CA Neeru Sharma
What is Transition?
Transition is a purposeful and planed movement and its represent a path to the next phase of your life.
“A statutory Provision that regulates a process that starts before an enactment of the statute comes into force and end after the enactment of the statute has come into force.”
This may not be a path that you want to take or that you will find enjoyable but it is a path with meaning for you and it will bring you to a new phase. Since Change is wall and transition is a gate in this wall and it’s for you to enter into it.
What is transition Provisions?
Transition Provisions are temporary provisions for short period which enable to people that difficulties due to changes less painful and disruptive.
Need of transitional provisions in GST –
Transition provisions take effect during the period between the movements of existing taxation i.e. Central Excise, Service Tax, and Vat and luxury tax etc. and Goods and Services tax. Such provisions are required for the smooth and successfully implementation of GST.
Transitional Provision need only to state that the existing law and existing department continue to function until they are replaced under new indirect taxation regime.
Migration of exiting taxpayers into GST-
The existing tax payers having a valid PAN would be granted provisional registration certificates under the GST Law. GST act shall come into force as on the date to be notified by central/state government. The government has issued detail procedures for the smooth migration of existing taxpayers into GST.
The Process as under:
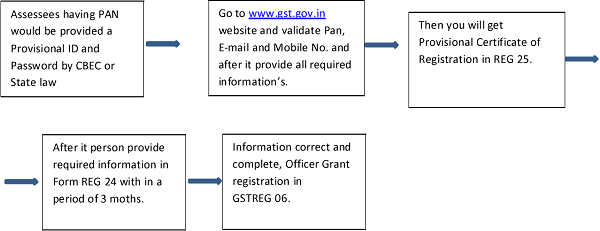
⇒ Provisional Registration-

All the existing taxpayers having a Permanent Account Number will be issued a provisional registration certificate in Form GST REG-25.Such Certificate shall be valid for an initial period of 3 months (or an extended period, as may be notified by the Central Government/State Government on recommendation of the Council) from the date of issue.
⇒ Final Registration-
After obtaining the provisional registration, an application in Form GST REG-26 needs to be submitted along with the required information and documents. This needs to be furnished within 3 months(or an extended period, as may be notified by the Central Government/State Government on recommendation of the Council) from the date of issue of provisional registration. If such information is found to be correct and complete, the final registration will be granted in Form GST REG-06.
If the information is not furnished within the prescribed time limit or information is incomplete or incorrect, registration will be canceled.
Documents to be uploaded—
1. Proof of Constitution of Business
- In case of Partnership firm: Partnership Deed of Partnership Firm (PDF and JPEG format in Maximum size of 1 MB)
- In case of Others: Registration Certificate of the Business Entity PDF or JPEG 1 MB
2. Photograph of Promoters/ Partners/ Karta of HUF JPEG 100 KB
3. Proof of Appointment of Authorized Signatory PDF or JPEG 1 MB
4. Photograph of Authorized Signatory JPEG 100 KB
5. Opening page of Bank Passbook/ Statement containing Bank Account Number, Address of Branch, Address of Account holder and few transaction details.
Different Provisions for input tax credit –
| S.No. | Situations | Conditions | Conclusion |
| 1 | Carried forward for ITC unutilized under existing laws | 1. ITC allowed in this act.
2. Filed all 6 months returns before appointed date. 3. Credit not related to goods manufactured and cleared under exemption notification. |
1. Must have been reflected as input credit carried forward in the return filed for the last month in existing Law.
2. Submit a declaration in Form TRAN-1 within 90 days for appointed date |
| 2 | Unavailed credit on Capital goods | 1. Unaviled credit on CG should eligible in both Acts i.e. Existing Laws and GST Law.
|
1. Credit not carried forward in the return filed for the last month in existing Law.
2. Submit a declaration in Form TRAN-1 within 90 days for appointed date |
| 3 | • Person not liable to be registered under the earlier law
• Person engaged in manufacture/ sale of exempted goods, provision of exempted services • Person providing works contract service and availing abatement under Notification no. 26/2012 • First/ Second stage dealer, • importer or • a depot of a |
1. Goods must be used for taxable supply.
2. Eligible to take the credit under GST law. 3. Such person should be in possession of invoice or other prescribed document 4. Invoice or other document should be within 12 months from the appointed day 5.Excess claims will be recovered as arrears of tax under GST law |
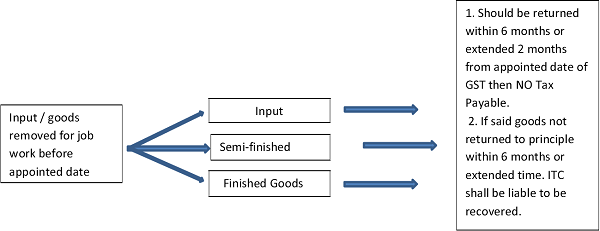
1. Inputs held in stock and inputs contained in semi-finished goods or finished goods held in stock as on appointed day.
2. Above benefit not available for input services. 3. Such credit can be taken in the electronic credit ledger. 4. Submit Form TRAN 1 for stock held on appointed date up to the 6 tax period. |
| Proviso to section-140(3) | If A Trader is not in possession of invoice and document of payment of duty/ tax. | 1. Such goods (stock held) not wholly exempt and Nil rate under existing law.
2. Possession a document relating to purchase of Goods. 3. Stock of such goods must be stored separately. |
1. Credit shall be allowed at the rate of 40%, of the central tax applicable on supply of such goods after the appointed date.
2. Registered person submit a statement of Form TRAN 1 at the end of each of the six tax periods. 3. Inputs held in stock and inputs contained in semi-finished goods or finished goods held in stock as on appointed day. |
| 4 | A registered person engaged in manufacturing of Taxable as well as Exempted goods in existing law | 1. For Input tax credit in respect of taxable supply refers section 140(1).
2. For Input tax credit in respect of exempted supply refers section 140(3). |
1. Inputs held in stock and inputs contained in semi-finished goods or finished goods held in stock as on appointed day (Not for Capital Goods).
2. Registered person submit a statement of Form TRAN 1 at the end of each of the six tax periods. |
| 5 | Invoices are raised in existing tax but input or input services received after appointed date. | 1. Invoices must be recorded in the books within 30 days or period extended. | 1.Submit following Details-
(i) A statement indicating the name & address of the supplier together with invoice details. (ii) Description, quantity and value of goods or services. (iii) The amount of taxes, duties, VAT, Entry tax charged by the supplier. (iv) The date at which receipt of goods or services are entered in the books of the recipient. |
| 6 | A person switching over from composition scheme to Regular scheme in GST law. | 1. Must be registered person under GST law.
2. Such input must be used for make taxable supply. |
1. Inputs held in stock and inputs contained in semi-finished goods or finished goods held in stock as on appointed day (Not for Capital Goods).
2. Registered person submit a statement of Form TRAN 1 at the end of each of the six tax periods. |
| 7 | Input service distributor | 1.Transferred to recipient in the same State
2. Transferred to recipient in the same State |
Transferred as it is.
Transferred as IGST |
| 8 | Taxable person has centralized registration under existing law | 1. Obtain registration under GST law.
2. ITC must eligiable under GST law. 3. Filing of return within 3 month. |
1. Allow taking credit or can transfer to other location having same PAN.
2. Registered person submit a statement of Form TRAN 1 at the end of each of the six tax periods. |
9. Where any CENVAT credit availed for the input services Provided under the existing law has been reversed due to non-payment of the consideration within a period of 3 months, such credit can be reclaimed subject to the condition that the registered person has made the payment of the consideration for that supply of services within a period of 3 months from the appointed day.
Transitional provisions relating to job work.
Transitional provisions relating to Miscellaneous Topics-
A. When Duty Paid goods are returned?
Where the sale was under the existing law and return is under the GST law, the seller would be eligible to refund of duty paid under the existing law. This provision would be applicable in the following circumstances-
– Duty was paid at the time of removal under existing act not earlier than 6 months prior to appointed date.
– Sales return should be any lace of business.
– Return of the goods should be within 6 months form the date of introduction of GST.
– Such return must be by an unregistered person.
IF such goods return by registered person, then the return of such goods shall be deemed to be a supply.
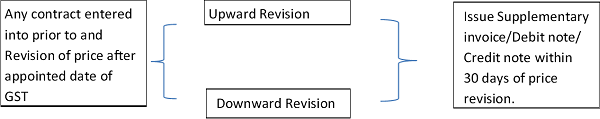
B. What happen if contract price after Appointed date?
C. Pending Refund related to existing Law-
Refund of claim filed under existing law or goods cleared, service provided and export related to existing law than all such refund disposed of under respective law.
Apply following conditions—
(i) The refund, if allowed, would accrue in cash under the existing law and would not be Credited to the electronic credit ledger or electronic cash ledger.
(ii) The refund if rejected, fully or partially would lapse.
(iii) No refund claim shall be allowed of any amount of Cenvat credit where the balance of The said amount as on the appointed day has been carried forward under this Act.
D. Where tax disposed before appointed date and service not provided—
Every claim for refund of any tax deposited under the existing law in respect of services not Provided, filed after the appointed day, shall be disposed of in accordance with the provisions of the existing law and any amount eventually accruing to him shall be paid in cash.
E. Where any matter in respect of CENVAT Credit is pending in an appeal or revision under of any existing laws
Above matter should be dealt with in accordance with the provisions of existing laws as follows:
– If the input credits are finally allowed: A refund would accrue to the claimant in cash.
– If the input credit is disallowed: It would become recoverable as an arrear of tax under the CGST.
– Amount so recovered would not be allowed as ITC under GST Law.
F. Where any matter in respect of Output tax liability is pending in an appeal or revision under of any existing laws
Above matter should be dealt with in accordance with the provisions of existing laws as follows:
– If the output liability is finally payable: It should be recovered as an arrear of tax under CGST Act.
– The amount so recovered would not be allowed as input tax credit under the CGST laws.
– If the output liability is finally allowable to the claimant: It would accrue to the claimant as refund in cash under the existing law. If any amount is rejected, the same shall not be available as input tax credit under CGST.
G. Where any amount payable and refundable due of revision of return in existing laws—
– If Payable recovered as an arrear of tax under the CGST Act. The amount so recovered would not be allowed as input tax credit.
– If refundable then the claimant as cash refund under the existing law.
H. Where any contract, the goods or services or both supplied on or after the appointed day, entered into prior to the appointed day shall be liable to tax under the provisions of this Act.
I. Progressive or periodic supply of goods or services, GST is not payable to the extent on which tax was paid under existing law.
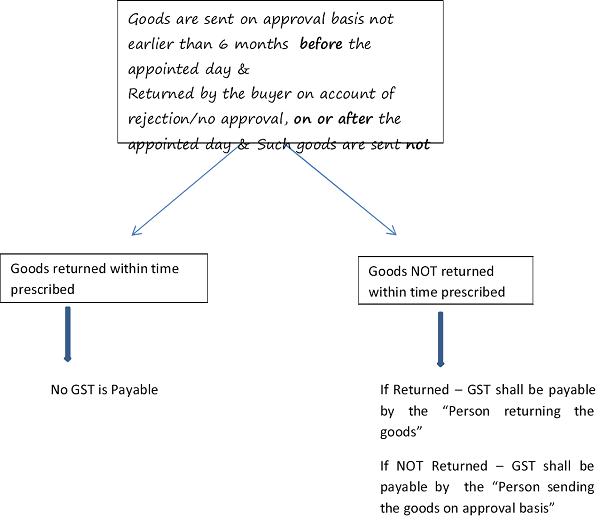
J. Where the goods sent on approval—
K. Supply of goods where TDS is to be deducted at source—Where:-
– The supplier had sold any goods under the existing law and
– TDS applies on such transactions under existing law and
– The supplier had issued the invoice before the appointed day
– Payment is made to the supplier after the appointed day.
It provides that merely because payment is made to the supplier after the date of introduction of GST, the TDS provisions under Section 51 of the CGST Act will not apply. In other words, no tax shall be deductible under CGST Act at the time of making payment to the supplier.
Conclusion –
For implementation of GST, transition provisions are prerequisite. This is first phase towards GST. Every businessman and every industry ready for transition provision for enter in new taxation regime .This provisions are help to industry that how to manage and convert itself according new taxation system.
Click here to Check GST Common Portal
| Disclaimer: The information in this article is true and complete to the best of our knowledge. All recommendations are made without guarantee on the part of the author. |






Nice