The introduction of Goods and Services Tax Act in July, 2017 brought a dynamic change in the structure of the Indian Economy. The transportation industry plays a pivotal role in the development of a nation’s economy. In fact, the progress of a nation and the progress of its transportation industry are complementary.
Good transport infrastructure is part of the enabling environment for rapid, efficient, and sustainable economic growth. India has an extensive and diversified transport system, comprising 3.31 million kilometres (km) of roads. Goods Transport Agency (GTA) Services are acquired by business houses as well as households. Having understood the importance of transport sector, it is equally important to understand the Indirect tax laws governing such sector i.e. Goods Transport Sector.
This article would enlighten you with following aspects: –
1. Analysis of term ‘Goods Transportation Agency’ (GTA)
2. Charge of GST in case of Goods Transportation Agency Services
3. Exemptions for GTA under GST
4. Place of Supply (S. 12 & 13 of IGST Act, 2017) [Special Discussion on Proviso for S. 12(8) of IGST Act]
5. Brief Discussion on Transportation of Goods through various modes of Transport (Summary Chart) [Special Discussion on Ocean Freight]
6. E-way Bills for Goods Transporters
7. Documentation, Accounts & Records
8. Time of Supply
Let us explore aforementioned points in its entirety.
1. Analysis of term “Goods Transportation Agency” (GTA)
The meaning of the term GTA is defined in the GST law vide Notification No. 12/2017- Central Tax (Rate) dated 28-06-2017 in Para 2, clause (ze) as “Goods transportation agency means any person who provides service in relation to transportation of goods by road and issues consignment note, by whatever name called”. Thus, GTA is any person who:
> Provides service in relation to transport of goods by road and
> Issues a consignment note by whatever name called.
Consignment Note: – ‘Consignment note’ is not defined in GST Law but reference for the same can be derived from explanation to Rule 4B of Service Tax Rules, 1994. Consignment note means a document, issued by a goods transport agency against the receipt of goods for the purpose of transport of goods by road in a goods carriage, which is serially numbered, and contains: –
> Name of the consignor and consignee,
> Registration number of the goods carriage in which the goods are transported,
> Details of the goods transported,
> Details of the place of origin and destination,
> Person liable for paying tax whether consignor, consignee or the goods transport agency (Analyzed in Para 2 of Article)
It is pertinent to note that issuance of a consignment note is the essential for a supplier of service to be considered as a Goods Transport Agency. If such a consignment note is not issued by the transporter, the he will not come within the ambit of GTA. If a consignment note is issued, it indicates that the lien on the goods has been transferred (to the transporter) and the transporter becomes responsible for the goods till its safe delivery to the consignee. It is only the services of such GTA, who assumes agency functions, that is being brought into the GST net.
Arranging Lorries & Issuing Lorry Receipts, Tantamount to GTA Service (AAR): – The Supplier is engaged in supplying goods along with arranging lorries from lorry owners to provide transport facilities to its customers. Applicant pays the requisite amount to the lorry owners, keeping some commission with him, for having arranged facility to the customers.
AAR observed that supplier (applicant) is issuing lorry receipts (LR) under his own name, containing details of GST registration, truck no., Date of issue of LR, consignee name with address, weight, freight charges etc. Therefore, it is clear that the applicant is issuing a consignment note and is providing a transport service. Thereby supplier would be construed as GTA.
Goods Transport Agency Vs. Goods Transport Operator: – The speech of the Union Finance Minister when the GTA was bought into tax net (in Service Tax Regime), specifically clarified vide Para 149 that the intent was to levy tax on Transport agent and not to tax the truck operators/owners. The issue was settled in the case C.C.E. & C., Guntur v. Kanaka Durga Agro Oil Products Pvt. Ltd. 2009 (15) S.T.R. 399 (Tri. – Bang.) where it was held that Service tax paid for services of individual truck operators is not liable on the basis of clarification given by Finance Minister and interpretation of the definition “agent”. However, this judgment did not discuss the concept of “any person” in the definition of “Goods Transport Agency” being provided specifically.
However, there was a contrary decision rendered in case of C.C.E., Salem v. Suibramania Siva Co-Op. Sugar Mills Ltd. (2014) 35 S.T.R. 500 (Mad.) where Madras High Court held that “any person” would cover all kinds of persons which also covers individual truck owners and also held that speech of Finance Minister cannot be taken in aid for understanding the scope of the clear terms of the provisions in the taxation laws.
Thus, the issue whether truck owners or operators (in case they issue a consignment note) would attract levy of GST for transportation of goods by road, is open to question.
Individual Truck / Tempo Operators out of purview of GTA: – As a corollary, the services provided by such individual transporters who do not issue a consignment note will be covered by the entry at Sr. No. 18 of Notification No. 12/2017 – Central Tax (Rate), which is exempt from GST.
Significance of Term “in relation to”: – The use of the phrase ‘in relation to’ has extended the scope of the definition of GTA. It includes not only the actual transportation of goods, but any intermediate/ancillary service provided in relation to such transportation, like loading/unloading, packing/unpacking, trans-shipment, temporary warehousing, etc. If these services are not provided as independent activities but are the means for successful provision of GTA Service, then they are also covered under GTA.
The various intermediary and ancillary services provided by GTA are not provided as independent services but as ancillary to the principal service, namely, transportation of goods by road. The invoice issued by the GTA for providing the said service includes the value of intermediary and ancillary services. In view of this, if any intermediary and ancillary service is provided in relation to transportation of goods by road, and charges, if any, for such services are included in the invoice issued, such service would form part of the GTA service, and thus will be composite supply, and not a mixed supply even though a single price is charged for the supply. However, if such incidental services are provided as separate services and are billed separately, whether in the same invoice or separate invoices, they will be treated as separate supply and not composite supply and there being no single price, the supply will also not be treated as mixed supply – (In terms of Q. 6 of the CBIC FAQs on Transport & Logistics). Ancillary services would be taxed @ 18% if separately billed.
Hiring vehicles on periodic basis for Transport of Goods per Kilometres basis is not a GTA Service as was decided in Judicial Pronouncement of Dinshaws Dairy Foods vs. CCE [2018] taxmann.com 139 (CESTAT). Since charges were not based upon destination but on basis of kilometres travelled, it is not GTA service.
2. Charge of GST in case of Goods Transportation Agency Services: –
“Charge of GST” means nature of tax payable in respect of services provided & person liable to pay tax to government. Briefly there are 2 options available with GTA for providing services. The below summary chart would elucidate “Person liable to pay tax (to government)” in respect of GTA services.
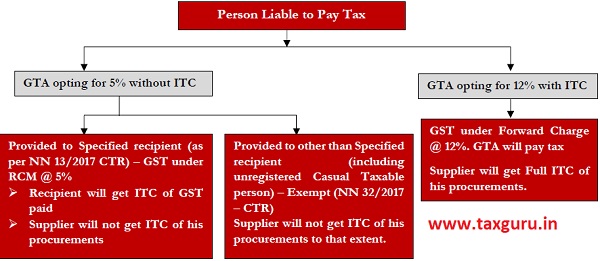
Accordingly, there are two options available with supplier, which are detailed in below paras.
2. 1 Option 1: – GTA Opting for GST @ 5% – No ITC (Recipient will pay tax)
If GTA avails this option, then as per Section 9(3) read with Notification 13/2017 – Central Tax Rate (CTR) & Notification 11/2017 – CTR, specified recipient will be liable to pay GST. Let us understand harmonious construction of above legal provisions.
As per section 9(3) of CGST Act, “The Government…..specify categories of supply of goods or services or both, the tax on which shall be paid on reverse charge basis by the recipient of such goods or services or both and all the provisions of this Act shall apply to such recipient as if he is the person liable for paying the tax in relation to the supply of such goods or services or both. (Emphasis Supplied)
Further, let us analyse who is the recipient for the purpose of GTA Service. As per Explanation to Notification 13/2017 – CTR dated 28th June, 2017, the person who pays or is liable to pay freight for the transportation of goods by road in goods carriage, located in the taxable territory shall be treated as the person who receives the service for the purpose of this notification.
Thus, following analysis can be done;
1) Supplier (of goods) is liable to arrange transportation and he is liable to pay to GTA: In such case, supplier of goods would be deemed to be recipient of GTA service and would be liable to pay tax if he is specified recipient (discussed below). Further, as per section 15(2)(c), incidental expense incurred by supplier and charged to recipient (of goods); it would be includible in value of supply.
Thus, freight amount in tax invoice shall be chargeable to rate of GST on goods and not 5% / 12%, as supplier is not GTA in this case.
2) Supplier (of goods) is liable to arrange transportation and recipient (of goods) is liable to pay to GTA: In such case, recipient of goods itself is deemed to be recipient of GTA service and would be liable to pay tax if he is specified recipient (discussed below).
The liability to pay tax of recipient is mentioned in Section 9(3) r/w as per Notification 13/2017 – CTR dated 28th June, 2017. Following is the extract of said entry in respect of GTA Service.
| Sr. No. | Category of Supply of Service | Supplier of Service | Specified Recipient |
| 1. | Supply of service by GTA in respect of transportation of goods by road- | Goods Transport Agency (GTA) | a) Any factory registered under or governed by the Factories Act 1948 (63of 1948); or
b) Any society registered under the societies Registration Act, 1860 (21 of 1860) or under any other law for the time being in force in any part of India; or c) Any co-operative society established by or under any law; or d) Any person registered under the Central Goods and Service Tax Act or the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act or the State Goods and Services Tax Act or the Union Territory Goods and Services Act; or e) Any body corporate established, by or under any law; or f) Any partnership firm whether registered or not under any law including association of persons; or g) Any casual taxable person; located in the taxable territory |
Thus, we have now arrived at a juncture where we understood that specified recipient will pay GST under reverse charge mechanism. Now let us invite our attention to rate of tax at which GST is to be paid by recipient. The rate of tax is mentioned in Notification 11/2017 – CTR dated 28th June, 2017. Following is the extract for ready reference.
| Sr. No. | Heading | Service | Rate % | Conditions |
| 9. | 9965 | [(iii) Services of goods transport agency (GTA) in relation to transportation of goods (including used household goods for personal use).
Explanation: – goods transport agency means any person who provides service in relation to transport of goods by road and issues consignment note, by whatever name called. |
2.5 | Provided that credit of input tax charged on goods and services used in supplying the service has not been taken.
[Please refer to Explanation no. (iv)] |
Explanation:
(iv) Wherever a rate has been prescribed in this notification subject to the condition that credit of input tax charged on goods or services used in supplying the service has not been taken, it shall mean that, –
(a) credit of input tax charged on goods or services used exclusively in supplying such service has not been taken; and
(b) credit of input tax charged on goods or services used partly for supplying such service and partly for effecting other supplies eligible for input tax credits, is reversed as if supply of such service is an exempt supply and attracts provisions of subsection (2) of section 17 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 and the rules made thereunder.
Further, as per section 17(2) of CGST Act, where the goods or services or both are used by the registered person partly for effecting taxable supplies (including zero-rated supplies) and partly for effecting exempt supplies the amount of ITC as is attributable to the said taxable supplies including zero-rated supplies shall only be available.
Moreover, as per section 17(3) of CGST Act, exempt supplies for purpose of Section 17(2) of CGST Act shall include outward supplies on which the recipient is liable to pay tax on reverse charge basis would be treated as exempt in the hands of the supplier.
On harmonious construction of above notifications & sections it can be inferred that if GTA is supplying services to specified recipient and GTA had opted for 5% option – without ITC option, then such specified recipient would be liable to pay GST @ 5% under reverse charge mechanism (RCM). Further, supplier will not get ITC of its procurements. However, recipient would be eligible to avail ITC of tax paid under reverse charge.
GTA opting for 5% without ITC, supplying to unregistered person – Exempt Supply: – It would be worth to note that if GTA has opted for 5% – without ITC option and is supplying to unregistered person including an unregistered casual taxable person other than the above seven recipients as per Notification No. 13/2017- CTR then as per Sr. No. 21A inserted by Notification No. 32/2017- CT dated 15th September, 2017 it shall be an exempt supply.
Other aspects for reverse charge mechanism on GTA Service: –
RCM not applicable to Tax Deductors: – This entry will not be applicable to recipient who has taken registration in GST for deducting Tax u/s 51 of CGST Act and not for making any taxable supplies. (NN 29/2018 – CT). Further, GTA providing supplies to recipient who has taken registration in GST for deducting Tax u/s 51 of CGST Act and not for making any taxable supplies are exempt (NN 28/2018 –CT).
RCM Taxpayer to obtain mandatory registration: – As per section 24 of CGST Act, 2017; all taxpayers required to pay tax under reverse charge have to mandatorily obtain registration and the threshold exemption is not applicable on them. Accordingly, by virtue of Section 23 of CGST Act, suppliers whose services are exclusively taxable under reverse charge are exempted from obtaining registration.
Payment of GST under RCM to be in cash: – Payment of taxes under Reverse Charge cannot be made with utilisation of Input Tax Credit and has to be made in Cash. Recipient paying tax under RCM would be eligible to avail ITC. (However, supplier would not be entitled to any ITC on its purchases if he avails option of GST @ 5%.)
Composition Taxable person liable to pay GST @ 5% under RCM (without ITC): – It may be noted that if a composition taxable person has availed services of GTA who had opted 5% – without ITC option, then composition person would be liable to pay GST @ 5% (not composition rates). Further, as composition person is ineligible to claim any ITC, he would not be eligible to claim ITC of GST paid under RCM.
2. 2 Option 2: – GTA Opting for GST @ 12% – Full ITC (Supplier will pay tax)
At the inception of GST, there was no option available with GTA to discharge Tax under forward charge, it was only reverse charge which was functioning. Thus, whole of Input Tax Credit was blocked credit for GTA. The option was need of an hour at that time as GTA who purchased Trucks and other vehicles for transporting goods were suffering from blockage of ITC, thereby inflating cost of transportation.
In view of need for trade and industry, CBIC vide Notification No. 20/2017 – Central Tax (Rate) dated 22nd August, 2017 gave an option to GTA to discharge CGST @ 6%, SGST @ 6% or IGST @ 12% (as the case may be) and take full ITC.
Analysis of ITC: – It is pertinent to note section 17(5)(a) of CGST Act as amended by CGST Amendment Act, 2017 in this regard, which reads as (Relevant Extract)
Input tax credit shall not be available in respect of the following: –
(a) motor vehicles for transportation of persons having approved seating capacity of not more than thirteen persons (including the driver), except when they are used for making the following taxable supplies, namely: –
(A) further supply of such motor vehicles; or
(B) transportation of passengers; or
(C) imparting training on driving such motor vehicles;
(Emphasis Supplied)
Thus, GTA would be eligible to avail ITC in respect of motor vehicles for transportation of goods as restriction is imposed only on motor vehicle for transportation of persons. Thus, credit shall be available on motor vehicles used for transportation of goods irrespective of its sitting capacity.
3. Exemptions for GTA under GST
Exemption on supply of various types of goods / consideration not exceeding specified limit: –
Various exemptions to GTA have been continued from Service Tax regime. CBIC vide Sr. No. 21 of Notification No. 12/2017 – CTR dated 28th June, 2017; exempts GST on services provided by GTA on below list of items.
a) Agriculture produce;
b) Goods, where consideration charged for the transportation of goods on a consignment transported in a single carriage does not exceed Rs. 1,500/-;
a) Goods, where consideration charged for the transportation of all such goods for a single consignee does not exceed Rs. 750/-;
b) Milk, salt and food grain including flour, pulses and rice;
c) Organic manure;
d) Newspaper or magazines registered with the registrar of newspapers;
e) Relief materials meant for victims of natural or man-made disasters, calamities, accidents or mishap; or
f) Defence or military equipment.
Services of Giving vehicle on hire to GTA – Exempt: – Services by way of giving on hire to GTA a means of transportation of goods is exempt vide Sl. No. 22(b) of Notification No. 12/2017 – CTR and Notification No. 9/2017 – Integrated Tax Rate (ITR) both dated 28th June, 2017.
Exemption on Modes of Transport is covered in Para 5 of this article
4. Place of Supply [S. 12 & 13 of IGST Act, 2017]
GST is understood as a ‘destination-based consumption tax’ but there is no provision that declares this fact. It is here in Place of Supply that we find that the destination principle of GST is fully captured (except 3 services as enumerated in section 13(8) of IGST Act). The law maker has declared, in each case of supply, its destination of supply.
It is also crucial to determine the place of supply of goods or services under GST Law to recognize the nature of tax to be paid. Place of Supply is determined as per sections of the IGST Act, 2017. Section 12 of IGST Act, 2017 is applicable only when location of the supplier of service AND recipient of service is in India.
Section 13 of IGST Act, 2017 is applicable for services when location of supplier OR location of recipient is outside India.
In the light of above provision place of supply for goods transportation services would be as below: –
| Description of service | Recipient | Place of Supply (POS) |
| Transportation of goods including mail or courier. (within India)
[Section 12(8) of IGST Act] |
Registered | POS is location of such registered Recipient |
| Unregistered | Place where goods are handed over for their transportation | |
| Transportation of goods where place of destination is outside India.
[Proviso to section 12(8) of GST inserted vide IGST Amendment Act, 2018 w.e.f. 1st February, 2019] |
Any person | Place of destination of goods
(Please refer analysis below) |
| Transportation of goods (where either recipient or supplier is outside India)
[Section 13(9) of IGST Act] |
Registered/
Unregistered |
Place of destination of goods |
| Transportation through mail or courier
(where either recipient or supplier is outside India) [Section 13(2) of IGST Act] |
Any person | Location of recipient
(Location of recipient is available) |
| Location of supplier
(Location of recipient is not available) |
Analysis of Proviso Inserted through IGST Amendment Act, 2018
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (Amendment) Act, 2018 was made effective from 1st February, 2019 by Notification No. 01/2019 – IT dated 29th January, 2019; among other amendments, a proviso was inserted in Section 12(8) of the IGST Act. The relevant provision is extracted as under:
“Provided that where the transportation of goods is to a place outside India, the place of supply shall be the place of destination of such goods.”
Prior to insertion of the proviso, the place of supply for transportation services was dependent on the location of the service recipient (& Location of supplier in few cases). If the service recipient was in the same state as that of service provider, then the supply was treated as intra-state supply otherwise inter-state supply.
Due to insertion of the proviso, the place of supply for goods which are to be exported shall always be outside India and thus supply shall always be inter-state supply, irrespective of the location of recipient. It is very crucial to note here that if a supplier (shipping agency such as FedEx) provides such services of exporting goods it would not be treated as export of service due to non-fulfilment of all conditions (especially recipient & foreign currency) as enshrined in Section 2(6) of IGST Act, 2017 (Export of Service).
The government did not pay attention on a fact that location of recipient and location of supplier still continues to remain in India & would such sector would not be benefited due to insertion of such proviso.
Therefore, such supply of service does not fulfil the criteria of export of service and accordingly, the intention of government does not get fulfilled.
5. Brief Discussion on Transportation of Goods through various modes of Transport
Taxability of Goods transportation through various modes is summarised with the help of below chart.

Importation of Goods & Ocean Freight
Import pricing is of two types, viz., FOB (Free on board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight). For the purpose of export, FOB Value is treated as Transaction Value. Under FOB pricing, the foreign suppliers bear all the cost upto loading the goods into the vessel and the importer has to bear the cost of freight.
In case of CIF (Cost, Insurance & Freight Value) expense is paid by a seller to cover the costs, insurance, and freight of a buyer’s order while it is in transit.
The importer may engage either an Indian based shipping line or a foreign based shipping line and the importer would be availing the services of such shipping line for ocean transport of the import goods.
Analytical Flow Chart of “Ocean Freight paid for Import of Goods”

A. Issue under Ocean Freight
Trade & Industry is of the view that IGST is already levied on (Total) CIF value, further notification 8/2017 IT(R) & Notification 10/2017 – IT(R) casts responsibility to pay GST on freight amount again which leads to double taxation.
B. Departments’ view on Ocean Freight
Department is of the view that there are two separate taxable events. The levy under the notification draws power from the charging section of the GST Act. In the present case, the levy on the transportation services received by the importer under the impugned notification draws power under Section 5 of the IGST Act, 2017, and that the levy on the import of goods is a separate taxable event, the levy of which is under Section 3(7) of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975.
Further, there is no violation of Article 14 or Article 19(1)(g) of the Constitution of India inasmuch as the importers are free to carry on their trade. This levy is on all importers and does not interfere with the right of the importers to practice any profession, or to carry on any occupation, trade or business.
C. Honourable High Court’s Observation in Judicial Pronouncement Mohit Minerals Private Limited vs. Union of India (SCA No. 726 of 2018), Gujarat High Court
The Hon’ble High Court concluded that no tax is leviable under the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, on the ocean freight for the services provided by a person located in a non-taxable territory by way of transportation of goods by a vessel from a place outside India upto the customs station of clearance in India and the levy and collection of tax of such ocean freight under the impugned Notifications is not permissible.
In the result, this writ-application along with all other connected writ-applications is allowed. The impugned Notification No. 8/2017 – Integrated Tax (Rate) dated 28th June 2017 and the Entry 10 of the Notification No. 10/2017 – Integrated Tax (Rate) dated 28th June 2017 are declared as ultra vires the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, as they lack legislative competency. Both the Notifications are hereby declared to be unconstitutional. Civil Application, if any, stands disposed of.
Thus, that department may file an appeal before the Hon’ble Supreme Court.
6. E-way Bills for Goods Transporters
Every registered person who causes movement of goods of consignment value (i.e. Invoice value including Taxes) exceeding Rs. 50,000/- in relation to a supply; or for reasons other than supply; or due to inward supply from an unregistered person shall generate E-way bill as per rule 138 of CGST Rules, 2017.
E-way bill can be generated by the supplier or recipient or transporter. E-way bill shall be generated in form GST EWB-01 and has two parts. In part A details of the recipient are to be filled and in part B vehicle details are to be filled. Where multiple consignments are intended to be transported in one conveyance, transporter can generate consolidated E-way bill in form GST EWB – 02.
It shall be noted that even an unregistered transporter can also generate E – way Bill by creating Unique Transporter ID & user name for themselves on the EWB portal.
7. Documentation, Accounts & Records
a) Tax Invoice
In addition to Tax Invoice issued under Rule 46 of CGST Rules, 2017 GTA in pursuance to Rule 54(3) of CGST Rules is required to furnish in Tax Invoice such additional information containing the gross weight of the consignment, name of the consigner and the consignee, registration number of goods carriage in which the goods are transported, details of goods transported, details of place of origin and destination, Goods and Services Tax Identification Number of the person liable for paying tax whether as consigner, consignee or goods transport agency.
Further, as per Rule 46(p), GTA has to indicate on his tax invoice whether the tax is payable on reverse charge basis.
b) Self-invoice
As per section 31(3)(f) of CGST Act a registered person who is liable to pay tax under section 9(3) / 9(4) of CGST Act shall issue an invoice in respect of goods or services or both received by him from the supplier who is /not registered on the date of receipt of goods or services or both.
Thus, recipient paying tax under RCM has to generate self-invoice for receipt of services from GTA.
c) Payment Voucher
As per section 31(3)(g) of CGST Act, 2017 a registered person who is liable to pay tax under section 9(3)/9(4) of CGST Act shall issue a payment voucher at the time of making payment to the supplier.
Thus, recipient paying tax under RCM has to generate payment voucher while making payment to GTA.
d) Accounts & Records
Rule 58(4) of CGST Rules, 2017 prescribes that any person (including unregistered transporter) engaged in the business of transporting goods shall maintain records of goods transported, delivered and goods stored in transit by him along with the GSTIN of the registered consignor and consignee for each of his branches subject to the provisions of Rule 56 of CGST Rules, 2017.
Further, as per section 122 of CGST Act, 2017 where a taxable person who transports any taxable goods without the cover of documents as specified shall be liable to penalty of Rs. 10,000 or an amount equal to tax evaded, whichever is higher.
8. Time of supply for GTA Services
a) Time of supply for GTA opting for FCM @ 12% [S. 13(2) of CGST Act, 2017 r/w Rule 47]
| Particulars | Time of Supply |
| Invoice issued within 30 days of provision of service | Earlier of following:
Date of issue to Tax Invoice or, Receipt of payment; |
| Invoice not issued within 30 days of provision of service | Earlier of following:
Date of supply of service or, Receipt of payment |
b) Time of supply for recipient paying GST @ 5% under RCM [Section 13(3) of CGST Act, 2017]
1. Date of payment as entered in the books of account of the recipient or the date on which payment is debited in his bank account – whichever is earlier.
2. The Date immediately following 60 days from the date of invoice or any other document issued by the supplier.
3. Where it is not possible to determine the time of supply from the above, the time of supply will be the date of entry in the books of accounts of the recipient of supply.
Other points for Time of Supply: –
> Where the supplier of taxable services receives an amount up to Rs. 1,000/- in excess of the amount indicated in the tax invoice, the time of supply to the extent of such excess amount shall, at the option of the said supplier, be the date of issue of invoice in respect of such excess amount.
> Where it is not possible to determine the time of supply of goods or services under RCM, the time of supply shall be the date of entry in the books of account of the recipient of supply.
Concluding remarks:
Thus, government has given 2 options to GTA, GTA has to properly undertake cost benefit analysis of both the options and choose accordingly. GTA purchasing heavy vehicles for transportation may go for 12% with Full ITC option, however, if ITC is minimal then GTA may go for 5% – without ITC option.






Ok