The Invoicing system in GST is defined for major overhaul in the coming financial year. This includes E-invoicing, Quick-Response Code and facility of digital payments to recipients. It is important for organizations to understand the same as all the above would not only require customization in their accounting/ ERP software but also require modification in the process of generation of invoice. This also has a direct implication on Availment of ITC, generation of E-way bill and filing of GST returns.
Page Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Why E-invoice?
- 3. Advantages of E-invoice
- 4. Types of Documents for which E-Invoicing is required
- 5. Glossary of terms
- 6. What is E-invoicing?
- 7. Legal Premise
- 8. Generation of Tax Invoice in standard format
- 9. Reporting of details of Invoice to a central system
- 10. Process for generation of E-invoice
- 11. Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
- 12. Other silent Features of E-invoice
- 13. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Introduction
The Invoicing system in GST is defined for major overhaul in the coming financial year. This includes E-invoicing, Quick-Response Code and facility of digital payments to recipients. It is important for organizations to understand the same as all the above would not only require customization in their accounting/ ERP software but also require modification in the process of generation of invoice. This also has a direct implication on Availment of ITC, generation of E-way bill and filing of GST returns.
2. Why E-invoice?
In the absence of any standard in invoicing, this is how current invoicing looks like
- Is your e-invoice taken into buyer’s billing/accounting system directly?
- If not, how is the data entered?
Manual data entry leads to following:
- Transcription Errors
- Wrong Entries
↓
- Need for standards to ensure complete inter-operability
- Elimination of need of manual data entry and transcription errors.
3. Advantages of E-invoice
4. Types of Documents for which E-Invoicing is required
E- Invoicing is required for below mentioned documents
- Invoices
- Debit Note
- Credit Note
For other Documents there is no requirement to generate E-Invoice
- Delivery Challan
- Bill of Supply
- Job works
5. Glossary of terms
E-Invoice: An electronic format of an Invoice that is prepared as per prescribed schema and registered with the Government-approved IRP.
Invoice Registration/Reference Portal (IRP): Website notified by the Government to receive and validate e-Invoices and issue Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and digital signature.
Invoice Reference Number (IRN): A unique number to identify an invoice. It is a 64 digital alphanumeric string that encodes the Supplier’s GSTIN, Financial Year, Document Type, and Invoice Number.
E-Invoice Quick Response Code (QR Code): A QR code that provides key invoice parameters such as supplier, recipient, invoice number, invoice total, HSN code of the predominant line item.
E-Invoice digital signature: The contents of the e-Invoice digitally signed by the government-approved IRP to indicate that an invoice is valid and has been received by the Government Portal. The taxpayer can use this as an acknowledgement.
6. What is E-invoicing?
- E-Invoicing or electronic invoicing is a process of validating invoices electronically through GST Network (GSTN) for further use on common GST portal.
- It does not mean generation of invoices from a central portal of tax department.
- E-invoicing’ or ‘Electronic Invoicing is a system in which B2B invoices are authenticated electronically by GSTN for further use on the common GST portal.
Under electronic invoicing system, an invoice reference number (IRN) will be issued against every invoice by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) to be managed by the GST Network (GSTN).
Technology aspects:
- It is important to note that Government shall not provide platform to punch in the details of invoices in order to generate an E-Invoice.
- Taxpayer will have to use some technology solution (third party E-Invoice software) to prepare the E-Invoice at their end and submit it to the IRP.
7. Legal Premise
Central Board of Indirect Tax and Custom (CBIC) has issued various notifications for implementation of E-invoicing which are given below:
| Notification No. | Date of Notification | Purpose of Notification |
| 68/2019 (Central Tax) | 13/12/2019 | Incorporation of E-invoicing for prescribed person through amendment in Rule 48 (Invoicing Rule) |
| 69/2019 (Central Tax) | 13/12/2019 | Set up of Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) |
| 70/2019 (Central Tax) | 13/12/2019 | Aggregate Turnover limit for E-invoicing (i.e. > 100 crores). |
| 71/2019 (Central Tax) | 13/12/2019 | E-invoicing effective from 1st April, 2020 |
| 72/2019 (Central Tax) | 13/12/2019 | Mandatory QR Code for B2C supply if aggregate turnover > 500. crore. |
| 02/2020 (Central Tax) | 01/01/2020 | E-invoice Schema i.e. mandatory or optional fields in invoice. |
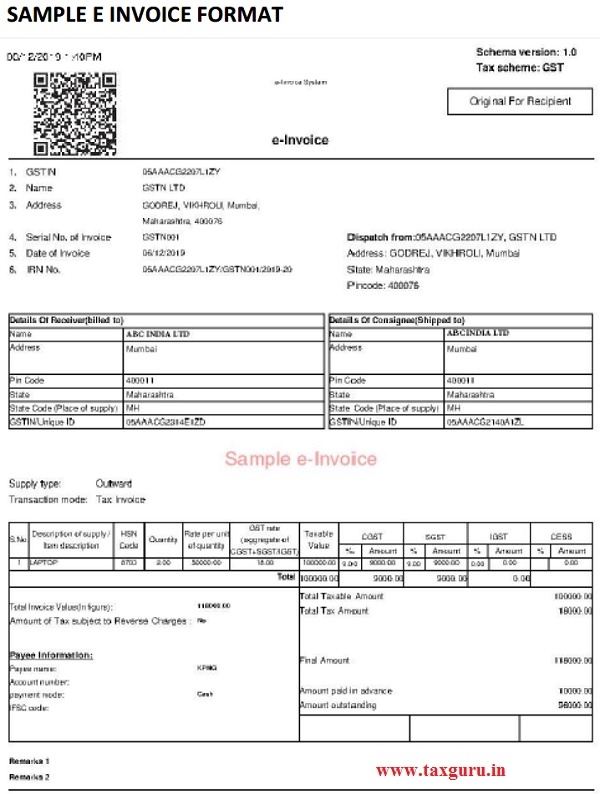
8. Generation of Tax Invoice in standard format
The most important requirement for generation of the E-invoice is that tax invoice must have certain mandatory parameters (fields) and must confirm to the e-invoice standard (schema) published in GST common portal. (https://www.gstn.org/e-invoice/).
At present billing of taxpayer is done through accounting/billing software, which is not compatible with the data requirement of IRP.
Taxpayer may require to develop accounting/billing software in such a way that the software itself fetched mandatory field* required for generation of e-invoice and generate JSON file which shall be used to upload it on the third party E-Invoice software (IRP) which shall ultimately be used to generate the IRN and QR Codes to make the invoice a legal document.
9. Reporting of details of Invoice to a central system
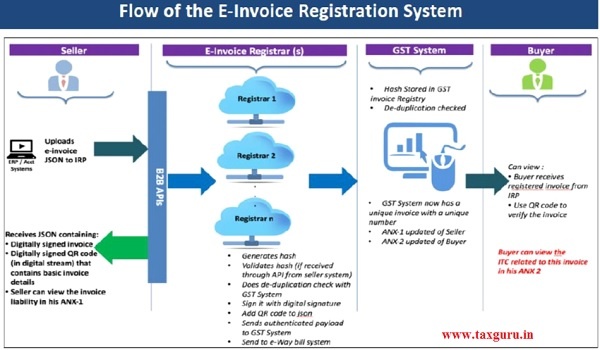
IRP of GST will verify from Central Registry of GST system to ensure that same invoice is not being uploaded again by taxpayer for the same financial year.
On receipt of confirmation, it will generate a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and digitally sign the invoice and also generate a QR Code. Portal shall return the same to taxpayer who has created the document. The IRP shall also send the signed E-invoice to the recipient of the invoice.
E-invoice Data will be used by GST system for generation of E Way Bill (Part 1) and updating ANX-1 of the seller and ANX-2 of the buyer automatically.
The QR code will contain mandatory parameters of the Invoice i.e. GSTIN of seller and buyer, Invoice Number, Invoice Date, Number of line items, HSN of major commodities.
10. Process for generation of E-invoice
Step: 1– Taxpayer shall have to re-configure their billing software. Taxpayer shall have to coordinate with the Software Service Provider to incorporate the standard set for E-Invoicing, i.e. E-Invoice schema (standards) and must have the mandatory parameters required for e-Invoicing. It should be capable of generating the JSON file for invoices.
Step: 2– Taxpayer must thereafter raise a normal Tax Invoice on that software. It must provide all the mandatory fields such as vendor name and address, GSTN of the supplier, transaction value, Item rate, GST rate applicable, and Tax amount.
Step: 3– Visit the Portal through the link www.einvoice1.gst.gov.in and upload the details of invoice raised in step: 2 especially mandatory fields into the invoice reference portal (IRP) using the JSON file only.
Step: 4 – IRP shall validate the key details of the B2B invoice, checks for any duplications and generates an Invoice Reference Number for reference. The Format of IRN will be Seller GSTIN, Invoice number, and FY in YYYY-MM). IRP generates the IRN, digitally signs the invoice and creates a QR code in Output JSON for the supplier. On the other hand, the recipient of the supply will also get intimated of the e-invoice generation through E-mail (if provided in the invoice).
11. Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
- User can upload invoice details
- Unique number (IRN) is generated for e-invoice.
- IRN is a HASH of (<Supplier GSTIN><Fin. Year><Doc Type> <Doc Number>)
- HASH is generated using SHA256
- Example :
–HASH of “01AAAAB1234C1Z02019-20INVAB1234” is 35054cc24d97033afc24f49ec4444dbab81f542c555f9d30359dc75794e06bbe
Note: Document number will be trimmed if prefixed with 0 / -, while generating HASH
– 00234 → 234 ; /A234 → A234 ; -0123/19 → 123/19
12. Other silent Features of E-invoice
Company LOGO on E-Invoice: The Logo will not be sent to IRP. It will not be part of JSON file to be uploaded on the IRP. However, Taxpayer can provide LOGO in the billing/accounting software.
Printing of QR Code on invoice: The QR code will be provided to the seller once it uploads the invoice into the Invoice Registration system and the same is registered there. Taxpayer can at his option may print the same on the Invoice.
QR Code on B2C Invoice: is mandatory for taxpayer, whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds five hundred crore rupees (>500 Crores) w.e.f. 1st April, 2020 and shall have to mandatorily generate QR Code whenever it enters into B2C transactions.
Validity of invoice without Invoice Reference Number (IRN): Invoice will be valid only if it has a valid IRN.
Printing of E-invoice: It will be possible for both the seller as well as the buyer to print the invoice, using the QR code as well as signed e-invoice returned by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
Cancellation of E Invoices: The E-Invoice mechanism enables invoices to be cancelled. This will have to be reported to IRN within 24 hours. Any cancellation after 24hrs could not be possible on IRN, however one can manually cancel the same on GST portal before filing the returns. E-Invoice can’t be partially cancelled. It has to be fully cancelled.
Amendments to the e-invoice: Amendments are allowed on GST portal as per provisions of GST law. All amendments to the e-invoice will be done on GST portal only.
E invoices for Exports: The e-invoice schema also caters to the export invoices as well.
E-invoice schema for reverse charge mechanism:- E-invoice system has a reverse charge mechanism reporting as well.
13. Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1 Will there be a time limit for E-Invoice uploading for registration?
Ans: a. Yes, that will be notified by the Government. Without registration of e-invoice the same will not be valid. Required changes will be made in the law.
b. Once uploaded to the invoice registration portal (IRP), it will be registered immediately, on real-time basis.
Q.2 Will it be possible to allow invoices that are registered on invoice registration system/portal to be downloaded and/or saved on handheld devices? a. Yes.
Ans: Reason. IRP System after registering the invoice, will share back digitally signed e-invoice for record of supplier. It will also be sent to the email address of recipient provided in the e-invoice.
Q.3 Will it be possible to print the e-invoice?
Ans: Yes.
Reason. It will be possible for both the seller as well as the buyer to print the invoice, using the QR code as well as signed e-invoice returned by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
i. Amendment/Cancellation of e-invoice:
Q.1 Whether e-invoices generated through GST system can be partially/fully cancelled? a. E-Invoice can’t be partially cancelled. It has to be fully cancelled.
Ans: Reason. The e-invoice mechanism enables invoices to be cancelled. This will have to be reported to IRN within 24 hours. Any cancellation after 24hrs could not be possible on IRN, however one can manually cancel the same on GST portal before filing the returns.
Q.5 How would amendments be allowed in e-invoice?
Ans: Amendments to the e-invoice are allowed on GST portal as per provisions of GST law.
All amendments to the e-invoice will be done on GST portal only.
ii. Relationship with e-way bill
Q.1 With the introduction of e-invoices, what are the documents need to be carried during transit of goods?
Ans: For transportation of goods, the e-way bill will continue to be mandatory, based on invoice value guidelines, as hitherto fore. This aspect will be notified by the Government when this mechanism will be notified.
iii. Export/Import
Q.1 Please clarify whether exports would require e-invoice compliance.
Ans: Yes.
Reason. The e-invoice schema also caters to the export invoices as well. The e-invoice schema is based on most common standard, this will help buyer’s system to read the e-invoice.
Q.2 Does the e-invoice allow the declaration of export invoices/ zero rated supplies?
Ans: Yes.
Reason. It allows the declaration of export invoices / zero rated supplies.
iv. Others
Q.1 What will be the workflow of the end to end e-invoice mechanism?
Ans: The end to end workflow will be provided by at the time of rollout of the e-invoice system.
Q.2 Will the industry be provided sufficient time for preparation?
Ans: a. Yes.
b. The e-invoice mechanism is expected to be rolled out in phases from 01st Jan 2020 on voluntary basis.
c. Initially, the e-invoice mechanism will be allowed for tax payers above turnover of 100 Crores
d. Subsequently, it will be enabled for all tax payers in a phased step-wise manner.
v. Generic- questions on e-invoice
Q.1 Will businesses now be required to generate e-invoices on the GST portal or the e-invoice portal or the IRN portal?
Ans: a. No.
b. Businesses will continue to generate e-invoices on their internal systems – whether ERP or their accounting/ billing systems or any other application.
c. The e-invoicing mechanism only specifies the invoice schema and standard so as to be inter-operable amongst all accounting/billing software and all businesses.
Q.2 Please clarify whether the current e-invoice schema is for the invoice to be issued by Govt. or has to be maintained in the IT system by the tax payer?
Ans: a. The invoice schema has to be maintained and invoices generated using this schema.
b. The GST portal or Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) will NOT provide facility to generate invoices. IRP is only to report the invoice data.
c. The ERP or accounting billing software or any other software tool to generate e-invoice of the seller shall only generate invoices.
Q.3 Will there be separate invoice formats required for Traders, Medical Shops, Professionals and Contractors?
Ans: a. No.
b. Same e-invoice schema will be used by all kinds of businesses. The schema has mandatory and non mandatory fields. Mandatory field has to be filled by all taxpayers. Non-mandatory field is for the business to choose. It covers all most all business needs and specific sectors of business may choose to use those non-mandatory field which are needed by them or their eco-system.
Q.4 How long will the e-invoice generated would be available at the Government portal?
Ans: a. It is again clarified that the e-invoice will not be generated at the GST portal.
b. It will be generated only at the seller’s system – whether ERP or the accounting/billing system/other software tools of the seller.
c. It will be uploaded into the GST ANX-1 only once it has been validated and registered by the invoice registration system.
d. After it has been validated and is available in the ANX-1, it will be visible to the counter party in his ANX 2.
e. Thereafter it will be visible and available for the entire financial year and archived.
f. As far as data on IRP is concerned, it will be kept there only for 24 hours.
vi. Contents of e-invoice
Q.1 There are certain fields today which are optional and some mandatory. How are these to be used?
Ans: a. The mandatory fields are those that MUST be there for an invoice to be valid under e-Invoice Standard.
b. The optional ones are those that may be needed for the specific business needs of the seller/business. These have been incorporated in the schema based on current business practices in India.
c. The registration of an e-invoice will only be possible once it has ALL the mandatory fields uploaded into the Invoice registration Portal (IRP).
d. A mandatory field not having any value can be reported with NIL.
Q.2 What is the maximum Number of line items supported by E-Invoice?
Ans: a. The maximum number of line items per e-invoice is 100.
Q.3 Does the e-invoice schema provide the maximum length of the various fields in the schema?
Ans: a. Yes.
b. Each field specification has been provided with the type of characters that are to be entered and its length as well.
Q.4 Will the e-invoice have columns to show invoice currency?
Ans: a. Yes, the seller can display the currency. Default will be INR.
Q.5 Whether the IRN is to be captured in the Supplier’s ERP?
Ans: a. The IRN (hash) will be generated by GST System using GSTIN of supplier or document creator, financial year and the unique serial number of the document/invoice. The IRN can also be generated by the seller.
b. The serial number of invoice will be unique for a GSTIN for a Fin Year and the same has to be captured by Supplier’s ERP.
c. Supplier has to keep the IRN against each of its invoice. It will be advisable to keep the same in the ERP as invoice without IRN will not be a legal document.
Q.6 Whether e-invoice generated is also required to be signed again by the taxpayer?
Ans: a. Not mandatory. However, if a signed e-invoice is sent to IRP, the same will be accepted.
b. The e-invoice will be digitally signed by the IRP after it has been validated. The signed e-invoice along with QR code will be shared with creator of document as well as the recipient.
c. Once it is registered, it will not be required to be signed by anyone else.
Q.7 Whether the facility of adding discount amount at line item-level would be mandatory in nature?
Ans: a. The e-invoice has a provision for capturing discount at line item level.
b. The discounting at line item level is to be mentioned only when and if it is applicable in the particular transaction.
Q.8. Can the seller place their LOGO in the e-Invoice Template?
Ans: a. There will NOT be a place holder provided in the e-invoice schema for the company logo.
b. This is for the software company to provide in the billing/accounting software so that it can be printed on his invoice using his printer. However, the Logo will not be sent to IRP. In other words, it will not be part of JSON file to be uploaded on the IRP.
Q.9 There should be a space provided for the QR code to be placed.
Ans: a. The QR code will be provided to the seller once he uploads the invoice into the Invoice Registration system and the same is registered there.
b. Seller can at his option may print the same on Invoice.
Q.10 Will we be able to provide the address and bill-to party and PAN details in the e-invoice?
Ans: a. Yes.
b. It will be possible to provide all these details in the placeholders provided in the schema.
Q.11 Would the Supplier be allowed to issue his own invoice and if yes, will the Invoice number and IRN be required to be mentioned?
Ans: a. Yes, the supplier will issue his own system’s invoice, in the standard e-invoice schema that has been published. Invoice number is a mandatory item under GST and hence for e-invoice.
b. IRN (Hash) can be provided after the e-invoice has been successfully reported to the IRP. E-Invoice will be valid only if it has IRN.
Q.12 The current e-invoice template provides for total discount for all the products or services. Will this be possible in the e-invoice?
Ans: a. yes
b. There is a mechanism and placeholders to provide discounting on item level as well as total discounts on the invoice value.
Q.13 Will there be an option for linking multiple invoices in case of debit note/ credit note?
Ans: Yes, it will be allowed to link the credit/debit notes as hitherto fore.
Q.14 Will the e-invoice schema cater to reverse charge mechanism?
Ans: a. yes.
b. E-invoice system has a reverse charge mechanism reporting as well.
vii. Method of reporting e-invoice to GST System
Q.1 In addition to the above, we understand that electronic invoice which will be uploaded on GST portal will be authenticated and IRN will be allocated for each e-invoices generated.
Ans: a. Yes, the e-invoice will be authenticated with the digital signature of the IRP (invoice registration portal).
b. IRN (Invoice Reference Number) will be the hash generated by the IRP.
c. The registered invoice will be valid to be used by the business.
Q.2 Will it be possible for bulk uploading of invoices for e-invoicing as well?
Ans: a. Invoices have to be uploaded on IRP one at a time.
b. The IRP will be able to handle a large sequence of invoices for registration and validate them. Essentially bulk upload will be required by large taxpayers who generate large number of invoices. Their ERP or accounting system will have to be designed in such a way that it makes request one by one. For the user, it will not make any difference.
Q.3 Will the requirement for such invoices to be authenticated by the supplier using a digital signature/signature be done away with?
Ans: a. The seller will need to upload the e-invoice into the Invoice Registration Portal.
b. The signing of e-invoice by seller is not mandatory.
| S. No. | Name of the field |
List of Choices/ Specifications/Sample Inputs |
Remarks |
| 1 | Invoice Type | Max length: 10 | Denotation for regular, SEZ supplies with payment, SEZ supplies without payment, deemed exports, sale from the bonded warehouse, export without payment of tax, export with payment of tax. |
| Can be one of the following: Reg./SEZP/SEZWP/EXP/EXPWP/D EXP | |||
| 2 | Invoice Type Code | Max length: 50 | A sub code may also be automatically added by the GSTN. |
| Will be auto-generated by GSTIN based on the invoice type specified by the user. | |||
| 3 | Supplier GSTIN |
Max length: 15 | GSTIN of the supplier raising the e-invoice |
| Must be alphanumeric | |||
| 4 | Invoice Number | Max length: 16 | For unique identification of the invoice, a sequential number. |
| 6 | Invoice Date | DD/MM/YYYY | The date when the invoice was issued. |
| 7 | Reverse Charge |
‘Y’ or ‘N’ as a single character | Mention whether or not the particular supply is subject to reverse charge mechanism. |
| 8 | GSTIN | Max length: 15 | The GSTIN of the buyer to be declared here |
| 9 | State Code | Max length: 2 | The place of supply state code to be declared here |
| 10 | Place | Max length: 50 | The place (locality/district/state) of the buyer on whom the invoice is raised/ billed to must be declared here if any |
| 11 | Pin code | Six digit code | The place (locality/district/state) of the buyer on whom the invoice is raised/ billed to must be declared here if any |
| 12 | Unique Identification Number | A unique number will be generated by GSTN after uploading of the e-invoice on the GSTN portal. An acknowledgement will be sent back to the supplier after the successful acceptance of the e-invoice by the portal. | |
| 13 | Shipping GSTIN |
Max length: 15 | GSTIN of the buyer himself or the person to whom the particular item is being delivered to |
| 14 | Shipping State |
Max length: 100 | State pertaining to the place to which the goods and services invoiced were or are delivered |
| 15 | Supply Type | Max length: 2 | It can be either interstate or intrastate supply. Further, it can be outward or inward supply |
| Sample values can be either of Supply/export/Job work | |||
| 16 | Transaction Mode | Max length: 2 | A combination of a ‘Bill To Ship To’ and ‘Bill From Dispatch From’ is also allowed |
| The schema specifies that the field can have either of regular/bill to/ship to | |||
| 17 | Item Description | Max length: 300 | Simply put, the relevant description generally used for the item in the trade. However, more clarity is needed on how it needs to be described for every two or more items belonging to the same HSN code |
| The sample value is ‘Mobile’ | |||
| The schema document refers to this as the ‘identification scheme identifier of the Item classification identifier’ | |||
| 18 | Quantity | Decimal (13,2) | The number of items (goods or services) that is charged on the invoice as a line item. |
| 19 | Rate | Decimal (10,2) | The unit price, exclusive of GST, before subtracting item price discount, cannot be negative |
| 20 | Assessable Value | Decimal (13,2) | The price of an item, exclusive of GST, after subtracting item price discount. Hence, Gross price (-) Discount = Net price item, if any cash discount is provided at the time of sale. |
| 21 | GST Rate | Decimal (3,2) | The GST rate represented as a percentage that is applicable to the item being invoiced. |
| 22 | IGST Value, CGST Value and SGST Value Separately | Decimal (11,2) | For each individual item, IGST, CGST and SGST amounts have to be specified. |
| 23 | Total Invoice Value | Decimal (11,2) | The total amount of the Invoice with GST. Must be rounded to a maximum of 2 decimals. |
Disclaimer
The above information includes general and legal provision in the GST law. We disclaim that this presentation has been prepared based on notification or rules issued by Government but since these provisions will be effective from 1st April, 2020, any change taking place in between need to be further addressed.
In case of any query relating to E-Invoicing, kindly contact
CA. Manoj Kumar/CA. Manu Katare
(Partners)
Rajesh Raj Gupta & Associates
Chartered Accountants,
412A, Chiranjiv Tower
Nehru Place
New Delhi-110019
Contact No: 011- 49424708/41066053





























How to Cancel B2B invoice in GSTr-1 (from GST portal) which was auto populated through E-Invoice after 24 hrs. we are the more than 500 line items
Dear Sir
Thanks for your article.
For job work charges collected on job whether einvoicing is required
Dear Sir, Greetings.We have two queries : 1- While updating export data on e-invoicing trial portal the profile selection for RCMS is compulsory . 2- if we updated b2b data for domestic invoice the system accepts discount on line item level but does not appear on invoice printed through portal. Kindly help : regards Manjeet Singh
Thank You so much to the writer.
Very useful article.