e-invoice is to be rolled out optional from 1st Jan 2020 and mandatory from 1st April 2020. It is already one month, and we need to work on the same if the same is not started as we are racing against time. The government has given access to the sandbox for the taxpayer to verify and test the same before rolling out to the production / actual use. E-invoice is being rolled as the Government has observed that there is a lot of tax evasion happening the system and tracking of the same is missing in the current system. Implementation of e-invoicing will provide tracking of the same, and at the same time, the Government will have a complete audit trail of the transactions, and evasion will be minimized. The benefits of e-invoicing are
- Lesser cost of invoice
- Reduced delivery time of invoice to suppliers
- Elimination or minimal cost for shipping of invoices to the customer (no courier costs)
- Reduction of usage of paper
- E-way bills to be autogenerated using e-invoice data
- Enabling filing of returns seamlessly by avoiding duplication of data entry and reconciliation issues
- Enabling digital tax administration
Unlike the rollout of GST, where the taxpayers have to make a lot many changes to their business process as well as for their IT Systems, implementation of e-invoice is simple, less time consuming, and huge budgets are not required. The sandbox for the e-invoice is being made available for the taxpayers who are having a turnover above Rs 500 crores in the previous financial year and for above Rs 100 Crores it will be made available from 1st of Feb 2020.
The tax invoice is still required to be generated from the existing ERP/Accounting/Billing system, but the data has to be transmitted to the IRP (Invoice Registration Portal ) for the validation of the data and once it is validated, an IRN (Invoice Reference Number will be generated and sent back to the taxpayer.
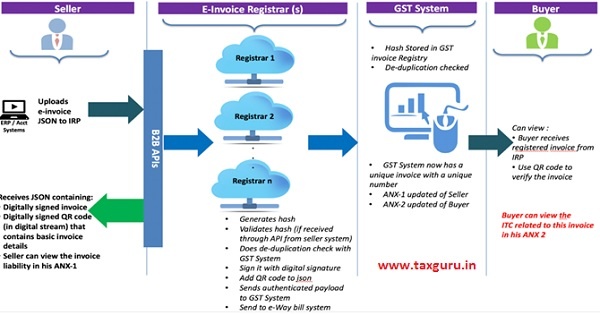
The following are to be considered while implementing the e-invoice
1. Requirements – Functional
It is proposed to have e-invoice in the 35th GST Council Meeting, and the same is decided in the 37th GST Council meeting. The basis on this it is notified wide Notification No. 70/2019 – Central Tax dated 13th Dec 2019 that e-invoice will be mandatory for all the taxpayers who are having aggregate turnover above Rs 100 crores in a financial year.
Quote
registered person, whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds one hundred crore rupees, as a class of registered person who shall prepare invoice in terms of sub-rule (4) of rule 48 of the said rules in respect of supply of goods or services or both to a registered person.
Un Quote
From the said notification, it is clear that e-invoice is required to be issued by all the taxpayers in case of B2B (Business to Business) transactions for either supply of goods or services or both.
Normally in all the GST provisions, it is worded that during the previous financial year but in this notification, it is used as “In a financial year.” This raises the question, what will happen if the turnover has crossed during the financial year. In such a case, does the taxpayer need to issue the same from the beginning of the year or from the date on which it has crossed or from the invoice which has triggered the threshold limit? The taxpayers have to take a judicious call on this and take it forward accordingly.
There is also a requirement to issue a QR code with a cross-reference to the payment to be made in case of B2C transactions for the taxpayers who are having a turnover of Rs 500 crores. The same is notified wide Notification No. 72/2019 – Central Tax dated 13th Dec 2019. This means for all the transactions related to B2C the invoice has to be issued with a QR code and this is an additional requirement.
Quote
hereby notifies that an invoice issued by a registered person, whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds five hundred crore rupees, to an unregistered person (hereinafter referred to as B2C invoice), shall have Quick Response (QR)code:
Provided that where such registered person makes a Dynamic Quick Response (QR) code available to the recipient through a digital display, such B2C invoice issued by such registered person containing cross-reference of the payment using a Dynamic Quick Response (QR) code, shall be deemed to be having Quick Response (QR) code.
Un Quote
It means the existing retail billing solutions have to be modified for the same. This will impact all the franchise stores, retail supermarket chains etc., The existing Point of Sales devices may not be supporting the printing of the same or if also supported the changes in the billing software has to make. The impact on the same has to be considered as the QR code has to be generated from the ERP/Accounting/Billing solution directly or the invoice information has to be transmitted to the e-invoice portal and generated?
2. Impact Analysis
Detailed impact analysis of the existing business process, as well as the flow in the system, has to be analyzed, and the corresponding changes are required to be made to ensure that all the statutory requirements have adhered.
In the current architecture, the e-waybill may be generated using the APIs, but with the requirement of e-invoice, the Part – A of e-waybill is going to be auto-generated, in such a case if APIs are being used, is it required to continue using the same or make necessary changes there or stop using the same, a call has to be taken based on the impact analysis.
Most of the organizations are using the ASP solutions for the filing of returns, the impact on the same also has to be considered. The e-invoice data is expected to update the records in the Anx-1 in the proposed new returns.
Apart from these two, if there are any customizations, is there any impact on the customizations? If yes, what are they, and how they address them has to be decided?
For capturing the data in the system, are new tables required or new columns to be added, or any of the existing columns in the table can be used? This has to be considered.
Some changes are specifically required in the case of OEM’s who issue invoices for supply of spares to their dealers in hundreds of lines. In the case of e-invoice, it is enabled only for 250 line items, companies which are in this category have to revisit their business process by having the validation of 250 lines only in the tax invoice.
3. Make or Buy
The next import point is to implement the same through inhouse or opt for the solution provided by the vendors like Oracle, Logo, SAP, etc.; the reason is there are not many changes to be made in the system only the API calls have to be made. The APIs can be accessed directly from the portal or through the GSP/ASP.
Typically some of the vendors charge for the same, and for the e-invoice, there is no additional requirement from a systems perspective but only on who to map the fields like IRN Number, ACK Number, ACK Date to name a few. They can be mapped using the existing CDF /DFF /GDFs in the product. Alternatively, if there is a discipline in the team, they can be captured in any of the existing fields or the remarks field.
The invoice print program in most of the cases is taxpayer specific, and they have to make necessary changes for the same in either of the approaches. It all depends on the IT policy of the organization.
4. Changes required in the System
Either the taxpayer can go for the in-house development or the software providers’ solutions, some changes are required. As the database access cannot be given to the third party solutions or the external servers, it is required to create a separate file folder for sending the data to the GSP/ASP or the IRP portal and receiving it.
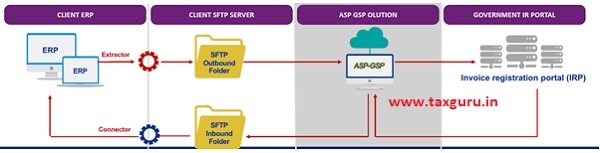
The data flow typically happens as in the given picture, and this will ensure that there is absolute data security, and at the same time, the statutory requirements are met.
If the number of transactions is small or very few like in the infra or turnkey based project companies, they can adapt the offline method, i.e., by using the Jason file provided.
5. Technical aspects of e-invoice
It is always good to know about some of the key technical aspects of e-invoice in GST in India.
Invoice Reference Number (IRN) – is issued for each tax invoice
The IRN issued will be 12 Characters ABX 99,99,99,999 A indicates the database identifier B indicates the year – A for 2019, B for 2020, C for 2021… X is a check digit 99999999 digits are running serial number, covers 100 Crore numbers A..99999999 provides more than 1000 Crores of IRN per year.
The IRN is generating using the most secure method so that it is valid for the lifetime, and anyone who has access to the same other than the intended user/authorized users cannot read the same. It is generated using the SHA 256, which is used in the DSCs.
Example
HASH of “01AAAAB1234C1Z02019-20INVAB1234” is
35054cc24d97033afc24f49ec4444dbab81f542c555f9d30359dc75794e06bbe
The Quick Responses (QR) code issued for each tax invoice will contain the following information
- GSTIN of supplier
- GSTIN of Recipient
- Invoice number as given by Supplier
- Date of the generation of invoice
- Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax)
- The number of line items.
- HSN Code of the main item (the line item having the highest taxable value)
- Unique Invoice Reference Number (hash)
The following are the APIs issued by the GSTN for e-invoice
- Authentication (POST)
- Generate IRN (POST)
- Cancel IRN (POST)
- Get e-Invoice by IRN (GET)
- Get GSTIN details (GET)
- Health Check API (GET)
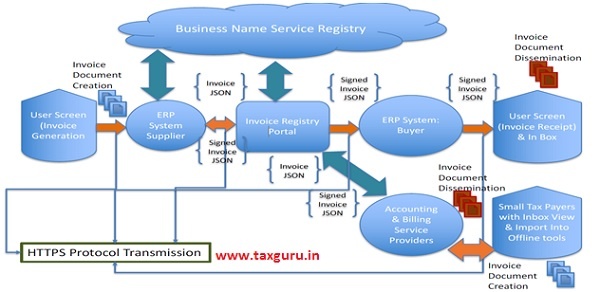
The IT teams have to keep in mind the following
1. e-invoice is required only for these following document – tax invoice, credit notes, debit notes issued for B2B (Business to Business), B2G (Business to Government) and for exports
2. The ERP/Accounting system has to be updated for the same either through the patch given by the software provider or through customization
3. The GSPs or the Taxpayers should have SSL (Secure Socket Layer) or Transport Layer Security 2.0 (TSL)
4. If the taxpayer is not accessing through GSP’s, he has to ensure that the GSP provides them access to the Production environment
5. It is recommended to have a staging or pre-production environment for testing
6. The authentication token is valid for 6 hours and is recommended to get a new token at least 10 minutes before the expiry of the token.
7. If e-waybills are being generated using the APIs, the same needs to be revisited as the IRP portal is expected to update the Part – A of the e-waybill basis of the data shared for the generation of IRN.
8. Taxpayers using GSP route will be given the API User Name and Password and who are accessing the IRP portal directly will be provided ClientId, ClientSecret, API UserName and Password
9. Taxpayers and GSPs are required to whitelist the Static IPs, and the system allows only Indian Static IPs.
10. In the initial stages, the Taxpayers and GSPs will be accessing the e-invoice system using the internet, and after a certain period, they will be allowed to access only through the MLPS.
The role of the CMAs is very vital, and they can do an analysis of all the requirements from a business perspective and tax perspective and share the inputs to their clients or where they are working.
The main reason for the introduction of e-invoicing is to curb tax evasion and also improve the rankings in the ease of doing business and for making payments. e-invoicing is implemented in about 75+ countries across the globe and we are not new for the same and most of the MNCs are aware of the same and they have started working in that direction based on the previous experience. The challenge comes only for the Indian companies who are new this process and they should try to implement the same using the inhouse team if they are capable of or engage the external consultants for the same so as the adaption is smooth and there is continuity of business. The invoicing process will work as it is, and only new additional data elements are captured. If planned and implemented properly the same can be rolled out by 1st April 2020 when it becomes mandatory else the business will be impacted.
Disclaimer
Any views or opinions represented above are personal and belong solely to the author and do not represent those of people, institutions or organizations that the author may or may not be associated with in professional or personal capacity unless explicitly stated. Any views or opinions are not intended to malign any religion, ethnic group, club, organization, company, or individual.






good article