Explore simplified provisions of E-Way Bill system under CGST Act. Understand rules, procedures, and compliance. Get insights into the E-Way Bill’s 5th anniversary journey, covering over 353 crore bills. Learn about E-Way Bill generation, validity, exceptions, and blocking scenarios. Stay compliant with E-Way Bill regulations.
The journey of the E-way Bill began on April 1, 2018, marking its 5th Anniversary in April 2023. Over the course of the past four years, more than 353 crore E-Way Bills have been issued. Throughout its existence, the E-Way Bill system has undergone numerous changes and amendments to its rules and portal. As time has passed, taxpayers have become familiar with the E-Way Bill rules, processes, and procedures, allowing for smoother operations.
The E-Way Bill is a mandatory electronically generated document as per Section 68 of the CGST Act’ 2017, in conjunction with rules 138, 138A, 138B, 138C, 138D, and 138E. It is required for the movement of goods valued at more than Rs. 50,000, with certain exceptions. Each consignment to be transported is assigned a unique E-Way Bill number (EBN), and the validity of this EBN depends on the distance of goods transportation. To ensure compliance, authorized officers may intercept vehicles at designated check posts to verify the necessary documents. Additionally, specific inputs on tax evasion may lead to a physical verification of the vehicle. In this article, we will provide a summary of the provisions related to the E-Way Bill system.
Electronic Way Bill (E-Way Bill): E-Way bill is an electronic document which is required for movement of goods through motorised conveyances. https://ewaybillgst.gov.in
- It facilitates faster movement of goods.
- It eliminates the state boundary check-posts being a digital interface.
- To generate e-way bill a person needs to register on GST portal and e-way bill portal and also from E-Invoice Portal.
- If unregistered transporter is generating e-way bill, he is required to be enrolled to be enrolled on e-way bill portal to get 15-digit unique transporter id.
- If a transporter is registered for GST in many States, he may apply for unique common enrolment number in a prescribed form.
- Once a unique common enrolment number is generated, transporter cannot use his GSTIN for generating the e-way bill for transportation purpose.
The registered person who causes movement of goods of consignment value exceeding Rs.50,000/-, is required to generate e-way bill in Part A of of EWB-01 before commencement of such movement.
Consignment value excludes the exempt supply of goods if the invoice is issued for both taxable as well as exempted goods.
Generation of e-way bill [Rule 138]: “Information to be furnished prior to commencement of movement of goods and generation of e-way bill”
- E-way bill contains two part A & B.Part A contains details about invoice and goods and Part-B contains details about transporter.
- E-way bill can be generated only after entering the details of Part-B.
- A registered person whether supplier or recipient is Primary responsible person to generate e-way bill.
- If e-way bill not generated by the registered persons then transporter shall generate the same.
- EWB may also be generated voluntary if value does not exceed Rs.50,000/-
- EWB part B is not mandatory if Goods transported up to a total distance of 50 km within a State from the consignor place to transporter place for further transportation or from transporter place to consignee place of business.
- If the goods transferred from one conveyance to another conveyance, then transporter shall update the Part-B in e-way bill before further movement.
- If goods are transported in more than one vehicle on single invoice, then transporter need to update Part-B using multi-vehicle option.
- The consignor or recipient or transporter may assign the e-way bill number to another person to update Part-B.
- After e-way bill is generated, where multiple consignment need to be sent in one conveyance, the transporter may indicate serial number for each e-way bill generated for each consignment and may also generate a consolidated e-way bill in EBW-02.
- If goods are transported through e-commerce operator or courier agency, then part-A may be furnished by e-commerce operator or courier agency.
- E-Way bill generation in case of transport of goods railways or by air or vessel – Where the goods are transported by the railways or by air or vessel, E-Way Bill shall be generated by the registered person, being the supplier or the recipient, who shall, either before or after the commencement of the movement, furnish, on the common portal, the information in Part B of FORM GST EWB-01. Provided that where the good are transported by the railways, the railways shall not deliver the goods if the e- way bill required under these rule is not produced at the time of delivery.
- If e-way bill needs to be cancelled due to any reason, then it may be cancelled within 24 hours from generation of e-way bill.
- Further, e-way bill cannot be cancelled if it has been verified in the transit.
- E-way Bill number will be valid for 15 Days for updating of Part-B.
- If person “A” orders to person “B” to deliver material directly to Person “C” on his behalf, it is called “Bill-To-Ship To” model. In ‘Bill-to-Ship to’ model, only one e-way bill will be required either by ’A’ or ‘B’.
- The linking between the E-Way Bill and GSTR-1 is established through the availability of information provided in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 on the common portal. This information is accessible to the registered supplier, who can utilize it for furnishing details in FORM GSTR-1. However, in the case of an unregistered supplier furnishing information in FORM GST EWB-01, they will be electronically notified if their mobile number or email is available.
- It is important to note that the E-Way Bill generated under this rule, or under rule 138 of the Goods and Services Tax Rules of any State, holds validity across all States and Union territories. This ensures that the E-Way Bill can be used seamlessly for the movement of goods throughout the country, regardless of the specific State or Union territory.

Compulsory e-way bill [3rd and 4th proviso to Rule 138(1)]:
(a) Where goods are sent by a principal located in one State to a job worker located in any other State, the E-Way Bill shall be generated by the principal irrespective of the value of the consignment.
(b) When an unregistered person sends handicraft goods from one State to another ,irrespective of value.
Validity period of e-way bill [Rule 138(10)]:
Up to 200 km – One day except dimensional Cargo or multi modal shipment.
For every 200 km or part thereof- One additional day in case of dimensional Cargo or multi modal shipment. Up to 20 km- One day in case of dimensional Cargo or multi model shipment.
For every 20 km or part thereof – One additional day in case of dimensional Cargo or multi modal shipment. (Vide Notification No.94/2020-Central Tax, dt.22-12-2020, w.e.f.01-01-2021 and Notification No.31/2019-Central Tax,dt.28-06-2019, w.e.f. 28-06-2019)
Note:- Validity will be counted from the relevant date and relevant date hereby means the day on which e-way bill has been generated and each day shall be counted as the period expiring at midnight of the day immediately following the date of generation of e-way bill.
The Validity of the e-way bill can be extended within 8 hours from the time of its expiry in case of unavoidable circumstances like natural calamity,accident of vehicle etc. after updating details in Part-B of EWB-01. Information in Part-A of EWB-01 is made available to registered person of recipient of goods who shall communicate his approval or rejection of the consignment.
E-way bill is not required in case of following goods [Section 68 r/w rule 138(14):- In this rule, no e-way bill is required to be generated-
a) LPG Supply to household and non-domestic exempted customer.
b) Kerosene oil under PDS
c) Natural or precious stones and metals
d) Postal baggage by postal department
e) Jewellery and other gold, silversmith items, Currency and personal household goods.
f) Goods are being transported by non-motorized vehicle
g) Goods are being transported from the custom port, airport, air cargo complex and land custom station to ICD or container freight station and vice versa
h) Exempted goods, other than de-oiled cake
i) Alcoholic liquor for human consumption, petroleum crude, high speed diesel, petrol, natural gas or aviation turbine fuel.
j) Supply under schedule III of CGST Act
k) Goods are being transported are transit cargo from or to Nepal or Bhutan
l) Any movement of goods by Ministry of defence as a consignor or consignee
m) Supply of heavy water by Atomic Energy to NPCIL
n) Where consignor is Central, State or local Government or authority for transportation of goods by rail.
o) Empty cargo containers
p) Goods transported up to a distance of 20 Km from the place of business of the consignor to a weighbridge and back
q) Empty cylinders for packing LPG for a reason other than supply.
r) Goods being transported are Specified in Annexure.
Documents to be carried by A Person-in-charge of a conveyance[Rule 138A]: The person in charge of the vehicle should carry the following documents:
1. Tax Invoice, bill of supply, delivery challan as required,
2. A copy of E-Way Bill, E-Way Bill number or E-Way Bill mapped to a Radio Frequency Identification Device, RFID
3. In case of e-invoice, IRN may also be provided to the proper officer.
As per provisions of Rule 138A in case of imported goods, the person in charge of a conveyance shall also carry a copy of the bill of entry filed by the importer of such goods.
Availability of generated E-Way Bill details[Rule 138(11)]: The details of E-Way Bill generated under sub-rule shall be made available to the recipient, if registered, on the common portal, who shall communicate his acceptance or rejection of the consignment covered by the E-Way Bill. The details of E-Way Bill generated under sub-rule shall be made available to the shall be made available to the supplier, if registered, on the common portal, who shall communicate his acceptance or rejection of the consignment covered by the E-Way Bill.
Rule 138 (12): Where the recipient referred to in sub-rule (11) does not communicate his acceptance or rejection within 72 hours of the details being made available to him on the common portal or the time of delivery of goods whichever is earlier, it shall be deemed that he has accepted the said details.
Verification of documents and conveyance [Rule 138B]: Jurisdictional commissioner may authorize the proper officer to verify e-way bill and other relevant documents in regards to movement of goods through conveyance. Where e-way bill is mapped with the RFID device then verification will be done through such device.
Inspection and verification of goods[Rule138C]: Proper officer shall record the summary report of every inspection of goods in transit in Part-A of a prescribed form GST EWB-03 with in 24 hours and final report in Part B within 3 days of inspection.
The commissioner may (on sufficient casue being shown) extend the final reporting time for further period not exceeding 3 days.
The above mentioned period shall be counted from the midnight of the date on which the vehicle was inspected. If verification of conveyance has been done in one state/territory, then no further verification will be carried out in respect of that conveyance unless any specific information relating to evasion of tax is made available subsequently.
Facility for uploading information regarding detention of vehicle [Rule 138D]:Where a vehicle has been intercepted and detained for a period exceeding 30 minutes, the transporter may upload the said information in FORM GST EWB-04 on the common portal.
Blocking of E-Way Bill[Rule 138E]:Restriction on furnishing of information in PART-A of FORM GST EWB01
On Blocking of e-way bill, taxpayer will not be able to generate e-way bill. Following are cases in which e-way bill will not be generated:
a) Composition dealer has not furnished his return for 2 consecutive quarters.
b) A regular scheme dealer has not furnished his return for 2 consecutive tax period.
c) A regular scheme dealer has not furnished his outward supply statement (GSTR-1) for 2 consecutive tax period/quarters.
d) A person whose registration has been suspended.
Jurisdictional commissioner on receipt of an application in form EWB-05 from a registered person, may allow by an order in EWB-06 to generate e-way bill subject to conditions and restrictions.
E-Way Bill- Generate Facility on E-Invoice Portal: https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in
This option is used to generate the e-Way Bill for already generated e-invoice. To generate a e-Way Bill, user needs to select the sub option ‘Generate e-Way Bill’ option under ‘e-Way Bill’ option in menu. On clicking this option, the below screen will be displayed.
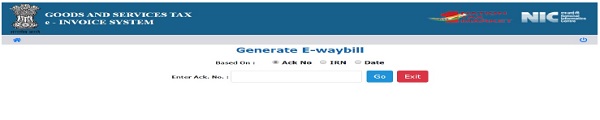
Next, the user has to select and enter the Ack No. or IRN or Date of e-invoice as per the availability and clicks go. System will display the Part A EWB details and prompts user to enter the details of transportation under ‘e waybill Details’. Here the user will first enter the transporter name, transporter ID and approximate distance (km) to be covered by the shipment.

The e-waybill system will Auto – calculate and display the estimated motorable distance between the supplier and recipient addresses as per the PIN codes entered in e-invoice entry form. User is also allowed to enter the actual distance as per the movement of goods. However, it will be limited to +/-10% more than the auto calculated distance displayed. In case, the PIN Code of both source and destination are same, the user is allowed to enter distance up to a maximum of 1 to 100 KMs only. The user has to select the mode of transportation – road, rail, air or ship and vehicle type.
Next he has to update the vehicle no. and transporter doc no. and date.
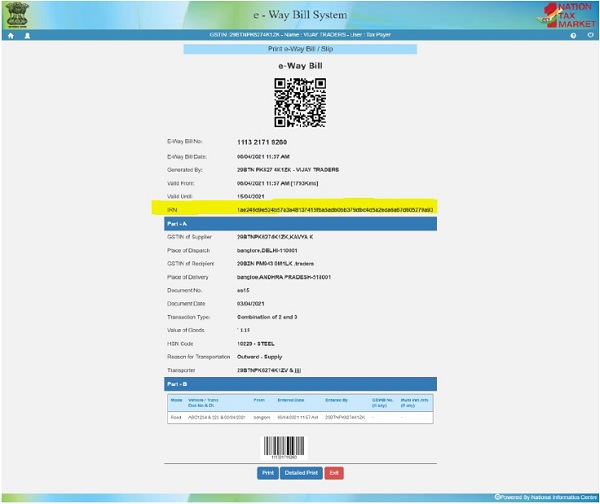
Once a request for EWB is submitted, the system validates the entered values and pops up appropriate message if there is any error. Otherwise the system generates the EWB with unique 12 digit number.
Note:- The e-Waybills generated in the e-invoice portal will be reflected in the e-waybill system. To Update Part B details, cancel or extend, you may login to e-waybill system with same credentials. The user can take the print out of the EWB using the ‘Print’ option provided.
If e-waybill is generated from the e-Invoice portal, then IRN information is also shown in the e-waybill print.
To conclude this article, It is important to understand the provisions on E-Way Bill. Once a taxpayer is caught non-complying with the e-way bill provisions, GST authorities keep tracking his/her movement of consignment. Therefore each and every taxpayer should take care before movement of goods, generate correct e-way bill and handover to vehicle along-with invoices and delivery challans and complete the transaction in proper manner. Taxpayer is also maintain the proper record and reconciliation of E-way bill with GSTR-1 Return.
*****
DISCLAIMER: This publication is merely a general guide meant for knowledge purposes only. All the references or content are for educational purposes only and do not constitute a legal advice. We do not accept any liabilities whatsoever for any losses caused directly or indirectly by the use/reliance of any information or conclusion contained in this publication. Prior to acting upon this publication, you’re suggested to seek the advice. This work is entirely in the interest of profession and to contribute into my beloved subject of GST.






thanks for usefull article. please also explain the ruling and process for import good from port to factory and export from factory to port.
Sir, Select Option Inward-Import in Supply Type for Import of goods and mention B/E No and Date and for Export Select Outward- Export type for export of goods and mention Tax Invoice no and date. Also selecting Transaction Type “Bill from & Dispatch from’ option in both cases and with using Port Address.