The Central Action Plan (CAP) 2024-2025, formulated by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), outlines a comprehensive strategy to enhance India’s direct tax administration in line with the Government’s ‘Viksit Bharat’ vision by 2047. The plan focuses on several key areas, including improved revenue collection, reduction of arrear demand, effective litigation management, and enhanced taxpayer services. With specific budget collection targets allocated to various regions, the plan emphasizes systematic efforts to maximize revenue. It also introduces measures to streamline the litigation process, reduce case backlogs, and ensure timely resolution of tax disputes. The CAP prioritizes the improvement of taxpayer services, including the resolution of grievances and adherence to service delivery standards outlined in the Taxpayers’ Charter. Additionally, the plan emphasizes strengthening assessment procedures and human resource management through capacity building and performance monitoring. The CAP 2024-2025 is designed to create a more efficient, transparent, and taxpayer-friendly system, ultimately contributing to the broader goals of economic growth and fiscal stability.
CENTRAL ACTION PLAN 2024-2025
Central Board of Direct Taxes
Ministry of Finance
Government of India
INTRODUCTION
The Central Action Plan (CAP) for 2024-25, meticulously designed by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), sets the stage for a strategic and comprehensive approach to managing India ’s direct taxation landscape. Aligned with the Government’s vision of ‘Viksit Bharat’ by 2047, the CAP outlines a series of initiatives aimed at enhancing tax administration, optimizing revenue collection, reducing arrear demand and improving taxpayer services. As we delve into the CAP 2024-25, the vision is to create a more efficient, transparent, and taxpayer-friendly system that aligns with the broader objectives of economic growth and fiscal stability.
1. Enhanced Revenue Collection: The CAP sets ambitious yet realistic budget collection targets that would require systematic and strategic efforts at all levels. These targets have been allocated to various regions, ensuring that each Principal Chief Commissioner of Income Tax (Pr. CCIT) region focuses on meeting its respective goals. The allocation considers the revenue potential and past performance of each region.
2. Reduction and cash collection in Arrear Demand: The plan sets a realistic target for reducing arrear demand out of the total outstanding demand as of April 1, 2024. The CAP outlines a region-wise allocation of reduction targets and sets specific timelines to achieve these goals.
3. Litigation Management: Effective litigation management is pivotal to reducing the backlog of cases and ensuring swift resolution of tax disputes. The CAP 2024-25 introduces several measures to streamline the litigation process.
4. Service Delivery: Improving tax payer services at multiple levels from resolving grievances received through the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) within stipulated timelines to setting clear timelines for key services, including issuing refunds, deciding on rectification applications, and giving effect to appellate orders and above all, adherence to the Taxpayers’ Charter, which lays down the standards of service delivery and the rights and responsibilities of taxpayers.
5. Focus on Assessment: Strengthening and streamlining assessment across Faceless, Jurisdiction, Central, International Tax and Exemption charges through plethora of steps including capacity building and training.
6. Human Resource Management: Strengthening the human resource framework to ensure a knowledgeable and responsive workforce with twin pillars of capacity building and performance monitoring as the focus
The Central Action Plan 2024-25 is a comprehensive roadmap designed to elevate India ’s direct tax administration. By focusing on key areas such as revenue collection, arrear demand management, litigation, service delivery and human resource development, the plan aims to create a more robust, efficient, and taxpayer-friendly system. The CBDT ’s commitment to continuous improvement and innovation is evident in this plan, which seeks to address current challenges while preparing for future demands. As we move forward, the successful implementation of the CAP 2024-25 will play a crucial role in achieving the government’s fiscal objectives and fostering a conducive environment for economic growth.
*******
CHAPTER I
ALLOCATION OF BUDGET TARGETS
1. DIRECT TAX COLLECTION DURING 2023-24
The major head-wise direct tax collection during F.Y. 2023-24 is as under:
(Fig. in Rs. crore)
| Major heads of Tax | Budget Estimates (F.Y. 2023- 24) | Revised Estimates (F.Y. 2023- 24) | Actual Collection (F.Y. 2023- 24) | % of RE Achieved |
| Corporation Tax | 9,22,675 | 9,22,675 | 9,11,055 | 98.74% |
| Taxes on Income (Incl. Wealth tax, etc.) | 8,72,950 | 9,90,325 | 10,10,948 | 102.08% |
| Other Taxes (STT, etc.) | 27,625 | 32,000 | 38,163 | 119.26% |
| Total | 18,23,250 | 19,45,000 | 19,60,166 | 100.78% |
Source: Pr.CCA, CBDT
2. PERCENTAGE COLLECTION CONTRIBUTION BY EACH REGION
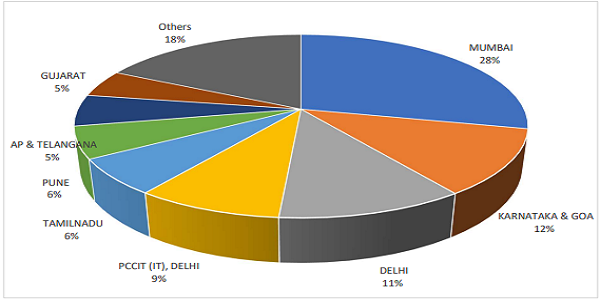
(Source: TINMIS)
3. Performance with respect to Net Direct Tax collection for the last three Financial Years prior to F.Y. 2023-24 is as under:
(Fig. in Rs. crore)
| Financial Year | Corporation Tax | Personal Income Tax | Other taxes incl. Wealth tax, Securities Transaction tax, etc.* | Total Tax |
| 2020-21 | 4,57,719 | 4,70,633 | 18,824 | 9,47,176 |
| 2021-22 | 7,12,037 | 6,73,413 | 26,972 | 14,12,422 |
| 2022-23 | 8,25,834 | 8,08,221 | 29,631 | 16,63,686 |
3.1 The Budget Targets for F.Y. 2024-25 as per the budget estimates are as follows:-
(Figure in Rs. crore)
| Major heads of Tax | Budget Estimates (F.Y. 2024-25) |
| Corporation Tax | 10,20,000 |
| Taxes on Income (Incl. Other taxes, etc.) | 11,50,000 |
| STT | 37,000 |
| Total | 22,07,000 |
4. ALLOCATION OF TARGETS
Allocation of budget target for each cadre-controlling Pr.CCIT has already been communicated separately vide letter through F.No. 380/03/2024- IT(B) dated 29th April 2024 for further allocation to various field units under the jurisdiction of respective Pr.CCIT keeping in view the revenue potential of the different charges.
Read Full




