Private Trust
A ‘trust’ is an obligation:
- annexed to the ownership of property, and
- arising out of a confidence reposed in and accepted by the owner, or declared and accepted by him,
- for the benefit of another, or of another and the owner
- There are public & private trusts.
Private Trust
Private trust is a trust created for the benefit of individuals other than a public or charitable purpose. It is created for the financial benefit of one or more designated beneficiaries rather than for the public benefit. It is usually governed by Indian Trusts Act, 1882.
The four distinct elements in a Private Trust are
- An intention of the settlor to create the trust
- a subject matter
- a trustee
- a beneficiary
Purpose of Private Trust
- Use of assets vs. transfer of assets
- Succession planning
- Ownership succession
- Protection of special purposes
- Wealth management
- Taxation
Benefits of a Family/Private Trust
Trust is designed to protect assets and benefit members of a group/family beyond lifetime. When assets of a group/family are in a trust, group/family members no longer have legal ownership of them – the assets are owned by the trustees, for the benefit of group or family members.
People usually set up a trust to get some benefit from no longer personally owning an asset. A trust may be useful to:
- Protect selected assets against claims and creditors – for example, to protect a family home from the potential failure of a business venture.
- Set aside money for special reasons, such as a child or grandchild’s
- Ensure children, not their partners, keep their inheritances.
- Manage the risk of unwanted claims on estate when one dies – such as from a former partner.
Reasons for Private Trust
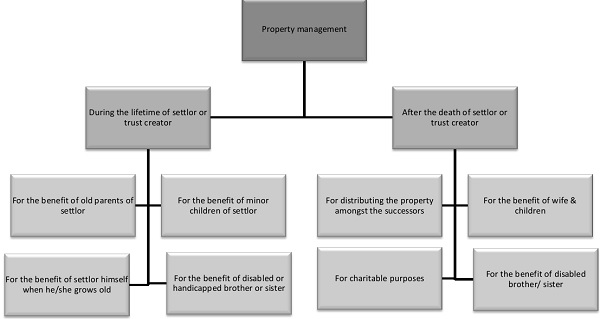
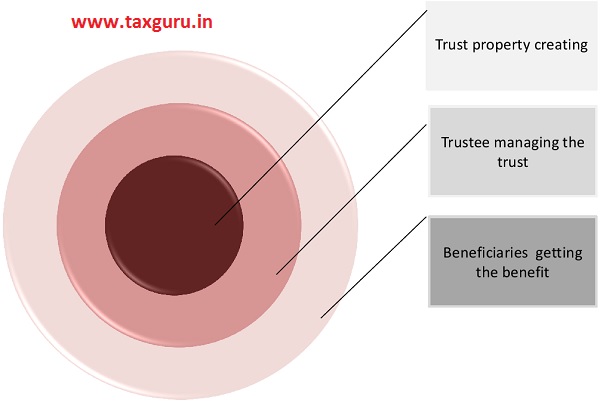
Working of Private Trust?
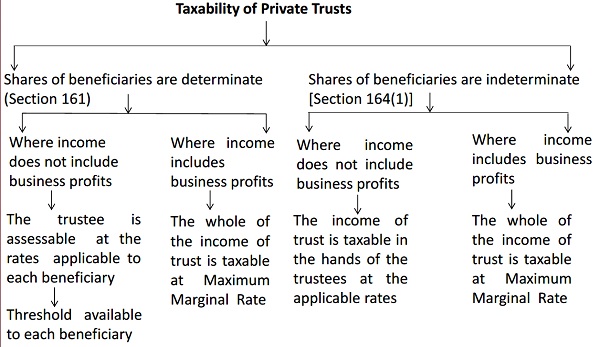
Kinds of Private Trust : Tax wise
As the income of a private trust is available only to the beneficiaries, taxation is carried out according to the structure in which the income has been received.
From tax point of view, there are two structures under which the income of a private trust is taxed:
Specific trust: The income is received by the representative assesses on behalf of a single beneficiary. As the individual share of the beneficiary is known, taxation is done accordingly.
Discretionary trust: With more than one beneficiaries, the individual shares are not known. Here the income of the trust is not received by a representative but determined by the trustees.
Taxability
Other Relevent Sections of Income Tax





My wife and I are U.S. citizens (Ages 80 and 83 respectively). Wants to pass wealth to grandchildren & their heirs in India for their welfare. Should we form an
investment company held in a TRUST or just a TRUST / FOUNDATION that invests the grantors’ wealth (USD in a million plus) in Indian growth stocks
and distributes a certain % of profit/dividend earned to these beneficiaries equally? Also, consider offering the best tax benefits to the beneficiaries and the structure. quote Fees for complete project?
the structure and beneficiaries perpetually.
equities equities (