Introduction: This comprehensive analysis delves into the key aspects of GST registration in India, examining crucial sections of the CGST Act. From eligibility criteria and application procedures to cancellation processes, gain valuable insights into Section 22, 23, 24, 25, 29, and 30.
1. Section 22 (CGST ACT 2017) – Persons liable for registration.
Section 22 of the CGST Act defines the criteria for mandatory GST registration. It covers the aggregate turnover threshold, special category states, and exemptions. The concept of aggregate turnover, including taxable supplies, exempt supplies, and inter-State supplies, is crucial in determining liability.
1. Every supplier shall be liable to be registered under this Act in the State or Union territory, other than special category States, from where he makes a taxable supply of goods or services or both, if his aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds twenty lakh rupees:
Provided that where such person makes taxable supplies of goods or services or both from any of the special category States, he shall be liable to be registered if his aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds ten lakh rupees.
Provided further that the Government may, at the request of a special category State and on the recommendations of the Council, enhance the aggregate turnover referred to in the first proviso from ten lakh rupees to such amount, not exceeding twenty lakh rupees and subject to such conditions and limitations, as may be so notified;
Provided also that the Government may, at the request of a State and on the recommendations of the Council, enhance the aggregate turnover from twenty lakh rupees to such amount not exceeding forty lakh rupees in case of supplier who is engaged exclusively in the supply of goods, subject to such conditions and limitations, as may be notified.
Explanation.–– For the purposes of this sub-section, a person shall be considered to be engaged exclusively in the supply of goods even if he is engaged in exempt supply of services provided by way of extending deposits, loans or advances in so far as the consideration is represented by way of interest or discount.
(2) Every person who, on the day immediately preceding the appointed day, is registered or holds a licence under an existing law, shall be liable to be registered under this Act with effect from the appointed day.
(3) Where a business carried on by a taxable person registered under this Act is transferred, whether on account of succession or otherwise, to another person as a going concern, the transferee or the successor, as the case may be, shall be liable to be registered with effect from the date of such transfer or succession.
(4) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-sections (1) and (3), in a case of transfer pursuant to sanction of a scheme or an arrangement for amalgamation or, as the case may be, demerger of two or more companies pursuant to an order of a High Court, Tribunal or otherwise, the transferee shall be liable to be registered, with effect from the date on which the Registrar of Companies issues a certificate of incorporation giving effect to such order of the High Court or Tribunal.
Sec. 2(6) (CGSTACT 2017) “aggregate turnover” means the aggregate value of all taxable supplies (excluding the value of inward supplies on which tax is payable by a person on reverse charge basis), exempt supplies, exports of goods or services or both and inter-State supplies of persons having the same Permanent Account Number, to be computed on all India basis but excludes central tax, State tax, Union territory tax, integrated tax and cess;
Meaning of Aggregate Turnover Sec. 2(6).
All Taxable Supplies 2(108)
+Exempt Supply 2(47) Means
- Nil Rated
- Wholly Exempt
- Non Taxable Supply 2(78)
+Exports
+Interstate Supply
(Made to persons with same PAN)
+Supply made on behalf of principal (Exp i to sec. 22)
Exclude:-
CGST, SGST, UTGST,. IGST and Cess
Inward Supply on which tax is payable by a person under RCM.
Supply of Goods after completion of job work by a registered job worker treated as supply of goods by principal and not to be included in turnover of job worker ( Expl ii to sec.22)
Net Total (Aggregate Turnover)
Special Category States.
However, the limit of Rs.20 lakh will be reduced to Rs. 10 lakh if the person is carrying out business in Special Category States. As per Article 279A(4)(g) of the Constitution, there are 11 Special Category States, namely, States of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jammu and Kashmir, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand. However, as per the explanation (iii) to section 22, for the purposes of registration, only Mizoram, Tripura, Manipur and Nagaland are Special Category States. Therefore, the threshold limit ` 10 lakh is applicable for Mizoram, Tripura, Manipur and Nagaland.
States can opt the Threshold limits. Following table shows the threshold limits applicable to different states.
Table No: 1

(Source: https://resource.cdn.icai.org/67768bos54359-cp9.pdf).
Table No: II.
| Tamil Nadu Sales (Rs. In Lakhs) | Kerala Sales (Rs. In Lakhs) | Manipur Sales (Rs. In Lakhs) | Reg. Required |
| 10 | 11 | 0 | Yes in both the states from where Taxable supply is made |
| 20(Exempt) | 10(Exempt) | 0 | No Reg. Required. Sec 23(1) |
| 20(Exempt) | 10 (Taxable) | 0 | Registration required in Punjab only. |
| 30(Exclusively Goods) | 5(Exclusively Goods) | 0 | Aggregate Turnover is less than 40Lacs, he can take Benefit of Not. 10/2019 and not liable to Register. |
2. Section 23(CGST ACT 2017) – Persons not liable for registration.
(1) The following persons shall not be liable to registration, namely:––
(a) any person engaged exclusively in the business of supplying goods or services or both that are not liable to tax or wholly exempt from tax under this Act or under the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act;
(b) an agriculturist, to the extent of supply of produce out of cultivation of land.
(2) The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification specify the category of persons who may be exempted from obtaining registration under this Act.
3. Section 24 – Compulsory registration in certain cases.
Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (1) of section 22, the following categories of persons shall be required to be registered under this Act,–
(i) Persons making any inter-State taxable supply;
(ii) Casual taxable persons making taxable supply;
(iii) Persons who are required to pay tax under reverse charge;
(iv).Person who are required to pay tax under sub-section (5) of section 9;
(v) Non-resident taxable persons making taxable supply;
(vi).Persons who are required to deduct tax under section 51, whether or not separately registered under this Act;
(vii) Persons who make taxable supply of goods or services or both on behalf of other taxable persons whether as an agent or otherwise;
(viii) Input Service Distributor, whether or not separately registered under this Act;
(ix) Persons who supply goods or services or both, other than supplies specified under sub-section (5) of section 9, through such electronic commerce operator who is required to collect tax at source under section 52;
(x) Every electronic commerce operator who is required to collect tax at source under section 52;
(xi) Every person supplying online information and database access or retrieval services from a place outside India to a person in India, other than a registered person; and
(Xia) every person supplying online money gaming from a place outside India to a person in India and
(xii) Such other person or class of persons as may be notified by the Government on the recommendations of the Council.
4. Composition Scheme
It is a simple and easy scheme under GST for taxpayers. Small taxpayers can get rid of tedious GST formalities and pay GST at a fixed rate of turnover. This scheme can be opted by any taxpayer whose turnover is less than Rs. 1.5 crore.
However, you cannot opt for the Composition Levy if you are/you make:
– any supply of goods which are not liable to be taxed under this Act
– inter-state outward supplies of goods
– supplies through electronic commerce operators who are required to collect tax under section 52.
– a manufacturer of notified goods
– a casual dealer
– a Non-Resident Foreign Taxpayer
– a person registered as Input Service Distributor (ISD)
– a person registered as TDS Deductor /Tax Collector
To opt for the Composition Levy, perform the following steps on the GST portal:
1. Log in to the Taxpayers’ Interface
2. Go to Services > Registration > Application to Opt for Composition Levy
3. Fill the form as per the form specification rules and submit
A Composition dealer will issue only bill of Supply.
5. GST Registration.
Sec 25(CGST ACT 2017) Procedure for registration.— (1) Every person who is liable to be registered under section 22 or section 24 shall apply for registration in every such State or Union territory in which he is so liable within thirty days from the date on which he becomes liable to registration, in such manner and subject to such conditions as may be prescribed:
Provided that a casual taxable person or a non-resident taxable person shall apply for registration at least five days prior to the commencement of business:
Explanation.—Every person who makes a supply from the territorial waters of India shall obtain registration in the coastal State or Union territory where the nearest point of the appropriate baseline is located.
(2) A person seeking registration under this Act shall be granted a single registration in a State or Union territory: [Provided that a person having multiple places of business in a State or Union territory may be granted a separate registration for each such place of business, subject to such conditions as may be prescribed.
(3) A person, though not liable to be registered under section 22 or section 24 may get himself registered voluntarily, and all provisions of this Act, as are applicable to a registered person, shall apply to such person.
(6A) Every registered person shall undergo authentication, or furnish proof of possession of Aadhaar number, in such form and manner and within such time as may be prescribed:
Provided that if an Aadhaar number is not assigned to the registered person, such person shall be offered alternate and viable means of identification in such manner as Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, prescribe:
Provided further that in case of failure to undergo authentication or furnish proof of possession of Aadhaar number or furnish alternate and viable means of identification, registration allotted to such person shall be deemed to be invalid and the other provisions of this Act shall apply as if such person does not have a registration.
(9) Notwithstanding anything contained in sub-section (1),––
(a) any specialised agency of the United Nations Organisation or any Multilateral Financial Institution and Organisation notified under the United Nations (Privileges and Immunities) Act, 1947, Consulate or Embassy of foreign countries; and
(b) any other person or class of persons, as may be notified by the Commissioner, shall be granted a Unique Identity Number in such manner and for such purposes, including refund of taxes on the notified supplies of goods or services or both received by them, as may be prescribed.
(10) The registration or the Unique Identity Number shall be granted or rejected after due verification in such manner and within such period as may be prescribed.
Picture 1: GST Registration Website.

(Source: https://www.gst.gov.in/)
Documents required for GST Registration
1. PAN card
2. Valid Phone no. and Email id for OTP.
3. Passport size photograph of the Applicant.
4. Proof of principle place of business (any one) • Electricity bill • Legal ownership document • Municipal khata copy • Property tax receipt
5. Proof of details of Bank Account • The first page of the passbook • Bank statement • Cancelled cheque
6. Other details
List of Goods and Services
Proof of appointment of Authorized Signatory (Letter of Authorization or copy of board resolution)
Authorized Signatories photo
Incorporation certificate (for Company and LLP)
DSC
Picture II: GST Registration

(Source:https://www.gst.gov.in/help/enrollmentwithgst)
Picture III: GST Registration

(Source: https://www.gst.gov.in/help/enrollmentwithgst)
Picture IV: GST Registration
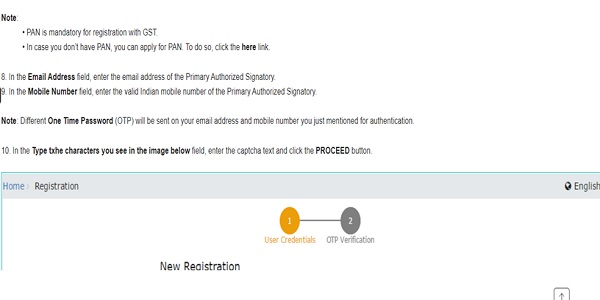
(Source: https://www.gst.gov.in/help/enrollmentwithgst)
Picture V: GST Registration
(Source: https://www.gst.gov.in/help/enrollmentwithgst).
Picture VI: GST Registration

(Source: https://www.gst.gov.in/help/enrollmentwithgst)
Picture VII: GST Registration

(Source: https://www.gst.gov.in/help/enrollmentwithgst)
Picture VIII: GST Registration

(Source: https://www.gst.gov.in/help/enrollmentwithgst)
Picture IX: GST Registration
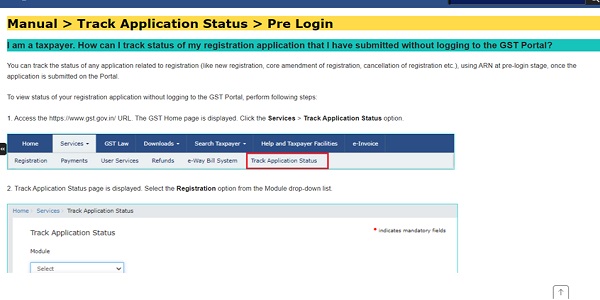
(Source : https://www.gst.gov.in/help/enrollmentwithgst)
Cancellation of Registration.
Sec 29. (1) (CGST ACT 2017).
1.The proper officer may, either on his own motion or on an application filed by the registered person or by his legal heirs, in case of death of such person, cancel the Deemed registration. Special provisions relating to casual taxable person and non-resident taxable person.
2.The proper officer may cancel the registration of a person from such date, including any retrospective date, as he may deem fit, where,–– (a) a registered person has contravened such provisions of the Act or the rules made thereunder as may be prescribed; or (b) a person paying tax under section 10 has not furnished returns for three consecutive tax periods; or (c) any registered person, other than a person specified in clause (b), has not furnished returns for a continuous period of six months; or (d) any person who has taken voluntary registration under sub-section (3) of section 25 has not commenced business within six months from the date of registration; or (e) registration has been obtained by means of fraud, wilful misstatement or suppression of facts: Provided that the proper officer shall not cancel the registration without giving the person an opportunity of being heard.
(3) The cancellation of registration under this section shall not affect the liability of the person to pay tax and other dues under this Act or to discharge any obligation under this Act or the rules made thereunder for any period prior to the date of cancellation whether or not such tax and other dues are determined before or after the date of cancellation.
(4) The cancellation of registration under the State Goods and Services Tax Act or the Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Act, as the case may be, shall be deemed to be a cancellation of registration under this Act.
(5) Every registered person whose registration is cancelled shall pay an amount, by way of debit in the electronic credit ledger or electronic cash ledger, equivalent to the credit of input tax in respect of inputs held in stock and inputs contained in semi-finished or finished goods held in stock or capital goods or plant and machinery on the day immediately preceding the date of such cancellation or the output tax payable on such goods, whichever is higher, calculated in such manner as may be prescribed:
Provided that in case of capital goods or plant and machinery, the taxable person shall pay an amount equal to the input tax credit taken on the said capital goods or plant and machinery, reduced by such percentage points as may be prescribed or the tax on the transaction value of such capital goods or plant and machinery under section 15, whichever is higher.
(6) The amount payable under sub-section (5) shall be calculated in such manner as may be prescribed.
Revocation of cancellation of Registration
Sec30 (CGST ACT 2017). (1) Subject to such conditions as may be prescribed, any registered person, whose registration is cancelled by the proper officer on his own motion, may apply to such officer for revocation of cancellation of the registration in the prescribed manner within thirty days from the date of service of the cancellation order.
The above section has been amended through the Finance Act 2023.Amendment is as follows:
In section 30 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, in sub-section (1),— (a) for the words “the prescribed manner within thirty days from the date of service of the cancellation order:”, the words “such manner, within such time and subject to such conditions and restrictions, as may be prescribed.” shall be substituted; (b) the proviso shall be omitted.
(2) The proper officer may, in such manner and within such period as may be prescribed, by order, either revoke cancellation of the registration or reject the application:
Provided that the application for revocation of cancellation of registration shall not be rejected unless the applicant has been given an opportunity of being heard.
(3) The revocation of cancellation of registration under the State Goods and
Services Tax Act or the Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Act, as the case may be, shall be deemed to be a revocation of cancellation of registration under this Act.
Amendment in the Finance Act 2023
Existing Provision:
Sec 23.Subsection (2):
The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, specify the category of persons who may be exempted from obtaining registration under this Act.
Amended Section:
In section 23 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, for sub-section (2), the following sub-section shall be substituted and shall be deemed to have been substituted with effect from the 1st day of July, 2017, namely:—
“(2) Notwithstanding anything to the contrary contained in sub-section (1) of section 22 or section 24, the Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, subject to such conditions and restrictions as may be specified therein, specify the category of persons who may be exempted from obtaining registration under this Act.”.
This analysis provides a comprehensive guide for businesses navigating the complexities of GST registration, ensuring adherence to legal provisions and procedural requirements. For more detailed information, refer to the official GST portal and relevant legal resources.
(Republished with amendments)




