Hemanta Kumar Behera,
B.Com, ACA, ACMA

Page Contents
1. Introduction:-
The concept of TDS on GST was initially introduced in the Income Tax Act and has now been introduced in GST as well. The purpose of introduction of TDS on GST is only to enable the govt to have a trail of transactions and to monitor and verify the compliance.It acts as a powerful instrument to prevent tax evasion and expands the tax net, as it provides for the creation of an audit trail.
Just like in the Income Tax Act, the person deducting the TDS is required to deposit the TDS with the Govt and issue Form 16 and Form 16A, similarly under GST Act as well, the person deducting the TDS would be required to deposit the same with the Govt by the 10th of the next month and issue Form GSTR 7A to the person whose TDS has been deducted.
2. Who is liable to deduct TDS under GST
As per Section 51 of the CGST Act, 2017
- A department or an establishment of the Central Government or State Government; or
- Local authority; or
- Governmental agencies; or
- Such persons or category of persons as may be notified by the Government.
As per the latest Notification dated 13th September 2018, the following entities also need to deduct TDS-
- An authority or a board or any other body which has been set up by Parliament or a State Legislature or by a government, with 51% equity ( control) owned by the government.
- A society established by the Central or any State Government or a Local Authority and the society is registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Public sector undertakings.
No TDS to be deducted if the payment is made by a person who is not mentioned in the above mentioned list.
3. When to deduct TDS under GST
TDS on GST is only required to be deducted where the payment made or credited to the supplier is done by the above mentioned category of persons.
- TDS is to be deducted at the rate of 2 percent on payments made to the supplier of taxable goods and/or services, and
- where the total value of such supply, under an individual contract, exceeds two lakh fifty thousand rupees.
*Explanation :- 1% TDS is required to be deducted under both the CGST and the SGST Act and therefore the total TDS to be deducted is 2%. In case of an inter-state transaction, IGST would be levied and 2% TDS would be levied in this case as well.
There are certain exceptions to this and in the following cases, TDS would not be deducted even if the payment is made by the above mentioned persons:-
a. Contract Value does not exceed Rs. 2.5 Lakhs
If the Contract Value does not exceed Rs. 2.5 Lakhs, no TDS is required to be deducted. But one important note that while determining the applicability of TDS on GST – it is the individual contract value which would be considered irrespective of the total no. of contracts.
This can be explained with the help of an example.
Ex- 1:- Mr. Ram enters into a contract of Rs. 2.25 Lakhs with a Local authority to provide Income Tax Advisory. He also enters into a contract worth Rs. 1 Lakhs to provide GST Advisory.
Ans :– The total value of services provided is Rs. 3.25 Lakhs which is more than Rs. 2.5 Lakhs. However, in this case – the provisions of TDS on GST would not be applicable as the value of each contract is less than Rs. 2.5 Lakhs.
Ex- 2:- Mr. Ram enters into a single contract to provide services worth Rs. 4 Lakhs. He receives Rs. 2 Lakhs as advance on the month Sep, 2018 and the balance Rs. 2 Lakhs on the month of June, 2019.
Ans :- The provisions of TDS on GST will get applicable as the contract value is more than Rs. 2.5 Lakhs.
b. Location of Recipient is different from Location of Supplier and Place of Supply
TDS on GST would not be applicable if the Location of Recipient is different from the Location of Supplier and the Place of Supply.
This can be explained with the help of an example.
Ex- 1:- Gujarat Govt. enters into a contract worth Rs. 3 Lakhs with Hotel Taj – Maharashtra to rent space for the purpose of conducting an event in their hotel.
Ans :- The provisions of TDS would not apply in this case irrespective of the contract value as the Place of Supply and Location of Supplier is different from the Location of Recipient.
Place of Supply – Maharashtra.
Location of Supplier – Maharashtra.
Location of Recipient – Gujarat.
Eg 2:- A vendor registered in Gujarat provides services to the Maharashtra Govt worth Rs. 4 Lakhs.
Ans:- The provisions of TDS will apply in this case.
Place of Supply – Maharashtra
Location of Supplier – Gujarat
Location of Recipient – Maharashtra
Therefore, while determining the applicability of TDS on GST, it is very important to determine the place of supply.
4. GST TDS deduct on which value :-
As per Notification No. 50/2018 – Central Tax Dated: 13th September, 2018 , For the purpose of deduction of tax specified above, the value of supply shall be taken as the amount excluding the central tax, State tax, Union territory tax, integrated tax and cess indicated in the invoice. This means TDS shall not be deducted on the CGST, SGST or IGST component of invoice.
5. Registration for deducting TDS under GST
A person who is liable to deduct TDS has to compulsorily register and there is no threshold limit for this. The registration under GST can be obtained without PAN and by using the existing Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN) issued under the Income Tax Act. Thus it can be said having TAN is mandatory.
6. Deposit of GST TDS, TDS Froms & TDS certificate
The amount of TDS deducted should be deposited with the govt by the deductor by the 10th of the next month in Form GSTR 7 through the online portal. The deductor would be liable to pay interest if the tax deducted is not deposited within the prescribed time limit as mentioned above.
A TDS Certificate would also be required to be issued by the deductor (the person who is deducting the tax i.e. the recipient) in GSTR 7A tothe deductee (the supplier whose payment is being deducted) within 5 days of depositing the TDS with the Govt.
7. Benefit of GST TDS
TDS will an automatic reflection in the electronic ledger of the deductee (supplier) once the deductor files his/her returns. The deductee can claim credit in his electronic cash ledger of this tax deducted and use it for payments of other taxes.
8. Penal Provision
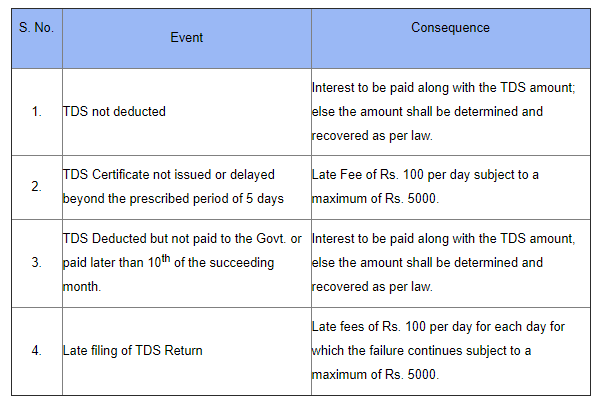
9. Conclusions
The concept of TDS under GST is a fairly new concept and has initially been implemented only on a small no. of assesses at a flat rate of 2%.
Courtesy :
- Background materials on GST by IDT Committee, ICAI & GST Act.
- FAQ on GST by CBEC.
(The author can be reached at [email protected])




