Introduction
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a self-regulating business model that helps a company be socially accountable to itself, its stakeholders, and the public. The term corporate social responsibility (CSR) refers to practices and policies undertaken by corporates that are intended to have a positive influence on the world. Every business works within the society, earns from the society and utilises resources of the society. In return, it is the responsibility of every business to cater the society.
Companies Act 2013
Section 135 of Companies Act 2013 and The Companies (Corporate Social Responsibility Policy) Rules, 2014 deals with provision related to Corporate Social Responsibility.
1. Applicability: Section 135(1)
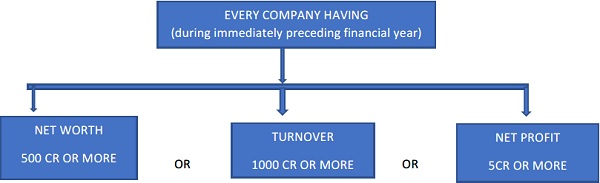
However, if a company cease to meet the above criteria for 3 consecutive financial years, then it is not required to comply with CSR Provision unless it meets the specified criteria.
CSR Committee
√ Every company on which CSR is applicable shall constitute a Corporate Social Responsibility Committee of the Board consisting of three or more director, out of which at least one director shall be an independent director. However, if a company is not required to appoint an independent director u/s 149(4) then two or more director is required.
√ The Board’s Report under sub-section (3) of Section 134 shall disclose the composition of the Corporate Social Responsibility Committee.
√ The Corporate Social Responsibility Committee shall:
a) formulate and recommend to the Board, a Corporate Social Responsibility Policy which shall indicate the activities to be undertaken by the company as specified in Schedule VII
b) recommend the amount of expenditure to be incurred on the activities referred to in clause (a); and
c) monitor the Corporate Social Responsibility Policy of the company from time to time. 1 The Board of every company referred to in sub-section (1) shall,
√ The Board of every company referred to in sub-section (1) shall,—
(a) after taking into account the recommendations made by the Corporate Social Responsibility Committee, approve the Corporate Social Responsibility Policy for the company and disclose contents of such Policy in its report and also place it on the company’s website, if any, in such manner as may be prescribed;
(b) ensure that the activities as are included in Corporate Social Responsibility Policy of the company are undertaken by the company.
CSR Expenditure
√ The Board of every company shall ensure that the company spends, in every financial year, at least two per cent. of the average net profits of the company made during the three immediately preceding financial years, in pursuance of its Corporate Social Responsibility Policy.
√ The company shall give preference to the local area and areas around it where it operates, for spending the amount earmarked for Corporate Social Responsibility activities.
√ If the company fails to spend such amount, the Board shall, in its report made under sub-section (3) of section 134, specify the reasons for not spending the amount.
√ Inclusion and Exclusion CSR Activity is defined under Schedule VII of Companies Act 2013.
Unspent amount in CSR
Any unspent balance related to ongoing project that comply with CSR Policy shall be transferred in Special Bank Account in a schedule bank within 30 days from the end of financial Year.
If a company has spent amounts more than the mandatory two percent on CSR, the company can set off such excess amounts against the CSR spends in the next three financial years. The board of directors, however, needs to pass a resolution for this. It’s important to note that such excess amounts cannot include the surplus arising out of CSR activities. For instance, if any interest is earned out of the assets acquired through the CSR funds, such interest would be treated as a surplus, but cannot be set off from the CSR budget of the following year.
Income Tax Provision regarding CSR
Any expenditure incurred by assessee on the activities relating to corporate social responsibility (CSR) referred to in section 135 of the companies Act, 2013 shall not be deemed to have been incurred for the purpose of business and hence shall not be allowed as deduction under section 37. However, the CSR expenditure which is of nature described in section 30 to 36 or section 80 G shall be allowed as deduction under those sections subject to fulfilment of conditions, if any, specified therein.
Input of GST Credit on expense incurred for CSR
Input Credit is available under GST Regime in case input and output services are used or intended to be used in Furtherance of business.
However, in the recent case law, The Customs, Excise and Service Tax Appellate Tribunal (CESTAT), New Delhi, in M/s Power Finance Corporation Ltd. v Commissioner (Appeal), Central Excise and Service Tax, has disallowed service tax credit on expense incurred in relation to CSR.
The CESTAT observed that there could be services which are used by the service provider to provide output services and there could be services which are not used for providing the said output services. The CESTAT ruled that CSR fell under the latter category and that it had no nexus with the input services utilized by the appellant to provide output services, i.e., the banking and other financial services. Thus, the CESTAT held that expenses incurred on CSR could not be termed as input services for providing the output services. The CESTAT added that the fact that the CSR is a legal responsibility does not make it an output service.
the CESTAT ruled that the appellant was not entitled to CENVAT Credit on the services utilised by it for its CSR activities.
Now let see how this judgement is interpreted under Goods & Service Tax (GST).
Disclaimer: The contents of this article are solely for informational purpose and for the reader’s personal non-commercial use. It does not constitute professional advice or recommendation of firm. Author is not liable for any loss or damage of any kind arising out of any information in this article.





