CA Ankit Agarwal
(CA, CS, IFRS (ICAI), DISA (ICAI))

Overview of GST
The introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) would be a very significant step in the field of indirect tax reforms in India. By amalgamating a large number of Central and State taxes into a single tax, it would mitigate cascading or double taxation in a major way and pave the way for a common national market. Introduction of GST would also make Indian products competitive in the domestic and international markets.
Salient Features of GST:
i. GST would be applicable on “supply” of goods or services as against the present concept of tax on the manufacture of goods or on sale of goods or on provision of
ii. GST would be based on the principle of destination based consumption taxation as against the present principle of origin based taxation
iii. It would be a dual GST with the Center and the States simultaneously levying it on a common base. The GST to be levied by the Center would be called Central GST (CGST) and that to be levied by the States [including Union territories with legislature] would be called State GST (SGST). Union territories without legislature would levy Union territory GST (UTGST)
iv. An Integrated GST (IGST) would be levied on inter-State supply (including stock transfers) of goods or services. This would be collected by the Center so that the credit chain is not disrupted
v. Import of goods would be treated as inter-State supplies and would be subject to IGST in addition to the applicable customs duties
vi. Import of services would be treated as inter-State supplies and would be subject to IGST
vii. GST would replace the following taxes currently levied and collected by the Center:
a. Central Excise Duty
b. Duties of Excise (Medicinal and Toilet Preparations)
c. Additional Duties of Excise (Goods of Special Importance)
d. Additional Duties of Excise (Textiles and Textile Products)
e. Additional Duties of Customs (commonly known as CVD)
f. Special Additional Duty of Customs (SAD)
g. Service Tax
h. Cesses and surcharges insofar as they relate to supply of goods or services
viii. GST would replace the following taxes currently levied and collected by the State:
a. State VAT;
b. Central Sales Tax;
c. Purchase Tax;
d. Luxury Tax;
e. Entry Tax (All forms);
f. Entertainment Tax (except those levied by the local bodies);
g. Taxes on advertisements;
h. Taxes on lotteries, betting and gambling;
i. State cesses and surcharges insofar as they relate to supply of goods or services
ix. GST would apply to all goods and services except Alcohol for human consumption
x. GST on five specified petroleum products (Crude, Petrol, Diesel, ATF & Natural gas) would be applicable from a date to be recommended by the GSTC
xi. Tobacco and tobacco products would be subject to GST. In addition, the Center would continue to levy Central Excise duty
xi. A common threshold exemption would apply to both CGST and SGST. Taxpayers with an annual turnover of ₹ 20 lakh (Rs. 10 lakh for special category States as specified in article 279A of the Constitution) would be exempt from GST. A compounding option (i.e. to pay tax at a flat rate without credits) would be available to small taxpayers (including to specified category of manufacturers and service providers) having an annual turnover of up to ₹ 50 lakh. The threshold exemption and compounding scheme would be optional
xiii. Exports would be zero-rated
xiv. Credit of CGST paid on inputs may be used only for paying CGST on the output and the credit of SGST/UTGST paid on inputs may be used only for paying SGST/UTGST. In other words, the two streams of input tax credit (ITC) cannot be cross utilized, except in specified circumstances of inter-State supplies for payment of IGST. The credit would be permitted to be utilized in the following manner:
a. ITC of CGST allowed for payment of CGST & IGST in that order;
b. ITC of SGST allowed for payment of SGST & IGST in that order;
c. ITC of UTGST allowed for payment of UTGST & IGST in that order;
d. ITC of IGST allowed for payment of IGST, CGST & SGST/UTGST in that order. ITC of CGST cannot be used for payment of SGST/UTGST and vice versa
xv. Various modes of payment of tax available to the taxpayer including internet banking, debit/ credit card and National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) / Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)
xvi. Electronic filing of returns by different class of persons at different cut-off dates
xvii. Obligation on certain persons including government departments, local authorities and government agencies, who are recipients of supply, to deduct tax at the rate of 1% from the payment made or credited to the supplier
xviii. Obligation on electronic commerce operators to collect ‘tax at source’, at such rate not exceeding two per cent. (2%) of net value of taxable supplies, out of payments to suppliers supplying goods or services through their portals
Invoicing under GST
i. Every Registered person supplying Taxable Goods or Services or Both shall issue a Tax Invoice.
ii. Following are the Contents of a Tax Invoice:
a. Name, address and GSTIN of the supplier
b. A consecutive serial number, containing alphabets or numerals or special characters
c. Date of its issue
d. Name, address and GSTIN or UIN, of the recipient; (if registered)
e. Name, address, of the recipient and the Address of Delivery, along with name of the State and its code (if Un-Registered) and where Value >= Rs. 50,000
f. HSN Code of goods or Service Accounting Code for services
g. Description of goods or services or both
h. Quantity of goods or services or both
i. Value of supply of goods or services or both
j. Rate of GST
k. Amount of GST charged
l. Place of supply along with the Name of the State
m. Address of Delivery
n. Whether tax payable on Reverse Charge basis
o. Signature or digital signature of the supplier
HOW AND WHERE TO ISSUE THE INVOICE?
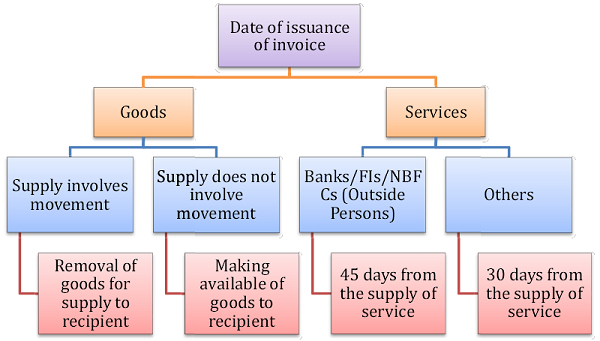
i. Every Registered Person has to Issue Tax Invoice before or at the Time of Removal of Goods for supply (when supply involves movement of goods)
ii. Every Registered Person has to Issue Tax Invoice before or at the Time of Delivery of Goods / making available to the Recipient (Other Cases)
iii. In case of Services, Tax Invoice has to be Issued before or after provision of services but within 30 days from the Date of Supply of Services.
iv. In case of Services, the aforementioned period will be 45 days where the Supplier of Services is an Insurer or a Banking Company or a Financial Institution, including NBFC.
v. For Small Dealers,
a. If the Amount of Invoice is less than Rs. 200 then no need to issue the invoice.
b. He should prepare an Invoice of Aggregate amount of the supply of goods below Rs. 200 in one day.
c. If the amount of Invoice exceeds Rs. 200 it mandatory to prepare ‘Tax Invoice.’
d. If invoice amount is more than Rs. 50,000 and if the receiver is Unregistered, then it is mandatory to mention the Name, Address, State of the Receiver on the Invoice.
vi. Further, if the taxpayer purchases from unregistered person then also Tax invoice is required to be issued to him.
vii. The Supplier of Goods, has to prepare three copies of invoice. One for purchaser, second for transporter and third for self.
viii. Similarly, person supplying services have to make two copies of invoice. One for service receiver and second for self.
ix. In case of Export of Goods or Services, the Invoice shall carry an Endorsement “Supply meant for Export on Payment of IGST” OR “Supply meant for Export Under Bond or Letter of Undertaking”
BILL OF SUPPLY
i. Bill of Supply is to be issued in 2 circumstances, by a Registered Person:
a. If he is supplying Exempted Goods or Services or Both
b. If he is Registered U/s 10
ii. Following are the Contents of a Bill of Supply
a. All the information except GST rate and GST amount as mentioned in Tax invoice is required to be given in it.
RECEIPT VOUCHER
i. Receipt Voucher is to be issued by a Registered Person, on receipt of Advance Payment, with respect to any supply of goods or services or both
ii. Appropriate tax to be charged i.e. SGST / UTGST / CGST / IGST as applicable
iii. Post receipt of Advance, if no supply is made and no tax invoice is issued, a refund voucher is to be issued by the Registered Person
PAYMENT VOUCHER
i. Section 9 sub-section (3) / (4) of the CGST Act, speaks with regard to supply of taxable goods / services or both, by an Un-Registered Supplier to a Registered Person
ii. In such a case, the Registered Person is liable to pay the tax on a reverse charge basis, and all the provisions of this Act shall apply to the Registered person as If he is the person liable for paying the tax in relation to supply of goods or services or both
iii. In such a case, the Registered Person shall issue a Payment Voucher at the time of making the Payment to the Un-Registered Supplier
CONTINUOUS SUPPLY OF GOODS
i. It Involves Successive Statements of Accounts or Successive Payments
ii. Invoice to be issued before or at the time each such Statement is issued or as the case may be, each such Payment is received
CONTINUOUS SUPPLY OF SERVICES
i. Where the due date of payment is ascertainable from the Contract, the Invoice shall be issued on or before the due date of payment
ii. Where the due date of payment is not ascertainable from the Contract, the Invoice shall be issued before or at the time when the supplier of service receives the payment
iii. Where the payment is linked to the Completion of the event, the Invoice shall be issued on or before the date of completion of that event
CESSATION OF SUPPLY OF SERVICES
i. In case, where the Supply of Service ceases under a Contract before the Completion of the Supply, the Invoice shall be issued at the time when the Supply ceases and such Invoice shall be issued to the extent of the Supply made before such cessation
REVISED TAX INVOICE
As per Section 25, every person who is liable to get Registered shall apply for Registration within 30 days from the date on which he becomes liable to registration
AND
As per Rule 2 of the Registration Rules, the Registration shall be effective from the date on which the person becomes liable to registration where the Application for Registration has been submitted within 30 days from such date
AND
As per Rule 6(2) of the Invoice Rules, every Registered person who has been granted Registration with effect from a date earlier than the date of issuance of Certificate of Registration to him, may issue REVISED TAX INVOICE in respect of taxable supplies effected during the period starting from the effective date of Registration till the date of issuance of Certificate of Registration
Please note:
a. A Registered person may issue a Consolidated Revised Tax Invoice in respect of all taxable supplies made to a recipient who is not Registered
b. In case of Inter-State Supply, where the value of Supply does not exceed Rs. 2,50,000, a Consolidated Revised Tax Invoice may be issued in respect of all Un-Registered recipients located in a State
c. Revised tax invoice to be issued within 1 month of Issuance of Certificate of Registration
d. Revised Tax Invoice shall contain the Serial No and date of corresponding Tax Invoice / Bill of Supply
CREDIT NOTE
i. Where a Tax Invoice has been issued for Supply of any Goods / Services or Both
ii. The Taxable Value / Tax charged in that Tax Invoice is > The Taxable Value / Tax Payable
OR
The Supplies are returned by the Recipient / where the goods / services are found to be deficient
iii. The Registered Supplier may issue a Credit Note to the Recipient
Please note:
a. The Issuer of Credit Note, in relation to supply of Goods or Services or both, shall declare the details of such Credit Note in the return
b. For the month during which such Credit Note has been issued but not later than September following the end of the Financial Year in which such Supply was made
OR
The date of Furnishing of the relevant Annual Return
whichever is EARLIER
c. The Tax Liability shall be adjusted in such manner as may be prescribed
DEBIT NOTE
i. Where a Tax Invoice has been issued for Supply of any Goods / Services or Both
ii. The Taxable Value / Tax charged in that Tax Invoice is < The Taxable Value / Tax Payable
iii. The Registered Supplier shall issue a Debit Note to the Recipient and shall declare the details of such Debit Note in the return for the month during which such Debit Note has been issued and the tax liability shall be adjusted in such manner as may be prescribed
DOCUMENTS IN LIEU OF TAX INVOICE
i. Bill of supply in case of composition / exempt dealers
ii. ISD invoice to be issued by an input service distributor
iii. Statements issued by banks / FIs / NBFCs
iv. Consignment note in case of goods transport agency
v. Tickets in case of transportation of passengers
CIRCUMSTANCES WHEREIN GOODS CAN BE TRANSPORTED UPON ISSUE OF DELIVERY CHALLAN
i. Supply of liquid gas where the quantity at the time of removal is not known
ii. Transportation of goods for job work
iii. Transportation of goods for reasons other than by way of supply
iv. Such other supplies as may be notified by the board
TRANSPORTATION IN SEMI-KNOCKED DOWN OR COMPLETELY KNOCKED DOWN CONDITION
i. Supplier to issue complete Invoice before dispatch of the first consignment
ii. Each consignment to be sent with delivery challan and certified copy of invoice
iii. Original copy of the Invoice to be sent with the last consignment





what is the tax rate for pulses,cereals,atta,maida,sooji & besan in branded and unbranded