A comprehensive analysis of goods and services tax (GST) in India
Abstract
In the midnight of June 30-july 1, 2017, India experienced a historic occasion as it move towards “one nation, one tax, and one market “economy.[1] Introduction of (GST) goods & services tax is regarded as the most revolutionary action taken in India taxation history’s is the single comprehensive indirect tax on supply of goods & services from manufacture to the consumer levied by central and state government. This paper concern an investigation into India’s recent introduction of goods & services tax and tries to find out the problem impact of this reform on Indian economy. The focus of the paper is to issues why India needs this reform & how GST impact on different sections of the economy. Finding suggests that earlier multiple taxes in the country with different rates and law divided the nation into single economic sphere. GST get rid the nation of cascading effects, high compliance costs and remove the barrier of trades, enhance ease of doing business, greater productivity &efficiency, making India competitive in the international market. Moreover, the conclusion describe that initially India suffer some inconvenience but ultimately it will have positive impact on economy.
Introduction
Tax is not only the source of revenue and growth of the nation, but also it enables a state to be accountable to its tax payers. Effective tax policy ensures the economic development of a nation. It provides resources to the government to support the social welfare as well as to promote the economic activities. Indian tax structure is always known for its complexities and rigidities. To get rid of all these complexions, and rigidities. To get rid of all these complexions, India took the most significant step. In its tax reform history, with the implementing goods & service tax from July, 1 2017. GST is an umbrella that subsumes all states and federal taxes for instance value added tax (VAT), exercise duty, service tax, entry tax, entertainment tax, etc. GST was first adopted by France in 1956 to fight against high sales taxes and tariff that promoted smuggling .as for 2016, 165 countries had adopted it. On 1stJuly 2017, India became 166th GST nation.[2] The idea of moving towards one tax economy first came in 2000, when government setup an empowered committee for discussion on GST, under aim das Gupta (finance minister of west Bengal).later in 2006-07 budget session it was proposed that it will be introduce by 1st April 2010.[3]In 2009, one task force was set up to discuss GST and due to disagreement among states on various issues, it proposed a revised date of introduction of GST to 1stApril2013. The reason to bring GST is that different tax paid at different rate would come under one single tax that includes all indirect taxes. GST would be one tax for one nation. Prior to GST we have to pay taxes ranging from 30% to 35% on different commodities but with the introduction of GST we will have to pay fewer taxes now. Another three major features of GST is that it will remain similar across the nation. By subsuming, the large numbers of central and states taxes, it is expected that GST would help to change the economic scenario significantly. This tax reform leads to create common national market. In reference to the consumer, the biggest benefit would be reduction of tax that mitigate the cascading effect of taxes; prices of goods expected to be transparent because of input tax credit between the manufacture and retailers and it would be helpful to make India more competitive on domestic & international market. The revenue of the government is anticipated to increase due to expansion of tax base, improved tax compliance, increasing the trade volume, reducing corruption by removing direct interface between the tax payer & tax administration. Last but not the least all above features would ultimately. Be helpful in poverty eradication through employment generation as well as through offering more financial resources.
Definition
Tax law is the practice of law that relates to the assessment and payment of taxes. Tax laws come from a variety of source they’re based in federal and state constitutions, laws and regulation. Tax law involves understanding, implementing and defending the payment or non-payment of taxes.
HISTORY
India has abolished multiple taxes with passage of time and imposed new ones. Few of such taxes includes inheritance tax[i] interest tax , gift tax ,wealth tax, etc. wealth tax act , 1957 was repealed in the year 2015 direct taxes in India were governed by two major legislations, income tax act, 1961 and wealth tax act, 1957. A new legislation, direct taxes code (DCT) was proposed to replace. The two acts (when?) however, the wealth tax act was repealed in 2015 and the idea of DCT was dropped.
The GST was implemented in India on 1 July 2017. However, the process of implementing the new tax regime commenced a long time ago. In 2000, atlas Bihari Vajpayee, then prime minister of India set up a committee to draft the GST law.[4] In 2004, a task force came to the conclusion that the new tax structure should be implemented to enhance the tax regime at the time.
In 2006, p, Chidambaram, then finance minister of India. Proposed the introduction of GST on 1 April 2010, and the constitution amendment bill was passed in 2011 to enable the introduction of GST law. [5]
In 2012, the stating committee started discussions regarding GST, tabled its report on GST a year later. In 2014, the new finance minister at the time, Arun Jaitleay, re-introduced the GST bill in parliament, and the bill was passed under the Lok Sabha in 2015. However, the implement of the law was delayed as it was not passed in Rajya Sabha. The president of India also gave assent to the law in 2016. 2017 saw the passing of four supplementary GST bills in ok Lok Sabah as the approve of the same by the cabinet credit rules, 2004 will be equally applicable under GST act also. Raja Sabah then passed 4 Supplementary GST bills and the new tax regime was implemented on 1 July, 2017.
Credit of GST paid on light diesel oil
As per article 279 A (5) date of imposition of GST on specified petroleum productize, petroleum crude, high speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly known as petrol),Natural gas and aviation turbine fuel will be recommend by GST council to the central government. Thus initially say during 2017-18, these products will not attract GST. Present tax structures i.e., levy of excise duty and VAT on this product will continue till they are included in the GST as per the recommendation of GST council.
Input tax as per the definition means CGST, SGST and IGST. It does not mean excise act. Therefore, excise taxable person. Thus even if these items are not specifically excluded it does not have any impact however, GST will be payable on light. Diesel oil (LDO). The credit paid on LDO will be available to the manufacture.
GST how to meet your obligations
Section 8 of the GST (compensation to states) act, 2017 provides that access to be called as GST compensation access will be levied at such rate on the value determined under section 15 of the CGST act, 2017.[6]in India GST is the single compensation tax they are very faster growth our economy GST also the less tax compliance and a simplified tax policy compared to current tax structure.
Benefits of GST to the Indian economy
- Removal of bundled indirect taxes such as VAT, CST, service tax, CAD, SAD and excise.
- Less tax compliance and a simplified tax policy compared to current tax structure. Removal of cascading effect of tax i.e. removes tax on tax.
- Reduction of manufacturing costs due to lower burden of taxes on the manufacturing sectors. Hence prices of consumer’s goods will be likely to come down.
- Lower the burden on common man i.e. public will have to shield less money to buy the same products that were costly earlier.
- Increased demand and consumption of goods.
- Control of black money circulation as the system normally followed by traders and shopkeepers will be put a mandatory check.
- Boost to Indian economy in the long run.
Quantum of tax payable
The person opting for composition scheme will be required to pay the tax calculated on such rate as may be prescribed. The section 10 (1) provides the maximum rate of tax payable by the person opting for composition scheme.
1. One percent of the turnover in state or turnover in union territory in case of a manufacturer.
2. Two and a half percent of the turnover in union territory in case of persons engaged in making supplies.
Judgments under central excise act
Similar words appear in the definition of ‘input’ given in central excise rules, 1944. The ratio of judgment which has been decided in the context of canvat rules, 2004 will be equally applicable under GST act.[7]
Laying of rules and notification
The section 166 of the GST act specifically provides that all rules make and notification issued under take act shall be published in the official gazettal. it shall also be laid before the parliament or state legislature during the period specified in section 166 of the GST act. India started its journey tax system in years 1980. GST is the comprehensive indirect tax on manufacture, sale of goods and services at national level.
Classification of GST
Zero –rated items
- Agriculture products- paddy & various fresh vegetables.
- Beef, mutton, swine
- Fish, salted fish, prawns, cuttlefish, crabs, oyster etc.
- Rice, sugar, table salt, plain flour, cooking oil.
- Selected poultry and eggs.
- Water for domestic use.
- First 200 units of electricity (domestic use) for minimum 28 days.
- Exported goods and services.
- Selected services related to exports.
Exempt item
♦ Public transportation- rail, bus, and taxi (excludes luxury/airport taxi).
♦ Tolled highway or bridge.
♦ Land for residential, agriculture or general use.
♦ Funeral- in- a- package.
♦ Private healthcare & education.
♦ Selected financial services.
♦ Childcare services.
♦ Selected accommodation (28 days or more).
GST council – constitution
1. Chairperson-finance minister.
2. Vice chairperson- is to be chosen amongst the ministers of state government.
3. Members –MOS (finance) and will ministers of finance taxation of each state.
4. Quorum is 50% of total members.
5. State has third weight age and center has one third weight age.
6. Decisions are taken by 75% of majority.
7. The council shall make recommendations on everything related to GST including rules rates etc.
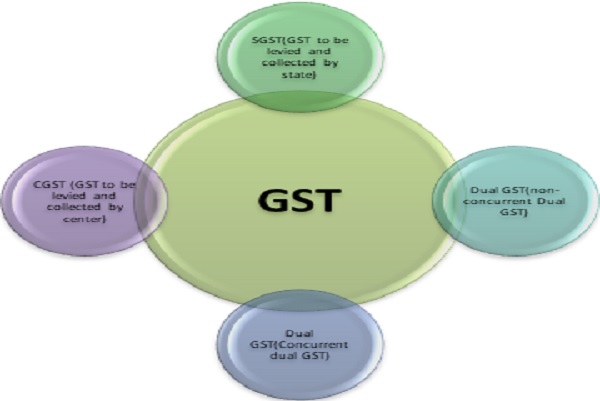
The salient features of GST
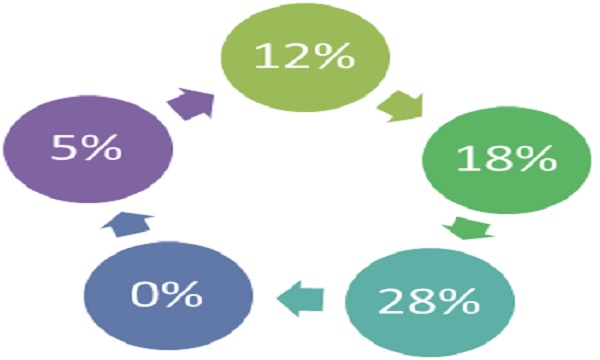
The territorial spread of GST is whole country including Jammu & Kashmir. GST is applicable on the supply of goods or services as against the present concept of tax on the manufacturer or sale of goods or on the provision of services. It is based on the principle of destination based consumption tax against the present principals of origin based taxation. Import of goods and services is treated as interstate supplies and would be subject to IGST in addition to the applicable custom duties. CGST (central government GST) SGST (state government GST) IGST (interstate GST) are levied rates mutually agreed upon by the Centre and states under the guidance of GST council. There are four tax slabs namely 5%, 12%, 18% and 28% for all goods or services. There is no tax on export and supplies to SEZ there are various modes of tax payment available to the tax payers including internet banking, debit/credit card, NEFT, RTGS etc.
Prospects of GST in India
- Manufacture will get the benefit of the GST, thus the tax burden on producer will be reduced and it wills faster growth through more production.
- Under GST structure no entry tax is charge for goods manufactured or sold in any part of India. Thus result when delivery of goods and services between two states can easily be made without any check post or no charge on toll they freely sold their goods and service in another state.
- When GST comes they made taxation simple. The end consumer now knows exactly how much tax is being charged and they also know how tax charge for a particular goods and services.
- GST tax credit phenomena is expected to boost up producer up producers to purchase raw material from different registered dealers and is hoped to bring up more vendors and suppliers under the purview of taxation.
- GST will increase the competitiveness of India in the global market as custom duties applicable on exports and imports of goods and services of another state.
- Ambiguity between goods and services has been removed, this will make various legal proceedings in relation to goods and as result distinction between and services shall no longer exist which will reduce tax evasion.
- In GST when society gives different tax they suffer lots of problem but when GST comes then they pay only single tax and also have a less burden of paying tax.
- GST is the single taxation law they control the inflation of the economy growth in India.
- High inflationary impact would be on telecom , real estate, construction , air and roads transport etc. thus services would increase the consumers cost.
Scope of tax laws
Law includes any ordinance, order, by- law, rule, regulation, notification, custom or usage which is passed or made by a legislature or other competent authority in the territory of country. In India, both direct and indirect taxes are being imposed according to law. There are constitutional provisions to impose taxes. In the constitution article 265 to 289 are directly related to taxes.[8] Any other duty or tax which having regard to nature or incidence, may be declared by the central government by notification in the official gazette to be a direct tax. The interest tax act, 1974 was made published in official gazette.
Computation and payment of advance tax
Computation: tax can be computed on the current income at the rates in force during the financial year. From the tax so computed, tax deducted or collected at source will be deducted. When calculation can made on similar lines in the case of upward or downward purpose of current income.
Payment: an absence that is liable to pay advance tax according to their monthly income when people get able to pay advance amount of tax then he will pay in advance. an assesses who liable to pay advance tax is required to estimate his current income and pay advance tax without having to submit any estimate or statement of income to the assessing authorities.
After making payment of first or second installments of advance tax, an assessed can revise estimate of current income and pay tax according without any requirements of filing the revised estimate of advance tax.
Liability for payment of advance tax (sec 207).
Under the schemes of advance payment of tax the paid all amount in advance at the financial year. State and central government charge the tax according to their income. When GST not comes in India it’s a so burden of paying the tax when GST comes in India people pay only single tax.[9]
Interest payable by government (sec 214).
The central government shall pay simple interest at one percent per month or part of the amount by which the aggregate of any installments of advance tax paid during any financial year. When GST come in India it’s very easy to pay the tax and they loss the less burden of paying tax, government also free for the lot of complains the free from the burden of tax.
Features of the GST to proposed
The GST system is based on the same concept as VAT. Following the features has been discussed:
Range of GST
GST to be structured on the destination principal so the tax base shifts from production to consumption whereby imports and exports of goods & services will libel to tax will be relived of the burden of GST.
CGST and SGST would be comprehensive applicable to all goods and services up to the final consumer .CGST and SGST would be applicable to all transaction involve supply of goods and services made for a consideration (expect alcoholic liquor for human consumption) and the exempted goods and services, goods which are the outside the preview of GST and the truncation which are below the prescribed threshold limits.
Tobacco products are included in GST along with central excise tax.
Initially the following products are expect but GST on following products shall be from date to be notified by the GST council
- Petroleum crude. High speed diesel. Motor spirit (commonly known as petrol)
- Natural gas. Aviation turbine fuel.
Collection of GST:
♦ GST has two components CGST and SGST as discussed above. CGST will be collected by central government whereas states government will collect SGST.
♦ IGST is paid on supplies in the course of interstate trade including import which is collected by central government exclusively and distribution to imported states as GST is destination based tax. The proportion of distribution between center and states is decided on recommendation of GST council. (proposed article 269A)[10]
Input of tax credit
1. At present, under the various state VAT laws, there is no uniformity and clarity of the quantum of tax paid by the people when GST comes in India it’s a comprehensive tax they also control the inflation of economic growth.
2. The facility of input tax credit at the central level will only be available in respect of central goods and services tax. In another words, the ITC of central goods and services tax shall not be allowed as a set off against sate goods and services tax.
Compensation to states
♦ For maximum of 5 years union will compensate states for the revenue losses arising out GST implementation.
♦ This compensation will be made on the recommendation of GST council.
♦ GST liability for the compensation to the central government and state.
♦ The distribution of goods in each tier has not officially been declared and most of the uncertainty lies in the allocation of the goods to the standard tax rates of either 12% or 18% tier.
♦ GST when comes in India it’s also effects in our GDP growth.
THE REASON IS THAT A HIGHER GST RATE WOULD DAMPEN THE RISE IN BGOTH DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL TRADE RELATIVE TO THE BASELINE , WHICH TRANSLATES TO AN INCREASE IN MANUFACTUREING PRODUCTION THAT IS 3% POINTS LOWERS.
CENVAT CREDIT RULES, 2004
CENVAT credit rules, 2004 (CCR 2004) have been notified wide notification no. 23/ 2004 –central excise act this also equally the GST act in India GST is the boost the economic growth. India has experienced one of the greatest indirect tax reforms in its history. In India GST is the comprehensive tax charge by the central government in 1 July, 2017 at the mid night.
Recommendations on GST
> Filling 37 returns per GSTIN is very time consuming and costly also where in every one may not have the resource to meet up the compliance .so processes must be simple.
> Reverse charge pay by resister dealer in case of purchase from non-register dealer shall be complete withdrawal.
> An intense and deep training is needed to made work force internally capably of handle regimens. However the workshops and conferences may add up to increases to knowledge about the GST.
> Concept of input tax credit needed a large volume of data to be made between the supplier and receiver. The processes have been simplified.
> Rates have been rationalized and non- field to make India is a captive in interest of economic development of the country and also reduce the complication in the India
> GST should not handle to regional imbalance in items of resources and responsibility among government a due care of it shall be taken from the society every people pay the tax at the financial years as the their income growth which they get at the monthly they paid the indirect tax but when the GST comes its less burden to the tax there pay only a comprehensive tax to the central government..
> A proper mointitrning system shall be constructed to manage non-real regenerations and refunds fields as these are the areas where loopholes invisibly exist.
> In GST tax the pay the indirect taxes in the every monthly at the financial year.
Challenges in implementation of GST
During fiscal year 2016-17 about rupees 17.10 lakh core tax was collected by the government of India. the tax collection raised by about 178% as compared to last year and indirect tax consist by about 178% as compared to last year and indirect tax consist of another service tax, VAT etc account for 50% of total returns forms taxes. With introduction of major tax reforms in indirect taxation system and introduction of GST of the country. By replacing the multiple tax system with a single non- field simple the inside indirect tax regime but a plethora of roadblocks that posed a challenge in its implication were not the rock of mud. Some of them are enumerated below:
> GST has made the tax system easy but entire process from involving to tax payment has been routed over wires. Every aspect has comes an online process. Most of the small and medium enterprises may not be technically sear to adopt this change. GST assume much higher technical standard which may still be a great impossibility for small enterprises.
> GST is designed to simply the tax structure and therefore a single tax rate is suggested and that’s actually the case in the country where GST has been implements so far. it is an non- told principal in GST that tax are the only one single compensation it is a comprehensive indirect tax amount is payable by the people at the end of the month people paid their compensation liability which one people get at the end of the years.
> Under GST as absence has to file 37 returns in years. 3 per month and in annual as compare to that of 13 returns in the years. in GST they are single indirect tax which one paid by the public for their economic develop of our country at the fiscal year at the India is the higher tax payer country .
> GST stand as consumption based destination tax which means that consumption state will collect the tax. It stands as a blessing for consuming state but manufacturing states would get nothing. To overcome this problems compensation act introduced which further ads up to the complication of calculation of the tax at end of the years when the government want to calculate.
> GST was absolutely a new concept for India. therefore it require that entire tax administration staff from state and central government needed to trained proper way for the tax knowledge purpose for the tax payer how much amount are charge at the particular goods and services at the tax in the fiscal years.
Contribution of GST towards economic development:
An economy has to function in the ecosystem. We cannot depart the economy from everyone as the when the GST comes in India our economy growth are inflation at the economy growth at very faster growing. GST is the tax credit paid to the government at the state and central government. The debate of GST is on between the manufacturing and consumption. The goods and services tax act GST is equally to the cenvat act rules 2004 they also talks about the liability for the paid by the people at the financial years.
Consideration for now- how (sec.180-A)
Where the time by individual who is restraint in India, for developing any know- how is more than twelve months, he may elect that the gross amount of any lump sum consideration received or receivable by him during the previous years for allowing use of such know – how shall be treated for the purpose of charging income taxes for that years and for each of the two immediately preceding previous years as if one- third therefore were included in his income chargeable to tax for each of these years respectively.
The Indian taxation system – scenario before GST
Tax policy plays a vital role in any country economy in terms of efficiency and equity. A goods taxation policy that which take care of the entire of the income distribution and also generates tax revenue in such manner for the central government which can deals with the overall benefits in the nation and some people security which one people deposit the government at the form of incomes and indirect tax which one paid at the fiscal policy system at the end of the years.
The CENVAT (excise duty) was imposed on the products manufactured in India. But issues arise regarding product valueioation. The issue regarding implementation of CENVAT only at the manufacturing level acted as a CENVANT barriers to efficient and natural flow of tax credit. This leads to replace of VAT to GST in many countries.
The Indian constitution has distributed the tax system between central and state governments. The state government has rights to impose any sort of tax on any condition or items under the state. In services tax the central government enjoys the powers to impose tax but in work contracts, the state. Government has dominated this sort of system created disorder in the paying of GST at the end of years at the financial years.
Various things like copyright, patents, software are not considered for the tax system by the government. So, complexity again arose for classifying these goods under the taxation policy.
Considering CST on the inter sale goods and services, on the set off was allowed which increased the effect on the economy development in the country.
The Indian taxation system was cumbersome and full of burdens and different taxes on same product in different states led to high inflation which has to be considering in the economy growth.
Under the indirect taxation system there were more than 15 different tax which had to filled under different norms and regulations so, it necessary to immediate and one system regulations of filling and calculating taxes at the end of the years.
Lacks of cross verifications of returns fields under the central and state taxation system handle to lot of discrepancies.
With the booming of the service sector, the central government has monopolistic right to impose tax. The state governments, on the others hand, are losing their revenue by not apply any tax on the services sector.
For better monitoring and administration of taxes laws , major transfer in technology are necessary , which is costly and timing consuming and has to be redressed.
Despite of the existence of multiple taxes in taxes in the Indian economy like excise, custom duty, services tax etc. still the GDP of India is much less as compared to the GDP of the other countries like USA – 13.84%, china-6.99%, Japan- 4.3% and France -2.05% . So, the GDP data of various countries demonstrates that there is almost need of tax policy that is implementation of goods and services tax in India (GST).
Goods and services tax (GST) – current scenario
(1) Need for the GST- goods and services tax: as per the my reports of task force of goods and services tax (2009),the Indian taxation system led to misallocation of resources and lower productivity in terms of economic growth, replace the existing tax system with a new engine of taxation of goods and services to attain the following:
♦ The tax incidence fell primarily on domestic consumptions.
♦ The optimization of efficiency and equity of the Indian system is an aims to efficiency are optimization.
♦ There should no export of taxes across the taxing jurisdiction.
♦ The Indian market should be brought under a single umbrella of common market.
♦ Enhancement to the cause of cooperative federalism.
(2) Introduction to the goods and services tax (GST):
New article 366 (12A) of the Indian constitution (GST India. Com, 2016) explain goods and services tax (GST) to mean any tax on supply of goods or services or the both expect taxes on the supply of alcoholic liquors for human consumption . New article 366(26A) explain services to means anything other hand goods. Existing article 366(12) explain goods to include all materials, commodities, and articles.
As per the government, goods and services tax (GST) is inform as a rather than amendment in the existing Indian taxation system to sort out all background and cons of the indirect taxation system .India was one of the 123 countries in the world following the VAT taxation system. VAT was designed and introduced on January 17, 2005 at the centre and sales tax system at the centre and states levels by finance minister p. Chidambaram. VAT can replace central excise duty taxation at the national level and sales tax system by final taxation at the national level and sales tax system levels tax system at the state level, bringing major reform in the taxation system.
Limitations of the study and scope for future research
The following are the limitations of the study:
♦ GST is stay in maturity phase, so tax reforms can occur from time to time via GST council meeting regarding finalization of tax rates and even imposition of new rates and even deduct of the existing rates.
♦ Most of the data has been cities in the my research paper which I have noted the point was speculatively exploratory in nature as GST getting are going and stay , a lots more needed to be done.
♦ Final conclusions on the point of my own view may vary consider different perceptions.
When GST implement there is emergent requirements of moderns technology based infrastructure like GSTNET for successful monitoring of taxation system as well as the GST council should regular are to be conduct meeting for the changes in tax reflections. These areas can be covered by the researchers in future studies.
Conclusion:
> India is the 166th country of the world that has adopted GST on July 2017.
> GST subsumed multiple taxes levied by defend authorities at different places.
> It is accepted that GST would faster the growth substainly and revenue of the government would increases many fold.
> Common man will be benefited by the GST.
> An absoluteness developed would be seen of the economy due to GST.
> Revenue would faster growth welfare and development programs of the government equally.
> The threshold limit for exemption from GST rates in India is lower than many others country of the world causing a great challenge for SMES.
> So there is need of second thought to increase and revised the threshold limit for SMES.
> Challenges before GST are many; however collectively we can overcome them.
> We study the comprehensive of the newly approved goods and services tax (GST) in India which is scheduled to take effect in mid 2017. We collected the most notable indirect taxes that the GST will subsume both at the central and the state level. In India GST is the single tax paying at the end of finical years. GST also arise the inflation and economy growth also GST is the single tax. when GST not comes in India then they pay the tax at the different tax at the different product at the different amount which is charged by the central government of the our country when GST comes in India they loss arise the less burden of taxpaying and government also free for the india.
References
Websites:
- https://www.researchgate.net.
- https://www.engpaper.com.
- academia.edu.
- https://www.omicsonline.org.
- publishingindia.com.
Books references:
- Book reference-authors Kailash rai (taxation laws).
- Book reference- authors DR. S.R. Mynenin (law of taxation)
- Book reference- authors v.k. singh.
- Hyperlink- A comprehensive analysis of goods and services tax.docx.
[1] One nation, one tax (GST).
[2] 1st July 2017, India became 166th GST nation.
[3] 2006-7 GST budget session.
[4] In 2000 atlas Bihari Vajpayee the new tax imposed after long time.
[5] 1 April 2010 constitution passed GST bill was passing on 2011 introduction on GST.
[6] 2006 tax paid at different product at different amount.
[7] Canvat rules act, 2004.
[8] Article 265-289 directly relates to taxes.
[9] GST come in India they have to less burden to pay tax.
[10] Article 269(A) proposed the GST taxs.





Very Informative …Thank You