In the GST regime, there is uniform penalty and prosecution provision for similar type of offence that may be committed by a registered person, depending upon its severity.
The word penalty is not defined in the GST Law, but as an English word it means punishment (in this case monetary as well as prosecution) given to a person for some wrongdoing. In the context of the GST law, contravention of the provisions of the law would attract a penalty(s).

Penalty is expected to be an area where the law will develop significantly to encourage voluntary compliance.
What is meant by the term penalty?
The word “penalty” has not been defined in the CGST/SGST Act, but judicial pronouncements and principles of jurisprudence have laid down that a penalty is:
(i) a temporary punishment or a sum of money imposed by statute, to be paid as punishment for the commission of a certain offence;
(ii) a punishment imposed by law or contract for doing or failing to do something that was the duty of a party to do.
Any breach of law/act is an offence. Accordingly, punishment for committing an offence is ‘Penalty’. The present article covers the provisions relating to penalty under GST Act’17 with section wise summarized penalties chart.
Penalty for certain Offences by a Taxable Person: Section 122(1) of the CGST Act- As per the provisions of sub-section (1) of section 122, there are 21 offences, for which a taxable person may be held liable to penalty. The list of offences punishable are summarized hereunderi.
i. Supply of goods or services or both without issue of any invoice or issues an incorrect or false invoice with regard to any such supply,
ii. Issuance of any invoice or bill without actual supply of goods or services or both,
iii. Collecting any amount as tax but failing to pay the same to the Government beyond a period of three months from the date on which such payment becomes due,
iv. Collecting any tax in contravention of the provisions of this Act and failing to pay the same to the Government beyond a period of three month from the date on which such payment becomes due,
v. Failing to deduct the tax at source or deducting lesser tax or failing to pay deducted tax to Government account.
vi. Failing to collect tax at source or collecting lesser tax or failing to pay collected tax to Government account.
vii. Taking or utilizing input tax credit without actual receipt of goods or services or both either fully or partially,
viii. Fraudulently obtaining refund,
ix. Taking or distributing input tax credit in contravention of Section 20, or the rules made thereunder,
x. Falsifying or substituting financial records or producing fake accounts or documents or furnishing any false information or return with an intention to evade payments of tax due under this Act,
xi. Failing to obtain registration under this Act,
xii. Furnishes any false information with regard to registration particulars, either at the time of applying for registration, or subsequently,
xiii. Obstructing or preventing any officer in discharge of his duties,
xiv. Transporting any taxable goods without the cover of prescribed documents,
xv. Suppressing turnover leading to evasion of tax,
xvi. Failing to keep, maintain or retain books of account and other documents in prescribed manner,
xvii. Failing to furnish information or documents called for by an officer or furnishing false information or documents,
xviii. Supplies, transporting or storing any goods which he has reasons to believe are liable to confiscation,
xix. Issuing any invoice or document by using the registration number of another registered person,
xx. Tampering with, or destroying any material evidence or documents,
xxi. Disposing off or tampering with any goods that have been detained, seized or attached under this Act.
For any of the above offences, the taxable person shall be liable to pay higher of the following amount as a penalty-
A. INR 10,000/- or
B. An amount equivalent to,any of the following (applicable as the case may be)-
i. Tax evaded; or
ii. Tax not deducted under section 51 or short deducted or deducted but not paid to the Government; or
iii. Tax not collected under section 52 or short collected or collected but not paid to the Government; or
iv. Input tax credit availed of or passed on or distributed irregularly; or
v. Refund claimed fraudulently
In section 122 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, after sub-section (1), the following sub-section shall be inserted, namely: — (w.e.f.1-1-2021 vide Notification No.92/2020-C.T.,dated 22-12-2020)
“(1A) Any person who retains the benefit of a transaction covered under clauses (i), (ii), (vii) or clause (ix) of sub-section (1) and at whose instance such transaction is conducted, shall be liable to a penalty of an amount equivalent to the tax evaded or input tax credit availed of or passed on.”. This section 122 is applicable to a taxable person is define in section 2(107) “Taxable person” as a person who is registered or liable to be registered under section 22 or section 24. Therefore, all the provisions of Section 122 would also be applicable to those who have not taken registration but are liable to do so.
Penalty for certain Offences by a Registered Person: Section 122(2) of the CGST Act- As per the provision of Sub-Section (2) of Section 122, any registered person-
(i) Who supplies any goods or services or both on which any tax has not been paid or short-paid or erroneously refunded, or
(ii) Where the input tax credit has been wrongly availed or utilized,-
The defaulter would be liable to pay penalty as under –
| (a) For any reason,other than the reason of fraud or any wilful misstatement or suppression of facts to evade tax | Shall be liable to a penalty for an amount equal to –
(a) Rs.10,000/- or (b) 10% of the tax due from such person Whichever is higher |
| (b) For reason of fraud or any wilful misstatement or suppression of facts to evade tax | Shall be liable to a penalty for an amount equal to-
(a) Rs.10,000/- or (b) Tax due from such person Whichever is higher |
Example : Mr. Mohan is the proprietor of two firm’s M/s Mohan Enterprises and M/s Sunny Marketing and he has taken GST registration in his name mentioning only M/s Mohan Enterprises as trade name and is showing the turnover of only M/s Mohan Enterprises. He is caught by the GST department for not showing turnover of his other proprietorship concern M/s Sunny Marketing. Under what Section will the department impose penalty on him?
Ans:- As he is the proprietor of both firms, he will be considered a registered person and penalty will be imposed under section 122(2).
Penalty for certain Offences by “Any Person”: Section 122(3) of the CGST Act –As per the provisions of Sub-section (3) of section 122, penalty is leviable for any of the following offences committed by a any person under the following cases, the person aiding/ abetting will be penalized up to a maximum amount of INR 25,000/-
(a) Aiding/ abetting for any of the offences listed in section 122(1) (refer above),
(b) Possessing/ concerning/ removing/ transporting/ concealing/ supplying/ dealing with goods which are liable to confiscation,
(c) Receives/ concerns/ deals with the supply of service which is in contravention of any of the provisions of the Act,
(d) fails to appear before the officer of central tax, when issued with a summon for appearance to give evidence or produce a document in an inquiry,
(e) fails to issue invoice in accordance with the provisions of this Act or the rules made there under or fails to account for an invoice in his books of account,
This Sub-section deals with offences where the person is not directly involved in any evasion of tax but may aid or abet or may be a party to evasion or if he does not attend summons or produce documents. Penalty in such a case will be up to twenty-five thousand rupees.
Example: A warehouse owner who provides warehouse services to multiple clients and keeps proper records of all the goods stored except for one of the clients knowing well that this client is involved in tax evading activities, will be held liable for abetting an offence punishable under the GST law, and penalty up to twenty-five thousand will be imposed on him.
Penalty for failure to furnish information return: Section 123 of the CGST Act –
If a person who is required to furnish an information return under section 150 fails to do so within the period specified in the notice issued under sub-section (3) thereof, the proper officer may direct that such person shall be liable to pay a penalty of one hundred rupees for each day (Rs.100/-) of the period during which the failure to furnish such return continues:
Provided that the penalty imposed under this section shall not exceed five thousand rupees (Rs.5,000/-)
Section 150 requires certain class of persons to maintain records and furnish information return (IR) within a stipulated time [Sub-section (2) & (3) of Section 150] and If any person who is required to furnish any information as per Section 150, by filing an information return, fails to do so, then he will be liable to pay a penalty of ` 100/- per day for which failure continues, subject to the maximum penalty of Rs.5,000/-.
Fine for failure to furnish statistics: Section 124 of the CGST Act-
If any person required to furnish any information or return under section 151,—
(a) without reasonable cause fails to furnish such information or return as may be required under that section, or
(b) wilfully furnishes or causes to furnish any information or return which he knows to be false,
he shall be punishable with a fine which may extend to ten thousand rupees (Rs.10,000/-) and in case of a continuing offence to a further fine which may extend to one hundred rupees for each day (Rs.100/-) after the first day during which the offence continues subject to a maximum limit of twenty-five thousand rupees.(Rs.25,000/-)
General Penalty: Section 125 of the CGST Act-
Any person, who contravenes any of the provisions of this Act or any rules made thereunder for which no penalty is separately provided for in this Act, shall be liable to a penalty which may extend to twenty-five thousand rupees.
If no separate penalty is prescribed anywhere in the law for any contravention of provisions of this law, then a penalty up to Rs.25,000/- can be imposed under Section 125.
Examples : Rule 18 requires every registered person to display registration certificate and Goods and Services Tax Identification Number on the name board. If a registered person contravenes this provision, a penalty under section 125 of up to Rs.25,000/- can be imposed.
General disciplines related to penalty: Section 126 of the CGST Act-
(1) No officer under this Act shall impose any penalty for minor breaches of tax regulations or procedural requirements and in particular, any omission or mistake in documentation which is easily rectifiable and made without fraudulent intent or gross negligence.
Explanation.––For the purpose of this sub-section,––
(a) a breach shall be considered a ‘minor breach’ if the amount of tax involved is less than five thousand rupees;(Rs.5,000/-)
(b) an omission or mistake in documentation shall be considered to be easily rectifiable if the same is an error apparent on the face of record.
(2) The penalty imposed under this Act shall depend on the facts and circumstances of each case and shall be commensurate with the degree and severity of the breach.
(3) No penalty shall be imposed on any person without giving him an opportunity of being heard.
(4) The officer under this Act shall while imposing penalty in an order for a breach of any law, regulation or procedural requirement, specify the nature of the breach and the applicable law, regulation or procedure under which the amount of penalty for the breach has been specified.
(5) When a person voluntarily discloses to an officer under this Act the circumstances of a breach of the tax law, regulation or procedural requirement prior to the discovery of the breach by the officer under this Act, the proper officer may consider this fact as a mitigating factor when quantifying a penalty for that person.
(6) The provisions of this section shall not apply in such cases where the penalty specified under this Act is either a fixed sum or expressed as a fixed percentage.
Power to impose penalty in certain cases: Section 127 of the CGST Act-
Where the proper officer is of the view that a person is liable to a penalty and the same is not covered under any proceedings under section 62 or section 63 or section 64 or section 73 or section 74 or section 129 or section 130, he may issue an order levying such penalty after giving a reasonable opportunity of being heard to such person.
This section gives power to the proper officer to impose penalty, after giving a reasonable opportunity to the person who is involved in any act or omission which is otherwise not covered by any of the penalty provision under this Act.
Power to waive penalty or fee or both: Section 128 of the CGST Act-
The Government may, by notification, waive in part or full, any penalty referred to in section 122 or section 123 or section 125 or any late fee referred to in section 47 for such class of taxpayers and under such mitigating circumstances as may be specified therein on the recommendations of the Council.
This Section provides for waiver of penalty leviable under Section 122 or Section 123 or Section 125 or late fee payable under Section 47 to those classes of taxpayers or under such mitigating factors as notified by the Government.
Till now, drawing power from this Section, the government has waived off late fee on many occasions. Some of the notifications issued drawing powers from section 128 are:
1. Notification No. 50/2017-C.T., dated 24-10-2017.
2. Notification No. 74/2019-C.T., dated 26-12-2019.
3. Notification No. 04/2020-C.T., dated 10-11-2020.
Detention, seizure and release of goods and conveyances in transit: Section 129 of the CGST Act-
(1) Notwithstanding anything contained in this Act, where any person transports any goods or stores any goods while they are in transit in contravention of the provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder, all such goods and conveyance used as a means of transport for carrying the said goods and documents relating to such goods and conveyance shall be liable to detention or seizure and after detention or seizure, shall be released,––
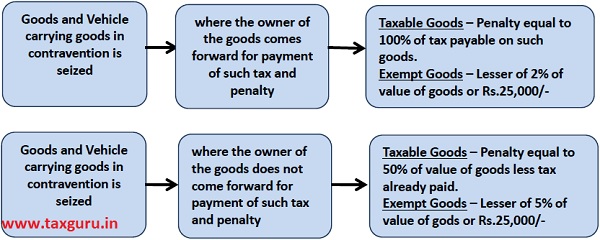
(a) on payment of the applicable tax and penalty equal to one hundred percent. Of the tax payable on such goods and, in case of exempted goods, on payment of an amount equal to two percent. of the value of goods or twenty-five thousand rupees, whichever is less, where the owner of the goods comes forward for payment of such tax and penalty;
(b) on payment of the applicable tax and penalty equal to the fifty percent. of the value of the goods reduced by the tax amount paid thereon and, in case of exempted goods, on payment of an amount equal to five percent. of the value of goods or twenty-five thousand rupees, whichever is less, where the owner of the goods does not come forward for payment of such tax and penalty;
(c) upon furnishing a security equivalent to the amount payable under clause (a) or clause (b) in such form and manner as may be prescribed:
Provided that no such goods or conveyance shall be detained or seized without serving an order of detention or seizure on the person transporting the goods.
(2) The provisions of sub-section (6) of section 67 shall, mutatis mutandis, apply for detention and seizure of goods and conveyances.
(3) The proper officer detaining or seizing goods or conveyances shall issue a notice specifying the tax and penalty payable and thereafter, pass an order for payment of tax and penalty under clause (a) or clause (b) or clause (c).
(4) No tax, interest or penalty shall be determined under sub-section (3) without giving the person concerned an opportunity of being heard.
(5) On payment of amount referred in sub-section (1), all proceedings in respect of the notice specified in sub-section (3) shall be deemed to be concluded.
(6) Where the person transporting any goods or the owner of the goods fails to pay the amount of tax and penalty as provided in sub-section (1) within seven days of such detention or seizure, further proceedings shall be initiated in accordance with the provisions of section 130:
Provided that where the detained or seized goods are perishable or hazardous in nature or are likely to depreciate in value with passage of time, the said period of seven days may be reduced by the proper officer.
Section wise summarized Penalties Chart
| Section | Type of Offence | Penalty | |
| 122(1) | Above Specified 21 offences | Rs.10,000 (or) Tax/ITC involved, whichever is HIGHER | |
| 122(2) | Other than Fraud etc., | Rs.10,000 (or) 10% of Tax/ITC involved, whichever is HIGHER | |
| Fraud etc., | Rs.10,000 (or) Tax/ITC involved, whichever is HIGHER | ||
| 122(3) | Offences where the person is not directly involved in any evasion but may be a party to evasion or if he does not attend summons or produce documents | Upto Rs.25,000 | |
| 123 | Person fails to furnish an information return u/s 150 fails to do so | Rs.100 per day (failure period) subject to a Max. Rs.5,000 | |
| 124 | Any Person required to furnish any information u/s 151 | Normal Cases – Upto Rs.10,000 Continuing offence – Rs.100 per day (failure period) subject to a Max.Rs.25,000 | |
| 125 | General Penalty | Upto Rs.25,000 | |
| 126 | No penalty for minor offences [Amount of tax/ITC involved is < Rs.5,000] which can be easily rectifiable and made without fraudulent intent or gross negligence. | ||
| 127 | Where PO is of the view that a person is liable to a penalty and the same is not covered under following proceedings, he may levy penalty after giving a reasonable opportunity of being heard.Sec.62 -Assessment of non filers of return; Sec.63- Assessment of unregistered persons; Sec.64- Summary assessment; Sec.73- Demand in case of non payment, short payment of GST or erroneous refund on account of reasons other than fraud etc.; Sec.74-Demand in case of non payment,short payment of GST or erroneous refund on account of fraud etc., Sec.129-Detention, Seizure and release of goods and conveyances in transit; Sec.130- Confiscation of goods or conveyances | ||
| 128 | Govt. may by notification, waive in part of full, any penalty referred to in Sec.122 (or) 123 (or) 125 (or) any late fee for delay in filling returns for such class of taxpayers as notified. | ||
| 129 | Release of goods and conveyance under detention or seizure | ||
| (A) Where owner comes forward for payment of tax & penalty | a) In case of taxable goods – Penalty equivalent to 100% of tax + applicable tax
b) In case of exempted goods – Penalty equivalent to 2% of the value of goods or Rs.25,000, Whichever is less |
||
| (B) Where owner does not come forward for payment of tax & penalty | a) In case of taxable goods – Penalty equivalent to 50% of value of goods+ applicable tax
b) In case of exempted goods – Penalty equivalent to 5% of the value of goods or Rs.25,000, Whichever is less |
||
| Sec. 20 of IGST Act | Penalty if leviable under CGST Act and SGST Act or the UTCGST Act | Sum total of penalties imposed under these Acts. | |
To conclude this article, It is important to understand the penalty provisions. Therefore each and every taxpayer should take care before complete the transaction in correct manner.
DISCLAIMER: This publication is merely a general guide meant for knowledge purposes only. All the references or content are for educational purposes only and do not constitute a legal advice. We do not accept any liabilities whatsoever for any losses caused directly or indirectly by the use/reliance of any information or conclusion contained in this publication. Prior to acting upon this publication, you’re suggested to seek the advice. This work is entirely in the interest of profession and to contribute into my beloved subject of GST.





