In this Article, we will discuss regarding the detailed procedure of compounding of offences and condonation of delay under Companies Act 2013. Our Discussion includes-
-Whether Compounding and Condonation are Synonyms?
-What are the key Differences between compounding and condonation?
-In which cases we should go for compounding and in which cases we should go for condonation?
-Whether for compoundable offences we can go for condonation?
-Due to absence of Rules and Regulations what are the specific procedures?
COMPOUNDING OF OFFENCES
Introduction
As we all know, In the current scenario there are lot of provisions along with different types of laws are applicable on a company and due to non-availability of expert advice and thief of time companies are unable to manage the compliance of all the laws and due to which they attract heavy penalties along with prosecution.
Today’s Corporate world, good governance means to comply with all the provisions of Corporate laws. Noncompliance will result in penalties or penalties with imprisonment. Corporate offences are classified into civil and criminal offences. Further it has been classified as Compoundable and Non compoundable offence. The Compounding of offences is a short cut method to avoid litigation
So the Act has clearly laid down the mechanism and the forum for speedy and smooth administration of judicial activities under the companies Act, 2013
Legal Meaning of Compounding
- There is no definition of the word “compounding” provided either in the Companies Act 1956 or the Companies Act, 2013
- However, the legal meaning of compounding is “doing good the default/noncompliance”. It is nothing but a “settlement” for the offence committed by any company or any officer.
- As per the Black’s Law Dictionary, “Compound” means “to settle a matter by a money payment, in lieu of other liability”. It is merely a Settlement Mechanism, a settlement by paying the penalty in lieu of facing the prosecution for the offence committed.
- Compounding is essentially a compromise or arrangement between administrator of the enactment and person committing an offence
Types of Offences can be compounded
As per Section 441 of the Companies Act, 2013, not all the Offences can be compounded. Only the following offences can be compounding under section 441(1) of the Act by certain authorities
- Compoundable Offences
1. Offence punishable with “Fine Only”
2. Offence punishable with “fine or imprisonment or both” or “Fine or Imprisonment”
No compounding shall be done in the following cases:
- Non Compoundable Offences
1. Offence punishable with “imprisonment only” or
2. Offence punishable with “imprisonment and fine” or
3. Where investigation has been initiated or is pending against the company; (Section 441(1))
4. Where similar offence has been compounded within last 3 years (Section 441(2))

Procedure for Compounding of offences under companies Act, 2013
- Step -1: Before filing of application for compounding of offences, the company shall make good the default by complying with the applicable provisions of the Act.
- Step-2:Hold a Board Meeting:
1. To consider and approve application or joint application for the company and/or officer in default
2. To authorise CS or CFO or any director of the company to make an application of compounding.
- Step-3:Form and documents filling:Make application in Form GNL-1 to ROC for the Compounding of offence along with the requisite documents and fees. (section 441(3)(a)
- Step-4:Date of Hearing:The company’s authorized representative will attend the hearing and explain the reasons for committing the offence
- Step-5:Payment of penalty:After obtaining the compounding order of RD or NCLT, follow the directions and pay the fee through MCA portal (mca.gov.in)
- Step-5:Filling the copy of order with the ROC in form INC-28 along with the requisite documents and fees within 7 days from the date of receipt of compounding order or such time as may be mentioned in the compounding order. (Section 441(3)(b)

Form GNL-1:
As per section 403 read with Rule 12 of companies (Registration offices and Fees) Rules,2014, the compounding application has to be made to ROC by filling e-Form GNL-1 along with following Documents:-
- Detailed Application (NCLT-1)*
- Affidavit verifying the petition (NCLT-6)
- Memorandum of appearance along with Board Resolution giving authority to appear (NCLT-12)
- Board Resolution giving authority to file Application
- ROC/RD notice is case received any
- Any other relevant document depend upon the matter of the compounding application
♦ The application can be filed for Company, Director or Manager/Secretary or CEO/CFO or Others.
♦ Details of only 8 persons can be entered in the e-Form. If number of persons is greater than 8, then additional details can be provided in optional attachment.
*Detailed Application should contain the following details:
- General profile and history of the company containing details such as name, date of incorporation, main objects of the company.
- Facts of the case mentioning nature of offence and period of default
- Whether the offence is made good, if yes then how and when (i.e. the date where applicable)
- Prayer to compounding authority for compounding of offence
Post Compounding of an offences:
- An intimation shall be given to the ROC within 7 days from the date on which, the offence is compounded.
- No prosecution shall be filed either by ROC or by any shareholder or by any person authorized by the Central Government.
- Where the compounding of any offence is made after the institution of any prosecution, such compounding shall be brought by the Registrar in writing, to the notice of the Court in which the prosecution is pending. And, on such notice of the compounding of the offence being given, the company or its officer in relation to whom the offence is so compounded shall be discharged.
- Payment of fine, as decided in the order of Compounding, to be made within the time prescribed in the order.
- Amount of fine for compounding shall not exceed the maximum amount of the fine which may be imposed under the relevant Section.
Now let’s take some examples on Compounding of offences:
Annual General Meeting:
As per Section 96 of the companies Act, 2013 every company shall hold its annual general meeting within 6 months from the closure of financial year and not more than 15 months shall elapse between two annual general meetings.
And As per section 99: If any default is made in holding an annual general meeting of the company in accordance with section 96 or in complying with any directions of the Tribunal, the company and every officer of the company who is in default shall be punishable with fine which may extend to one lakh rupees and in the case of a continuing default, with a further fine which may extend to five thousand rupees for every day during which such default continues.
Now the question is that what company is required to do to make the compliance good.
Firstly company is required to conduct its annual general meeting (as non-compliance of Section 96 does not interpret that company is not required to conduct its annual general meeting is time period exceeds)
Secondly Due to non-compliance of section 96, ROC can impose fine on officer on default and to the company as well and may send show cause notice why the prosecution should not be start on the company.
So, to get relief from prosecution and heavy penalties which may be imposed by the ROC. Now company may get compound their offences as per section 441 of the companies Act, 2013 after made the default good so that officers in default not required to go for personal hearings in the court.
Decided Case Laws:
1. M P Purusothaman v. ADIT (2003): It was held that authority can reject the application for compounding and it is not necessary to give personal hearing before rejecting application for compounding
2. S V Bagi v. State of Karnataka (1992): A person having agreed to the composition of offence is not entitled to challenge the said proceeding by filling an appeal
3. In Re. Amadhi Investments ltd: Neither of the NCLT or the RD has been authorized with discretionary power to reject a compounding application without due consideration.
4. UW International Training and Education Centre for Health Private Limited: NCLT held that the principle of imposing minimum fine on compounding matters is not mandatory, as compounding of an offence can be accepted by a Court even by admonishing the defaulter or issuing a warning.
Condonation of Delay by Central Government in Certain Cases
Introduction
- The condonation of delay means the extension of prescribed time in certain cases subject to sufficient cause.
- The term condonation means an implied pardon of an offence by treating the offender as if he had not been committed any offence. {Here, the referred offence is the offence of ignoring the law of period that has been prescribed by the Limitation Act,1963.}
Legal Provision
As per section 460 of Companies Act,2013:-
- where any application required to be made to the Central Government, and
- Where any document required to be filed with Registrar
is not filed within the prescribed time, the Central Government may , for reasons to be recorded in writing, condone the delay
When It is Required to be Done
- As the immunity provided to companies to file within additional 270 days has been done away with. Therefore, any filing beyond timeline specified in respective section will invite additional fees as well as condonation of delay.
- However, obtaining condonation of delay is not a pre-requisite to filing a document. It is a separate process under section 460 in respect of all belated filings
- And Additional fees shall be paid as per Section 403
Procedure
In the absence of any specific guidelines or process for making the application for condonation of delay, companies shall file the said application in e-form CG-1 (which is used for filing application with the Central Government).
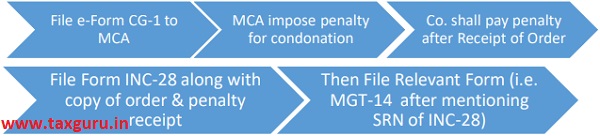
Further, as the said form does not require any specific attachments, companies shall submit the followings:
a) Documents for which the company is making an application for condonation of delay.
b) Certified True Copy of the board resolution for filling the application and appointing authorized representative, if any.
c) Application with reasons for delay and relief soughts.
d) Other documents/ clarifications, if any.
Now Let’s an Example of e-Form MGT-14
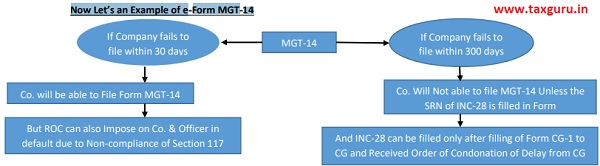
- *However, in case of “Alteration in object clause” , then it shall be mandatory to enter the SRN of Form INC-28 filed for condonation of delay (that means if co. did not file form within 30 days then it is mandatory to condone the delay from 31st day)
Condonation Vs. Compounding
| Condonation | Compounding |
| 1.Unable to upload Form thereby unable to make the default Good | 1.Form taken on record/Default is made Good |
| 2. Move an Application in Form CG-1 to MCA | 2.Move Application for Compounding to the Concerned Authority (NCLT/RD) GNL-1 |
| 3.Central Government may either impose Fine or approve to file form in delay time period | 3. Concerned authority will always impose Fine which will not be exceed the amount of penalty given under relevant provision |
| 4. SRN of INC-28 inbuilt in relevant e-Form | 4.SRN of INC-28 not inbuilt in relevant e-Form |
CONCLUSION:
1. If any specific event is not done by the Company For example holding of Annual General Meeting, Mandatory Conversion of One Person Company Within 6 months etc., then it is Required to do compounding of offences. So that, MCA will not impose any heavy penalty on Officer in default and does not start any prosecution and investigation on specific Company.
2. Condonation of Delay is FORM’s Specific i.e. If any Form under Companies Act, 2013 did not file within the time period Specified in Law, then to file Form in Delay time period with additional Fees, We should go for Condonation Application.
3. However, Condonation of Delay is not a pre-requisite to file a Form. Filling of Form with additional fess is separate procedure and to take Condonation of Delay is Independent thing.
4. Due to absence of Rules on Compounding and Condonation there is no such clarity regarding that for Each and Every delay filling of e-Form whether condonation is mandatory or Not.
5. However, As per Strict Interpretation of Section 460, Every delay filling of e-Form is Required Condonation of Delay.
6. Further, Where the delay is not condoned/ application is not made, this will be specified in the secretarial audit report given in Form MR—3 as well as Certificate in relation to annual return given in Form MGT-8





Knowledgeable. Thanks for sharing
whether compounding fees levied by the authority for compounding of an offence, shall be considered as a penalty even after the compounding?