1. The objective of audit of taxpayers is to measure the level of compliance of the taxpayer in the light of the provisions of the CGST Act 2017 and the rules made there under.
1.1 Audit examines the declarations of taxpayers to not only test the accuracy of the declaration and the accounting systems that produce the declared liability, but also evaluate the credibility of the declared or assessed tax liability. The taxpayer’s anticipation of such actions has preventive and deterrent effects. The deterrent effect is the extent to which audit actions discover and stop taxpayers from continuing to under-declare or manipulate their tax liability. The preventive effect is the extent to which registered persons decide not to evade tax, because they are aware of audit activity and fear of detection by the tax auditors.
1.2 An effective audit program generally results in the discovery of under-declared liabilities either by omission, error or deliberate deception. The amount of additional revenue raised depends not only on the level of compliance by the taxpayers, but also on the effectiveness of the auditors and the audit planning and implementation. An efficient and effective audit system will assist the government in its pursuit of increasing taxpayer’s voluntary compliance and facilitate the tax administration’s aim of getting “the right tax at the right time.”
2. Principles of audit:
The basic principles of audit are –
i. Conducting audit in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
ii. Emphasis on the identified risk areas and scrutinizing the records maintained in the normal course of business.
iii. Applying audit techniques on the basis of materiality i.e. degree of scrutiny and application of an audit tool depending upon the identified nature of risk factors.
iv. Proper recording of all checks and findings made during the entire audit.
v. Identifying the unexplored compliance verification
vi. Educating the taxpayer for voluntary compliance.
3. General Guidelines for Auditor:
While conducting audit, the auditors are required to keep in view, the prevalent trade practices, the economic realities as also the industry and business environment in which the Registered person operates. Therefore, the auditor should take a balanced and rational approach while conducting the audit. Besides, the auditor is expected to play a key role in promoting voluntary compliance by the Registered persons. During the course of the audit, if certain technical infractions, without any revenue implications, arising due to bona fide oversight or ignorance of the Registered person, are noticed, the Registered person should be guided for immediate correction. Such cases should also be mentioned in working papers. An auditor is responsible for conduct of audit and should endeavour to take a final view on all issues raised by him during the audit. The working papers for each of the step of audit should be filled in as soon as that step is completed. They should be ‘speaking documents’ that clearly explain why a particular area was included in the audit plan as well as the basis for arriving at every objection that goes into the draft audit report after audit verification. The documentary taxguru.in evidence which has been relied upon in arriving at certain conclusion should invariably be cited and included.
Verification of records mandated by the statute is necessary to check the correctness of assessment and payment of tax by the registered person in the present era of self-assessment. In keeping with the principles of audit outlined above, audit has to be conducted in a transparent and systematic manner with focus on business records of the registered person and according to the audit plan for each registered person.
4. Confidentiality should be maintained in respect of sensitive and confidential information furnished to an auditor during the course of audit. All records submitted to the audit parties in an electronic or manual format, should be used only for verification of levy of GST or for verification of the tax compliance. These shall not be used for any other purposes without the written consent of the registered person. Maintaining the confidentiality is necessary to secure the trust and co-operation of the registered person.
5. Period to be covered during audit
The period to be covered under audit is prescribed in Rule 101 (1) of The Central Goods and Service Tax Rules, 2017 as financial year, or part thereof or multiples thereof to cover the retrospective period up to the previous audit or the limitation period specified in Section 73 or 74 of the CGST Act, 2017.
6. Duration of audit
6.1 Efforts should be made to complete each audit within the following general time limits:-
The indicative duration for conduct of Audit that is inclusive of desk review, preparation and approval of audit plan, actual audit and preparation of audit report wherever necessary, for each category would be as under:
i. Large taxpayers – 6 to 8 working days
ii. Medium taxpayers – 4 to 6 working days.
iii. Small taxpayers – 2 to 4 working days (including audit of the Deductor, who fall under the provisions of Section 51 of CGST Act, 2017 {who pay TDS} and operators who collect tax at source as per provisions of Section 52 of CGST Act, 2017)
The above mentioned working days are indicative and applicable for conduct of GST audit covering one year period. In case the audit coverage is for five years, the number of days may be increased to maximum of 16/12/8 days for Large, Medium and Small taxpayers respectively. In other words the number of days for conduct of audit may be increased proportionately, with an increase of 25% of working days for every additional year of coverage.
The duration, as above, covers the effective number of working days spent by the audit group for the audit of a particular registered person from desk review to preparation of audit report (i.e. days spent in office as well as at the premises of the registered person). In exceptional cases, the aforesaid period may be extended with the approval of Deputy/Assistant Commissioner of the Circle. Further, in accordance with the requirements of the audit of a particular registered person such duration can suitably be reduced with the express, prior concurrence of the Additional/Joint Commissioner, provided the verification as per the audit plan has been completed in the prescribed manner.
7. Stage wise action for audit
The processes involved in conducting GST audit are enumerated below for the ease of the officers involved in the auditing.
i. Creation of Audit teams.
ii. Preparation of schedule on the basis of the risk assessment list provided by DG (Audit). The same is divided into annual and quarterly audit schedules.
iii. Allotment of taxpayers to the audit groups.
iv. Intimation to the Registered Person (GST ADT-01).
v. Reviewing the taxpayer data – Tax Payer at a Glance (TAG), Registration, Returns, Payments, Dispute Resolution, Audit Report Utility, E-way bills & Third Party data if available.
vi. Conducting desk review in offline / online mode (wherever available) and uploading the result of desk review.
vii. Preparing the audit plan in offline / online mode (wherever available) and uploading the audit plan.
viii. Carrying out verification and uploading the verification report, within twenty four hours of completion of audit.
ix. Uploading the draft audit report (DAR) for the MCM, within 10 – 15 days
x. Examining the audit paras in MCM.
xi. Uploading the minutes of the monthly monitoring committee meetings (MCM), within twenty four hours of the meeting.
xii. Uploading final audit report, within thirty days of the Meeting.
xiii. Communicating the audit report to taxpayer (ADT-02).
xiv. Communicating to the Registered Person the future course of action in case of contested paras.
A Process Flow Diagram for the above mentioned processes is as under:
Process Flow –
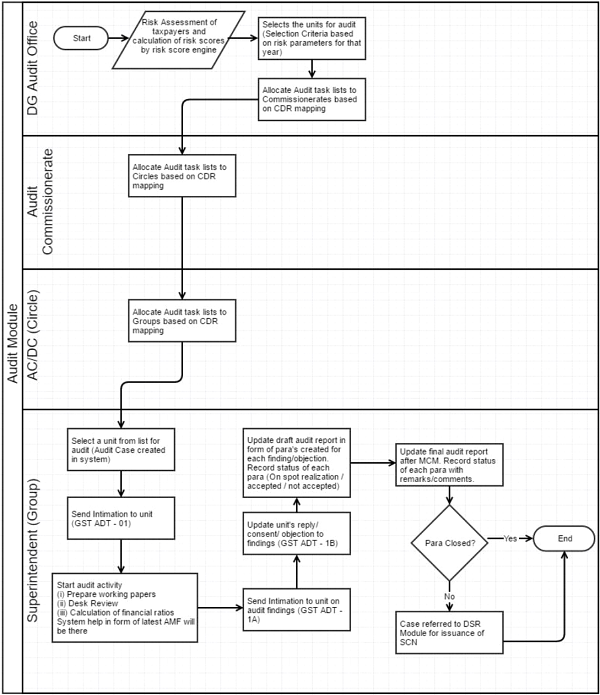
AMF – Assessee Master File




