Goods and Services tax (popularly known as GST) would soon be the new system of indirect taxation in India that will subsume all the other indirect taxes that has been levied and collected in India so far.
From the viewpoint of a taxpayer, registration under GST would be the key factor. The aim of this article is to enlighten the reader with various aspects of registration covered under Chapter VI of Model Goods and Services Act.
1. Provisions governing Registration Process
- Chapter VI of the Model GST Law
- Schedule III of the Model GST Law
- Report of Joint Committee on Business Processes on GST Registration
- Draft Rules for Registration
2. Advantages of getting Registration under GST regime
2.1 Legally recognized as a supplier of goods or services;
2.2 Proper accounting of taxes paid on the input goods or services that can be utilized for payment of GST due on supply of goods or services or both by the business;
2.3 Pass on the credit of the taxes paid on the goods or services supplied to purchasers or recipients; and
2.4 A single platform for all the Indirect Taxes.
3. Key Areas Covered in this article
| S.No | Areas Covered |
| 1 | Persons liable for Registration |
| 2 | Documents required for Registration |
| 3 | Time Limit for Registration |
| 4 | Procedure for Application of Registration |
| 5 | Grant of Registration certificate |
| 6 | Structure of Registration Number |
| 7 | Multiple Registrations in case of Multiple Business Verticals |
| 8 | Migration of persons registered under Earlier Law |
| 9 | Registration under Special Categories |
| 10 | Case Studies |
4. Persons liable for Registration
There are selected reasons for which a person is required to take registration under GST. The applicable reason also required to mention in the application form:
4.1 Crossing the threshold limits
4.1.1 Threshold should be worked out taking into account both the supply of goods and services on gross turnover basis. Such turnover would include the turnover of exempted goods and services (including non-taxable) and exports excluding the taxes charged under CGST Act, SGST Act and the IGST Act.
4.1.2 Threshold limit of turnover for the purpose of registration is kept Rs 10 Lakhs for North East States including Sikkim and Rs 20 Lakhs for other states.
4.2 Due to Inter-state taxable supply
4.3 Due to liability to pay as recipient of services
4.4 Due to being Input Service Distributor (ISD)
4.5 UN bodies for allotment of Unique Identification Number ( the same is to mention on the invoices)
4.6 Due to transfer of Business which includes change in the ownership of business (If transferee is not a registered entity)
4.7 Due to death of the Proprietor (If the successor is not a registered entity)
4.8 Due to De-merger
4.9 Due to change in the constitution of business
4.10 Due to Merger/Amalgamation of two or more registered taxpayers
4.11 Being Casual taxable persons
4.12 Being Non-resident taxable persons
4.13 Due to deduction of tax under section 37
4.14 Persons who supply goods/services on behalf of other registered taxable persons whether as an agent or otherwise
4.15 An aggregator who supplies services under his brand name or his trade name
4.16 Persons who supply goods and/or services, other than branded services, through electronic commerce operator
4.17 Electronic commerce operator
4.18 None of the above- on voluntary basis
Note: Registration under SGST means registration under CGST also and vice versa. Also, an entity having a single PAN but effecting supplies from multiple States would be required to take registration in each of the States from where the supply is being made.
5. Time Limit for Registration
5.1 Every Manufacturer or a Service provider or a dealer registered under Central Excise Act or under Service tax law or State Vat law will get automatic PAN based registration number without fresh application.
5.2 In case of new dealer, he has to apply online for the registration within a specified period as stated below:
| S. No | Category | Time Limit |
| 1 | A dealer crossing threshold limit as specified under GST Law (Rs 9 Lakhs or Rs 4 Lakhs). (This limit may get changed under the final GST law) | Within 30 days from crossing of such limit. |
| 2 | Other than 1 above | Within 30 days from the date on which he become liable for registration |
6. Documents required for Registration
6.1 An assessee has to provide support of documents to substantiate the information required to be filled in some fields of application form for getting registration under GST. The field number, name and documents required therein are listed in the below table:
| Field Number | Field Name | Related Information | Supporting documents |
| 2 | Constitution of Business | Partnership | Partnership Deed |
| Society, Trust (Not captured in PAN) | Registration Certificate | ||
| Companies | CIN Number (Certificate of Incorporation) | ||
| 11 | Details of Principle place of business | Owned | Any document in support of ownership like latest tax paid receipt or electricity bill copy |
| Rented/Leased Premises | Copy of Valid Rent/Lease Agreement with any document in support of ownership of the premises of lessor | ||
| Premises obtained other than by way of Rent/Lease | Copy of Consent Letter with any document in support of ownership of premises of Consenter | ||
| 12 | Details of Bank Account | Opening page of the Bank Passbook held in the name of the Proprietor/ Business Concern- containing the Account No., Name of the Account Holder, MICR and IFS Codes and Branch details | |
| 17 | Details of Authorised Signatory | Letter of Authorisation or Copy of resolution of the Managing Committee or BOD to that effect | |
| Photograph | Proprietary Concern | Proprietor | |
| Partnership Firm/LLP | Personal details of all Partners (photos of only 10 partners including managing partner) | ||
| HUF | Karta | ||
| Company | Managing Director or the Authorised Person | ||
| Trust | Managing Trustee | ||
| AOP or BOI | Members of managing committee (photos of upto 10 members) | ||
| Local Body | CEO or his equivalent | ||
| Statutory Body | CEO or his equivalent | ||
| Others | Person in Charge |
7. Application for registration – Procedure
7.1 The Model GST Law does not describe procedure relating to registration. The Empowered Committee had released Report on Business Processes for GST on GST Registration Process in July 2015 giving procedure for registration. Recently the Government has also released the ‘Draft Registration Rules’ for public comments. With the combined reading of both the documents, registration procedure is explained as follows:
Application for Registration (Rule 1)
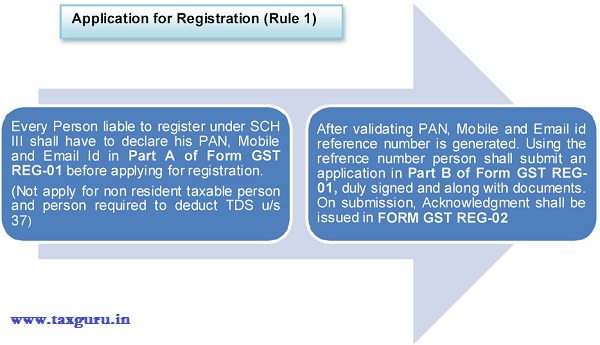
Verification of Application (Rule 2)

Note: The clarification includes modification or correction of particulars declared in the application for registration, other than PAN, mobile number and email address declared in PART A of Form GST REG-01 . If Officer is not satisfied with the information furnished, he shall reject the application and inform the applicant electronically in FORM GST REG-05.
Grant of Registration certificate
7.2 The Central/State authorities must respond on application to GSTN portal within 3 working days, either communicating approval or raising a query. In case non-communication of approval or rejection, the application shall be deemed to be approved by the authorities and GSTN portal shall generate the registration certificate in FORM GST (Rule 3).
7.3 The registration shall be effective from the date on which the person becomes liable to registration where the application for registration has been submitted within thirty days from such date. Where an application for registration has been submitted by the applicant after thirty days from the date of his becoming liable to registration, the effective date of registration shall be the date of grant of registration.
8. Structure of the Registration Number
8.1 PAN based GSTIN- Each tax payer will be allotted a State wise PAN based 15- digit Goods and Services Taxpayer Identification Number (GSTIN). First 2 digits will be State Code. Next 10 digits will be Income Tax PAN. 13th digit will be entity code. 14th digit will be blank for future use. 15th digit will be check digit which is a form of redundancy check used for detection of errors.
| State Code | PAN | Entity Code | Blank | Check Digit | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
9. Multiple Registrations in case of Multiple Business Verticals
9.1 A person having multiple business verticals in a state may obtain separate registration for each business vertical by filing separate application for each vertical in FORM GST REG-01.
9.2 “Business vertical” shall have the meaning assigned to a ‘business segment’ in Accounting Standard 17 issued by ICAI- Section 2(18) of GST Model Law 2016.
9.3 As per Accounting Standard-17
“A business segment is a distinguishable component of an enterprise that is engaged in providing an individual product or service or a group of related products or services and that is subject to risks and returns that are different from those of other business segments. Factors that should be considered in determining whether products or services are related include:
(a) the nature of the products or services;
(b) the nature of the production processes;
(c) the type or class of customers for the products or services;
(d) the methods used to distribute the products or provide the services; and
(e) if applicable, the nature of the regulatory environment, for example, banking, insurance, or public utilities.”
9.4 For example ITC Ltd. is an Indian conglomerate headquartered in Kolkata, West Bengal. Its diversified business includes five segments: fast moving consumer goods, hotels, paperboards & packaging. It may go for separate registration for each business vertical or may continue with single registration of all the verticals in a state. It needs to take registration of principle place of business in every state from where the supplies are being made.
10. Migration of persons registered under Earlier Law
10.1 Existing Migrants are those who are either registered with States or with the Centre or with both.
10.2 At present, taxpayers are separately registered with State and/ or with Central tax administrations or with both based on their business activity. In the GST regime, a taxpayer will have to obtain State wise registration. Procedure for Migration is explained in Rule 14 of Draft Registration Rules would work out as follows:
| Steps | Procedure | FORM |
| 1 | Existing taxable persons will be given provisional registration certificate | GST REG-21 |
| 2 | Provisional registration holder shall submit application duly signed and along with the documents required in the application form electronically within period of 6 months | GST REG-20 |
| 3 | If the application and documents found in order, Registration Certificate would be granted | GST REG-06 |
| 4 | If there is found any discrepancy in the application then proper officer can cancel the provisional registration and issue an order | GST REG-22 |
| 5 | No provisional certificate would be cancelled without serving a notice to show cause | GST REG-23 |
| 6 | Person registered under earlier law, if not liable to register under this law due to any reason shall file an application | GST REG-24 |
11. Registration under Special Categories
| Categories | Procedure |
| Casual Taxable Persons- Person who occasionally undertakes transactions involving supply of goods and/or services in the course or furtherance of business whether as principal, agent or in any other capacity, in a taxable territory where he has no fixed place of business.(Section 2(21) of Model GST Act) | Procedure for application is same as explained above for new applicant with a slight difference that a casual taxable person shall be given a temporary identification number by the Common Portal for making advance deposit of tax under acknowledgement in FORM GST REG—02 shall be issued electronically thereafter. |
| Non Resident taxable Persons- means a taxable person who occasionally undertakes transactions involving supply of goods and/or services whether as principal or agent or in any other capacity but who has no fixed place of business in India (Section 2(69) of Model GST Act) | Non Resident taxable person shall submit an application in FORM GST REG-10 atleast 5 days prior to the commencement of business. |
| Compounding Dealers- Dealers below the Compounding ceiling (50 lakhs) will be provided with an option of availing the Compounding scheme i.e. they can pay the tax at Compounding rate (to be decided) without entering the credit chain. | Although the Compounding scheme is only a temporary phase before the taxable person starts functioning as a normal taxable person. When the taxable person opts for Compounding scheme he should indicate so in the registration form and GST Common Portal would internally flag him as a Compounding dealer. Later on when he goes out of the Compounding scheme due to his turnover crossing the Compounding ceiling (change will be triggered by the tax return values) or he opts out of the scheme (through an amendment application), the said flag will be removed and he would continue operating with the same registration number, without undertaking any fresh registration. |
Note: The Registration Certificate issued to casual taxable person or a non resident taxable person shall be valid for a period of 90 days from the effective date of registration. For extension of the same, an application in FORM GST REG-25 shall be furnished electronically.
12. Case Studies
Case 1. ABC Ltd., located in Delhi supplies goods in Delhi as well as in neighbouring states Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. The company has noted its turnover never exceeds 20 lakhs. Examine whether ABC Ltd is required to register under GST. If yes, in which states registration are required.
Comments. Yes, ABC Ltd is required to register under GST law. Though the turnover is below threshold but since the company is making inter-state sales, it is required to apply for registration under GST.
As per Schedule III of the Model GST law every supplier shall be liable to be registered under this act in State from where he makes a taxable supply of goods/services.
As per the Schedule III, ABC Ltd is required to register in all the states from where it is affecting taxable supplies of goods or services. In case the supplies are affected only from Delhi, then registration shall be in Delhi only.
Case 2. PQR Ltd., located in the state of Maharashtra is engaged in selling designer shirts. The process of designing is completed at the job worker premises, located within Maharashtra. Goods are sold from the location of PQR Ltd. How will the process of registration work in this matter?
Comments. If the supply of goods is made from the premises of PQR Ltd., then the job worker would be required to take registration only if its turnover exceeds the maximum threshold limit. However, the value of goods supplied to PQR Ltd after completion of job work, would not be taken into account while computing turnover of the job worker.
Case 3. State whether PQR Ltd is required to take registration. The value of supplies made during the FY 2017-18 is as follows:
| Particulars | Value of supplies (excluding GST) |
| Supply of goods | 5 lakhs |
| Supply of goods from registered job worker premises | 2 lakhs |
| Supply of exempted goods | 12 lakhs |
| Supply of goods under reverse charge | 20 lakhs |
| Supply of non taxable goods | 0.5 lakhs |
Comments. Since the aggregate turnover of PQR Ltd does not exceed 20 Lakhs without taking into account the value of supplies on which tax is levied on reverse charge basis, the company is not liable for registration under GST.
Note: Aggregate turnover does not include the value of supplies on which tax is levied on reverse charge basis and the value of inward supplies.
Case 4. Company A Ltd. is operating in 10 states under the same PAN number. It is having at least 3 branches in each state. How does the provisions of registration apply on the company?
Comments. If a company is operating in different states with the same PAN number, it is liable to get registered separately for each of the states where it has a business operation and from where supplies are being made.
In the given case, Company A Ltd. is liable for registration in all those states from where it is making supply of goods/services.
For the branches within each state, single registration number can be used for each state. Also, the company may also obtain separate registration for each business vertical in terms of sub-section (2) of section 19.
Case 5. A logistics company operates in different parts of country. It has warehouses in the state of Haryana, Maharashtra, West Bengal and Punjab. Also, the company is headquartered in Delhi from where no supplies are made. Supplies made by various warehouses are given below:
| Supplies From | Supplies to | Turnover |
| Warehouse in Haryana | Other Warehouses only | 8 lakhs |
| Warehouse in Maharashtra | Customers With in Maharashtra only | 5 lakhs |
| Warehouse in West Bengal | Customers with in West Bengal only | 22 lakhs |
| Warehouse in Punjab | Customers outside the state of Punjab | 2 lakhs |
Which all states does the company need to register?
Comments. Since the Company is headquartered in Delhi with no supplies made therefrom, there is no need to take registration. However, if the company avails taxable services, it can explore the possibility of obtaining registration as Input Service Distributor (ISD). For ISD registration threshold limit is not required.
Assuming all the warehouses are operating under the same PAN. All are considered as place of business as per the definition given under section 2(75) of Model GST law. The gross turnover of all warehouses is exceeding 20 lakhs therefore separate registration is required in each state from where the supplies are made.
Case 6. A Chartered Accountancy firm has branches in Delhi, Mumbai and Bangalore. The HO is in Delhi from where majority of the services are supplied. However, services are also provided from Mumbai and Bangalore. Currently, the firm has taken centralised registration in Delhi and all the billing happens from Delhi. How will the position change under GST?
Comments. The concept of centralised registration has been done away with under the Model GST law. Consequently, each office of the CA firm that is supplying services, i.e., Delhi, Mumbai and Bangalore would need to get registered under GST. This also means that each office will need to issue invoices for supplies made in the respective states and maintain all the necessary records and documentation.
Conclusion
Though the process of registration should be smooth without too much human intervention as envisaged by the government, it still needs to be seen how effectively will it be managed by the GSTN.
Service providers that were enjoying the benefit of centralised registration are likely to be hit the most with no such provision available under the GST. This shall significantly increase the compliance burden on service assessees.
Disclaimer: Views expressed are strictly personal. The content of this document are solely for informational purpose. It doesn’t constitute professional advice or recommendation. The Author does not accept any liabilities for any loss or damage of any kind arising out of information in this article and for any actions taken in reliance thereon.
——————————————————
 Authored by Nimish Goel, Head of Indirect Taxes/GST at International Business Advisors. Nimish has spent almost 13 years practicing indirect taxes including VAT, Service tax, Excise and Customs. He has worked with BIG4s including EY and KPMG both in India and in Europe. For any queries Nimish can be reached at nimish.goel@ibadvisors.co
Authored by Nimish Goel, Head of Indirect Taxes/GST at International Business Advisors. Nimish has spent almost 13 years practicing indirect taxes including VAT, Service tax, Excise and Customs. He has worked with BIG4s including EY and KPMG both in India and in Europe. For any queries Nimish can be reached at nimish.goel@ibadvisors.co
International Business Advisors (www.ibadvisors.co) is a boutique audit, tax and consulting firm run by ex-BIG4 professionals and working extensively with multinational companies operating in varied sectors including e-commerce, mobile, manufacturing, real-estate and hospitality. IBA operate out of its offices in Delhi, Mumbai and Bangalore.
Nimish was assisted by CA Ravi Arora, who works as a Senior Associate in Macquarie India and can be reached at caraviarora2009@gmail.com




