Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented her 8th Budget in total & second in Modi 3.0 government on 01st Feb 2025.She emphasized on four engines of growth, Viz Agriculture, MSME, Investments and Exports. She outlined that “A country is not just its soil, a country is its people.” to Ensure the aspiration of Viksit Bharat emphasis was given on accelerate growth, Secure Inclusive Development, Enhance Spending Power of India’s Rising Middle Class, Invigorate Private Sector Investments and Uplift Household Sentiments. This Union Budget focused on development measures on Garib, Youth, Annadata and Nari.
Good to see that the fiscal deficit has shown a continuous decline trend from 6.7 % of GDP (20-21) to 4.4% GDP (2025-26).
On the Direct Taxation front, a major relief was given by increasing the threshold limit of income to Rs 12 Lacs as exempted from Income Tax. Also, the much-awaited introduction of Direct Tax code was announced to be elaborated in next few days.
The influence of Allies was visible in the budget speech in the form of various schemes and benefits to Bihar state.
Overall, one common feel is that government is successful in leaving impression of progress and development in the country towards a well-defined goal.
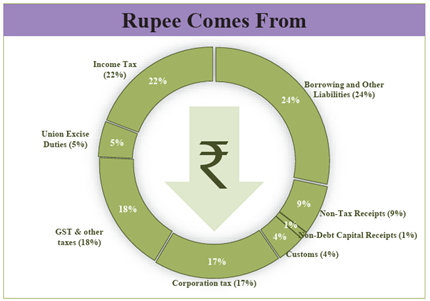
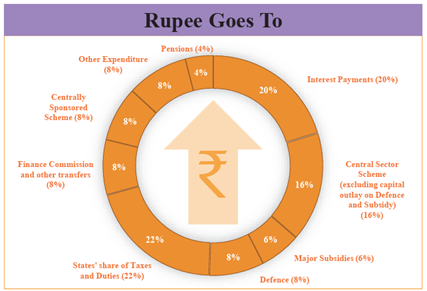
Overall Receipts and Expenditure
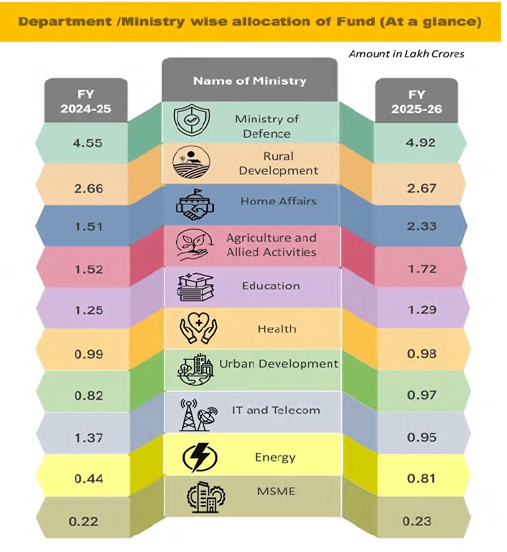
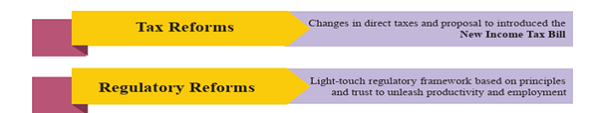
Major Proposed Reforms
Indirect Tax Proposals
1. Rationalisation of Customs Tariff Structure for Industrial Goods
- Removal of 07 tariff rates
- Apply not more than one cess or surcharge
- Apply equivalent cess to maintain effective duty incidence on most items and lower cess on certain items
2. Sector specific proposals
- Make in India- Exemption to open cell for LED/LCD TV, looms for textiles, capital goods for lithium-ion battery of mobile phones and EVs
- Promotion of MRO – exemption for 10 years on goods for ship building and ships for breaking, extension of time limit for export of railway goods imported for repairs
- Export promotion – duty free inputs for handicraft and leather sectors
3. Improved access to lifesaving medicines
Addition of:
- 36lifesaving drugs/medicines in exempted list;
- 6medicines in 5%dutylist;
- 37medicines and 13 new patient assistance programmes in exempt list.
Direct Tax Proposals
1. Ease of doing business
- Introduction of a scheme for determining length price international transaction arms of for a block period of three years.
- Expansion of scope of safe harbour rules to reduce litigation and provide certainty in international taxation.
2. Personal Income Tax reforms with special focus on the middle class
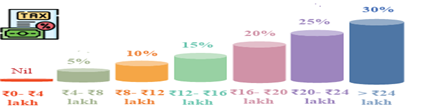
3. Personal Income Tax reforms with special focus on the middle class
- Tax deduction limit for senior citizens doubled from ₹ 50,000 to ₹ 1 lakh.
- The annual limit of ₹2.40 lakh for TDS on rent increased to ₹ 6lakh.
4. Encouraging voluntary compliance
- Extension of time-limit to file updated returns, from the current limit of two years, to four years.
5. Reducing compliance burden
- Reduced compliance for small charitable trusts/institutions by increasing their period of registration from 5 years to 10 years
- Tax payers to be allowed to claim the annual value of 02 self-occupied properties
Detailed Explanation of Changes in Direct Tax
Corporate Tax
TDS related changes w.e.f 1st April2025
| Sl. No. | Section | Nature of Transaction | Existing Threshold limit | Proposed Threshold limit |
| 1 | 193 | Interest on securities by public company / other securities | 5,000/ Nil | 10,000 |
| 2 | 194 | Dividend | 5,000 | 10,000 |
| 3 | 194A | Interest other than “interest on securities” | ||
| a. in case of senior citizen | 50,000 | 1,00,000 | ||
| b. in case of others when payer is bank, cooperative society and post office |
40,000 | 50,000 | ||
| c. in case of others | 5,000 | 1,000 | ||
| 4 | 194D | Insurance commission | 15,000 | 20,000 |
| 5 | 194G | Income by way of commission, prize etc. on lottery tickets | 15,000 | 20,000 |
| 6 | 194H | Commission or brokerage | 15,000 | 20,000 |
| 7 | 194I | Rent | 2,40,000 during the FY | 50,000 per month or part of a month |
| 8 | 194J | Fee for professional or technical services | 30,000 | 50,000 |
| 9 | 194K | Income in respect of units payable to resident person | 5,000 | 10,000 |
| 10 | 194LA | Income by way of enhanced compensation | 2,50,000 | 5,00,000 |
TCS related changes w.e.f 1st April, 2025
| Sl. No. | Section | Proposed Changes |
| 1 | 206C(1G) | Threshold on remittance outside India under LRS scheme proposed to be increased from 7 lakh to 10 lakh |
| 2 | 206C(1G) | TCS on remittance outside India under LRS Scheme for specified education loan proposed to be removed |
| 3 | 206C(1H) | TCS on sale of goods proposed to be removed |
| 4 | 206AB and 206CCA | Higher rate on account of non- filers of income tax return proposed to be abolished |
| 5 | 276BB | No prosecution proceedings to be initiated if TCS paid before return filing in line with |
Extension of time limit to file updated return from24 months to 48months
| Sl. No. | If the Updated return is filed | Additional income tax payable |
| 1 | After expiry of the time available for revised return and belated return and before completion of 12 months from the end of the relevant AY | 25% of aggregate of tax and interest payable |
| 2 | After the expiry of 12 months from the end of the relevant AY but before 24 months from the end of the relevant AY | 50% of aggregate of tax and interest payable |
| 3 | After the expiry of 24 months from the end of the relevant AY but before 36 months from the end of the relevant AY | 60% of aggregate of tax and interest payable |
| 4 | After the expiry of 36 months from the end of the relevant AY but before 48 months from the end of the relevant AY | 70% of aggregate of tax and interest payable |
Personal Tax
New tax slab rates (changes made only in new tax regime u/s115BAC)
| Sl. No. | Slabs | Rates |
| 1 | Up to INR 4 lakh | Nil |
| 2 | Above INR 4 lakh to INR 8 lakh | 5% |
| 3 | Above INR 8 lakh to INR 12 lakh | 10% |
| 4 | Above INR 12 lakh to INR 16 lakh | 15% |
| 5 | Above INR 16 lakh to INR 20 lakh | 20% |
| 6 | Above INR 20 lakh to INR 24 lakh | 25% |
| 7 | Above INR 24 lakh | 30% |
Detailed Explanation of Changes in Indirect Tax
Goods and Services Tax
1. Provision allowing Input Service Distributors to distribute input tax credit for inter-state supplies subject to reverse charge, effective from April 1, 2025
2. Time of supply in respect of transaction in vouchers removed, considering it is neither supply of goods nor supply of services.
3. Output tax liability of the supplier to be adjusted against the credit note issued only if the recipient has reversed input tax related to such credit note, if claimed earlier.
4. “Plant & machinery” to substitute the term “plant or machinery” in Section 17(5)(d) of the Central Goods and Services tax, 2017 (“CGSTAct,2017”), retrospectively wef 1 July 2017.
5. Section 148A of the (“CGST Act, 2017) being inserted to establish frame work for Track and Trace Mechanism for specified commodities which mandates unique identification markings for certain goods, with provisions for electronic storage and reporting by specified entities.
6. Supply of goods warehoused in a Special Economic Zone or a Free Trade Warehousing Zone to any person before clearance for exports or to Domestic Tariff Area, neither be treated as a supply of goods nor supply of services. No refund if tax has already been paid on such transactions.
7. Section 38 and Section 39 of the CGST Act, 2017 amended to provide new conditions and restrictions for filing returns
8. Failure to comply with Track and Trace mechanism to attract penalty of INR 1 lac or 10% of tax payable, whichever is higher
9. 10% mandatory pre deposit of penalty amount required for filing appeals before Appellate Authority as well as Appellate Tribunal in cases involving only demand of penalty without any demand for tax, as against 25% earlier.
Customs
1. Time period of 2 years for finalization of provisional assessment with an extension of 1 year by the Commissioner of Customs introduced vide Section 18 of the CustomsAct,1962
2. New Section 18A introduced for voluntary revision of entry post clearance so that the importers and exporters may revise any entry that is made in relation to the goods with in a prescribed time and according to certain conditions as may be prescribed. It also provides for treating such entry as self assessment and allowing payment of duty or treating the revised entry as a refund claim
3. Import of goods at concessional rates, 2022 amended to increase time limit for end use from 6 months to 1 year and filing of quarterly statement instead of monthly statements.
4. Social Welfare Surcharge (SWS) exemption granted on specified items.





