Digital Technology is prevalent across every aspect of our daily lives and has transformed the way we live, communicate and conduct business. With an objective to Digitize Tax Administration & ease out the way business is conducted, the Government of India has introduced E-Invoicing for businesses in India. E-invoicing is considered as an important pillar of the digital architecture of tax administration both from tax payer’s and government’s perspective.
“E-Invoice” or “Electronic Invoice” is a form of electronic billing. It’s a system in which B2B (business to business) invoices are electronically uploaded and authenticated by Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). The entire invoice information shall be transferred from IRP to both GST portal and e-way bill portal on real time basis. An Invoice Reference Number (IRN) will be issued under E-invoicing system against every invoice by IRP to be managed by GST Network. IRN is a unique alphanumeric number which is generated once the server validates the invoice. National Informatics Centre (NIC) launched the first IRP einvoice1.gst.gov.in to facilitate taxpayers upload invoices, obtain IRN & track e-invoices. E-Invoices can be generated by suppliers only. E-commerce operators can also generate e-invoices on behalf of the sellers on their platform.
E-Invoicing applicability released by CBIC (Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs)
The CBIC decided to implement E-invoicing in different phases for an uninterrupted adoption of the new system.
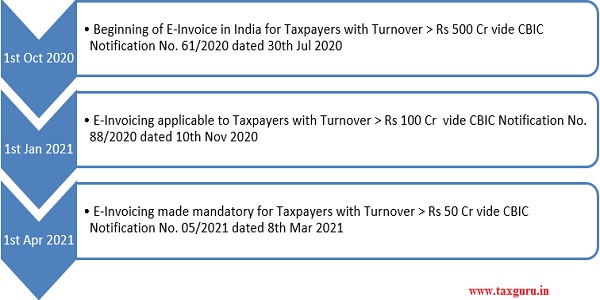
In the first leg of implementation effective from 1st October 2020, E-Invoicing was made applicable to taxpayers with turnover exceeding Rs 500 Crore in any of the preceding financial year starting from 2017-18 to 2019-20.
In the second phase made effective from 1st January 2021, E-invoicing was made applicable to taxpayers with turnover exceeding Rs 100 Crore in any of the preceding financial year starting from 2017-18 to 2019-20.
With an intent to further increase the usage of E-invoicing system, the CBIC decided to bring all taxpayers with turnover exceeding Rs 50 Crore in any of the preceding financial year starting from 2017-18 onwards under the ambit of E-invoicing system with effect from 1st April 2021.
Thus for computing the applicability, turnover is to be considered of any preceding Financial Year from 2017-18 onwards in the beginning of every Financial Year. Once the Taxpayer becomes eligible for E-invoicing, he will continue to issue the same forever (eligibility need not be checked again).
Irrespective of turnover, E-Invoicing will not be applicable to following categories as notified by CBIC:
> Banking, Insurance, NBFC or a Financial Institution
> Goods Transport Agency (GTA)
> Suppliers Passenger Transport Services
> SEZ Unit including Free Trade and Warehousing Zones (FTWZ); SEZ Developers are not exempted
> Multiplexes & Admission to Cinematographic Films
E-Invoice generation Process flow
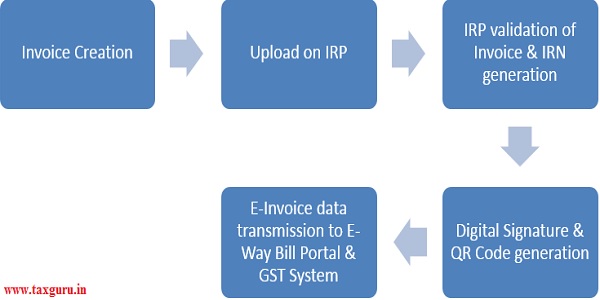
1. Invoice creation: – Taxpayer can continue using his current accounting software/ERP with an up gradation to generate invoice in the given E-invoicing format.
2. Upload on Invoice Registration Portal: Every B2B Invoice generated by the accounting software is uploaded on Invoice Registration Portal.
3. IRP validation of Invoice Information: IRP will authenticate the file uploaded against any duplication and generate the unique IRN for each invoice. There are four parameters basis which IRN is generated – Seller GSTIN, Invoice Number, FY in YYYY-YY and document type (Invoice/ Debit Note/ Credit Note)
4. Digital Signature and QR code generation: The invoice will be updated with IRP’s digital signature on the invoice along with a QR code, upon successful verification.
5. E-invoice data transmission to E-way bill portal and GST system: Subsequently, the validated data will be shared with E-way bill portal and GST system, and will be used for generation of E-way bill and auto population of GSTR-1 for the relevant tax period. Also, digitally signed invoice along with IRN and QR code will be sent back to Seller and buyer on their registered email id.
Prerequisites for effective implementation of E-invoicing
1. E-invoicing applies to only taxable supplies and not the exempted or non GST supplies. Hence every business needs to segregate transactions for compliance.
2. Accounting Software/ ERP needs to be updated to generate invoices as per the format required for E-invoicing.
3. Since B2B invoices are auto populated in GST system, preparation for GST return filing needs to be modified.
4. Decide on the mode to be adopted for generation of IRN.
Transition to Digitised system of E-Invoicing will help in following ways:
1. Auto population of GSTR-1 hence reducing mismatch/ human errors and reconciliation issues and also speeding up the return filing process.
2. Part A of E-way bill is auto filled and can be quickly completed by providing the vehicle details in Part B.
3. E-invoices can be tracked on real time basis by Tax authority for all compliances. Also, buyer will have complete information about the goods or service being invoiced.
4. Having a set format, e-invoicing will facilitate standardisation in invoicing across all B2B invoices.
5. Information on the Input Tax credit is easily available.
6. E-invoicing will be a big check on tax evasion since tax authorities will have access to all the information at transaction level. E-invoices are generated prior to the movement of goods, making the manipulation of invoices difficult. Thereby, fake GST invoices will be reduced and only the genuine input tax credit will be claimed.
Major Challenges
1. Partial cancellation of E-invoices is not possible. It has to be cancelled in full within 24 hrs. After 24 hrs it can be amended manually in GST portal before the return is filed. In such situations, it will create difference between GST portal and IRP which needs to be reported.
2. Each invoice needs to be uploaded on IRP which may take time due to technical glitch leading to delay in invoice generation thus delaying the movement of goods.
3. E-invoicing will be an additional load for the taxpayers both in terms of work and cost in implementation of the system and providing the training for efficient adoption of the process.
Penal Actions on Violations
1. Non generation of E-invoice can be penalised for up to INR 10,000 per invoice
2. Incorrect invoicing can lead to a penalty of INR 25,000 per invoice
Apart from penalty, delay in E-invoice generation can lead to following repercussions:
1. Customers may refuse to accept invoices that are not compliant with the provisions as it can affect their eligibility to claim Input Tax credit
2. E-way bill will not get generated in the absence of IRN
3. GSTR-1 will not get auto populated thus delaying the filing process
About the Author
Author is Amit Jindal, ACA working as Manager Taxation in Neeraj Bhagat & Co. Chartered Accountants, a Chartered Accountancy firm helping foreign companies in setting up business in India and complying with various tax laws applicable to foreign companies while establishing their business in India.






Very good article on the E invoice provisions.
Grateful for a clarification on the following query:
1. Is there any provision in GST law to generate an E INVOICE at a later date when omitted for generation earlier.
2. If not what is the solution for the taxpayer, without attracting penal provisions under sec.122/125.
Regards….