A process is a collection of activities which creates an output of value to the customer and often goes beyond departmental or functional boundaries. A business process comprises a combination of number of independent or interdependent processes as:
- Developing new product
- Customer order processing
- Bill payment system
Core business process
- Creates value by the capabilities it provides to the competitiveness.
- Core business processes are critical in a company‘s evaluation by its customers.
- They are vital for success in the industry sector within which the company is positioned.
- They are crucial for generating competitive advantages for a firm in the marketplace.
Examples:
In the electronics and semi-conductor industries, new product development is a core process.
In the Banking space, the work of development of loan product is a core process, while services like documentation, formalities, and follow ups are noncore activities.
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is an approach to unusual improvement in operating effectiveness through the radical redesigning of critical business processes and supporting business systems. It is revolutionary redesign of key business processes that involves examination of the basic process itself. It looks at the minute details of the process, such as why the work is done, who does it, where is it done and when it is done. BPR refers to the analysis and redesign of workflows and processes both within the organization and between the organization and the external entities like suppliers, distributors, and service providers. The orientation of redesigning efforts is basically radical. In other words, it is a total re-construction and re-thinking of business process in its entirety, unconstrained by its existing structure and pattern.
Its objective is to obtain quantum jump in process performance in terms of time, cost, output, quality, and responsiveness to customers. BPR is a revolutionary redesigning of key business processes.
Hammer and Champy defines BPR as the “fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in critical, contemporary measures of performance, such as cost, quality, service and speed”. In fact a BPR effort changes practically everything in the organisation: people, jobs, managers and values, because these aspects are linked together.
Hammer and Champy call these aspects the four points of the business system diamond, which is depicted below:

- The operational excellence of a company is a major basis for its competitiveness.
- The business strategy of a company should be oriented towards leveraging its operational excellence into the marketplace.
- A customer-focused organization needs to be realigned in terms of a process orientation.
- For considering totally new ways of redesigning processes, each and every concept, assumption, purpose, and principle, needs to abandon temporarily.
- Continuous improvement is a deficient approach when a company is far behind the industry standards, and needs rapid quantum leaps in performance.
- Dramatic improvement in performance is the prerequisite for overcoming competition.
- How to compete is more important than deciding about where to compete.
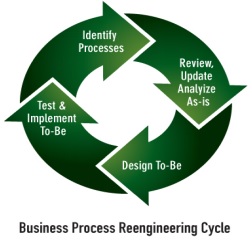
BPR involves the following steps:
1. Determining objectives and framework: Objectives are the desired end results of the redesign process which the management and organization attempts to achieve. This will provide the required focus, direction, and motivation for the redesign process. It helps in building a comprehensive foundation for the re-engineering process.
2. Identify customers and determine their needs: The designers have to understand customers – their profile, their steps in acquiring, using and disposing a product. The purpose is to redesign business process that clearly provides added value to the customer.
3. Study the existing process: The existing processes will provide an important base for the redesigners. The purpose is to gain an understanding of the “what”, and “why” of the targeted process. However, some companies go through the reengineering process with clean perspective without laying emphasis on the past processes.
4. Formulate a redesign process plan: The information gained through the earlier steps is translated into an ideal redesign process. Formulation of redesign plan is the real crux of the re-engineering efforts. Customer focussed redesign concepts are identified and formulated. In this step alternative processes are considered and the best one is selected.
5. Implement the redesign: It is easier to formulate new process than to implement them. Implementation of the redesigned process and application of other knowledge gained from the previous steps is key to achieve dramatic improvements. It is the joint responsibility of the designers and management to operationalise the new process.
It refers to the analysis and redesign of workflows and processes both within and between the organizations:
1. Reengineering begins with a fundamental rethinking.
2. Reengineering does not begin with anything given.
3. Reengineering involves radical redesigning of process.
4. It aims at achieving dramatic improvement in performance.
5. Its main focus is on the process
The Role of IT in BPR:
According to Hammer and Champy, IT plays a crucial role in BPR, especially when it is used to challenge the assumptions inherent in the work processes that have existed since long before the advent of modern computer and communication technology. Inductive thinking is needed in order to recognise the power inherent in modern IT and to visualize its application. This means that instead of first defining a problem and then seeking and evaluating different solutions to it, it is more efficient to first recognise a powerful solution and then seek the problems it might solve. Since, reengineering is about innovation and not automation, one of its most difficult parts is recognizing the “new” capabilities of technologies.
A reengineered business process, characterized by IT-assisted speed, accuracy, adaptability and integration of data and service points, is focused on meeting the customer needs and expectation quickly and adequately, thereby enhancing his/her satisfaction level (by way of improved products and services). With the help of tools of information technology organizations can modify their processes to make them automatic, simpler, time saving. Thus IT can bring efficiency (by way of increased productivity) and effectiveness (by way of better management) in the functioning of business. Thus main benefits are:
- Compression of time
- Overcoming restrictions of geography and/or distance
- Restructuring of relationships.
Central Thrust of BPR:
THE REDUCTION OF THE TOTAL CYCLE TIME OF A BUSINESS PROCESS “by
- Eliminating the unwanted and redundant steps
- By simplifying the systems and procedures
- By eliminating the transit and waiting times
- Maintaining a continuous effort for more and more
Problems in BPR
- Only few cost/ processes have the courage of having BPR
- It disturbs established hierarchies and functional structures and
- Creates serious repercussions and involves resistance among the work-force.
- As it takes time and expenditure, many companies are reluctant to go for BPR
- Possibility of losses in the transition period.
- Target setting is tricky and difficult.
- It may turn-out as a failure if targets are not properly set or the whole transformation is not carried out properly.





