Agenda
1. Journey so far
2. Design of GST
3. Main features of GST Law
4. Administration and IT Network
5. Benefits of GST and Way Forward
The Journey so far
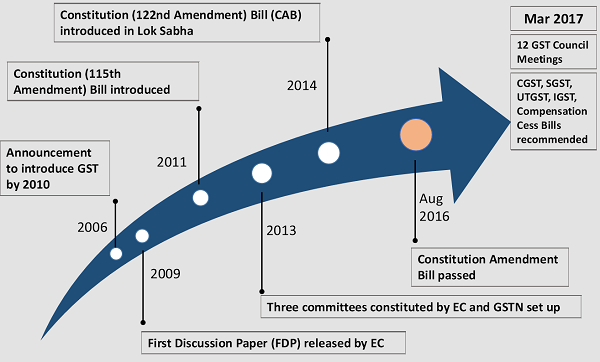
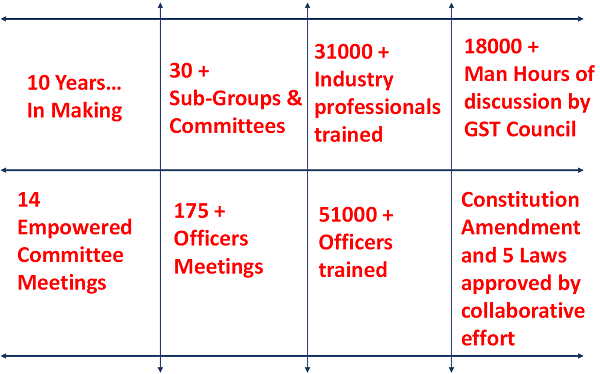
The Effort and Work Done
Existing Indirect Tax Structure in India
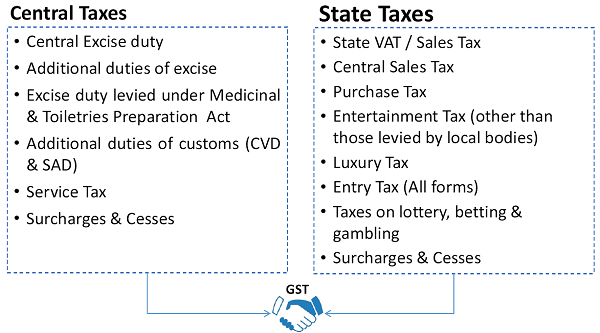
Constitution amended to provide concurrent powers to both Centre & States to levy GST (Centre to tax sale of goods and States to tax provision of services)
Understanding CGST, SGST, UTGST & IGST
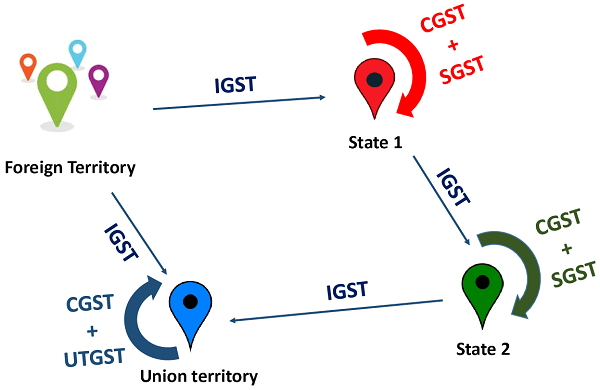
IGST Credit can be used for payment of IGST, CGST, SGST / UTGST in that order
Features of Constitution Amendment Act
♦ Concurrent jurisdiction for levy & collection of GST by the Centre (CGST) and the States (SGST)
♦ Centre to levy and collect IGST on supplies in the course of inter-State trade or commerce including imports
♦ Compensation for loss of revenue to States for five years
♦ GST on petroleum crude, high speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly known as petrol), natural gas & aviation turbine fuel to be levied from a later date on recommendations of Council
GST Council – Constitution
♦ Consists of Finance Minister, the MOS (Finance) and the Minister of Finance / Taxation of each State
♦ Chairperson –Union FM
♦ Vice Chairperson – to be chosen amongst the Ministers of State Government
♦ Quorum is 50% of total members
♦ Decision by 75% majority
♦ Council to make recommendations on everything related to GST including laws, rules and rates etc.
GST Council – Decisions
◊ Threshold limit for exemption to be Rs. 20 lac (Rs. 10 lac for special category States)
◊ Compounding threshold limit to be Rs. 50 lac –not available to inter-State suppliers, service providers (except restaurant service) & specified category of manufacturers
◊ Government may convert existing Area based exemption schemes into reimbursement based scheme
◊ Four tax rates namely 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%
◊ Some goods and services would be exempt
◊ Separate tax rate for precious metals
◊ Cess over the peak rate of 28% on specified luxury and sin goods
◊ To ensure single interface –all administrative control over
♦ 90% of taxpayers having turnover below Rs. 1.5 cr would vest with State tax administration
♦ 10% of taxpayers having turnover below of Rs. 1.5 cr. would vest with Central tax administration
♦ taxpayers having turnover above Rs. 1.5 cr. would be divided equally between Central and State tax administration
Compensation Mechanism for States
Compensation = (State’s Revenue for FY 2015-16)* 14% x -State’s Revenue (for x year)
♦ Revenue of all taxes subsumed in GST by the State for 2015 –16 as the base
♦ Assumption of 14% Annual Growth Rate
♦ Compensation to be provided through Cess
♦ Cess only on few specified luxury and sin goods
Main Features of the GST Act
◊ GST to be levied on supply of goods or services
◊ All transactions and processes only through electronic mode –Non-intrusive administration
◊ PAN Based Registration
◊ Registration only if turnover more than Rs. 20 lac
◊ Option of Voluntary Registration
◊ Deemed Registration in three days
◊ Input Tax Credit available on taxes paid on all procurements (except few specified items)
◊ Credit available to recipient only if invoice is matched –Helps fight huge evasion of taxes
◊ Set of auto-populated Monthly returns and Annual Return
◊ Composition taxpayers to file Quarterly returns
◊ Automatic generation of returns
◊ GST Practitioners for assisting filing of returns
◊ GSTN and GST Suvidha Providers (GSPs) to provide technology based assistance
◊ Separate electronic ledgers for cash and credit
◊ Tax can be deposited by internet banking, NEFT / RTGS, Debit/ credit card and over the counter
◊ Cross utilization of IGST Credit first as IGST and then as CGST or SGST /UTGST
◊ Concept of TDS for Government Departments
◊ Concept of TCS for E-Commerce Companies
◊ Refund to be granted within 60 days
◊ Provisional release of 90% refund to exporters within 7 days
◊ Interest payable if refund not sanctioned in time
◊ Refund to be directly credited to bank accounts
◊ Comprehensive transitional provisions for smooth transition of existing tax payers to GST regime
◊ Special procedures for job work
◊ System of GST Compliance Rating
◊ Anti-Profiteering provision
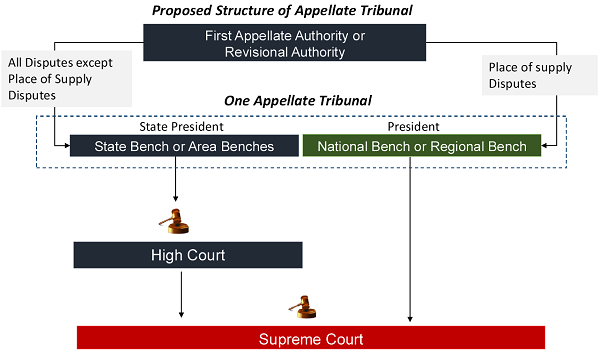
Appeals and Revision under GST
GST Network (GSTN)
◊ A section 25 private limited company with Strategic Control with the Government
◊ To function as a Common Pass-through portal for taxpayers-
♦ submit registration application
♦ file returns
♦ make tax payments
◊ To develop back end modules for 25 States (MODEL –II)
◊ Infosys appointed as Managed Service Provider (MSP)
◊ 34 GST Suvidha Providers (GSPs) appointed
Role of CBEC
◊ Role in Policy making: Drafting of GST Law, Rules & Procedures –CGST, UTGST & IGST Law
◊ Assessment, Audit, Anti-evasion & enforcement under CGST & IGST Law
◊ Levy & collection of Central Excise duty on products outside GST –Petroleum Products & Tobacco
◊ Levy & collection of Customs duties
◊ Developing linkages of CBEC – GST System with GSTN
◊ Training of officials of both Centre & States
◊ Outreach programs for Trade and Industry
Benefits of GST
1. Overall reduction in Prices for Consumers
2. Reduction in Multiplicity of Taxes, Cascading and Double Taxation
3. Uniform Rate of Tax and Common National Market
4. Broader Tax Base and decrease in “Black”transactions
5. Free Flow of Goods and Services –No Checkpoints
6. Non-Intrusive Electronic Tax Compliance System
Way Forward
◊ Passage of CGST, UTGST, IGST & Compensation Law by Parliament and passing of SGST laws by State Legislatures
◊ GST Council to fit tax rates to various categories of Goods or Services
◊ Rules relating to registration, returns, valuation, transitional, Input Credit etc. to be finalized
◊ Migration and handholding of existing tax payers
◊ Outreach program for trade and industry
◊ Change Management





Good Artcile has given idea of GST and its present status.