
Introduction
A. What is GST ?
GST is a comprehensive Value Added Tax on Goods and Services. It is collected on value added at each stage of sale and purchase in the supply chain without state boundaries. The proposed GST is a destination based indirect tax that will be levied on supply of Goods and Services, which is set to subsume the various indirect taxes currently levied by the Centre and States. These taxes are levied at various stages i.e. manufacture, sale, entry of goods, rendition of services.
B. Why GST ?
India’s messy plethora of indirect taxes, duties, surcharges, and cesses is fraught with the following pitfalls:-
-Multiplicity of taxes – Cascading effect
-Complexities in administration – Multiple points of Taxation
-Lack of uniformity in provisions and rates – Inability of States to levy Service Tax
-Complexity in determining nature of transaction – Goods vs. Services
Taxes subsumed under GST
| Central Taxes | State Taxes |
| -Central Excise Duty | -VAT |
| -Additional Excise Duty | -CST |
| -Excise Duty under Medical and Toilet Preparations | -Entry Tax |
| -Additional duties of excise | -Purchase Tax |
| -Service Tax | -Luxury Tax |
| -Additional Customs Duty (CVD) | -Entertainment |
| -Special Additional Duty of Customs (SAD) | -Taxes on Advertisement |
| -Central surcharges and cesses | -Taxes on lottery, betting and gambling |
Taxes not subsumed under GST
| -Basic Custom Duty | -Electricity and Power |
| -Tax on Petroleum Products
Petroleum Crude High Speed Diesel Motor Spirit Natural Gas Aviation Turbine Fuel |
-Stamp Duty |
| -Alcohol for human consumption |
The term GST is defined in Article 366 (12A) to mean “ any tax on supply of goods or services or both except taxes on supply of the alcoholic liquor for human consumption.”
Let us understand the concept of supply
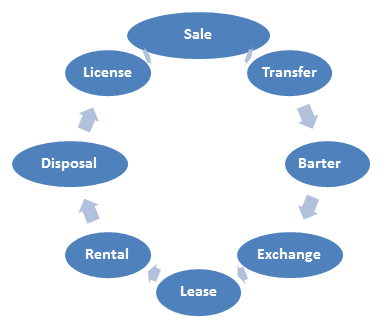
Supply includes the above eight transactions subject to the below mentioned conditions :
– Consideration ( Except entries in Schedule I)
– By a person,
– In the course or furtherance of business,
The concept of Transfer of Goods against “F” forms is now abolished and every transfer will be treated as independent transaction and chargeable under the new regime.
Barter – Means exchange (goods or services) for other goods or services without using money. Barters are also taxable under GST for ex. Mr. A (manufacturer of invertors) has exchanged his Invertor with Mr. B (dealer in Microwaves) for his Microwave. Here, the transactions shall be taxable in the hands of both the persons.
Similar shall be the treatment in case of exchange transactions.
Tax on Reverse Charge basis by the recipient: Government has notified supply of goods or services or both, on recommendation of GST council.
Purchase from unregistered person: The tax in respect of supply of taxable goods or services r both by a supplier, who is not registered, to a registered person shall be paid by such person on reverse charge basis as the recipient.
Composition Levy: Any registered person whose Turnover did not exceed Rs. Fifty Lakhs in the preceding Financial Year, may opt for composition scheme and may pay tax at the rate of 2% (1% CGST+ 1% SGST) in the case of manufacturer, 5% (2.5% CGST + 2.5% SGST) in case of Restaurant services and 1% (0.5% CGST+ 0.5% SGST) in case of other supplies.
Following persons are not allowed to opt for composition scheme:-
1. Supply of services other than restaurant
2. Supply of non-taxable goods
3. Inter-state outward supply
4. Supply of goods through e-commerce operator
Where more than one registered persons are having the same PAN number, registered person shall not be eligible to opt for composition scheme unless all the registered persons opt for scheme.
A taxable person under composition scheme shall not collect any tax from the recipient on the supplies made by him, nor shall he be entitled to take credit of any input tax.
Input Tax Credit
- ITC allowed on almost all items (except goods and services such as motor vehicle related services, catering services, employee insurance, construction of civil structure)
- 100% ITC on capital goods in 1st year itself
- ITC on Inter-state purchases allowed
- No ITC on personal consumption of goods or services
- Conditions for taking ITC: Tax invoice, receipt of goods or services, payment of tax and filing of return
- If ITC claim missed on any invoice or debit note, allowed to claim it by the end of September in the following year.
- Adjustment of taxes:
| Tax | Priority of Adjustment | ||
| First | Second | Third | |
| CGST | CGST | IGST | – |
| SGST | SGST | IGST | – |
| IGST | IGST | CGST | SGST |
- CGST not adjustable with SGST and vice-versa
- There are certain special cases in which ITC shall be provided such as:

- There are certain special cases in which ITC shall be reversed such as:

- Input Tax Credit shall be allowed for inputs or capital goods sent to job worker if:
– Such inputs are received back / sold from job worker’s premises within 1 year;
– Such capital goods are received back / sold from job worker’s premises within 3 years (except moulds, dies, jigs, fixtures which are deemed to be consumed);
– Otherwise, the tax credit claimed has to be paid in cash along with interest from the day of sending out the goods.
- Input Service Distributor is authorised to distribute input tax credit of services availed on behalf of its branches which may be located all over India.
– Distribution through a document and maximum upto credit available for distribution.
– Distribute ITC for specific services to specific entities
– If common service, then as per ratio of turnover of all entities.
– If distributed wrongly or in excess, then such excess shall be recovered along with interest.
- Branch transfers taxable; credit available to branches; no cascading
- Import of goods: IGST applicable in place of CVD and SAD; full credit available
- Import of services: IGST to be paid on reverse charge basis; full credit available
- Export of goods or services: To be treated as Zero-rated; full credit of inputs allowed to be adjusted; if not, refund can be claimed
Taxable Person: Taxable Person means a person who is registered or liable to be registered.It will cover all types of person carrying on business activities i.e. manufacturer, job worker, trader,exporter, all types of service providers.
Threshold: INR 20Lakhs
INR 10Lakhs in the case of special category states
No registration for following persons:-
> Any person engaged exclusively in either non taxable or wholly exempt supply
> An agriculturist
Compulsory registration for certain category of persons:-
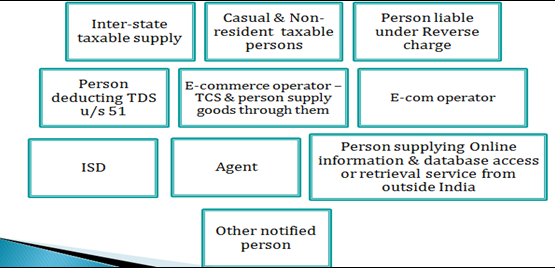
Every supplier shall be liable to be registered in the state from where he makes a taxable supply

Example: A manufacturer has two factories in Gujarat and sale office in 5 states (including Gujarat). It also has centralized service tax registration at Gujarat. What would be difference in registration requirements under GST?
Total Present Registration: 2 (excise) + 5 (VAT) + 1 (Service Tax) = 8
Registration under GST: 5 (5 -In each state)
Time limit for applying for Registration
| Application to be made by | Within-Time limit |
| Taxable person | Within 30 days of becoming liable |
| Casual Taxable person | 5 Days ahead |
| Non-Resident Taxable person | 5 Days ahead |
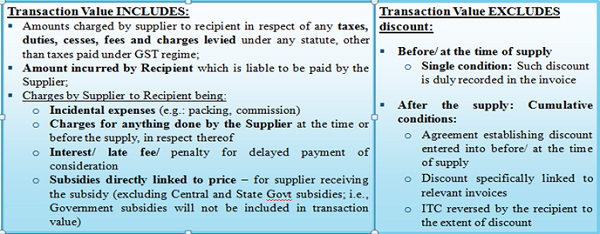
Value of Taxable Supply: The value of supply shall be the transaction value, which is price actually paid or payable for the said supply of goods or services where the supplier and the recipient are not related and price is the sole consideration. In case, the conditions are not fulfilled, the value shall be the open market value.
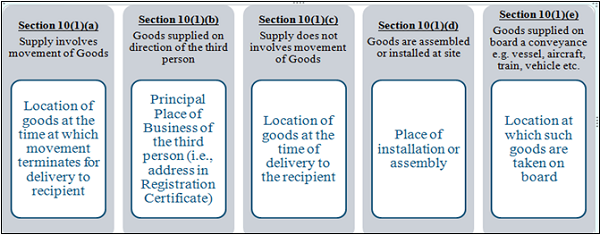
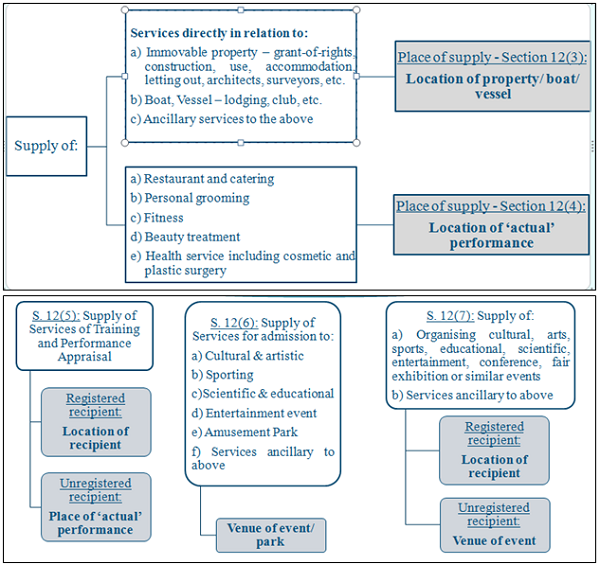
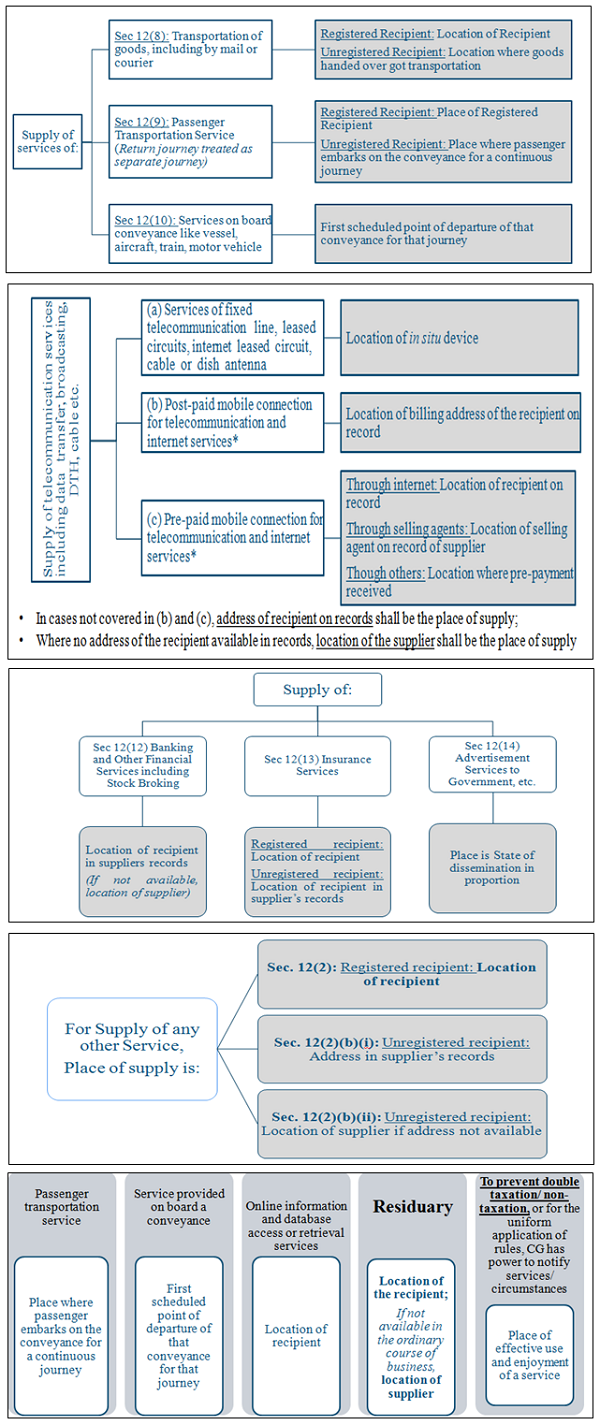
Concept of Place of Supply
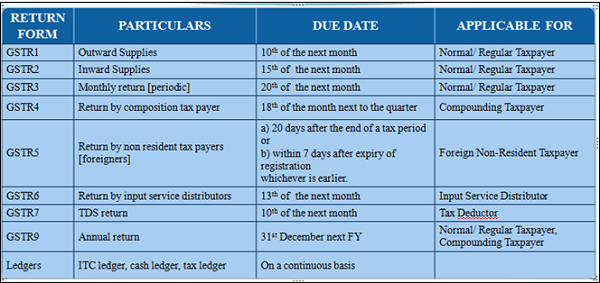
Returns under GST
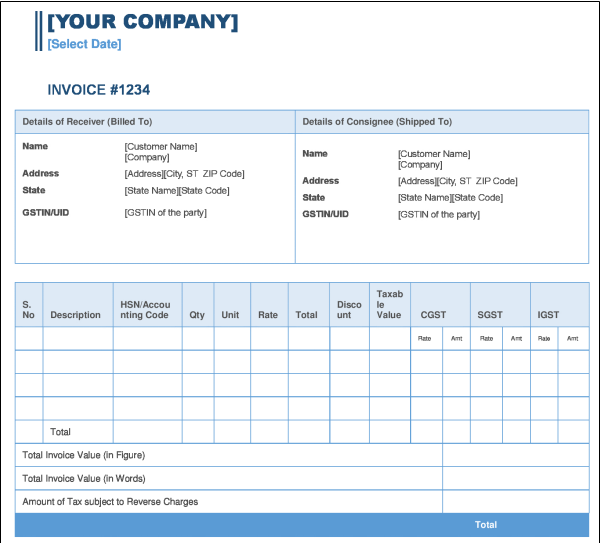
Tax Invoice
Below is the Performa of a Tax Invoice under GST
Transitional Provisions
- All registered persons having valid PAN to be automatically migrated
- Credits carried forward in return to be allowed as ITC in GST. So last return before GST is very important
- Unavailed Cenvat Credit on Capital goods allowed in GST in single shot.
- For manufacturers, traders, first stage dealers, second stage dealers, those not registered earlier, claiming exemption, providing works contract service or claiming abatement shall be entitled to avail credit on closing stock if tax paying documents are available. If not, Transitional Rules prescribe that 40% credit can be taken in case of supply of such goods within 6 months, subject to certain conditions.
- For goods in transit as on appointed day, ITC to be allowed if they are recorded within 30 days and declared in prescribed statement next month.
- Credit on closing stock to be allowed to composition dealer moving to regular scheme.
- Any person having Centralised Registration is allowed to transfer credits carried forward to GST to any branch having the same PAN.
- If any credit has been reversed due to non-payment of consideration under the existing law, such credit can be reclaimed if the payment of consideration is made within 3 months of the appointed day.
- Where any duty paid goods sent 6 months prior to the appointed day are returned within 6 months of appointed day by:
– an unregistered person : Supplier can claim refund
– a registered person : Deemed to be independent supply
- If goods sent to job-worker are received within 6 months of the appointed day (2 months extension allowed), no tax to be paid. If not, ITC to be reversed. [Similar for goods on approval]
- For price revision upward or downward, Supplementary invoice to be issued within 30 days of such revision. For downward, reversal of ITC required from recipient’s side.
- Any refund arising in earlier law to be received in cash.(not hard currency)
- Any demand arising from earlier law to be paid under earlier law; if not, then to be paid under GST as an arrear of tax.
- Previous contracts continuing in GST shall attract GST if tax has not been paid in earlier regime
- TDS/TCS not required to be deducted if already deducted under earlier law.
♦ Impact on Traders
(a) Tax on value addition: The impact of tax on the wholesaler or retailer would be limited to the value addition. The tax paid at earlier stages (except CGST & SGST of other States) would be available as set off for payment of GST on supplies. Therefore, traders would prefer to buy/receive supplies with invoice pre-and post GST.
(b) Reduce cascading: Cost of products and services would reduce normally due to the cascading effect of tax being reduced. Service tax credits would be available and going forward even the capital goods used for storing, handling etc.
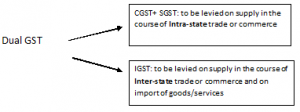
(c) SGST levy: CGST and SGST would be levied on the local supply of goods within State. IGST (comprising of CGST and SGST) would be levied on inter-State supply of goods. Bird Eye View of GST Law A-20
(d) No subsequent sale or sale in transit under the CST Act against Forms E-1/2: This exemption as per section 6(2) of the CST Act is not continued under GST levy. GST would be charged on both transactions.
(e) Export supplies Under Form H Supplies to SEZ under Form” I”: Not available.
(f) Stock transfers: Presently, stock transfer is done without charging CST against Form F. Under GST law, stock transfers from one State to other would be liable to GST.
(g) Stock transfers to branches/consignment agents within the State: Under GST, these transfers would not be taxed as the registration number of transferor and transferee is same. Where the division/ branch or agent has a different registration CGST & SGST would be charged.
(h) Small Traders: They would be eligible for the composition scheme upto Rs 50 lakhs provided their aggregate turnover in the preceding financial year did not exceed Rs. 50 lakh. After that, normal rate will apply. The essential conditions to be complied for availing the benefit of the aforesaid Composition Scheme are as under:
(i) No credit to dealer/ customer;
(ii) No inter-state supply of goods. Only suitable for Business to Consumer transactions





what will happen when an unregistered dealer sold
taxable goods to another unregisterd dealer within the same state