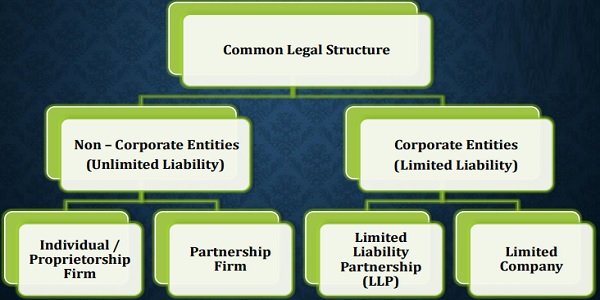
In India, the process of starting a business involves understanding various legal structures. Non-corporate entities, such as sole proprietorships, involve a single owner with unlimited liability, whereas corporate entities like partnerships, LLPs, and private limited companies offer distinct features. Sole proprietorships are simple with no separate legal entity, while partnerships require a partnership deed, and LLPs combine features of both partnerships and companies with limited liability. Private limited companies have shareholders and directors, offering limited liability. Phase 1 covers the different entity types and their governing regulations, tax structures, and liabilities. Phase 2 explains the step-by-step process of entity formation, including registering PAN, Aadhaar, and other documents. For instance, proprietorships require basic registrations and licenses, while forming a private limited company involves more paperwork, such as drafting MOA and AOA. Phase 3 highlights key post-setup tasks, including GST registration, intellectual property rights, and employee-related compliances. The entire setup process varies depending on the business structure, with duration ranging from 10 to 30 days.
Common Legal Structures for Starting a Business in India
Phase 1: Understanding Different Entity Structures in India and Their Key Differences
Phase 2: Step-by-Step Process for Forming Each Business Entity
Phase 3: Key Considerations After the Legal Setup of the Business
PHASE – 1
| Sr. | Questions | Incorporated as | |||
| Non-Corporate Entities | Corporate Entities | ||||
| Individual / Proprietorship | Partnership Firm | LLP | Private Limited Company | ||
| 1 | Nature or Definition ? | Single Person is a owner
running a business – Same PAN Card of Individual no new apply |
Two or More person comes together as Owner for running a business – Separate PAN card of Partnership Firm | Just like Partnership firm but given corporate Status like Company – hybrid combination of Partnership and Company features – Separate PAN card of LLP | Concept of Shareholders and Directors with Limited Liability – Separate PAN card of Company |
| 2 | Number of Owners | Sole Owner -1 | Minimum – 2 Maximum – 50 | Minimum – 2 Maximum – Unlimited | Minimum – 2 Maximum – 200 |
| 3 | Person who starts the entity would be called as? | Person would be called as “Proprietor” | Persons would be called as “Partners” | Persons would be called as “Partners” and specified person as “Designated Partner” | They became “sharehc:der” and those managing as “Director” |
| 4 | Liability is Limited or Unlimited? | Unlimited Liability | Unlimited Liability | Limited Liability of Partners | Limited Liability of Shareholders |
| 5 | Separate Legal Entity | NA | No | Yes | Yes |
| 6 | Any Document to be prepared? | No such | Partnership Deed | LLP Deed | 140A and A OA |
| 7 | Which Act governs this | No such specific Act | Indian Partnership Act, 1932 | Limited Lab iLit.–y Partnership Act. 2008 | Companies Act 2013 |
| 8 | Income Tax | As per Slab rate | 30% after Partners
remuneration and Interest |
30% a:ter Partners
remuneration and Interest |
25% |
Phase – 2: Step by Step Process of Each Entity Formation
(A) Proprietorship Firm
> Apply Pan Card & Adhar Card of Individual
> Decide The Firm Name
> Prepare A Registered Rent Agreement Mentioning Your Firm Name As “Tenant” With Police Verification
> Apply For Shop and Establishment Licence
> Apply For Professional Tax Licence of Firm
> Apply For Current Bank Account
> Apply For MSME Certificate
> Apply For Required Licence / Approval from Your Institute Like for Architect – Coa (Council of Architecture) To Practice
Duration – 10 To 15 Days
Phase – 2: Step by Step Process of Each Entity Formation
(B) Partnership Firm
> Apply Pan Card & Adhar Card of All Partners
> Decide The Firm Name
> Prepare A Partnership Deed and Notarised It
> Apply For Pan Card of Firm
> Apply For Tan Card of Firm
> Prepare A Registered Rent Agreement Mentioning Your Partnership Firm Name As “Tenant” With Police Verification
> Registered Your Partnership Firm with ROF (Registrar of Firm) – Recommendation
> Apply For Shop and Establishment Licence
> Apply For Professional Tax Licence of Firm
> Apply For Current Bank Account
> Apply For MSME Certificate
> Apply For Required Licence / Approval from Your Institute If Required Like for Architect – Coa (Council of Architecture) To Practice
Duration – 15 To 20 Days
Phase – 2: Step by Step Process of Each Entity Formation
(C) LLP (Limited Liability Partnership)
> Apply Pan Card & Adhar Card of All Partners
> Decide The LLP Name & Apply with MCA For Name Approval
> Incorporate LLP with MCA
> Prepare A Notarised LLP Deed and Filed With MCA
> Apply For Pan Card
> Apply For Tan Card
> Prepare A Registered Rent Agreement Mentioning Your LLP Name As “Tenant” With Police Verification
> Apply For Shop and Establishment Licence
> Apply For Professional Tax Licence of LLP
> Apply For Current Bank Account
> Apply For MSME Certificate
> Apply For Required Licence / Approval from Your Institute If Required Like for Architect – Coa (Council of Architecture) To Practice
Duration – 20 To 25 Days
Phase – 2: Step by Step Process of Each Entity Formation
(D) Private Limited Companies
> Apply Pan Card & Adhar Card of All Shareholders and Directors
> Apply For Digital Signature of All Shareholders and Directors
> Decide The Company Name & Apply with MCA For Name Approval
> Prepare Draft Moa and AOA
> Incorporate Company with MCA (Pan and Tan Card Comes Automatically with Incorporation)
> Pay The Stamp Duty on Share Certificate to Respective State Government
> Prepare A Registered Rent Agreement Mentioning Your Company Name As “Tenant” With Police
Verification
> Apply For Shop and Establishment Licence
> Apply For Professional Tax Licence of Company
> Apply For Current Bank Account
> Apply For MSME Certificate
> Some Institute Like for Architect to Practice – COA (Council of Architecture) Does Not Allow To Form A Company
Duration – 25 To 30 Days
Phase – 3: Common Points to Take Care After Legal Set Up
> Apply For GST Certificate – If Turnover Is More Than Rs.20 Lakhs for Services and Rs.40 Lakhs for Goods. You Can Even Apply Voluntary Also for Various Reasons
> Apply For Trademarks / Patents / Designs / Copyrights – IPR Https://Ipindia.Gov.In/ Https://Copyright.Gov.In
> Apply For Professional Tax Number of Employees – Even If One Employee
> Apply For ESIC & PF – If Crossed the Threshold for Number of Employees
> Apply For IEC (Import Export Code) – If Export Goods or Services
> Prepare NDA or Other Various Agreements with Clients, Employees, Vendors Etc.
> Apply For Startup Program If All Conditions Are Fulfilled
> Maintain Proper Books of Accounts and Keep Invoices of Each Payments And Receipts – Compulsory For Each Entity
*****
Disclaimer: The points stated above are general in nature and may not cover all conditions, restrictions, or options applicable to individual cases. The views expressed are personal. Unauthorized sharing of any content from this article without the author’s written consent may result in legal action. This presentation is tailored for the intended participants and not for the general audience. For further details, please contact us at capmehtaco@gmail.com, visit www.capmj.com, or call +91-9426339047.





