INTRODUCTION
First of all, what is GST? Full form of GST is GOODS and SERVICES TAX.
It is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination based tax, which will be levied on every value addition. It is touted to be the biggest tax reform and will simplify the current taxation system. It will replace all indirect taxes (like service tax, value addition tax, central sales tax, excise duty) levied on goods and services in India.
PM Narendra Modi called GST a “Good and Simple Tax”.
ADVANTAGES OF GST
- Possible reduction in prices.
- Increase in government revenues.
- Less compliance and procedural cost.
- Removal of current cascading effect.
There are two types of GST structure in the world. These are:
i. Single GST
ii. Dual GST
India has adopted the DUAL GST system whereby a CGST and SGST will be levied on the taxable value of every transaction of supply of goods and services. It is the Canadian model of Dual GST (central and state) implemented in 1991 that the Indian model of the indirect tax reform finds similarities with.
The government has decided 5 different tax slab rates- 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, 28%. The government has categorized 1211 items under tax slabs.
While the implementation of the tax reform in India may be historic for the scale of change that it envisages, India is not the first country to move to a unified indirect taxation system. France was the first country to adopt GST in 1954.
FORMER TAX STRUCURE
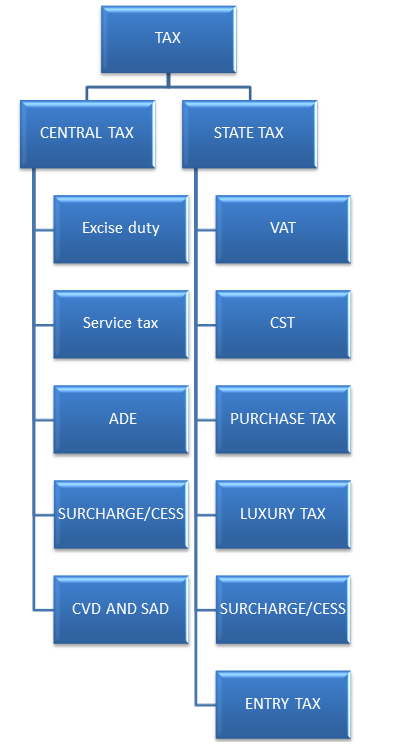
NEW TAX STRUCTURE

CGST: CGST refers to Central Goods and Service Tax. It is levied on the intrastate movement of goods and services. The revenue collected under CGST is for the central government. However, Input tax credit on CGST is given partly to the centre and partly to the states as it will be utilized against the payment of both CGST and IGST.
SGST: SGST refers to State goods and service tax. SGST falls under State Goods and Service Tax Act 2016. The revenue collected under SGST is collected State Government. The State Government levies it on the intrastate movement of goods and services.
| PRESENT TAX SYSTEM | GST SYSTEM
|
|
| PRODUCT SOLD FROM PUNJAB TO DELHI | PRICE=100 | PRICE=100 |
| VAT@10% =10 | CGST@5% =5 | |
| TOTAL COST = 110 | SGST@5% =5 | |
| TOTAL COST=110 | ||
| `PRODUCT SOLD FROM DELHI TO BIHAR | COST PRICE=110 | COST PRICE=110 |
| PROFIT=100 | PROFIT=100 | |
| SELL PRICE=210 | SELL PRICE=210 | |
| CST@10%=21 | IGST@10%=11 | |
| TOTAL PRICE=231 | TOTAL PRICE=221 |
IGST: IGST refers to Integrated goods and service tax. It is levied on the interstate movement of goods and services. Integrated GST will be collected by the centre. IGST will also be applicable on the import of goods.
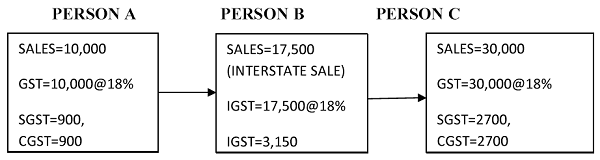
FOR EXAMPLE:
CASE: Suppose person “A” from Maharashtra sells goods to person “B” in Maharashtra for 10,000. Further person “B” sells goods to person “C” in Punjab for 17,500. Finally, person “C” sells goods to person “D” in Punjab for 30,000. GST @18% comprises of SGST @9% and CGST@9%?
SOLUTION:
SOME FACTS ABOUT GST
- ONE NATION – ONE TAX REGIME
- It has been 17 years since GST was first conceptualized in India.
- About 160 countries in the world have GST.
- India, after Canada is only second country in the world to adopt dual GST model.
- GST is arguably one of India’s most significant and ambitious reforms ever attempted.
- Till now, 33 GST Acts have been passed.
- Liquor has been kept outside the scope of GST.
- GST as well as the former taxes will be applicable on Tobacco.
- IT will generate many employment opportunities.
Name – GAGANDEEP GARG
Address – GONIANA MANDI (DIST. BATHINDA)





