximum deduction allowed for Life insurance premium is 10% of the actual sum assured.
- Life Insurance Premium paid on the life insurance policies issued by LIC or by any registered Indian Insurance company will qualify for deduction under section 80C.
- If the assessee terminates the contract or contract ceases to be in force by reason of failure to pay any premium:
A) in case of any single premium policy, within two years after the date of commencement of insurance; or
B) in any other case, before premiums have been paid for two years
- then no deduction is allowed for any premium paid in that financial year. The premium for such insurance policy which was allowed as deduction in earlier years is taxable in year in which insurance policy is terminated or ceases to be in force.
- Maturity benefits received including bonus on the death of the insured person is tax free in the hands of recipient u/s 10(10D).
- Any maturity benefits including bonus received by the insured person himself are also exempt from tax.
- TDS @ 1% on the proceeds which is not exempt u/s 10(10D) if the amount exceeds Rs. 1 Lakh.
- Proposed to deduct 5% on the proceeds received after 1st Sep, 2019.
- Types of Insurance: Life Insurance, Term Insurance, ULIP, Money Back Policy, Pension Plans.
Tax Saving Fixed Deposit
- The FD can be placed with a minimum amount which varies from bank to bank.
- These deposits have a lock-in period of 5 years. Premature withdrawals and loan against these FD’s are not allowed.
- A person can invest in these FD’s through any public or private sector bank except for co-operative and rural banks.
- Investment in Post Office Time Deposit of 5 years also qualifies for deduction under section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- One can hold these FD’s either in ‘Single’ or ‘Joint’ mode of holding. In the case the mode of holding is joint, the tax benefit is available only to the first holder.
- The interest earned is taxable as per the investor’s tax bracket and therefore, TDS is applicable. The interest on deposits is payable on either monthly/quarterly basis or can be reinvested.
- Nomination facility is available for these FDs.
Pension Plans
- Also known as Annuity Plans of Life Insurance Corporation of India or any other insurer for receiving pension from the Fund referred to in clause (23AAB) of section 10. One time investment plan.
- Designed to offer regular income to people after retirement.
- Pension plans allow the policyholder to choose the date (also known as the vesting date) from which they can start receiving the pension. This date need not be after retirement and can be much earlier. No locking period.
- Tax saving benefit u/s 80CCD. (part of 80C)
- Additional Benefit upto Rs. 50,000/- for self contribution u/s 80CCD(1B)
- Keep aside at least 40% of the corpus to receive a regular pension from a PFRDA-registered insurance firm.
- The remaining 60% is tax-free now.
- Minimum Amount of Investment: 1000/- p.a.
- Maximum Amount of Investment: No Limit
- As a pension scheme, it is important for you to continue investing until the age of 60.
- If you have been investing for at least 3 years, you may withdraw up to 25% for certain purposes. These include children’s wedding or higher studies, building/buying a house or medical treatment of self/family, among others.
- Withdrawal for up to 3 times (with a gap of 5 years) in the entire tenure.
- From FY 2019-20, people with a second house, lying vacant will not be required to pay any income tax on the notional rent from this house.
- The notional rent is the amount of the rent which the individual would have earned if the house was let out by him.
Notional Rent
- From FY 2019-20, people with a second house, lying vacant will not be required to pay any income tax on the notional rent from this house.
- The notional rent is the amount of the rent which the individual would have earned if the house was let out by him.
Benefit of investing capital gains in two residential houses
- Taxpayers who have sold their house property will now have the option to invest the long-term capital gains (LTCG) in two houses instead of one in order to avoid paying LTCG tax on the amounts so invested.
- However, one must remember that this benefit can be availed only if the capital gains does not exceed Rs. 2 crores and can be availed once in a lifetime.
Budget
- Income-tax return can be filed using Aadhaar Number.
- PAN allotted to a person shall be deemed to be invalid, if he failed to intimate the Aadhaar to the Dept.
- In case of failure to file an Income-tax return, the prosecution proceedings are initiated under Section 276CC if the tax payable by the assessee is Rs. 3,000 or more. This threshold limit has been increased to Rs. 10,000.
Budget (Applicable from FY 2019-20)
Section 80EEA – Interest on housing loan: Deduction @ 1.5 Lacs w.e.f. AY 20-21
- Housing loan must be taken from a financial institution or a housing finance company for buying a residential house property.
- Stamp duty value of the house property should be Rs 45 lakhs or less.
- The individual taxpayer should not be eligible to claim deduction under the existing Section 80EE.
- The taxpayer should be a first-time home buyer.
- The residential loan should have been sanctioned between the period 1stApril 2019 to 31st March 2021.
Section 80EEA
Conditions with respect to the carpet area of the house property. These conditions have been specified in the memorandum to the finance bill, but not mentioned in section 80EEA:
- Carpet area of the house property should not exceed 60 square meter ( 645 sq ft) in metropolitan cities of Bengaluru, Chennai, Delhi National Capital Region (limited to Delhi, Noida, Greater Noida, Ghaziabad, Gurgaon, Faridabad), Hyderabad, Kolkata and Mumbai (whole of Mumbai Metropolitan Region)
- Carpet area should not exceed 90 square meter (968 sq ft) in any other cities or towns.
Section 80EEB: Deduction in respect of interest paid on loan taken for the purchase of electric vehicle @ Rs 1.5 Lacs
- The loan must be taken from a financial institution or a non-banking financial company for buying an electric vehicle.
- The loan must be sanctioned anytime during the period starting from 1 April 2019 till 31 March 2023.
List of Deductions under Chapter VIA
List of Deductions under Chapter VIA
Wealth Management
- Age 20 – 28
1) Save at least 17% of your annual income or 2 Months salary in SB Account.
2) Establish a positive credit history.
3) Don’t rush to move out from parents house. Create a strong financial base.
4) EMI = SIP or atleast 75% of EMI
5) Buy a life insurance at early age. Low premium for early birds.
6) Invest 75% of SIP in equity.
7) Buy a Mediclaim.
- Age 29 – 50
1) Save at least 25% of your annual income or 3 Months salary in SB Account.
2) Plan for a House at the beginning.
3) Review your credit and current debt load.
4) EMI = SIP or at least 75% of EMI.
5) Buy a life insurance of all dependents of a sum assured based on the financial needs and also buy a pension plan.
6) Invest 65% of SIP in Equity.
7) Try to pay off all consumer durable loans.
8) Buy a Mediclaim for spouse and children.












A very good and informative article.
I AM RETIRED EMPLOYEE GETTING EPS-95 PENSION RS.2712/-P.M. & ANNUITY PENSION FROM LIC RS.3990/- I HAVE NO HOUSE IN MY NAME NOR IN MY WIFE NAME. LIVING IN ANCESTRAL HOUSE(MY PARENTS ARE NOT LIVE). MY QUESTION IS THAT CAN I CLAIM HRA DEDUCTION U/S 80GG UP TO RS.60000/-P.A.(MAXIMUM) FROM TOTAL TAXABLE INCOME. CAN I ALSO GET STANDARD DEDUCTION ON EPS-95 & ANNUITY PENSION RECEIVED FROM LIC TOTALLING RS.80,424/-P.A.(2712-3990=6702*12=RS.80,424-00?
IF NRI FILLING ITR IN RESIDENTIAL STATUS. HIS/HER INCOME IN FROM FIXED DEPOSITS OF BANK, POST OFFICE MIS SCHEMES JOINTLY WITH HIS MOTHER WHO IS RESIDENT STATUS AS 2 ND JOINT HOLDER OF THESE FIXED DEPOSIT & POST OFFICE MONTHLY INCOME SCHEMES ARE BELOW RS. EIGHTY thousand ONLY
AS THERE WAS CASH WITHDRAWAL LIMIT IMPOSED BY GOVT. ON SAVING A/C, MY QUESTION IS THAT IF SOMEONE HOLD JOINT A/C i.e. A+B+C NAMES. THEN THERE WITHDRAWAL INCOME INCREASE AS PER GOVT. LIMIT ON CASH WITHDRAWAL.