CA Lalit JR Sharma
1. Introduction:
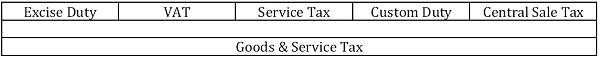
In order to impose any tax, there must be a taxable event. Taxable Event mean– Any Event or transaction, that results in a tax consequence for the party who executes the event. The Present system of Indirect Tax in India has different taxable Events. The major heads of Indirect Tax Structure have following taxable events:
1.1 —-Excise Duty:
Section 3 of Excise Act 1944 define the taxable event for the levy of Excise Duty as- “There shall be levied and collected in such manner as may be prescribed—
A duty of excise to be called the Central Value Added Tax (CENVAT)] on all excisable goods (excluding goods produced or manufactured in special economic zones) which are produced or manufactured in India as, and at the rates, set forth in the First Schedule to the Central Excise Tariff Act, 1985 (5 of 1986); {Section 3(1)(a)}
Hence taxable event under Excise Act 1944 is ‘Manufacture or Production of Goods in India”
1.2 VAT
Section 3 of DVAT Act 2004, prescribe the Taxable Event as—
Every Dealer shall be liable to pay tax at the rates specified in Section 4 of the Act on Every Sale of Goods effected by him {Section 3(2)}
Hence taxable event under VAT is ‘Sales of Goods in the course of Intra- State”
1.3 Service Tax
Section 66B of Finance Act 1994 prescribe the Taxable Event as —
There shall be levied a tax herein after referred to as the Service Tax at the rate of 14% on the value of all service other than those services specified in the negative list, provided or agreed to be provided in taxable territory by one person to another and collected in such manner as may be prescribed {Section 66B}
Hence taxable event under Service Tax is “Service provided or agreed to be provided by one person to another person in the Taxable Territory”.
1.4 Customs
Section 12 of custom Act 1962 prescribe the Taxable Event as —-
Except as otherwise provided in This Act or any other Law for the time being force, duties of customs shall be levied at such rates as may be specified under the Customs Tariff Act 1975 (51 of 1975) or any other law for the time being in force on goods imported into or exported from India {Section 12(1)}
Hence the Taxable Event under Custom Act 1962 is “Import or Export of Goods into or from India”
1.5 Central Sale Tax
Section 6 of Central Sale Tax Act 1956 prescribe the Taxable Event as—-
Subject to other provisions contained in this Act , every dealer shall with effect from such date as the Central Government may by notification in the Official Gazette, appoint not being earlier than thirty days from the date of such notification, be liable to pay tax under this Act on all sales of goods other than electrical energy effected by him in the course of inter-state trade or commerce during any year on and from the date so notified {Section 6(1)}
Hence the Taxable Event under Central Sale Tax Act 1956 is “Sale of Goods in the course of inter- state trade”
2. —-The Taxable Event Under Goods and Service Tax Act
The Constitution Act 2016 (Constitution Amendment Act) has inserted Article 366 (12A) to define the term Goods and Service Tax, as
Goods and Service Tax Means “Any tax on Supply of Goods or Service or both except taxes on the supply of the alcoholic liquor for human consumption.
Hence the Taxable Event under Goods and Service Tax Act is “Supply of Goods and Service”
Hence all present taxable events under Different Indirect Tax Acts have been subsumed with one taxable event.
2.1 Meaning of Supply (Section 7)
1. Supply includes:
a) All forms of supply of goods and or services such as
(i) Sales
(ii) Transfer
(iii) Barter
(iv) Exchange
(v) License
(vi) Rental
(vii) Lease
(viii) Disposal
made for a consideration by a person in the course or furtherance of business. (Clause a Sub Section 1 of Section of 7)
b) Import of Service, for a consideration and whether or not in the course or furtherance of business.
(clause b Sub Section 1 of Section of 7)
c) A supply specified in Schedule I made or agreed to be made without (clause c Sub Section 1 of Section of 7)
d) The activities to be treated as supply of goods or supply of service as referred in Schedule II. (clause c Sub Section 1 of Section of 7)
2. Nothing anything contained in Sub Section (1)—-
a) Activities or transactions specified in Schedule III or
b) activities or transactions undertaken by the Central Government, a State Government or any local authority in which they are engaged as public authorities as may be notified by the Government on the recommendation of the council shall be treated neither as a supply of goods nor a supply of service
3. Subject to subsection (1), and sub section (2) the Central or State Government may, upon recommendation of the council, specify, by notification, the transactions that are to be treated as
(i) a supply of goods and not as a supply of service; or
(ii) a supply of services and not as a supply of goods; or
3.0––In general sense Supply means “The amount of goods or service available for purchase at specified price or consideration. However the Law has provided an inclusive meaning to the word “Supply”. Its mean above specified list of transactions are illustrative. The Supreme Court has interpreted the signification of “Include” as follow
When the word “Includes” is used in an interpretation clause, it must be construed as comprehending not only such things as they signify according to the nature and import but also those things which the interpretation clause declares that they shall include”.
Hence inclusive definition of supply gives a wider scope to include something which is not specifically describes in Section 3 Sub Section (1).
4.0—-Description of Form of Supply specifically mentions in Section 3(1)(a)
4.1- Meaning of Goods:
Goods includes all material, commodities and articles (Clause 12 of Article 366 of Constitution of India)
The Constitution of India has not specifically defined the meaning of Goods which create a path of ambiguity and misinterpretation of about the real sense of meaning of Goods. Hence we can take help of meaning of “Goods” defined in other Statutory Act
Goods” means every kind of movable property other than actionable claims and money; and includes stock and shares, growing crops, grass, and things attached to or forming part of the land which are agreed to be severed before sale or under the contract of sale” (Clause 7 of Section 2 of Sales of Goods Act 1930)
The model GST Law has adopted the above definition with certain modification and defines the Goods as
4.1.1 “Goods’’ means every kind of movable property other than money and securities but includes actionable claim, growing crops, grass and things attached to or forming part of the land which are agreed to be severed before supply or under a contract of supply {Clause 52 of Section 2}
4.1.2. “Actionable Claim shall have the meaning assigned to it in Section 3 of the Transfer of Property Act 1882. {Clause 1 of Section 2}
“Actionable Claim” means a claim to any debt, other than a debt secured by mortgage of immovable property or by hypothecation or pledge of movable property, or to any beneficial interest in movable property not in the possession, either actual or constructive, of the claimant, which the civil courts recognize as affording grounds for relief, whether such debt or beneficial interest be existent, accruing, conditional or contingent {Section 3 of Property Act 1882}
In simple sense actionable claim means any claim which is enforceable under legal action or claim to any beneficial interest in movable property not in possession for which relief can be claimed in civil court. Hence actionable claim can be segregated between two components
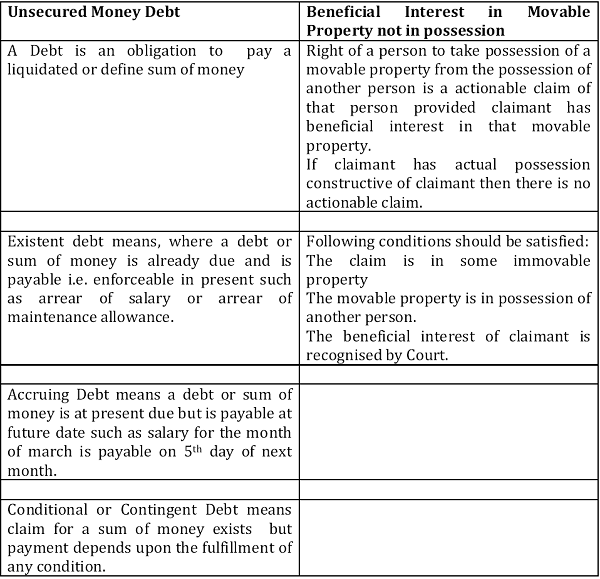
Following are the example of Actionable Claim:
1. The right to claim benefit of the contract for the purchase of goods.
2. A share in partnership firm.
3. A claim on arrear of rent.
4. Right to get back the purchase price when sale is set aside. A claim on return of earnest money.
“Beneficial interest in movable property is considered intangible movable property.”
4.1.3- “Money means Indian Legal Tender or any foreign currency, cheque, promissory note, bill of exchange, letter of credit, draft, pay order, traveler cheque, money order, postal or electronic remittance or any other instrument recognised by the Reserve Bank of India when used as consideration to settle an obligation or exchange with Indian Legal tender of another denomination but shall not include any currency that is held for its numismatic value.
4.1.4 – Meaning of Securities
“Securities shall have meaning assigned to it in sub section (h) of Section 2 of Securities Contract Regulation Act 1956
Under Securities Contact Regulation Act 1956, “Securities include
(i) shares, scrips, stocks, bonds, debentures, debenture stock or other marketable securities of a like nature in or of any incorporated company or other body corporate;
(ii) derivative;
(iii) units or any other instrument issued by any collective investment scheme to the investors in such schemes;]
(iv) Security receipt as defined in clause (zg) of section 2 of the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002;]
(v) Units or any other such instrument issued to the investors under any mutual fund scheme;] 12
(vi) Government securities;
(vii) Such other instruments as may be declared by the Central Government to be securities;
(viii) rights or interest in securities
4.2 Meaning of Service
Service means anything other than Goods {Clause 26A of Article 366 of Constitution of India).
The aforesaid definition has been adopted under Model GST Law and prescribes as follow:
“Services mean anything other than goods, money and securities but include activities relating to use of money or its conversation by cash or by any other mode, from one form, currency or denomination, to another form, currency or denomination for which a separate consideration is charged. {Clause 102 of Section 2)
4.2.1- Following activities are considered as transaction in money only:
a) The deposit or withdrawal of principal amount from Bank
b) Advancing or repayment of loan.
c) Investment of fund with another such as investment by a partner into partnership firm where return on investment is returned without retaining any portion of return on such investment.
4.2.2- Following activities are not considered as transaction in money only:
a) Making of draft or pay order by a bank should not be considered as transaction in money only since Bank charge commission and such commission should be considered as service to the extent of amount of
b) Transaction of chit fund business where chit fund receive certain commission from its members.
c) Investment of fund with another, where a portion of return on investment is retained as commission is not considered as transaction in money only..
4.3.0—Meaning of Terms used under subsection 1 of Section 7
> Meaning of Sale:
Exchange of a commodity for money: the action of selling something(Dictionary meaning)
The Act of selling; specifically: the transfer of ownership of and title to property from one person to another for a price (Dictionary meaning)
“Sale” with its grammatical variations and cognate expression means any transfer of property in goods by one person to another for cash or for deferred payment or for other valuable consideration (not including a grant or subvention payment made by one government agency or department, whether of the central government or of any state government, to another) {Section 2(zc) of DVAT Act 2004}
> Meaning of Transfer:
Move from one place to another. An act or process of moving someone or something from one place to another (Dictionary meaning)
“Transfer of property” means an act by which a living person conveys property(whether movable or immovable), in present or in future, to one or more other living persons, or to himself and one or more other living persons; and “to transfer property” is to perform such act. (Section 5 of Transfer of Property Act 1882)
> Barter
Exchange (goods or services) for other goods or services without using money.
> Exchange
An act of giving one thing and receiving another (especially of the same kind) in return; or
The changing of money to its equivalent in the currency of another country; or Give something and receive something of the same kind in return; or
> License
Permission or freedom to do what you want; an official document that gives you permission to own, do or use something usually after you have paid money and or taken a test.
> Rental
The amount of money paid or collected as rent.
> Lease
A lease is an agreement whereby the lessor conveys to the lessee in return for a payment or series of payments the right to use an asset for an agreed period of time. (Accounting Standard 19 issued by ICAI)
> Disposal
To get rid of something, especially by throwing it away; something that is sold by a company, such an asset, property or part of its business or the act of doing this.
4.3.1—Business: includes: {Clause 17 of Section 2}
a) Any trade, commerce, manufacture, profession, vocation or any other similar activity whether or not it is for a pecuniary benefit.
b) Any transaction in connection with or incidental or ancillary to (a) above.
c) Any activity or transaction in the nature of (a) above whether not there is volume, frequency, continuity or regularity of such transaction;
d) Supply or acquisition of goods including capital assets and services in connection with commencement or closure of business.
e) Provision by a club, association, society or any such body (for a subscription or any other consideration) of the facilities or benefits to its members as the case may be.
f) Admission, for a consideration of person to any premises;
g) Services supplied by a person as the holder of an office which has been accepted by him in the course or furtherance of the trade or profession or vocation (Input Service Distributor)
h) Services provided by a race club by way of totalisator or a license to book maker in such club; and
i) Any activity or transaction undertaken by Central Government, a state government or any local authority in which they are engaged as public
In normal parlance; business means An organization or economic system where goods and services are exchanged for one another or for money. Hence any organization which runs with the objective to make profit is called business. It can be in any form as illustrated above.
Further the terms used above can be understood as follows:
Meaning of Trade:
The action of buying and selling goods and services, with a commercial motive.
Meaning of Commerce:
The activity of buying and selling, especially on a large scale with a commercial motive.
Meaning of Manufacture
An activity to bring into existence a new substance with distinct name and nature.
Meaning of Profession
Any type of work that needs special training or a particular skill, often one that is respected because it involves a high level of education; jobs that need special training and skill, such as being a doctor or lawyer, chartered accountant rather than a job in business or industry;
Meaning of Vocation
A strong desire to spend your life doing a certain kind of work; that work that a person does or should be doing; the work in which a person is employed.
4.3.2—Meaning of Consideration
“Consideration” in relation to the supply of goods or services or both includes––
| a) Any payment made or to be made, | The first part of definition covers the |
| whether in money or otherwise, in respect | payment by way of money or in kind which |
| of, in response to, or for the inducement of, the supply of goods or services or both, whether by the recipient or by any other person but shall not include any subsidy given by the Central Government or a State | has been paid or payable for the supply of goods or service. jnterpreted by the
wording “in respect of, in response to”} Further the part of definition prescribes that |
| Government; | any advance payment made for the supply of goods or service would be taxable under |
| GST Law. | |
| b) The monetary value of any act or | The Second part covers the act or |
| forbearance, in respect of, in response to, or | forbearance of receipts of goods or service |
| for the inducement of, the supply of goods | such as penalty paid for earlier termination |
| or services or both, whether by the recipient or by any other person but shall not include any subsidy given by the Central | of contract of sale. |
| Government or a State Government: |
Provided that a deposit given in respect of the supply of goods or services or both shall not be considered as payment made for such supply unless the supplier applies such deposit as consideration for the said supply
4.3.3. Meaning of Person {Clause 84 of Section 2}
Person” includes—
a. An individual;
b. A Hindu Undivided Family;
c. A company;
d. A firm;
e. A Limited Liability Partnership;
f. An association of persons or a body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, in India or outside India;
g. Any corporation established by or under any Central Act, State Act or Provincial Act or a Government company as defined in clause (45) of section 2 of the Companies Act, 2013;
h. Any body corporate incorporated by or under the laws of a country outside India;
i. A co-operative society registered under any law relating to co-operative societies;
j. A local authority;
k. Central Government or a State Government;
l. Society as defined under the Societies Registration Act, 1860;
m. Trust; and
n. every artificial juridical person, not falling within any of the above
The aforesaid definition is in align with the definitions of person under the various Statutory Act.
4.4.0 “Import of Service” {Section 3(1)(b)}
Clause 11 of Section 2 of IGST Act provides that the supply of any service shall be treated as an “IMPORT OF SERVICE” if
a) The supplier of service is located outside India.
b) The recipient of service is in India.
c) The place of supply of service is in India and
Hence importation of service for a consideration and whether or not in course of or furtherance of business would be treated as supply. Person importing the service even for personal consumption would be treated as taxable person and liable to pay GST under reverse charge mechanism subject to threshold limit. Person shall pay IGST as it would be treated as Inter –State supply. {Further discussion in IGST Act}
4.5.0– A supply specified in Schedule I made or agreed to be made without consideration {Section 3(1) (c)}
1. Permanent Transfer or disposal of Business Assets:
When business assets are transferred (delivery) from one person to another person without the intention or requirement to receive back the said goods.
2. Supply of goods or service or both between related persons or distinct persons as specified in Section 25 when made in the course or furtherance of business. Provided that gift not exceeding Fifty Thousand rupees in value in a financial year by an employer to an employee shall not be treated as supply of goods or service or both.
Meaning of Related Person
For the purposes of this Act,––
1. Persons shall be deemed to be “related persons” if––
a. Such persons are officers or directors of one another’s businesses;
b. Such persons are legally recognised partners in business;
c. Such persons are employer and employee;
d. Any person directly or indirectly owns, controls or holds twenty-five per cent or more of the outstanding voting stock or shares of both of them;
e. One of them directly or indirectly controls the other;
f. Both of them are directly or indirectly controlled by a third person; .
g. Together they directly or indirectly control a third person; or they are members of the same family
2. The term “person” also includes legal persons;
3. Persons who are associated in the business of one another in that one is the sole agent or sole distributor or sole concessionaire, howsoever described, of the other, shall be deemed to be related.
Now the questions raises
1. whether perquisites such as a rent free accommodation forming the part of remuneration provided by Employer to employee would be taxable under GST Law {Detailed discussion with input tax credit)
Meaning of Distinct Person
1. A person who has obtained or is required to obtain more than one registration, whether in one State or Union territory or more than one State or Union territory shall, in respect of each such registration, be treated as distinct persons for the purposes of this Act {transaction between one business vertical with another in one state or Union Territory} {Sub Section 4 of Section 25)
2. Where a person who has obtained or is required to obtain registration in a State or Union territory in respect of an establishment, has an establishment in another State or Union territory, then such establishments shall be treated as establishments of distinct persons for the purposes of this Act {Branch Offices of same person in different state) {Sub Section 5 of Section 25)
3. Supply of goods—
a. By a principal to his agent where the agent undertakes to supply such goods on behalf of the principal; or
b. By an agent to his principal where the agent undertakes to receive such goods on behalf of the principal
4. Import of Service by a taxable person from a related person or from of his other establishments outside India, in the course or furtherance of business and would taxable on reverse charge basis.
4.6.0— Schedule II: Matters to be treated as Supply of Goods or Supply of Service
| S.No. | Nature of Transaction | Supply of Goods or Service |
| 1. | Transfer of Title of Goods along with possession (Sales Transaction) |
Supply of Goods |
| Explanation
Transfer of tile means change in ownership from one person to another person, where transferor has no right over the goods transfer such as sale transaction in which seller transfer the ownership in goods to buyer |
||
| 2. | Transfer of possession of goods without the transferring the title of goods (Leasing of Assets) | Supply of Service |
| Explanation
Lease of assets in which lessor transfer the beneficial ownership /interest in goods to lessee is transaction of providing the service, Meaning of Lease can be interpreted by AS -19. |
||
| 3 | Transfer of title of goods at stipulate future date only after the payment of entire
consideration as agreed (Hire purchase |
Supply of Goods |
| Explanation
Under Hire Purchase Transaction, the buyer is leasing the goods and does not obtain ownership until the full amount of the contract is paid. |
||
| 4. | Leasing, Renting, tenancy, easement, license to occupy Land and Building | Supply of Service |
| Explanation
It is important to understand the meaning of terms used as above and try to find the difference in the different term Lease A lease has a set term, such as three years or five years, during which the tenant agrees to rent the property. During that time (also known as the duration of the lease), the tenant and the landlord must adhere to the agreement Neither party can change any terms of the agreement until the lease expires, unless both parties agree to the change. A tenant can’t vacate the property without breaking their lease, in which case they can be held liable for the rest of the rent due under the lease, or can be required to find someone else to take over the lease. Tenancy Agreement Rental agreements are month to month, with no set period of residence. At the end of each 30-day period, both you and your tenant are free to change the rental agreement (subject to any rent control laws) |
||
| Easement
The right to use the real property of another for a specific purpose. The assessment is itself a real property interest but the legal title to the underlying land is retained by the original owner for all other purposes. License Permission or freedom to do what you want; an official document that gives you permission to own, do or use something usually after you have paid money and or taken a test. |
||
| 5. | Any Lease or renting building including
Industrial, Commercial or Residential Building or Complex for business or commerce either wholly or partly is a supply of service |
Supply of Service |
| 6. | Job Work i.e. any treatment or process applied on another person |
Supply of Service |
| 7. | Where goods forming part of the assets of a business are transferred or disposed of by or under the directions of the person carrying on the business so as no longer to form part of those assets, whether or not for a consideration | Supply Goods |
| Explanation
This means where any capital asset or goods held for trading purpose held by Taxable Person is transferred or disposed of on permanent basis with or without the consideration is considered as supply of goods. Goods forming the part of the assets transferred as gift shall be deemed as transferred and taxable as supply of goods even no consideration is charged. Disposal of capital assets (machinery} as scarp is considered as supply of goods. |
||
| 8 | Where, by or under the direction of a person carrying on a business, goods held or used for the purposes of the business are put to any private use or are used, or made available to any person for use, for any
purpose other than a purpose of the business, whether or not for a consideration, the usage or making available of such goods |
Supply of Service |
| Explanation
When a company gives a car to its employee for personal use is covered under this clause. |
||
| 9. | Where a taxable person cease to be taxable | Supply of Goods |
| person, then goods held by him immediately before cessation; unless—
(i) the business is transferred as a going concern to another person; or (ii) the business is carried on by a personal representative who is deemed to be a taxable person |
||
| Explanation
Where a taxable person closes its business due to any reason like heavy losses or business, then any assets (other than immovable property) held by such person would be taxable as supply of goods. |
||
| 10. | Renting of Immovable Property | Supply of Service |
| Explanation
Meaning of immovable property has not been defined under GST Law. However as per Section 2(90)(a) of Finance Act 1994 “Renting of Immovable Property” includes renting, letting, leasing, licensing or other similar arrangements of immovable property for use in the course or furtherance of business or commerce but does not include — (i) Renting of immovable property by a religious body or to a religious body; or (ii) Renting of immovable property to an educational body, imparting skill or knowledge or lessons on any subject or field, other than a commercial training or coaching centre. Explanation1. – For the purposes of this clause, “for use in the course or furtherance of business or commerce” includes use of immovable property as factories, office buildings, warehouses, theatres, exhibition halls and multiple-use buildings. Explanation2.- For the removal of doubts, it is hereby declared that for the purposes of this clause “renting of immovable property” includes allowing or permitting the use of space in an immovable property, irrespective of the transfer of possession or control of the said immovable property . Under the Service Tax Act, only commercial property is covered under Service Tax preview. However no explanation has been given to include only commercial property under GST Law. Hence both commercial and residential properties are covered under GST Law. Meaning of Immovable Property: Immovable Property includes land, benefits to arise out of land, and things attached to the earth or permanently fastened to anything attached to the earth. |
||
| 11. | Construction of a complex, building, civil | Supply of Service |
| structure or a part thereof, including a complex or building intended for sale to a buyer, wholly or partly, except where the entire consideration has been received after
issuance of completion certificate, where required, by the competent authority, or after its first occupation, whichever is earlier |
||
| Explanation
Explanation.—For the purposes of this clause— (1) The expression “competent authority” means the Government or any authority authorised to issue completion certificate under any law for the time being in force and in case of non-requirement of such certificate from such authority, from any of the following, namely:— (i) An architect registered with the Council of Architecture constituted under the Architects Act, 1972; or (ii) A chartered engineer registered with the Institution of Engineers (India); or (iii) A licensed surveyor of the respective local body of the city or town or (2) The expression “construction” includes additions, alterations, replacements or remodelling of any existing civil structure. Under the present Section of 66E(b) of Service Tax: Construction of a complex, building, civil structure or a part thereof, including a complex or building intended for sale to a buyer, wholly or partly, except where the entire consideration is received after issuance of completion-certificate by the competent authority. There is one difference in present situation and situation described under GST Law, Under the Present situation, service tax would not be applicable if entire |
||
| consideration is received after the issuance of completion certificate by the competent | ||
| authority | the Proposed Law, GST would not be applicable if the entire | |
| Under | ||
| consideration is received either | or | |
| 1. After the issuance of completion certificate | ||
| 2. First occupation whichever is earlier | ||
| This means if first occupancy is proved before the issuance of competent authority, even then there is no applicability of GST.
Meaning of Terms used above: a) Construction The creation of an abstract entity. |
||
| b) Building
A relatively permanent enclosed construction over a plot of land,having a roof and usu ally windows and often more than one level, usedfor any of a wide variety of activities, as living, entertaining, or manufacturing. c) Complex Composed of many interconnected parts; compound; composite. |
||
| 12. | Work Contract including the transfer of
property in goods whether as goods or in other some form involved in execution of work contract |
Supply of Service |
| Explanation
As per Section 2(119): Work Contract means a contract for building, construction, fabrication, completion, erection, installation, fitting out, improvement, modification, repair, maintenance, renovation, alteration or commissioning of any immovable property wherein transfer of property in goods (whether as goods or in some other form) is involved in the execution of such contract. In present indirect systems, both vat and service tax are applicable on work contract. This double taxation has come to end in New Tax Regime, where it is specifically considered as work contract. Meaning of Terms used in above a) Fabrication: To make by assembling parts or sections b) Erection Put together and set upright. c) Commissioning Bring (something newly produced) into working condition. |
||
| 13. | Temporary transfer or permitting the use or enjoyment of any intellectual property right; | Supply of Service |
| Explanation
Meaning of Intellectual Property Right The term of Intellectual Property Right is not defined under GST Law. However as per Section 65(55a) of Finance Act 1994: Intellectual property right” means any right to intangible property, namely, trademarks, designs, patents or any other similar intangible property, under any law for the time being in force, but does not include copyright. Meaning of Intellectual Property Service As per Section 65(55b) of Finance Act 1994: |
||
4.6.0 Intellectual property service” means: (a)Transferring, temporarily, or (b)Permitting the use or enjoyment of, any intellectual property right
Now first question arises, whether Intellectual Property is :Goods Or Services: The Proposed GST Law doesn’t provide any specifically guideline about this.
The definition of Goods covers all kind of movable property, whereas Service means anything other than goods, money and securities.
In common parlance “Movable Property means any property of description other than immovable property. In common parlance personal property is generally considered property that can be movable. In civil law systems, personal property is often called movable property i.e. property that can be moved from one location to another.
Personal Property can be described into variety of way i.e. tangible property or intangible property
Tangible Property
Tangible personal property refers to any type of property that can generally be moved, touched or felt.
Intangible Property
As per AS -26 issued by ICAI “An intangible asset is an identifiable non-monetary asset, without physical substance, held for use in the production or supply of goods or services, for rental to others, or for administrative purposes” It represent something of value such as negotiable instruments, securities.
Intangible asset is also considered as movable property and hence considered as Goods
The aforesaid clause covers only temporary transfer of intangible asset as supply of service. In case of permanent transfer, such sale shall be considered as sale of goods and would be taxable accordingly.
Example of Intellectual Property
1. Patent
A patent is a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for detailed public disclosure of an invention. An invention is a solution to a specific technological problem and is a product or a process. Inventors and designers file for patents. A patent protects inventions with a new or improved function. This includes machines, processes, or chemical compositions, or the design for some product.
2. Copyright
Copyright is a legal right created by the law of a country that grants the creator of an original work exclusive rights for its use and distribution. This is usually only for a limited time. The exclusive rights are not absolute but limited by limitations and exceptions to copyright law, including fair use. A major limitation on copyright is that copyright protects only the original expression of ideas, and not the underlying ideas
| themselves. Copyrights extend beyond copyright laws copyright laws
c) Trademark Business and symbol, design, from others in by providing nationwide exclusive case calls for valid for an unlimited d) Design Design is the or measurable |
are considered territorial rights, which means that they do not the territory of a specific jurisdiction. While many aspects of national have been standardized through international copyright agreements, | |
| vary by country.
product owners file for a trademark. It protects |
a name, word, slogan,
and distinguishing it the rights of a person It is proof enough of a sue an infringer if the Though a trademark is 1 0 years. of an object, system blueprints, engineering |
|
| and/or image identifying a business or brand the same field. Registering a trademark enhances legal evidence and public notice of ownership.
right to the mark and allows the holder to it. Registered trademarks can use the ® symbol. |
||
| period of time, it must be renewed every
creation of a plan or convention for the construction |
||
| human interaction (as in architectural | ||
| processes, circuit diagrams, and sewing patterns). Design has | ||
| different connotations the direct construction and graphic design) | in different fields (see design disciplines below). In some cases, | |
| of an object (as in pottery, engineering, management, coding, | ||
| is also considered to use design thinking | ||
| 14. | Agreeing to the obligation to refrain from an act, or to tolerate an act or a situation, or to do an act; and | Supply of Service |
| 15. | Transfer of the right to use any goods for any purpose (whether or not for a specified period) for cash, deferred payment or other valuable consideration | Supply of Service |
| Explanation
The applicability of this clause would be restricted to the situation whereas only transfer of the right to use any goods without transferring the effective control in goods. In case whereas effective control would be transferred even at later date would be considered as supply of goods. |
||
| 16 | Composite supply
The following composite supplies namely:— (a) works contract as defined in clause (119) of section 2; and (b) supply, by way of or as part of any service or in any other manner whatsoever, of goods, being food or any other article for |
Supply of Service |
| human consumption or any drink (other than alcoholic liquor for human
consumption), where such supply or service is for cash, deferred payment or other valuable consideration |
||
| 17 | Supply of goods by any unincorporated association or body of persons to a member thereof for cash, deferred payment or other valuable consideration | Supply of Goods |
4.6.0. ACTIVITIES OR TRANSACTIONS WHICH SHALL BE TREATED NEITHER AS A SUPPLY OF GOODS NOR A SUPPLY OF SERVICES
1. Services by an employee to the employer in the course of or in relation to his employment.
2. Services by any court or Tribunal established under any law for the time being in force.
3. (a)
a) The functions performed by the Members of Parliament, Members of State Legislature, Members of Panchayats, Members of Municipalities and Members of other local authorities;
b) The duties performed by any person who holds any post in pursuance of the provisions of the Constitution in that capacity; or
c) The duties performed by any person as a Chairperson or a Member or a Director in a body established by the Central Government or a State Government or local authority and who is not deemed as an employee before the commencement of this clause.
4. Services of funeral, burial, crematorium or mortuary including transportation of the deceased.
5. Sale of land and, subject to clause (b) of paragraph 5 of Schedule II, sale of building.
6. Actionable claims, other than lottery, betting and gambling.
Explanation.—For the purposes of paragraph 2, the term “court” includes District Court, High Court and Supreme Court.
4.7.0 In nutshell , In order to constitute the supply following elements should be satisfied:
a) Supply of Goods or Services i.e. it should involve the delivery of goods or service or both to another person.
b) Supply should be made for a consideration i.e. supply should be made for quid- Its means supply should be made for something in return from the recipient of goods or service or both to supplier of goods or services. It is important that something in return should be money, or money’s worth.
c) Supply is made in the taxable territory;
d) Supply is made a taxable person. {Taxable person shall have the meaning as assigned to it in Section 9 of this Act)
e) Supply is made in the course of or furtherance of business. Following guiding principles should be applied to find out whether a transaction(supply) has been made in the course of or furtherance of business:
(i) The activity should predominately undertake to make a taxable supply for profit motive or consideration.
(ii) The activity should be undertaken on sound and recognised business manner on regular manner.
(iii) The activity should be pursued with reasonable or recognizable
(iv) The activity should be undertaken by an earnest undertaking.
(v) The occasional supply even if made for consideration will not be considered as supply i.e. if any assets purchases for personal use, and sale that at later date, would not be considered as supply.
f) Transfer of property in goods from the supplier to recipient is necessary. It is important to mention here that in normal circumstances both title and possession have to be transferred for a transaction to be considered as a supply. In cases where the title in goods is transfer at later date even possession has been transferred at earlier date like, goods sent on return approval basis or hire purchase agreement, such transaction will have to be termed as supply of goods.





Sir, how’s advance payment cover under GST and its fall under the meaning of supply!?