Sample illustrative SOP for Major Accounting Areas
Background of the Organization
<ABCL> is a registered Company established under the _____ Act, in the year ____. <Nature of business>
Scope & Purpose
This document covers the Standard Operating Procedures for the entire Finance & Accounting activities of <ABCL>.
About the Finance & Accounts Department
The aim of this SOP is to lay down necessary directives for the smooth and efficient administrative functioning, handling/ operating funds, functioning of F&A Department and to ensure that Statutory compliances are made in the following areas : v’ Delegation of Authorities and Financial Powers
√ General Ledger accounting and book keeping procedures
√ Accounts Payable process
√ Accounts Receivable process
√ Maintenance of Cash and Bank Balances
√ Bank reconciliation
√ Fixed assets purchases and its accounting
√ Disbursement of Salaries / Payroll
IT System for accounting
<ABCPL> uses the WINGS E-Biz Version 18.2 package for its accounting activities.
<ABC & COMPANY LIMITED>
Structure of the Finance & Accounts Department
<Insert flow chart of hierarchy>
Roles and Responsibilities
The roles and responsibilities described below are in reference to the Finance and accounting functions only.
Finance Controller
√ Responsible for the functioning of the Finance & Accounts Department as a whole lParticipate in discussions regarding commencement of new projects, closure of existing projects, geographical expansion etc
√ Signing loan proposals
√ Formulation and maintenance of Accounting, Investment and Funding policies of the organization
√ Participate in the working of the Purchase Committee
√ Approving authority for interest and penalty payments for statutory dues, filing of tax returns, Legal and audit fees etc.
√ Approval of GL closing entries
√ Approval of internal audit reports
√ Approval of provisioning entries
√ Fund raising activities
√ Participate in the financial budgeting activity of the organization
√ Approval of Payroll register for Payment Preparing and Reviewing Periodical Financial Statements and Annual Reports to Regulatory authorities and Donors. Reviewing Compliances
Finance Manager
√ Physical cash handling at the HO
√ Approval of BRS for HO accounts
√ Approval of transfer of funds for expenses to branch offices
√ Approval of payment vouchers for payments made by HO
√ Approval of monthly tax payments and quarterly tax filing
√ Making arrangements for salary payments
√ Responsible for data entry in the accounting system cost center wise
√ Comparison of actual expenses with the budget, when required
√ Preparation of Payment Vouchers and cheques for various payments
√ Preparation of monthly BRS of respective bank accounts
√ Preparing and Reviewing Financial Statements and submission to Regulatory Authorities
√ Preparing Compliance Reports
√ Preparing Budgets and comparison of Actuals with Budgets and Variance Analysis
Accountant
√ Maintenance of books of accounts for activities of the district office
√ Preparation of monthly BRS of respective branch bank accounts
√ Coordinate with HO for receipt of funds for expenses and subsequent settlement of the same with relevant documents
√ Coordinate with branches for disbursement of funds for expenses
Schedule of Authority
A clearly defined Schedule of Authority is essential for delegated working, faster decision making at appropriate levels and at the same time maintaining desired level of Internal controls.
The SOA has been devised for clarity and ease in rendering finance functions. The division recognizes each and every individual as an important member of a unified team with a common goal, irrespective of the position he/she may have in the organization.
The Company is governed by a Board of Directors which has empowered the Chairman and Managing Director and CFO for managing the activities of the Company.

| Sr. | Particulars | Authority/Limits |
| General | ||
| 1 | Commencement of a new project Closure of a project or Geographic expansion | Chairman and Managing Trustee along with the Secretary Trustee and the National Convenor with inputs from Coordinators |
| 2 | Signing of contracts with clients | Project Chairman and Managing Trustee/ and Secretary |
| 3 | Signing legal / regulatory / compliance agreements | Chairman and Managing Trustee /and Secretary |
| 4 | Signing loan documents | Chairman and Managing Trustee/ and Secretary |
| 5 | Signing Lease deeds (Rental)
a . F o r H O b . For Branches |
Secretary Branches |
| 6 | Banking Operations | |
| 6.1 | Opening of bank accounts | Chairman and Managing Trustee and Secretary |
| 6.2 | Authorized signatories for cheques and other instruments
For HO Main Accounts For Branches Office |
Chairman and Managing Trustee and Secretary/Member Secretary Trustee/Branches Head and Branches Accounts Head. |
| 7 | Expenditure | |
| 7.1 | Payroll | |
| Approval of Payroll register for Payment | Finance Manager | |
| 7.2 | Purchase of Fixed Assets of value > Rs.5000 | Purchase Committee at Head Office and Branches levels |
| 7.3 | Statutory Payments | |
| 7.4 | Monthly payment of taxes, Approval of tax remittances | Finance Manager |
| 7.5 | Interest and penalty payments for statutory dues | Finance Manager |
| 7.6 | Approval of tax returns prior to filing | Finance Manager |
| 7.7 | Legal & Audit fees | Finance Manager |
| 8 | Cash | |
| 8.1 | Limit for physical cash holding: At HO At Branches At Mandal | Rs. 500000/- Rs.100000/- Rs 50000/ |
| 8.2 | Limit for single cash payment: At HOAt Branches At Mandal |
Rs.20000/- Rs.20000/- R s 20000/- |
| 9 | Rights for adding/managing GL accounts | Finance Manager |
| 10 | Writing off Bad Debts | Finance Advisory Committee |
| 11 | Approval of monthly Bank Reconciliation Statements For HO Accounts For Branches Office | Finance Manager Branches Head |
| 12 | Disposal of Movable Assets | Finance Advisory Committee |
| 13 | Investments in Short Term Deposits | Managing Trustee and Secretary Trustee |
Purchase Committee
A Purchase Committee consisting of the respective User Department/Project Head, Finance Manager and Coordinator (<Project Related> Support) must be formed. This committee will be responsible for authorizing all expenses for purchase of Movable Assets and for entering into agreements with vendors/service providers as required. The role of the Purchase Committee is to ascertain the need for the asset, decide on the best possible product, obtain market quotes and finalise the purchase.
The Purchase Committee shall also review whether the purchases are within the approved budgets of the respective programs
The Purchase of All Capital items shall be placed before the FAC for approval. Expenses
<ABCL>’s expenses can be divided into <Project Related> and Administrative Expenses. The former constitutes all expenses incurred specifically for a <Project Related>, while the latter comprises those expenses that cannot be associated directly with any of the <Project Related>s and are incurred for the organization as a whole.
<Project Related> and administrative expenses are incurred at all levels, viz. Head Office and Branches Offices.
All expenses incurred at the HO (<Project Related> and Administrative) are being accounted in the respective projects.
Various expenses are incurred and accounted for at branch levels. Advances are made by the HO to the branches.
| Sr. | Expense description | Head Office | Branches Office |
| 1 | Salaries, wages and allowances | ~ | ~ |
| 2 | Communication expenses | ~ | ~ |
| 3 | Meeting expenses | V | V |
| 4 | Repairs & Maintenance | V | V |
| 5 | Travelling & Conveyance | ~ | ~ |
| 6 | Training Expenses | ~ | ~ |
| 7 | Printing & Stationery | ~ | |
| 8 | Postage & Courier | V | V |
| 9 | Insurance | V | |
| 10 | Vehicle Fuel & Maintenance | V | V |
| 11 | Rent | V | V |
| 12 | Computer Maintenance | V | V |
Budgeting
Budgeting is an important activity for any organization. At <ABCPL>, <Project Related> budgets are prepared on a monthly basis by each branch in charge in discussion with the Branches in charge. The individual Project Budgets are then consolidated to prepare the budget for the activities of <ABCPL> as a whole.
Monthly Budgeting of expenses
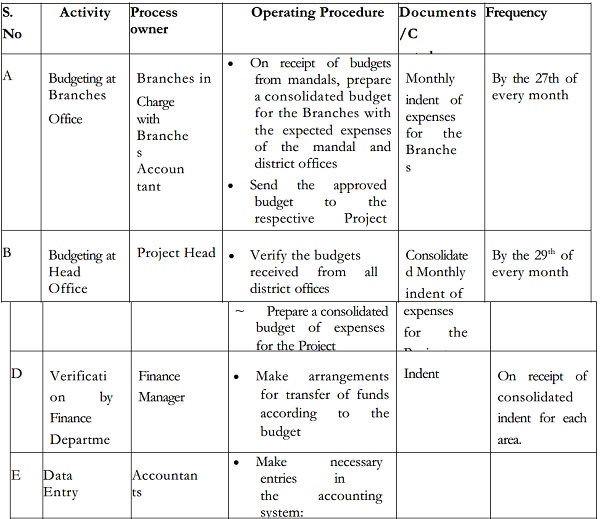
Transfer of funds for expenses for all projects.
Expenses of all levels are incurred at branches. Based on monthly indents for expenses, the Head Office transfers the requisite amount of money to the designated branch bank accounts, which then disburses the same in cash.
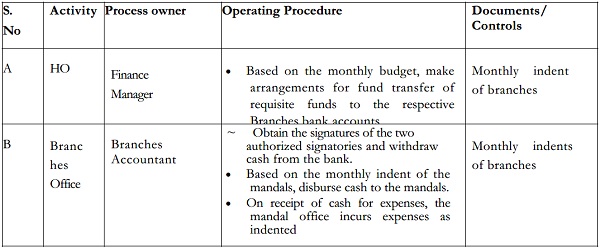
Detailed Operating Procedures
Salaries, wages and allowances.
This expense relates to all employees on the payroll of the organization. Salary expenses relate to employees of the Head Office and the Branch Offices. While the expense may be incurred at any of the three levels, the payroll processing and accounting is centralized at the Head Office.
Payment of honorarium, consultants’ fees, casual wages etc. will not be included under Salaries, Wages and allowances.
The same procedure is followed for <Project Related> expenditure.
Insurance
Insurance is taken by <ABCPL> for the following categories:
√ Cash in Transit at HO and branch
√ Fidelity at HO and branch
General Ledger Accounting
Transactions are captured in the <ERP Module> through the general ledger. Financial Operations maintains a chart of accounts, which provides for standard account coding across all <ABCL> departments.
New Accounts
Additions to the chart of accounts are authorized by Financial Operations. Department users are encouraged to use existing accounts when possible, unless tracking needs warrant the use of a new segment not currently available in the chart of accounts.
General Ledger Entries
Entries may be posted to the general ledger from <ERP Module> Finance or through feeds from integrated modules outside of Finance. The following are common types of entries found in the general ledger:
√ Journal Entries – Specific employees in Financial Operations have been provided with the authority to enter journal entries. Upon entry, <ERP Module> assigns a unique journal entry number (starting with ‘J’) which appears in the general ledger. Monthly purchasing card entries are uploaded with a ‘PC’ document number followed by the month-end date (i.e. March 2022 document number = PC033122).
√ Invoices – Staff in Accounts Payable enter invoices into the <ERP Module> system with a unique vendor invoice number. <ERP Module> then assigns a sequential invoice number (starting with ‘I’) to each invoice entered in the system.
√ Fixed Asset Adjustments – <ERP Module> automatically capitalizes Fixed Asset purchases over the College’s designated capitalization threshold. Financial Operations enters Fixed Asset adjustments directly into the Fixed Assets system, as necessary. These entries are coded in the system with an ‘M’.
√ Feeds – Most other entries are fed into the general ledger from other <ERP Module> modules. Examples include cash receipts in the Cashier’s Office and College Advancement, Financial Aid transmittals, student billings, and payroll transactions. Feeds are assigned a specific entry number in <ERP Module> (starting with ‘F’).
Maintenance and Distribution of General Ledger
Departmental budget officers have access to the general ledger through <ERP Module> Self Service. In <ERP Module> Self Service, users can view non-salary account activity (including budget availability) in their designated departmental accounts. Any corrections of errors or transfers of funds must be communicated to Financial Operations. Transactions are typically corrected via a journal entry.
Budget officers allocate their overall budget to individual line items during the budget planning process. Budget officers are responsible for monitoring their available funds and use of those funds during the year. Budget allocations during the year must go through the Budget Office. Budget requests for additional funds during the fiscal year must go through the All-College Committee on Planning and Budget.
Additional budget and financial reports can be generated by Financial Operations using the reporting tool.
Fiscal Year-End Closing Procedures
The Company maintains its books on a fiscal year ending March 31. This means that the Company’s records of account must show all revenues earned and expenditures incurred during the year ended March 31, and the College’s assets and liabilities must be accurately reflected as of March 31. Specific cutoff instructions are as follows:
√ Year-end purchasing –In order for purchases to be recorded in the current fiscal year, goods must be received and/or services must be performed by March 31. In addition, financial managers must ensure vendors submit invoices within a month after year-end. After the end of April, Accounts Payable books will be ‘closed’ and subsequent invoices will be expensed in the following year (unless specifically accrued or prepaid by Financial Operations).
√ Internal charges/transfers – All internal charges and other transfers relating to the closing fiscal year
must be submitted to Financial Operations by the end of July so these charges can be properly posted in the March ledger.
√ Physical Inventories – Inventories must be conducted on an annual basis (at a minimum) and may be conducted more frequently to meet departmental needs. Inventory counts must be conduct at or near year-end to ensure the most accurate inventory is reflected in the Company’s books as of March 31. Purchasing and receiving should be suspended before the inventory to facilitate the actual count. Inventories of Fixed Assets are conducted on a rotating basis every two years.
Financial Operations will continue to post journal entries in the general ledger during April and May to close the books and prepare for the year-end audit. Financial Operations is responsible for external financial reporting and populates the Company’s financial statements and related footnotes. All information is provided to the external auditors for final review in April. Only auditor adjustments will be allowed after the beginning of their year-end test work.
SOP: Sales Invoices
Objective
To produce a sales invoice, which is used to create both a journal entry and unbilled transactions for the services
rendered pending invoicing.
Procedure
Stage I: Recording a Sales Invoice
1. Enter the Sales Invoices form.
2. Specify the Customer Number and appropriate customer Contact. A temporary Invoice No. number (with the prefix T) is assigned when you leave the column.
3. Today’s Date appears automatically, but may be revised.
4. In the Price tab, the customer’s default Currency appears automatically, but may be revised.
5. Click the References tab, and link the invoice to the relevant customer Order, if any. Alternatively, link the invoice to a price quotation in the Price Quotation column.
6. If you do not want the invoice to be taken into account during credit calculations, enter the Invoice – Additional Details sub-level form and make sure the Consider Credit column is not flagged.
7. Enter the Invoice Items sub-level form.
8. If the invoice is linked to a sales order or price quotation, the items appear automatically.
9. If there are special payment terms for this invoice, enter the parallel Payment Installments sub-level form and define those terms.
10. Return to the upper-level form. In the Price tab, check the invoice totals and discounts.
11. Return to the upper-level form.
12. Finalize and/or print the invoice by selecting Finalize Invoice/Memo or Finalize & Print Invoice from the list of Direct Activations.
13. To prepare a receipt for the invoice, run the Record a Receipt program by Direct Activation.
Results
√ A journal entry is created for the invoice, and unbilled transactions are created for pending invoicing.
√ The invoice is assigned a permanent number (without the prefix T).
Stage II: Canceling a Sales Invoice
√ If the invoice is still pending (that is, the Finalize Invoice/Memo program has not yet been run in Stage I), then return to the upper-level form and select Delete Pending Invoice/Memo from the list of Direct Activations.
√ To cancel a final sales invoice for the original invoice date, select Cancel Document (Original Date) from the list of Direct Activations.
√ To cancel a final sales invoice for a designated date, select Cancel Document For Date from the list of Direct Activations (and indicate the date in question).
√ If you have already prepared a receipt, first cancel the receipt. See the Customer Receipts SOP for details.
Results (when the invoice was final)
√ The procedure opens a cancellation invoice and a corresponding reversing journal entry, dated according to the chosen cancellation program (the original invoice date or the date the program was run).
√ In the original invoice, the Canceled column is automatically flagged (in the Price tab).
√ Any reconciliations for the original invoice are cancelled.
SOP: Accounts Receivable
OVERVIEW
The purpose of monitoring accounts receivable (A/R) is to ensure timely payment by clients and minimize write-offs. A project wise A/R is created when an invoice is sent to a client for payment. This document details the steps completed to manage project wises A/R.
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
Accounts Receivable Accountant (ARA)
√ Creates all accounts receivable reports relating to project wise.
√ Monitors invoice payments and sends late payment notification letters to clients who have outstanding invoices.
√ Contacts the Finance Controller to remedy any issues the client has with an invoice or to assist in determining payments that were not received.
√ Sends e-mails to notify Department Head (DH) to complete remaining tasks so that payment can be received.
√ Creates journal entry to transfer funds from PI’s college or department to the project wise.
Fiscal Affairs Accountant (FAA)
√ Sends a copy of the invoice to the ARA for their records and tracks payment after an invoice is created.
√ Assists in correcting or investigating any unpaid invoices that may have a financial misstatement or other invoice related errors.
Finance Controller
√ Monitors and manages the A/R process for project wises.
√ Works with Department Head to determine the best approach to obtain payment from clients for A/R.
Accounts Receivable Internal Procedure
Department Heads (DH)
√ Serves as the primary point of contact for the FAA and the ARA when determining the cause of an unpaid invoice.
√ Contacts the PI to determine if any outstanding issues relating to technical reports may affect the payment.
Informs the ARA of the outstanding issues.
√ Contacts the PI and client to resolve any additional issues.
PROCEDURE
A. Obtain A/R Reports
1. Accounts Receivable Accountant (ARA) generates the Project wise Invoice Aging Report form on a monthly basis. This report lists all unpaid invoices for project accounts and the number of days the invoice is outstanding. The invoice wise details are shown by:
a. 1 to 30 days
b. 31 to 60 days
c. 61 to 90 days
d. 91 to 180 days
e. 181 to 365 days
f. Over 365 days
2. There are times when adjustments are made to an invoice and the amount may change on the invoice. In this case, either Debit Note or Credit Note is issued.
B. Sending the Late Notification Letter
1. The outstanding invoices remaining on the Project wises Invoice Aging Analysis require follow-up by Department to collect payment. A late invoice notification letter is sent to all customers with outstanding invoices older than 45 days from the invoice date.
2. The ARA sends letters to vendors on the 45th day, 90 day and 120th day stating that the invoice is outstanding.
3. ARA gives the letters to the Department Heads Accountant to sign and approve.
C. A/R Follow-up
1. The ARA follows-up with the DH after the second Late Notification Letter is sent to the client on the 90th day from the invoice date.
2. If no payment has been received after three months, the ARA sends an email under the Controller’s name to
the DH inquiring about any outstanding. This email also notifies that if the DH does not complete his/her tasks within one additional month, then the amount will be written off.
3. A monthly write off report is send to Department Heads and Finance Controller for their signature and record purpose
D. Invoices Filing and Record Keeping
1. All Project wise Invoice Aging Reports and Invoice Payment Reports are maintained in the file cabinet and soft copies stored in a folder named “Monthly Invoices” organized by month.
2. The ARA attaches any late payment notification letters and any correspondence about the invoice to the original invoice
3. A monthly statement of write offs signed by Department Heads and Finance Controller is stored in the file cabinet and soft copies stored in a folder named “Write Offs” organized by month.
SOP -BANK RECONCILIATION
1.0 OBJECTIVE
To make sure that all current transaction concerning to bank account in general ledger are reconciled with bank statement
2.0 POLICY
All bank accounts must be reconciled within ten (10) days of the prior month end.
3.0 SCOPE OF THIS SOP
A. Bank Reconciliation Definition and Overview
B. House Bank Concept
C. Bank Ledgers
D. Automatic and Manual Reconciliation
E. Month End Process
F. Quality Assurance
4.0 ROLES INVOLVED IN THIS SOP
F&A User (GL)
F&A User (AR)
Section A. Bank Reconciliation Definition and Overview
1. Bank Reconciliation is a process that identifies and explains the difference between the bank balance shown in an organization’s bank statement as supplied by the bank, and the corresponding amount shown in the organization’s own accounting records (General Ledger – nominal bank account) at a particular time.
2. The recommended interval for bank reconciliation for entries with deployed <ABCL> solution is daily.
3. The vast majority of bank reconciliation activities are based around identifying two types of transactions: Outgoing Payments and Incoming Payments .
Section B: House Bank Concept
The <ABCL> solution has introduced the concept of House Banks. All bank accounts now belong to one of three Treasury Pool Funds:
- Collection Pool – All collection and credits
- Payments Pool – All Payments and Debits
Section C: Bank Ledgers
1. In <ABCL>, each House Bank has 3 related General Ledger (GL) accounts. The first is the Nominal Account which reflects the actual cash balance in the physical bank account.
2. Besides the Nominal Account opened for each physical bank account, there are 2 other GL accounts associated with the same bank account. These GLs are Open Item Managed (OIM) ledgers and are the ones that are cleared when users are carrying out the reconciliation.
Section D: Automatic and Manual Reconciliation
1. The task of reconciling transactions with the bank, which result from created Outgoing Payments, is essentially the processing of the credits that are temporarily booked to these clearing accounts when the cashier generates payments. While some of the transactions will reconcile automatically, others will have to be cleared manually.
2. Automatic clearance takes place when the details (reference and amount) on the outgoing payment document (KZ) exactly matches the details on the bank reconciliation document (ZR – the bank statement upload document). The automatic clearance process takes place every day, when the bank statement is uploaded into <ABCL>.
3. Where the automatic reconciliation fails, the bank reconciler will have to manually reconcile the bank ledgers.
4. In <ABCL>, a bank account is termed as fully reconciled when one of the following conditions are satisfied:
√ There are no open line items on the bank GLs (i.e. the balances on the bank clearing GLs are zero) or
√ All Open Items are identified and explained (e.g. unpresented cheques).
Section E: Month End Process
1. At the close of every month in <ABCL>, the Month End Bank Reconciliation statement is prepared.
2. The reconciler downloads the open items for all the ledgers of the required bank account, including the nominal ledger.
3. The open items are then entered into a pre-formatted excel template (Annex A), signed and dated.
4. The following supporting documentation is attached when the reconciler submits the reconciliation for approval:
√ Print screen of <Bank Names> balance at month end, showing balance per bank equal to Nominal. 1′ Printout showing GL account balances for all reconciling GL Accounts for that bank
√ Printout of bank statement obtained from bank (if available) or soft copies saved in folder named <Bank Statements> arranged month wise
√ Cancelled cheques are to be stored separately from the reconciliation folders and are to be maintained in the hotel’s permanent files
5. The signed month-end reconciliation report is filed for audit purposes.
Section E: Quality Assurance
The key Quality Assurance (QA) Requirements for Bank Reconciliations are as follows:
a) Supervising Officers are to ensure that all original documents are properly secured and that access to documents is restricted to External Auditors or properly-
b) Bank Reconciliation team is to submit Monthly Management Report highlighting
c) Risks and Issues and measuring performance against benchmarks.
Example of a fully reconciled house bank month end report
BANK ACCOUNT: HSBC BANK MIDDLE EAST A/C NO.___________
BANK RECONCILIATION 31ST MARCH 2022
Description G/L
Account Document Type
Assignment Document Number
Posting Date Amount in doc. curr.
Document currency
Clearing Document
Clearing date Text
Balance as per Bank
Outstanding Cheques Outgoing
Outstanding Cheques Incoming
Bank Charges / Revenue
Unidentified cash Movements
Total: Balance as per General Ledger
Prepared By: Reviewed By: Approved By:
Fixed Asset and Inventory
Control
Policy and Procedures Manual
1. OVERVIEW
A. PURPOSE
The purpose of this Policy and Procedures Manual is as follows:
√ To provide adequate internal control over capital equipment and help ensure the safeguarding of <ABCL> assets.
√ To document the inventory policy for Capitalization and Inventory Control
General Information:
The Asset Management Personnel (AMP), in the Administration & Information Technology (IT) Department, under the respective Department Heads recommends the following:
√ Administrative Departments: Chairs and equipment located within and other departments. They may assign responsibility to a Business Manager (BM). Where there is no designated BM, the Admin Head may designate responsibility of managing the department’s assets to the appropriate personnel. However, the Admin Head is ultimately responsible.
√ The Business Manager (BM) manages the assets and their record keeping.
√ All Business Managers and those assigned to manage department assets (Accountability Officers) are responsible for reporting their department’s asset information to the Asset Management Personnel.
√ The Asset Management Personnel (AMP) are responsible for managing and conducting a Company-wide physical inventory observation once every TWO years.
√ The Asset Management Personnel (AMP) must ensure that all departments conduct an inventory count and provide a report.
√ Each Accountability Officer is required to maintain an accurate inventory of all property within his/her area of responsibility.
√ All departments including the information technology department (ITD) and procurement department must notify AMP of new capital assets purchased upon approval of the purchase order.
√ All departments must ensure that an employee separating from the <ABCL> accounts for the return of all <ABCL> assets in their custody. Such assets include, but are not limited to, technology equipment such as computers, and office equipment. Separating employees must have their department heads, the ITD, and the AMP sign-off on the separation asset accountability form to be obtained from the AMP.
B. RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE CONTROLLER’S OFFICE
The F&A Department is responsible for the following:
√ Determining what items shall be classified as capital equipment and applying the appropriate accounting standard in the <ABCL>’s financial records.
√ Maintaining central records of all capital equipment by recording all equipment additions, disposals, and adjustments in <ERP System Name (ERP)>.
√ Asset Management Personnel must run queries every month to determine whether capital asset purchases have been made.
√ All tagging of assets will be performed by the Asset Management Personnel.
√ Providing training in the proper procedures in the use of the <ERP System Name (ERP)>.
√ Conduct physical inventory of all capital inventory at least once every two years.
√ Maintain accurate records for audit purposes.
√ Reconcile the AM system with the General ledger
C RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE PROCUREMENT OFFICE
√ Deliver all computer and computer related items such as Laptops, Desktops, IPADs, Tablets, etc. to ITD, NOT to the department requesting it.
√ The procurement office must designate a Business Manager or Accountability Officer who will liaise with the AMP.
√ Ensuring accurate account coding for equipment acquisitions on purchase orders.
√ Ensuring <ABCL> departments follow proper procedures for the repurposing, transfer, and disposal of <ABCL> property.
√ The procurement department MUST provide the AMP with copies of manual purchase orders (i.e. PO’s not created in <ERP System Name (ERP)>) issued for capital item purchases.
D RESPONSIBILITIES OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT (ITD)
The Office of Information Technology is responsible for the following:
√ Notify AMP upon receipt of any computer or computer related equipment received. v’Ensuring that each item of capital and non-capital computer equipment is tagged.
√ Capturing acquisition information as to description, cost, etc. and providing same to the Asset Management Personnel to facilitate updates to <ERP System Name (ERP)>.
√ Ensuring <ABCL> departments follow proper procedures for the repurposing, transfer, and disposal of computer equipment.
E <ERP SYSTEM NAME (ERP)>
What is AMS?
The Asset Management System <ERP System Name (ERP)> is the asset database module of <ERP System Name (ERP)>. All capital assets items as defined by the <ABCL> are recorded in AMS.
System Features and Benefits
√ All purchased capital assets items are recorded in the AMS by the Asset Management Personnel of the F&A Department.
√ Each capital asset item record contains detailed information about the asset, such as proper description, account number, acquisition cost, acquisition method (e.g., purchase order, gift, loan, and transfer-in), vendor name, manufacturer, model and serial numbers, acquisition date, tag number, location, and custodian of the asset.
√ MS will record capital assets directly into the general ledger and automatically calculate the depreciation of capitalized assets.
II. POLICIES:
CAPITAL EQUIPMENT:
Capital equipment for the purpose of this document is defined as moveable property owned by or assigned to the custody of the <ABCL> having a useful life greater than one year and a purchase price or other acquisition value of Rs. 5,000 or more. Capital equipment includes all such items whether they are purchased or received in kind/ in lieu of settlement of debts.
Purchases
The following costs are applied towards the Rs. 5,000 acquisition cost and should be capitalized.
√ Any initial modifications, attachments, or auxiliary apparatus that are necessary to make an item of capital equipment useable for its acquired purpose
√ Shipping or freight charges, in-transit insurance, and installation cost
√ Upgrades, modifications, or enhancement parts that increase the useful life of the equipment by one or more years
The following cost may not be capitalized:
√ Equipment repair cost
√ Separate warranty cost or maintenance contracts
√ Demolition or dismantling cost
√ Spare or replacement parts cost
D Assets received in kind/ in lieu of settlement of dues to the <ABCL>
All equipment received in kind/ in lieu of settlement of dues to <ABCL> must be recorded at the fair value of the equipment on the date of the donation.
Acquisition by Installment Purchase or Leases
All leased equipment must be capitalized if it meets the criteria outlined in Ind-AS which provides that a lease is capitalized if at inception it meets one of the following criteria:
√ It transfers ownership to the lessee by the end of the lease term
√ It contains a bargain purchase option
√ The lease term is 75 percent or more of the estimated economic life of the leased property
√ At the beginning of the lease, the present value of the minimum lease payments (excluding executory cost), equals or exceeds 90 percent of the excess of the fair value of the leased property.
The leased equipment is recorded at the total cost net of interest expense (the present value at the inception of the lease).
Capital equipment does not include “fixtures”_________ i.e., an item that is an integral part of a Campus building — but does include special purpose installations which are readily removable from buildings.
REAL PROPERTY
Real Property includes land, building and building improvements, land improvements (other than building), infrastructure and construction in process. Valuation principle outlined for buildings and building improvement also apply to infrastructure, land improvements and construction in process.
A. Land
Purchased
All land acquired by purchase is recorded at cost. The cost includes:
I) The amount paid for the land itself
II) All related acquisition cost
a. Title fees,
b. Legal/ Attorney fees
c. Broker Commissions
d. Cost of real estate surveys
e. Cost of razing an old building
f. Cost of canceling an unexpired lease
g.Payment of accrued or unpaid taxes
Assets received in kind/ in lieu of settlement of dues
Land acquired in kind/ in lieu of settlement of dues is recorded at fair market value at the date of acquisition.
Land Acquired with building Erected thereon
For land acquired with a building erected thereon, the cost is allocated between the land and the building in reasonable proportions at the date of acquisition. If the transfer document does not show the allocation, other sources of information may be used such as an expert appraisal or the real estate tax assessment record.
Land Improvement
These include fencing, athletic fields, landscaping or modifications to the land of a permanent nature requiring no or minimal upkeep. These items will be capitalized if their cost exceeds Rs. 500,000. Land improvement has a useful life of 20 years.
B. Building
Building includes all buildings and permanent structures such as fixtures, machinery, and other accessories that cannot be easily moved without disruptions to the basic building structure or services to the building. Buildings should be capitalized at cost.
All buildings including those constructed or purchased or received in kind/ in settlement of dues have a useful life of 40 years beginning on the date the building is placed in service. The cost includes:
I. Construction cost
II. Cost of excavation, grading or filling of land for the specific building
III. Cost of preparation of designs and plans
IV. C o s t of building permits
V. Interest cost during the construction of the building
Renovations that replace all internal and external structures of a building should be considered a new building and depreciated as such.
Building Improvement
Significant additions, alterations, renovations or structural changes that extend the useful life or enhances the existing
building and which exceed Rs. 500,000 in cost should be capitalized.
C. Infrastructure
Infrastructure includes roads, bridges, curbs, water, sewer and utility distribution systems which exceed Rs. 500,000 in cost
should be capitalized.
D. Construction in Process (CIP)
This includes all cost associated with building, building improvement, or land improvement construction projects that are not completed at the end of the fiscal year.
- The department of Facilities and Capital Planning and the AMP of the F&A Department will meet regularly during the fiscal year to discuss the status of future and ongoing projects:
>For larger long-term projects AMP of the F&A Department shall be assigned as a member of the project committee and shall attend all committee meetings for the duration of the project.
>For smaller short-term projects, the Facilities and Capital Planning department staff and AMP of the F&A Department shall meet quarterly to discuss progress on current projects.
> Additionally, the department of Facilities and Capital Planning must provide monthly written updates on all projects to the AMP.
Useful Life Guide for Coppin State <ABCL> Assets
|
Particulars |
Useful Life |
| Building | |
| Land Improvements | |
| Equipment (office-Computers, AV equipment) | |
| Equipment Non-office (Kitchen) | |
| Computer Software | |
| Office Equipment (Chairs, desk, file cabinets) | |
| Vehicles |
Depreciation Policy:
√ All depreciable items will be depreciated on a Straight Line basis over the useful lives of an asset.
√ <ABCL> will depreciate all items based on the following month convention.
| Table of Contents | Page | |
| 1. | Abbreviations and Symbols used in Standard Operating Procedures | |
| 2. | Payroll Processing | |
| 3. | Functions of payroll vendor | |
| 4. | G/L reconciliation | |
1. Abbreviations and Symbols used in Standard Operating Procedures
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
| HR | Human Resources |
| MRF | Manpower Requisition Form |
| HOD | Head of Department |
| CEO | Chief Operating Officer |
| CFO | Chief Financial Officer |
| T&D | Training and Development |
| PMS | Performance Management System |
| CV | Curriculum Vitae |
| FFS | Full and Final Settlement |
| HMRC | Her Majesty Revenue and Customs |
| KRA | Key Result Area |
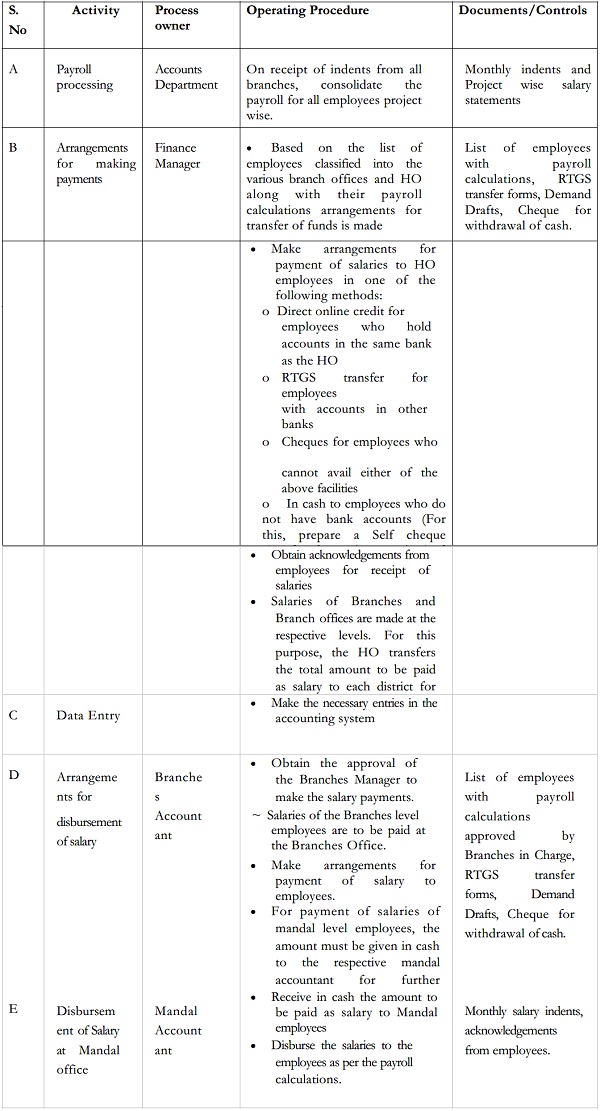
2. Payroll Processing
Process Flowchart
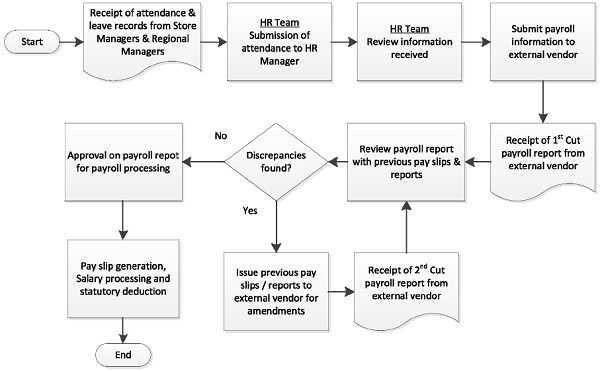
Roles and responsibilities
| Activity | Department | Responsibility | TAT |
| Sharing of Attendance record to payroll vendor | Human Resource | HR Manager | Before 20th of every month |
| Timely updation to attendance record & submission to HR for payroll processing | Human Resource | Reporting Manager | Before 20th of every month |
| Pay slip, Salary processing and statutory deduction | Human Resource | Payroll Vendor | 1st week of next month |
2. Payroll processing
1) The Human Resources Department will pull together the payroll information for the Head Office and Branches, up to the 20th of each month.
2) All new starter, leaver, overtime and changes must be completed using the online forms that are on <HR Management System>.
3) The Human Resources Department must also carry out for all new starters’ signed, dated security checks, and original in date copies of Company approved identification.
4) The only time information will be processed after the 20th of each month is if there is a leaver.
5) Any other details received after the 20th will be added to the following month’s payroll.
6) The Human Resources department will not add any new starters or make any changes to the payroll if forms are submitted incomplete or the relevant security checks have not been completed.
7) Once all the Head office and Branches payroll data is collated.
8) Human Resources Assistant will open the new payroll spreadsheets in <HR Management System> Permanent data and Temp data and populate the spreadsheets accordingly.
9) The Human Resources Manager will then carry out the necessary checks before submission.
10) All spreadsheets are uploaded to the external payroll provider’s domain by the 20th of each month
11) The external payroll providers will submit the 1st run of reports 1-2 days after the initial submission.
12) The Human Resources Department will carry out initial spot checks of the pay slips against the previous months pay slip’s and the completed spreadsheets.
13) The Human Resources Department will then re issue the checked pay slips back to the external payroll provider for further amendments if necessary.
14) The external payroll provider will process payroll by no later than the 25th of each month.
15) Salary payments made on the last working day of the month.
3. Functions of payroll vendor
Payroll Vendor performs the payroll processing following way:
A. Salary Processing through Pay Check Plus / Pay Plus – Salary payments,
B. Deposit of Statutory Dues
C. Salary Calculation Check
D. Pay Slip preparation and distribution for employee
4. G/L reconciliation
A monthly G/ reconciliation will be prepared the F&A team member for each G/L account head used for salary and monthly paysheet shared/ uploaded by Payroll vendor :
| GL Codes | Account Head | Balance as per G/L | Balance as per Paysheet | Difference |
| 100001 | Basic | |||
| 100002 | HRA | |||
| 100003 | Allowance | |||
| 100004 | Bonus | |||
| 100005 | PT Deduction | |||
| 100006 | EPF Deduction | |||
| 100007 | VPF Deduction | |||
| 100008 | Income Tax Deduction | |||
| 100009 | Recoveries | |||
| 100010 | Gratuity Paid | |||
| 100011 | Leave encashment paid |
–
| SOP | Accounts Payable |
| Date and Version | |
| 1.Objective | |
| The objective of this procedure is to describe all the activities associated in handling the payable Accounts of Axiom Telecom. | |
| 2. Scope | |
| The procedure covers the activities carried in the regions where Finance carries out its activities | |
| 3. Inputs | |
| · Reconciliation Report | |
| · Creditors Ledger | |
| · Asset Form | |
| · Bills | |
| · Expenses Claim Form | |
| · Invoice | |
| · Purchase Order | |
–
| Activity : | Pre-activities Requirements | KPI : | Supplier control set up in system | |
| Input / Reference | Process Sequence | Process Step |
Responsibility | Record Generated |
| Supplier Creation (Stock) |
In case the supplier is a group supplier; creation to be done by ERP Finance Analyst. Category Manager sends E-mail requesting the creation with the following information | |||
| (Supplier payment terms & countries to be activated), As for merchandize local suppliers, Category Manager sends notification as E-mail plus hard copy of the contract. If it is a tax supplier photo copy from tax card to be provided too.
In case of Foreign suppliers, Category Manager must send formal letter from the supplier include bank detail (account No. Swift code, etc) as reference of any further payment of invoice s to this account. |
Category Manager |
E-mail (Supplier creation requisition – before any activity took place) |
||
| For local suppliers; create supplier in Oracle and sends supplier number to Category Manager (Within 24hrs).
Liability Account has to be mentioned according to the nature of the supplier, & if tax available, specify the tax % category + withholding tax (if any). |
AP Supervisor/ ERP Finance Analyst |
E-mail (Supplier creation) |
||
| Supplier Creation (Non-stock) |
Sends E-mail in details with supplier name, contacts, payment terms and hard copy from the contract, tax card (if any). | Purchase Coordinator |
E-mail (Supplier creation requisition – before any activity took | |
| create supplier in Oracle and sends supplier number to Purchase Coordinator (Within 24hrs.) Liability Account has to be mentioned according to t he nature of the supplier, & if tax available, specify the tax % category + withholding tax if any. | AP Supervisor | E-mail (Supplier creation) |
||
–
| Activity : | Capturing invoices | KPI : | ||
| Input / Reference | Process Sequence | Process Step | Responsibility | Record Generated |
| Stock supplier / Non stock suppliers items received in warehouse | Prepare Warehouse Stock Received Vouchers (SRV) log sheet for the day sign it & get it signed by Warehouse Manager | Payables Accountant (located at warehouse) |
Stock Received Vouchers log sheet signed. | |
| Reconcile warehouse stock received Received Vouchers log sheet match with ERP Supplier Goods Receipt Report confirming all the GRNS’ have been captured in system
In Case of short delivery, inform AP supervisor about the difference & the gap to be covered by Whom (insurance Credit note on supplier, forwarded…) |
Payables Accountant | Reconciliation between SRV log sheet & ERP Supplier Goods Receipt Report | ||
| Validate documents of GRNS’ against log sheet or Supplier good receipt report. Documents to be validated should contain the following:
1- SRV 2- Supplier invoice 3- Air Way bill 4- Copy of the PO (ERP will run automatically pay on receipt auto invoice which will push the GRN to Payables Module) |
Payables Accountant (located at warehouse) |
GRN available in supplier account & ready for future payments.
Send all document of that day to AP Supervisor (located at the office) for review & filing. |
||
| Review all GRNS’ documents sent by accountant & the log sheet to confirm correctness of information & file the same for future payments | AP Supervisor | Sign log sheet confirming all documents received & having all necessary documents attached. | ||
| Non stock suppliers/ expense suppliers/ services (no stock delivered to warehouse) + Fixed assets |
Create PO in system as per DOA requirements & specify the related account allocated (for fixed assets it will always be assets cl earing account) | Purchase Coordinator | ERP PO creation as per DOA | |
| Reviews PO with allocated account & provides the same for Finance Manager for approval | GL Supervisor/ Finance Manager | Approved PO as per DOA & correct data entry. | ||
| Non stock suppliers/ expense suppliers/ services (no stock delivered
to warehouse) |
Insure the following:
1.3 quotations available when stated by DOA (or approved supplier list). 2. Insure approved PO is already available (if stated by DOA) 3. Confirm item receivable (i.e.stationary …), or service already rendered by obtaining the signatory of the requestor department. 4. Validate the system invoice (Pay on receipt auto invoice) against physical document & account the same (ERP create accounting) & initiate for approval. Write down the system generated voucher # on the invoice for easy tracking. 5. Organize all documents, & forward for AP supervisor for review & approval. |
Manager Payables Accountant |
DOA chapter I / ERP PO approved + invoice created | |
| Verify all documents received, & approve ERP. Once approved, Payables transfers to GL (Auto run by day end) will push the entry to GL module. | AP supervisor | By day end Auto run to GL Module | ||
| Non stock suppliers/ fixed assets purchases | Insure the following:
1. 3 quotations available when stated by DOA (or approved supplier list). 2. Insure approved PO is already available (if stated by DOA) 3. Confirm item receied (installed or ready for service) or services rendered by obtaining the signatory of the requestor department. 4. Validate the system invoice (Pay on receipt auto invoice) against physical document & account the same (ERP create accounting) & initiate for approval. Write down the system generated voucher # on the invoice for easy tracking. 5. Organize all documents, & forward for AP supervisor for review & approval. |
Payables Accountant | DOA chapter II / ERP PO approved + invoice created | |
| Review PO with allocated account & provide the same for Country Finance Manager for approval | GL supervisor/ Finance manager | Approved PO as per DOA & correct data entry. | ||
| Provide copy of the fixed asset invoice to the GL Supervisor for updating fixed asset module by running ‘Mass Addition Create’ which will transfer the data to fixed asset module.
For immaterial fixed assets (less than Rs. 5,000 EGP or funded from the supplier (as marketing activity) we should book in the fixed asset module with amount 0.1 country currency for tracking purposes. |
AP Supervisor | Copy of document provided to GL Accounts Supervisor | ||
–
| Activity : | Supplier Reconciliation | KPI : | To maintain NIL Reconciliation variations |
|
| Input / Reference | Process Sequence | Process Step | Responsibility | Record Generated |
| Monthly basis Reconciliation | Stock supplier cases,
All suppliers GRN already posted in the system up to the date of the reconciliation. For Non stock suppliers Insure all invoices captured & posted |
AP Supervisor | Confirm all GRN captured (Max previous day log sheet & GRNS’ yet to be posted) | |
| Statement from supplier to be received on monthly bases & reconciliation against supplier ledger to be conducted | AP Supervisor | ERP Creditors Ledger Report |
||
| In case supplier account s common between two countries; provides the list of un-reconciled entries to the other countries to in sure documents are recorded in that country | Payables
Accountants of both countries |
Pending items for reconciliation (information should be coordinated with 48 hours & feedback received | ||
| Cases of un-reconciled entries:
1- Invoice appearing in supplier statement & not in our records. A) items are Good in transit & this is only if the stock not yet cleared or fresh delivery (max 7 days) B) Ask supplier for invoice copy plus airway bill as proof of delivery & confirm with logistics for the same. |
AP Supervisor & Country Finance Manager |
Un-reconciled accepted cases |
||
| Payment appearing in our records but not in supplier statement (keep copy of payment as proof of settlement with all the documentations | AP Supervisor & Country Finance Manager |
Un-reconciled accepted cases |
||
| Items related to other country & verification from the other country to be obtained. | ||||
–
| Activity : | Supplier Payments | KPI : | On-Time payment to suppliers | |
| Input / Reference | Process Sequence | Process Step | Responsibility | Record Generated |
| Invoice Received by Accountant from
Respective Department |
Check invoice with purchase order for approval of Department Head | Accountant | Invoice / Purchase order |
|
| Any variations / Purchase Order missing it will be clarified with concerned Department Head | Accountant | |||
| Book it in the ERP system for payment | Accountant | |||
| Payment terms are entered in the system | Accountant | |||
| Aging Report run on weekly basis for all existing suppliers for payments | Accountant | Aging Report | ||
| Based on this the, Payments are made and send for signatures | Accountant | |||
| Bank payments vouchers made for approved invoices | Accountant | Bank payments vouchers | ||
| Cheques prepared, gives to FM for verification and signed by CFO | Finance Manager & CFO | |||
| Payment delivered to the suppliers and obtained the signatures in the copy of the Cheque | Accountant | |||
| Supplier payment can be steam lined with Fixed dates-Recommendation | ||||
| Supplier payment can be steam | ||||
| Activity : | Bank Payments | KPI : | ||
| Input / Reference | Process Sequence | Process Step | Responsibility | Record Generated |
| Travel Claims / Local Expanses (Above petty cash limits) | Received from concern Personnel by Accountant in Expenses Claim Form | Accountant | Expenses Claim Form |
|
| Verify for Departments Head’s Authorization | Department Head |
|||
| Authorization for Bank payments should be defined related to, Tickets, purchases & personnel, etc | With proper Authorization the Cheque been made and with approval it has been issued | Accountant | ||
| Upon issue sign obtained from the Receiver and handover of Cheques | Accountant | |||
–
| Activity : | Travel Expenses | KPI : | To maintain the Reconciliation variation < Rs. 10,000 |
|
| Input / Reference | Process Sequence | Process Step | Responsibility | Record Generated |
| Expenses claim form from concern Personnel. Advance for traveling will be approved by CEO only | CEO & Concern Dept. Head | Expenses Claim Form |
||
| Department Heads will approve the same | Department Head |
|||
| Verify the vouchers attached in the claim form | Payable Supervisor /GL Accountant | Voucher | ||
| Any variations will be clarified with department heads and resolved prior to payment. | Payable Supervisor /GL Accountant | Claim form | ||
| Upon approvals and then the receivers signature has been obtained in the Expenses Claim Form, also all receipts are attached with the same | Payable Supervisor | |||
| All payments are made as per SOP | ||||
–
| Activity : | Utility Bill Payments | KPI : | Make immediate payments for all approved Bills |
|
| Input / Reference | Process Sequence | Process Step | Responsibility | Record Generated |
| Electricity, Telephone, Rent, etc | Bills are received by Admin. Dept | Admin Coordinator |
Bills | |
| Admin. Verifies the bills for misuse of the same and forward to Accounts Department | Admin Coordinator |
|||
| Any variation / misuses payments will be agreed with the concern by Admin. and the info. Passed to Accounts | Put it in the excel sheet for payment to be done | Accountant | Utility Bill
Monitoring Sheet |
|
| Send to Finance Manager for this approval | Finance Manager |
|||
| Cheques are prepared by the accountant for the payments and Bank Payment voucher made for all cheques prepared prior to issue | Accountant | Payment voucher |
||
| Issue the Cheques along with Bills / to the concern Eletrcitiy Vendor, etc | Accountant | |||
| Bills need to be checked prior to payment for any personal calls for Reconciliation to be with Admin. | ||||
–
| Activity : | Fixed Assets | KPI : | ||
| Input / Reference | Process Sequence | Process Step | Responsibility | Record Generated |
| LPO / Invoice along with Asset form given to accounts |
Approval by CFO / Concerned Manager will be verified by Accountant. Limits for approval to be Fixed & documented | CFO | Asset Form | |
| As per the credit terms agreed, the payment process starts. | Admin. Manager | |||
| Along with invoice approval payments will be done. | Accountant | Invoice | ||
| For work-in-progress will be treated as supplier credit, upon completion it will be transferred to Fixed Asset | Fixed assets will be transferred in system upon completion of payments | Payable Supervisor | ||
| Any warranty claims are maintained by the concerned department and upon approvals from concern Dept. only any payments will be made | Accountant | Invoice | ||
| No verification for approval of invoices by the terms & conditions agreed with suppliers | ||||
| Prepare the analysis of working progress also to inform the concerned – Recommendation |
Then the management does the Depreciation based on the fixed dues | Payable Supervisor | ||
–
| Account Payables |
| Ver : 1.4 |
| 6. Outputs |
| • Purchase Order |
| • Supplier Reconciliation Report |
| • Invoice |
| • Payment voucher |
| • Reconciliation Report |
| • Aging Report |
| 7. Monitoring and Measurement |
| Refer to Process Control Sheet |
| 8. Forms and Records |
| Name |
| Reconciliation Report |
| Purchase order |
| Creditors Ledger |
| Statements of Accounts |
| Supplier Reconciliation Report |
| Asset Form |
| Invoice |
| Utility Bill Monitoring Sheet |
| Payment voucher |
| Expenses Claim Form |
| Aging Report |
| Invoice |
| Purchase order |
| 9. Interfaces |
| None |
| 10.Process Tailoring |




