OFFENCES AND PENALTIES
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 This Chapter deals with the different types of offences and the penalties leviable under GST law. The contents of this Chapter would aid the officers, especially while issuing Demand Notices/Show Cause Notices and Adjudication orders.
1.2 The provisions of CGST Act and the CGST Rules, relevant to this Chapters, are as under-
| Sr. No. | Section/Rules | Provisions pertaining to |
| 1 | Section 122 | Penalty for certain offences |
| 2 | Section 123 | Penalty for failure to furnish information return |
| 3 | Section 124 | Fine for failure to furnish statistics |
| 4 | Section 125 | General penalty |
| 5 | Section 126 | General disciplines related to penalty |
| 6 | Section 127 | Power to impose penalty in certain cases |
| 7 | Section 128 | Power to waive penalty or fee or both |
| 8 | Section 129 | Detention, seizure and release of goods and conveyances in transit |
| 9 | Section 130 | Confiscation of goods or conveyances and levy of penalty |
| 10 | Section 131 | Confiscation or penalty not to interfere with other punishments Section 132 |
| 11 | Section 132 | Punishment for certain offences |
| 12 | Section 133 | Liability of officers and certain other persons |
| 13 | Section 134 | Cognizance of offences |
| 14 | Section 135 | Presumption of culpable mental state |
| 15 | Section 136 | Relevancy of statements under certain circumstances |
| 16 | Section 137 | Offences by companies |
| 17 | Section 138 | Compounding of offences |
| 18 | Rule 162 | Procedure for compounding of offences |
1.3 GST is levied on every value addition at each stage of supply. Apart from the tax, the CGST Act, 2017 and the rules made thereunder, lays down provisions for registration, manner of determination of the tax, classification and valuation of the supply, various mandatory compliances to be made by the taxpayer, etc.
1.4 Any breach of these laws leads to offences. Under GST laws, offences are well explained in the CGST Act, 2017. This Act also provides for imposition of penalties, fines, and imprisonment for some type of offences.
1.5 The specific identification of offences and defined penal actions for any law is the teeth, which the lawmakers provide to the statute. Without the provision of proportionate punishment, neither deterrent nor retributive, let alone persuasive effect can be created in general. The institutions of State require an effective enforcement mechanism and GST administration, created by the GST law, is no exception.
1.6 For effective compliance by the taxpayers, CGST/SGST statutes have codified the offences and penalties in a detailed manner. A cursory reading of the relevant provisions gives an idea that GST Law is complete in itself and merely takes assistance of Criminal Procedure Code and others, only where it is required.
1.7 Under the GST system, businesses can commit various offences, resulting in penalties and fines. The penalties and fines deter businesses from engaging in fraudulent activities, non-compliance with tax laws and regulations, and other illegal activities. Some common GST offences include evasion of taxes, failure to register for GST, issuance of incorrect invoices, and claiming excess Input Tax Credit (ITC).
1.8 The penalties for these offences can range from monetary fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the violation. The CGST Act lists the GST-related offences and the penalties that may be imposed. Sections 122 to 128 of the CGST Act deal with the laws governing offences and penalties. (Section 122 to 128 of the CGST Act, 2017)
1.9 The CGST Act provides for prosecution of the person indulging in various types of offences covered under the Act, which may lead to imprisonment for the period ranging from six months to five years, depending upon the amount of tax evasion involved. The CGST Act also provides for compounding of offences, subject to the conditions prescribed.
2. COMPLAINCES PRESCRIBED UNDER CGST ACT, 2017
2.1 Various Chapters/Sections of the CGST Act, 2017 require compliances by the registered taxpayers and in some cases even by persons not registered under this Act. Non-compliance with the provisions of these sections may lead to imposition of penalties/fines and prosecution under this act. An illustrative list of these chapters is given as under:
(i) Chapter III covering Sections 7 to 11 provide for levy and collection of tax. (Sections 7 to 11 of CGST Act, 2017)
(ii) Chapter V provides for provisions relating to availing of input tax credit.
(iii) Chapter VI obliges the taxable person(s) to get themselves registered under the GST laws.
(iv) Chapter VII provides for rules relating to issue of tax invoices, debit notes and credit notes.
(v) Chapter VIII obliges the registered taxable person(s) to maintain books of accounts.
(vi) Chapter IX obliges the registered taxable person(s) to file certain periodical returns.
(vii) Chapter X obliges the registered taxable person(s) to pay tax. The chapter also provides for obligations to deduct/ collect tax at source and deposit the same with Government.
2.2 Non-compliance of the provisions of any of these Chapters or the rules made thereunder, may lead to levy of interest, imposition of fine/penalty and prosecution of the defaulting taxable persons. In particular, Chapter XIX, Sections 122 to 138 of the CGST Act, 2017 read with Rule 162 of the CGST Rules give details of various offences penalties prescribed for these offences. These provisions also apply to State/UT Goods and Service laws and Integrated Goods and Service Tax Act, 2017. (Sections 122 to 138 of the CGST Act, 2017) (Rule 162 of the CGST Rules, 2017)
3. OFFENCES UNDER GST LAW
3.1 An offence under GST is a breach of the provisions of CGST Act and the rules made thereunder. Under the CGST Act, 2017 or any other GST laws there is no specific definition of an offence, however, the provisions for the offences and its penalties are explained in CGST Act, 2017. Hence, any act or conduct that commits a breach of the provisions under the CGST Act is known as an offence under GST laws.
3.2 Provisions related to offences are covered under Section 122 of the CGST Act. This section constitutes those offences that attract penalties for any infringement or breach and also apply tax and interest. The provisions of Section 122 of the CGST Act is applicable to the taxable person, meaning that these provisions are not only applicable to the registered persons but also to the persons liable to be registered. (Section 122 of CGST Act 2017)
3.3 Some of the offences are also provided under Section 132 liable for prosecution, depending upon the gravity of the offences. (Section 132 of CGST Act, 2017)
3.4 These provisions are made applicable to various State and Union Territories Goods and Service Laws and Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017.
4. TYPES OF OFFENCES

Section 122 of the CGST Act, consists of a list that includes 21 offences on which the law imposes penalty. For the sake of better understanding, such offences are divided into four broad categories, and these are as follows: – (Section 122 of the CGST Act,2017)
(I) GST Offences related to Invoicing and Documentation:
- Issuing false/incorrect invoice or not issuing invoice for goods/services that have been supplied;
- Issue of GST invoice without actual supply of goods/services;
- Issue of invoice/document using GSTIN of a different GST registered person/entity;
- Transport of taxable goods without adequate/correct documentation;
- Failure to maintain relevant documents/records in line with requirements of the CGST Act, 2017.
(II) GST Offences related to Fraudulent Intent:
- Submission of false information at the time of GST registration or at a later date;
- Obtaining GST refund by supplying fraudulent information;
- Falsifi cation of documents/records or providing false information with the intent of tax evasion;
- Not registering under GST even though required to do so under CGST Act, 2017
- Tampering with/disposing off goods that have been attached, seized or detained under CGST Act, 2017
- Knowingly supplying, transporting or storing any goods that are liable to be confiscated as per GST rules.
(III) GST Offences related to Tax Evasion:
- Under reporting/suppressing turnover resulting in tax evasion;
- Failure to pay tax to the government within three months of due date after collecting the tax from receiver of goods/services;
- Failure to pay tax to the government within three months of due date even though such tax has been collected in contravention of provisions specified by the CGST Act, 2017;
- Taking or utilizing Input Tax Credit (ITC) without actual receipt/supply of goods or services;
- Failure to deduct tax, deducting tax amount less than the actual amount deducted or not paying the tax owed to the government (Tax liability under sub-section 2 of Section 52 of CGST Act, 2017); (Section 52(2) of CGST Act, 2017)
- Failure to deduct tax, deducting tax amount less than the actual amount deducted or not paying the tax owed to the government (Tax liability under sub-section 3 of Section 52 of CGST Act, 2017); (Section 52(3) of CGST Act, 2017)
- Taking/utilizing input tax credit in breach of Section 20 and its sub-sections under the CGST Act, 2017. (Section 20 CGST Act,2017)
(IV) GST Offences related to Obstruction:
- Obstructing/preventing any officer from discharging his/her duties as per the CGST Act, 2017;
- Destroying/tampering with documents or material evidence;
- Providing false documents or failure to furnish documents/information demanded by an officer acting with authority provided by the CGST Act, 2017.
5. MINOR BREACH AND MAJOR BREACH UNDER CGST ACT, 2017
5.1 In context of GST Penalties, a minor breach is defined as a situation where the amount of tax involved is less than Rs. 5,000. Additionally, a minor breach also includes easily rectifiable documentation errors/omission. Under existing rules, minor breaches do not attract substantial GST penalties.
5.2 In case the tax amount involved exceeds Rs. 5,000, the situation is classified as a major breach under the CGST Act, 2017 and penalties under GST, including jail sentences may be applicable depending on the tax amount consideration. The minor vs. major breach clause is designed to help businesses, especially those with small turnovers including SME by ensuring that they do not get penalized for genuine errors.
6. PENALTIES UNDER GST LAW
6.1 If any of the offenses are committed then a penalty will have to be paid under GST. The principles on which these penalties are based are mentioned by law. Penalty means a temporary punishment (monetary as well as prosecution) imposed by the statute given to a person for the commission of a certain offence.
6.2 GST Penalties resulting from breach of the CGST Act, 2017 are subject to fines depending on various factors, including but not limited to the severity of the breach.
6.3 Section 122(1) of the CGST Act, 2017 prescribes penalty of Rs. 10,000/- or an amount equivalent to the tax involved, whichever is higher, on the taxable person for the following omissions and commissions – (Section 122(1) of the CGST Act, 2017)
(i) supply of goods or services or both without issue of any invoice or issuance of incorrect or false invoice with regard to any such supply;
(ii) issuance of invoice or bill without supply of goods or services or both in violation of the provisions of the CGST Act or the rules made thereunder;
(iii) failure to pay any amount collected as tax to the Government beyond a period of three months from the date on which such payment becomes due;
(iv) collection of any tax in contravention of the provisions of CGST Act and failure to pay the same to the Government beyond a period of three months from the date on which such payment becomes due;
(v) failure to deduct the tax (TDS) in accordance with the provisions of sub-section (1) of Section 51 of the CGST Act, or deduct an amount less than the amount required to be deducted under the said sub-section, or failure to pay to the Government the amount deducted as tax; (Section 51(1) of CGST Act, 2017)
(vi) failure to collect tax (TCS) in accordance with the provisions of sub-section (1) of Section 52 of the CGST Act, or collect an amount less than the amount required to be collected under the said sub-section or failure to pay to the Government the amount collected as tax; (Section 52(1) of CGST Act, 2017)
(vii) availment or utilisation of input tax credit without actual receipt of goods or services or both either fully or partially;
(viii) obtaining refund of tax fraudulently;
(ix) availment or distribution of input tax credit by Input Service Distributor (ISD) in contravention of Section 20 of the CGST Act; (Section 20 of the CGST Act, 2017)
(x) falsification or substitution of financial records or producing fake accounts or documents or furnishing false information or return, with an intention to evade payment of tax;
(xi) failure to obtain registration despite being liable to be registered;
(xii) furnishing of false information with regard to registration particulars, either at the time of applying for registration, or subsequently;
(xiii) obstructing or preventing any officer in discharge of his duties;
(xvi) transporting any taxable goods without the cover of specified documents;
(xv) suppression of turnover leading to evasion of tax;
(xvi) failure to keep, maintain or retain books of account and other documents in accordance with the provisions of CGST Act, 2017 or the rules made thereunder;
(xvii) failure to furnish information or documents called for by an officer or furnishing false information or documents during any proceedings under CGST Act;
(xviii) supplying, transporting or storing any goods liable to confiscation under CGST Act;
(xix) issuance of invoice or document by using the registration number of another registered person;
(xx) tampering or destroying any material evidence or document;
(xxi) dispose off or tamper with any goods detained, seized, or attached under CGST Act.
6.4 The following Table depicts the list of offences subjected to penalty under Section 122 of the CGST Act and the applicable penalty – (Section 122 of the CGST Act, 2017)
| Section | Person liable to pay | Penalty | |
| 122(1) | Any taxable person who has committed the following offence | · Rs.10,000/- OR· An amount equivalent to:(i) tax evaded OR(ii) Tax not deducted or short deducted or deducted but not paid to the GovernmentOR(iii) Tax not collected or short collected or collected but not paid to the Government OR (i) Input tax credit OR (i) the refund claimed fraudulently. Whichever is higher.
|
|
| S.No. | Nature of Offence Committed | ||
| (i) | Supplying any goods or services or both without issue of any invoice or an incorrect or false invoice. | ||
| (i) | Issuing any invoice or bill without supply of goods or services or both in violation of GST. | ||
| (ii) | Collecting any amount as tax but failing to pay the same to the Government beyond a period of three months from the due date. | ||
| (iii) | Collecting any tax but failing to pay the same to the Government beyond a period of three months from the due date. | ||
| (iv) | Failing to deduct tax, or deducting an amount which is less than the amount required to be deducted, or failing to pay deducted tax to the Government. | ||
| (v) | Failing to collect tax in accordance, or collecting an amount which is less than the amount required to be deducted, or failing to pay deducted tax to the Government. | ||
| (vi) | Taking or utilizing input tax credit without actual receipt of goods or services or both either fully or partially, in contravention of provisions of CGST Act, 2017 & Rules thereunder. | ||
| (iv) | Fraudulently obtaining refund of tax. | ||
| (vii) | Taking or distributing input tax credit in contravention of provisions of CGST Act, 2017 & Rules thereunder. | ||
| (viii) | Falsifying or substituting financial records or producing fake accounts or documents or furnishing any false information or return with an intention to evade payment of tax. | ||
| (xi) | Failing to obtain registration though liable to be registered as per the CGST Act, 2017. | ||
| (v) | Furnishing any false information with regard to registration particulars either at the time of applying for registration, or subsequently. | ||
| (vi) | Obstructs or prevents any officer in discharge of his duties under CGST Act, 2017. | ||
| (vii) | Transports any taxable goods without the cover of
documents as may be specified in this behalf. |
||
| (viii) | Suppresses his turnover leading to evasion of tax under CGST Act, 2017. | ||
| (ix) | Fails to keep, maintain or retain books of account and other documents in accordance with the provisions of CGST Act, 2017 or the Rules made thereunder. | ||
| (x) | Fails to furnish information or documents called for by an officer in accordance with the provisions of CGST Act, 2017 or the Rules made thereunder or furnishes false information or documents during any proceedings under the CGST Act, 2017. | ||
| (i) | Supplies, transports or stores any goods which he has reasons to believe are liable to confiscation under the CGST Act, 2017. | ||
| (xi) | Issues any invoice or documents by using the registration number of another registered person. | ||
| (xii) | Tampers with, or destroys any material evidence or
document. |
||
| (xiii) | Disposes off or tampers with any goods that have been detained, seized, or attached under the CGST Act, 2017. | ||
6.5 In cases pertaining to non-issuance of invoice or issuance of invoice without supply of goods and/or services, availment of ITC without receipt of goods and/or services and distribution of ITC by ISD, Section 122(1A) of CGST Act, 2017 prescribes penalty of amount equivalent to the tax evaded or ITC availed or passed on. (Section 122(1A) of CGST Act, 2017)
As per Section 122(1A) of the CGST Act, any person who retains the benefit of a transaction covered under the below mentioned clauses of Section 122(1) of CGST Act and at whose instance such transaction was conducted, shall be liable to a penalty of an amount equivalent to the tax evaded or an amount equivalent to the Input tax credit availed of or passed on. (Section 122(1) of CGST Act, 2017)
| (i) | Supplying any goods or services or both without issue of any invoice or an incorrect or false invoice. |
| (ii) | Issuing any invoice or bill without supply of goods or services or both in violation of GST. |
| (vii) | Taking or utilizing input tax credit without actual receipt of goods or services or both either fully or partially, in contravention of provisions of CGST Act, 2017 & Rules thereunder. |
| (ix) | Taking or distributing input tax credit in contravention of provisions of CGST Act, 2017 & Rules thereunder. |
6.5 Section 122(1B) of the CGST Act, 2017 prescribes penalty of ten thousand rupees, or an amount equivalent to the amount of tax involved, whichever is higher, on the e-commerce operator if he allows supply of goods or services through their platform, by an unregistered person other than a person exempted from registration, allows an inter-State supply of goods or services by a person who is not eligible to make such inter-State supply or fails to furnish the correct details in the statement to be furnished of any outward supply of goods effected by a person exempted from obtaining registration. (Section 122(1B) of the CGST Act, 2017)
6.6 Penalty for short payment or non-payment of tax or wrong availment of ITC or erroneous refund – If the taxpayer supplies goods and services, on which the tax is not paid or partially paid or erroneously refunded or ITC wrongly availed or utilised, penalty is imposable under Section 122(2) of the CGST Act, 2017. The quantum of penalty for the above offences are divided into two parts, i.e. offence committed for any reason other than fraud or any wilful misstatement or suppression of facts or offence committed for reasons of fraud or any wilful misstatement or suppression of facts. The two sets of penalties provided under Section 122(2) are as under: (Section 122(2) of the CGST Act, 2017)
| For any reason other than reasons of fraud or any willful misstatement or suppression of facts |
|
| For reasons of fraud or any willful misstatement or suppression of facts |
|
6.7 It is pertinent to mention here that penalty under Section 73(9) and 74(9) of the CGST Act, as applicable, is liable to be imposed in cases where determination of tax not paid or short paid has been ordered. Therefore, if penalty has been imposed on a person under Section 73 or Section 74 of the CGST Act then no penalty for the same act shall be imposed on that person under any other provision of CGST Act. (Section 73(9) and 74(9) of CGST Act)
6.8 Penalty on person other than taxable person – Section 122(3) of CGST Act, 2017, provides for levy of penalty extending to Rs. 25,000/-, on any person, other than the taxable person for five specific nature of offences as detailed hereunder: (Section 122(3) of CGST Act, 2017)
| No. | Nature of Offence |
| a | Aiding or abetting any of the 21 offences specified in Section 122(1). |
| b | Acquires possession of, or in any way concerning in transporting, removing, depositing, keeping, concealing, supplying, or purchasing or in any other manner dealing with any goods, which are liable to confiscation under CGST Act, 2017. |
| c | Receives or is in any way concerned with the supply of, or in any other manner deals with any supply of services which he knows or has reasons to believe are in contravention of any provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder. |
| d | Fails to appear before the officer of Central tax, when issued with a summon for appearance to give evidence or produce a document in an inquiry; |
| e | Fails to issue invoice in accordance with the provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder or fails to account for an invoice in his books of account. |
6.9 Penalty for failure to furnish information return:
(I) It is mandatory for all taxable persons to provide information return as per Section 150 of the CGST Act. If the person fails to furnish the return within the specified duration, then such person needs to pay penalty at the rate of Rs. 100/- per day for the period during which the failure to provide such information return continues, subject to maximum of Rs. 5000/-, as per Section 123 of the CGST Act. (Section 150 & 123 of CGST Act, 2017)
(II) As per Section 150(1) of the Act, the following persons responsible for maintaining record of registration or statement of accounts or any periodic return or document containing details of payment of tax and other details of transaction of goods and/or services or transactions related to a bank account or consumption of electricity or transaction of purchase, sale or exchange of goods or property or right or interest in a property under any law for the time being in force, shall furnish an information return in respect of such periods, within the stipulated time and in prescribed form and manner – (Section 150(1) of CGST Act, 2017)
(a) a taxable person; or
(b) a local authority or other public body or association; or
(c) any authority of the State Government responsible for the collection of value added tax or sales tax or State excise duty or an authority of the Central Government responsible for the collection of excise duty or customs duty; or
(d) an income tax authority appointed under the provisions of the Income-tax Act, 1961 (43 of 1961); or
(e) a banking company within the meaning of clause (a) of section 45A of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 (2 of 1934); or
(f) a State Electricity Board or an electricity distribution or transmission licensee under the Electricity Act, 2003 (36 of 2003), or any other entity entrusted with such functions by the Central Government or the State Government; or
(g) the Registrar or Sub-Registrar appointed under section 6 of the Registration Act, 1908 (16 of 1908); or
(h) a Registrar within the meaning of the Companies Act, 2013 (18 of 2013); or
(i) the registering authority empowered to register motor vehicles under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 (59 of 1988); or
(j) the Collector referred to in clause (c) of section 3 of the Right to Fair Compensation and Transparency in Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation and Resettlement Act, 2013 (30 of 2013); or
(k) the recognised stock exchange referred to in clause (f) of section 2 of the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 (42 of 1956); or
(l) a depository referred to in clause (e) of sub-section (1) of section 2 of the Depositories Act, 1996 (22 of 1996); or
(m) an officer of the Reserve Bank of India as constituted under section 3 of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 (2 of 1934); or
(n) the Goods and Services Tax Network, a company registered under the Companies Act, 2013 (18 of 2013); or
(o) a person to whom a Unique Identity Number has been granted under sub-section (9) of section 25; or
(p) any other person as may be specified, on the recommendations of the Council, by the Government.
(III) The Proper officer in respect of the above said Section150(1) of the CGST Act, is the Assistant/Deputy Commissioner of Central Tax.
6.10 Penalty for failure to furnish statistics – Commissioner is empowered under Section 151 of CGST Act, 2017 to collect the statistics relating to any matters dealt with under the Act. He may direct the person to furnish the information or return to collect the statistics that he feels necessary. If such person fails to provide the information called for without reasonable cause or provides any false information or returns wilfully, then as per Section 124 of the CGST Act, he shall be liable to pay penalty up to Rs. 10,000/-. If the offence continues, then the penalty may further extend to Rs. 100/- each day after the first day during which the offence continues, subject to maximum of Rs. 25,000/-. (Section 151 of CGST Act, 2017) (Section 124 of the CGST Act, 2017)
6.11 General penalty – If in respect of any violation, contravention, omission or commission under GST a penalty is not specified under any other provision of the CGST Act, then a General Penalty of an amount up to Rs. 25,000/-can be imposed on the person.
6.12 Violations in respect of which no Penalty is applicable – In case of certain instances no GST penalties are applicable despite some provision being violated/contravened, but these GST offences can incur interest at a specified rate for delayed payment on the amount of tax under consideration. The following are some instances where no penalty under GST is applicable:
- No penalty is applicable for charging incorrect GST, such as charging CGST/SGST instead of IGST. The registered business/entity has to pay the correct GST and get a refund for the wrong GST paid.
- No penalty under CGST Act, 2017 for incorrect filing of GST returns but interest at the rate of 18% p.a. is chargeable on the tax amount shortfall.
- No penalty is applicable for delayed invoice payments. But any input tax credit claimed in lieu of such invoices is liable to be reversed if invoice payment is delayed beyond 6 months.
Further, no penalty is imposed for minor violations, as under –
- Amount involved in the offense is less than Rs. 5000.
- The offense is easily rectifiable, like an omission or an erroneous record in a document.
6.13 The Section wise summarised penalty chart is as under: (Section 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129 of the CGST Act, 2017)
| S. N | Section | Type of Offence | Penalty |
| 1 | 122(1) | Specified 21 offences | Rs. 10,000/- (or) equivalent to Tax/ITC involved, whichever is higher |
| 2 | 122(2) | Other than fraud, suppression, mis-statement, etc. | Rs. 10,000/- (or) 10 % equivalent to Tax/ ITC involved, whichever is higher |
| Fraud, suppression, misstatement, etc. | Rs. 10,000/- (or) equivalent to Tax/ITC involved, whichever is higher | ||
| 3 | 122(3) | Offences where person is not directly involved in any evasion but may be the party to evasion or if he does not attend summons or produce documents | Upto Rs. 25,000/- |
| 4 | 123 | Person fails to furnish an information returns u/s 150. | Rs. 100/- per day (failure period), subject to Max. of Rs. 5,000/- |
| 5 | 124 | Any person required to furnish information u/s 151 | Normal Case- Upto 10,000/- Continuing offence- Rs. 100/- per day (failure peri-od), subject to Max. Rs. 25,000/- |
| 6 | 125 | General penalty | Upto Rs. 25,000/- |
| 7 | 123 | Delayed filing of GST Returns | Rs. 200/- per day (Rs. 100/- per day under CGST + Rs. 100/- per day under SGST), up to a maximum of Rs. 5,000/-. Late fee not applicable to IGST unpaid by delayed filing. |
| 8 | 122(3) | Issuing incorrect invoice | Rs. 25,000/-. |
| 9 | 126 | For minor rectifiable offences and amount of tax/ ITC is less than Rs. 5,000/-, which is made with- out fraudulent intent. | Nil |
| 10 | 127 | Where the Proper Officer is of the view that a per-son is liable to a penalty and the same is not covered under proceedings related to Assessment of non-filers (Sec, 62), Assessment of unregistered persons (Sec. 63), Summary Assessment (Sec. 64), Demand of tax/ITC on account of reasons other than fraud, suppression, etc. (Section73), Demand of tax/ITC on account of reasons of fraud, suppression, etc. (Section 74), Detention, Seizure, and release of goods and conveyance (Sec. 129), Confiscation of goods and convey-ance (Sec. 130). | Power to levy penalty is with the Proper Officer. |
| 11 | 128 | Waiver of penalty referred in Section 122, 123 and 125 and late fee for delay in filing returns. | Power to waive penalty and late fee with Government on recommendation of GST Council, for the notified class of taxpayers. |
| 12 | 129 | Release of goods and conveyance under detention or seizure:
(A) Where owner comes forward for payment of tax and penalty. (B)Where the owner does not come forward for payment of tax and penalty |
(a) In case of taxable goods – Penalty equivalent to 200% of the tax payable
(b) In case of exempted goods – Penalty 2% of the value of goods or Rs. 25,000/-, whichever is less (c) In case of taxable goods – Penalty equivalent to 50% of value of goods or 200% of the tax payable whichever is higher (d) In case of exempted goods – Penalty equivalent to 5% of the value of goods or Rs. 25,000/-, whichever is less. |
7. GENERAL DISCIPLINE RELATED TO PENALTY
7.1 Section 126 of the CGST Act deals with General disciplines related to Imposition of penalty. It says that penalty is not to be imposed for minor breaches of tax regulations or procedural requirements and in particular, any omission or mistake in the documentation which is easily rectifiable and made without fraudulent intent or gross violations. It explains the circumstances as mentioned below, under which a breach and omission or mistake can be considered. (Section 126 of the CGST Act, 2017)
(a) a breach shall be considered a “minor breach” if the amount of tax involved is less than five thousand rupees;
(b) an omission or mistake in documentation shall be considered to be easily rectifiable if the same is an error apparent on the face of record.
7.2 Section 126 of the CGST Act, 2017 lays down the general principles for imposing penalty, as under –
(i) The penalty imposed under this Act shall depend on the facts and circumstances of each case and shall be commensurate with the degree and severity of the breach.
(ii) When a penalty is proposed to be imposed, the offender will be sent a notice and given a fair opportunity to be heard by the tax officials.
(iii) The tax authorities will give the offender a summary of the reasons for the penalty and the legal provisions under which the penalty is imposed.
(iv) If the offender chooses to voluntarily disclose infringement of law, the tax authorities may use the disclosure as leverage to reduce the penalty.
7.3 The provisions of this section shall not apply in cases where the penalty specified is either a fixed sum or expressed as a fixed percentage.
8. POWER TO IMPOSE PENALTY IN CERTIN CASES
8.1 Section 127 of the CGST Act deals with power to impose penalty in certain cases. The section states that where the proper officer is of the view that a person is liable to a penalty and the same is not covered under any proceedings under Section 62 or Section 63 or Section 64 or Section 73 or Section 74 or Section 129 or Section 130, he may issue an order levying penalty after giving a reasonable opportunity of being heard to such person. (Section 127, 62, 63, 64, 73, 74, 129, & 130 of the CGST Act, 2017)
8.2 The Proper officer assigned to function in respect of this section is the Deputy or Assistant Commissioner of Central Tax.
9. POWERS TO WAIVE PENALTY
Section 128 of the CGST Act, 2017 provides the power to the Government, to waive the penalty imposable under Section 122 or 123 or 125 or the late fees to be paid for delay in filing returns, on such class of taxpayers under justifying circumstances specified in the notification issued in this regard. (Section 128, 122, 123 & 125 of the CGST Act, 2017)
10. DETENTION, SEIZURE AND RELEASE OF GOODS AND CONVEYANCES IN TRANSIT AND PENALTY THEREOF
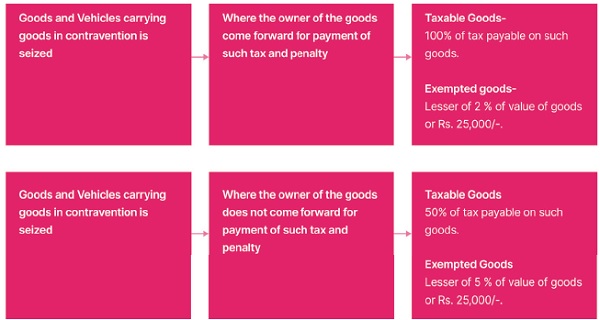
10.1 Section 129 of the CGST Act deals with detention, seizure and release of goods and conveyances in transit. It states that where any person transports any goods or stores any goods while they are in transit in contravention of the provisions of the CGST Act or the rules made thereunder, all such goods and conveyance used as a means of transport for carrying the said goods and documents relating to such goods and conveyance shall be liable to detention or seizure. (Section 129 of the CGST Act, 2017)
10.2 Section 129 of the CGST Act further specifies the quantum of penalties as detailed below:
| Situation | Quantum of Penalty | |
| a | Where the owner of the goods come forward for payment of such penalty | Penalty equal to two hundred per cent of the tax payable on such goods and, in case of exempted goods, on payment of an amount equal to two per cent of the value of goods or twenty-five thousand rupees, whichever is less. |
| b | Where the owner of the goods does not come for- ward for payment of such penalty | Penalty equal to fifty per cent of the value of the goods or two hundred per cent of the tax payable on such goods, whichever is higher, and in case of exempted goods, on payment of an amount equal to five per cent of the value of goods or twenty-five thousand rupees, whichever is less. |
| c | In both the situations as mentioned in a & b above | Upon furnishing a security equivalent to the amount payable under clause (a) or clause (b) in such form and manner as may be prescribed: |
10.3 As per the proviso to Section 129(1) of the CGST Act, an order of detention or seizure of such goods has to be served on the person transporting the goods before detention/seizure of goods or conveyance.
10.4 As per Section 129(3) of the CGST Act, the proper officer detaining or seizing goods or conveyance shall issue a notice within seven days of detention or seizure, specifying the penalty payable. The proper officer shall pass an order within a period of seven days from the date of service of such notice, for payment of penalty under clause (a) or clause (b) of sub-section (1) of Section 129(1) of the CGST.
10.5 The Proper officer assigned to function in respect of Section 129(3) is the Deputy or Assistant Commissioner of Central Tax.
10.6 As per Section 129(4) of the CGST Act, no penalty shall be determined under sub-section (3) without giving the concerned person an opportunity of being heard.
10.7 As per Section 129(5) of the CGST Act, all proceedings in respect of the notice specified in sub-section (3) shall be deemed to be concluded on payment of the amount mentioned in Section 129(1) by the concerned person.
10.8 As per Section 129(6) of the Act, if the person transporting any goods or the owner of goods fails to pay the amount of penalty within fifteen days from the date of receipt of the order passed by the proper officer, the goods or conveyance detained or seized shall be liable to be sold or disposed of otherwise, within the prescribed time and manner, to recover the penalty payable.
10.9 The conveyance shall be released on payment of penalty or one lakh rupees, whichever is less, by the transporter. If the detained or seized goods are perishable or hazardous in nature or are likely to depreciate in value with passage of time, the stipulated period of fifteen days may be reduced by the proper officer.
10.10 The Proper officer to function in respect of this section is the Additional or Joint Commissioner.
11. CONFISCATION OF GOODS AND CONVEYANCES AND PENALTY THERE0F
11.1 Section 130 of the CGST Act deals with confiscation of goods or conveyances and levy penalty on the concerned person.
11.2 As per Section 130(1) of the CGST Act, where any person indulges in the following acts, then all such goods or conveyances used shall be liable to confiscation and the person shall be liable to penalty under Section 122 of the CGST Act – (Section 122 & 130 of the CGST Act, 2017)
(i) supplies or receives any goods in contravention of any of the provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder with intent to evade payment of tax; or
(ii) does not account for any goods on which he is liable to pay tax under this Act; or
(iii) supplies any goods liable to tax under this Act without having applied for registration; or
(iv) contravenes any of the provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder with intent to evade payment of tax; or
(v) uses any conveyance as a means of transport for carriage of goods in contravention of the provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder unless the owner of the conveyance proves that it was used without the knowledge or connivance of the owner himself, his agent and the person in charge of the conveyance.
11.3 As per Section 130(2) of the CGST Act, whenever confiscation of any goods or conveyance is authorised by this Act, the officer adjudging it shall give an option to the owner of the goods to pay fine in lieu of confiscation, as the said officer thinks fit. However, such fine leviable shall not exceed the market value of the confiscated goods, less the tax chargeable thereon. Also, the aggregate of such fine and penalty shall not be less than the penalty equal to 100% of the tax payable on such goods.
11.4 If any conveyance is used for the carriage of the goods or passengers for hire, the owner of the conveyance shall be given an option to pay fine equal to the tax payable on the goods being transported thereon in lieu of the confiscation of the conveyance.
11.5 As per Section 130(4) of the CGST Act, no order for confiscation of goods or conveyance or for imposition of penalty shall be issued without giving the person an opportunity of being heard.
11.6 As per Section 130(5) of the CGST Act, if any goods or conveyance are confiscated under this Act, the title of such goods or conveyance shall thereupon vest in the Government.
11.7 As per Section 130(6) of the CGST Act, the proper officer adjudging confiscation shall take and hold possession of the things confiscated and every officer of Police, on the requisition of such proper officer, shall assist him in taking and holding such possession.
11.8 The Proper officer to function in respect of this section is the Deputy or Assistant Commissioner.
11.9 As per Section 130(7) of the CGST Act, the proper officer if satisfied that the confiscated goods or conveyance are not required in any other proceedings under this Act and after giving reasonable time not exceeding three months to pay fine in lieu of confiscation, dispose of such goods or conveyance and deposit the sale proceeds thereof with the Government. The Proper officer to function in respect of this section is the Deputy or Assistant Commissioner.
12. CONTINUATION OF ALL OTHER PROCEEDINGS UNDER GST LAW
Section 131 of the CGST Act provides that in addition to confiscation of goods or penalty already imposed, all other proceedings may also be initiated or continued under the GST law or any other law, as applicable. This could be prosecution, arrest, cancellation of registration, etc., as applicable, provided for the relevant non-compliance. Therefore, for the same offence both penalty and punishment can be levied. (Section 131 of the CGST Act,2017)
13. PROSECUTION
13.1 Section 198 of the Criminal Procedure Code defines “prosecution” as the institution and carrying on of the legal proceedings against a person. It is the process of exhibiting formal charges against the offender.
13.2 Section 132 of the CGST Act deals with the punishments for certain offences. Punishments are proposed in respect of the following offences committed or causes to commit and retain the benefits arising out of the same by any person – (Section 132 of the CGST Act,2017)
(a) supplies any goods or services or both without issue of any invoice, in violation of the provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder, with the intention to evade tax;
(b) issues any invoice or bill without supply of goods and/or services in violation of the provisions of this Act, or the rules made thereunder leading to wrongful availment or utilisation of input tax credit or refund of tax;
(c) avails input tax credit using the invoice or bill referred to in clause (b) or fraudulently avails input tax credit without any invoice or bill;
(d) collects any amount as tax but fails to pay the same to the Government beyond a period of three months from the date on which such payment becomes due;
(e) evades tax or fraudulently obtains refund and where such offence is not covered under clauses (a) to (d);
(f) falsifies or substitutes financial records or produces fake accounts or documents or furnishes any false information with an intention to evade payment of tax due under this Act;
(g) acquires possession of, or in any way concerns himself in transporting, removing, depositing, keeping, concealing, supplying, or purchasing or in any other manner deals with, any goods which he knows or has reasons to believe are liable to confiscation under this Act or the rules made thereunder;
(h) receives or is in any way concerned with the supply of, or in any other manner deals with any supply of services which he knows or has reasons to believe are in contravention of any provisions of this Act or the rules made thereunder;
(i) attempts to commit, or abets the commission of any of the offences mentioned in above clauses of this section. 13.3 The punishments prescribed are as under: –
| Offence Involved (imprisonment extending to) | Punishment |
| Amount of duty evaded (or)
Amount of ITC wrongly availed or utilized (or) Amount of refund wrongly taken -Exceeds Rs.5 Crore Repeated offenders – for the second and every subsequent of- fence {Section 132(2)} |
5 years and fine |
| Amount of duty evaded (or)
Amount of ITC wrongly availed or utilized (or) Amount of refund wrongly taken -Between ₹2 crore and ₹5 crore |
3 years and fine |
| Amount of duty evaded (or)
Amount of ITC wrongly availed or utilized (or) Amount of refund wrongly taken -Between ₹1 crore and ₹2 crore |
1 years and fine |
| Where he commits or abets the commission of an offence specified in: –
Clause (f) – falsifies or substitutes financial records or produces fake accounts or documents or furnishes any false information with an intention to evade payment of tax due under this Act; |
6 months |
13.4 As per Section 132(3) of the CGST Act, in the absence of special and adequate reasons to the contrary to be recorded in the judgment of the Court, the imprisonment referred to in sub-section (1) and sub-section (2) of Section 132 shall be for a term not less than six months. (Section 132(3), (4), (5) & (6) of the CGST Act, 2017)
13.5 In terms of Section132(4) and132(5) of CGST/SGST Act-
(a) All offences where the evasion of tax is less than ₹5 crores shall be non-cognizable and bailable;
(b) all offences where the evasion of tax exceeds ₹5 crores shall be cognizable and non-bailable.
13.6 As per Section 132(6) of the CGST Act, to launch prosecution against any person for any offence committed under this section, previous sanction of the Commissioner is necessary.
13.7 The term “ tax” shall include the amount of tax evaded or the amount of input tax credit wrongly availed or utilised or refund wrongly taken under the provisions of CGST Act, the SGST Act, the IGST Act or the UTGT Act and cess levied under the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act.
13.8 Section 133 of the CGST Act deals with liability of officers and certain other persons. Section 133(1) provides for punishment with imprisonment for a term, which may extend to six months or with fine which may extend to twenty-five thousand rupees, or with both, to any person engaged in connection with the collection of statistics under Section 151 or compilation or computerization thereof or having access to information specified under Section 150(1), or engaged in connection with the provision of service on the common portal or the agent of common portal, who wilfully discloses any information or the contents of any return furnished under the CGST Act or rules made thereunder otherwise than in execution of his duties or for the purposes of prosecution for an offence under this Act or under any other Act. (Section 133, 150 & 151 of the CGST Act,2017)
13.9 As per Section 133(2) of the CGST Act, for prosecuting a Government servant under this section, previous sanction of the Government is necessary and for prosecuting a person who is not a Government Servant for any offence under this Section, previous sanction of the Commissioner is necessary.
13.10 Section 134 of the CGST Act states that no court shall take cognizance of any offence punishable under this Act or the rules made thereunder except with the previous sanction of the Commissioner, and no court inferior to that of a Magistrate of the First Class, shall try any such offence.
13.11 Section 135 of the CGST Act deals with presumption of culpable mental state of an accused and prosecuted under this Act. It states that in any prosecution for an offence under this Act, which requires a culpable mental state on the part of the accused, the court shall presume the existence of such mental state but it shall be in defence for the accused to prove the fact that he had no such mental state with respect to the act charged as an offence in that prosecution. “Culpable Mental State” includes intention, motive, knowledge of a fact, and belief in, or reason to believe, a fact. A fact is said to be proved only when the court believes it to exist beyond reasonable doubt and not merely when its existence is established by a preponderance of probability. (Section 134, 135, 136, 137 of CGST Act, 2017)
13.12 Section 136 of the CGST Act deals with relevancy of statements under certain circumstances. It states that a statement made and signed by a person on appearance in response to any summons issued under Section 70 of the CGST Act, during the course of any inquiry or proceedings, shall be relevant for the purpose of proving an offence in any prosecution under this Act.
13.13 Section 137 of the CGST Act deals with offences related to GST committed by companies. Section 137(1) states that if an offence committed by a person under this Act is a company, then every person who was in charge at the time the offence was committed and was responsible for the conduct of business of the company, as well as the company, shall be deemed to be guilty of the offence and shall be liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly.
13.14 Section 137(2) of the CGST Act states that if an offence has been committed by a company and it is proved that the offence has been committed with the consent or connivance of, or is attributable to any negligence on the part of, any director, manager, secretary or other officer of the company, then such director, manager, secretary or other officer shall also be deemed to be guilty of that offence and shall be liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly.
13.15 As per Section 137(3) of the CGST Act provides that a partnership firm or a limited liability partnership or a Hindu Undivided Family or a trust, the partner or karta or managing trustee shall be deemed to be guilty of the offence committed and shall be liable to be proceeded against and punished accordingly.
13.16 As per Section 137(4) of the CGST Act, if any person accused of an offence proves that the offence was committed without his knowledge or that he had exercised all due diligence to prevent the commission of such offence, then such person will not be liable for any punishment provided in the Act.
14. COMPOUNDING OF OFFENCES
14.1 Section 138 of the CGST Act deals with compounding of offences. Compounding of offences can be made before or after the institution of prosecution. It can be compounded by the Commissioner. (Section 138 of the CGST Act 2017)
14.2 Offences can be compounded only after payment tax, interest and penalty involved in such offences by the person accused of the offence, to the Central or State Government, as the case may be. Compounding allowed
under the provisions of this section shall not affect the proceedings, if any, instituted under any other Law.
14.3 In respect of the following cases, compounding cannot be made – Section 138
(a) a person who has been allowed to compound once in respect of any of the offences specified in clauses (a) to (f), (h), (i) and (l) of sub-section (1) of section 132; (Section 138 of CGST Act, 2017)
(b) a person who has been accused of committing an offence under clause (b) of sub-section (1) of section 132;
(c) a person who has been convicted for an offence under this Act by a court;
(d) any other class of persons or offences as may be prescribed:
14.4 Section 138(2) of the CGST Act stipulates the minimum and maximum amount for compounding the offences. The minimum amount not being less than 25% of the tax involved and the maximum amount not being more than 100% of the tax involved. (Section 138(2) & (3) of the CGST Act,2017)
14.5 As per Section 138(3) of the CGST Act, on payment of such compounding amount, as determined by the Commissioner, no further proceedings shall be initiated under this Act against the accused person in respect of the same offence and any criminal proceedings, if already initiated in respect of the said offence, shall stand abated.
14.6 Rule 162 of CGST Rules, 2017 prescribes the procedure for compounding of offences. The applicant desiring to compound his offences has to make application in FORM GST CPD-01 to the Commissioner. (Rule 162 of the CGST Rules,2017)
14.7 The Commissioner shall call for a report from the concerned officer with reference to the particulars furnished in the application and after taking into account the contents of the said application, pass an order in FORM GST CPD-02, on being satisfied about the disclosure of facts relating to the case, indicating the compounding amount and grant him immunity from prosecution or reject such application, within ninety days of the receipt of the application.
15. PROVISIONS TO BE FOLLOWED BY THE OFFICER
The Officers have to follow the following relevant provisions for imposition of penalties:
-
- Provisions related to offences and their corresponding penalties are covered under Section 122 of the CGST Act.
- If a person who is required to furnish an information return under Section 150 fails to do so within the period specified in the notice issued under sub-section (3) thereof, the proper officer may direct that such person shall be liable to pay a penalty of one hundred rupees for each day of the period during which the failure to furnish such return continues.
- Section 124 of the CGST Act, 2017 prescribes penalty for failure to furnish any information or return under Section 151 of the CGST Act.
- Any person, who contravenes any of the provisions of this Act or any rules made thereunder, for which no penalty is separately provided for in this Act, shall be liable to a penalty which may extend to twenty-five thousand rupees under Section 125 of the CGST Act, 2017.
- Section 127 of the CGST Act prescribes power to impose penalty in cases where the proper officer is of the view that a person is liable to a penalty and the same is not covered under any proceedings under Section 62 or Section 63 or Section 64 or Section 73 or Section 74 or Section 129 or Section 130, he may issue an order levying such penalty after giving a reasonable opportunity of being heard to such person.
- Section 129 of the CGST Act governs the detention, seizure, and release of goods and conveyances in transit.
- Confiscation of goods or conveyances and levy of penalty are provided under Section 130 of the CGST, Act, 2017.
*****
Source: Handbook of GST Law and Procedures for Departmental Officers issued by Ministry of Finance.




