Before knowing about the Union Budget Presented by our Finance Minister for the Year 2023-23, let’s know more about Union Budget first.
The Union Budget of India also referred to as the Annual Financial Statement in Article 112 of the Constitution of India, is the annual budget of the Republic of India. The Government presents it on the first day of February so that it could be materialised before the beginning of the new financial year in April. Until 2016 it was presented on the last working day of February by the Finance Minister in Parliament. The budget division of the department of economic affairs (DEA) in the finance ministry is the nodal body responsible for producing the budget. It is presented by means of the Finance bill and the Appropriation bill has to be passed by Lok Sabha before it can come into effect on 1 April, the start of India’s financial year.
An interim budget is not the same as a ‘Vote on Account’. While a ‘Vote on Account’ deals only with the expenditure side of the government’s budget. An interim budget is a complete set of accounts, including both expenditures and receipts. An interim budget gives the complete financial statement, very similar to a full budget. While the law does not disqualify the Union government from introducing tax changes, normally during an election year, successive governments have avoided making any major changes in income tax laws during an interim budget.
The Union Budget contains details about the projected receivables and payables of the government for a particular fiscal year. This budget statement is divided into two major parts-capital budget and revenue budget.
> Capital budget
Capital budget accounts for government-related capital payments and receipts. Capital receipts include loans from the public or from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), while capital payment includes expenses incurred towards health facilities, development and maintenance of equipment, as well as educational facilities.
> Revenue budget
As the name suggests, a revenue budget accounts for all the revenue expenditures and receipts. If the revenue expense is in excess of the receipts, the government suffers a revenue deficit.
UNION BUDGET 2023-24
Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitaraman, on February 1st, 2023, presented the Union Budget 2023.
In a big boost for taxpayers and the economy, Sitharaman announced major changes in tax slabs under the new tax regime and a big hike in allocation for railways and capital expenditure.
Income Tax payers:
Changes in the old tax regime:
- New tax regime to become the default tax regime. However, citizens can opt for the old tax regime.
- No tax on income up to Rs 7.5 lakh a year in the new tax regime (with the inclusion of standard deduction).
- Govt proposes to reduce the highest surcharge rate from 37% to 25% in the new tax regime.
New Income Tax Slabs Under New Tax Regimes:
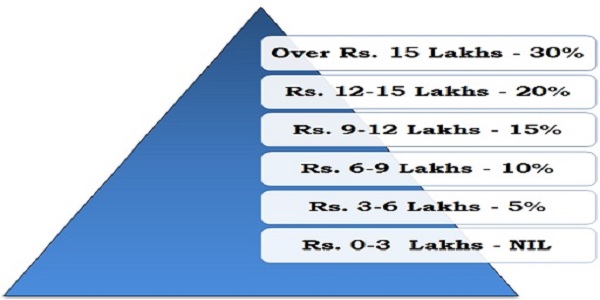
- An individual with an annual income of Rs 9 lakh will have to pay only Rs 45,000 in taxes.
- Income of Rs 15 lakh will fetch Rs 1.5 lakh tax, down from Rs 1.87 lakh.
- A Rs 50,000 standard deduction to taxpayers has been introduced under the new regime.
- Payment received from Agniveer Corpus Fund by Agniveers to be exempted.
- Tax exemption removed in insurance policies with premiums over Rs 5 lakh.
- For online games, govt proposes to provide for TDS and taxability on net winnings at the time of withdrawal or at the end of the fiscal year.
- Tax exemption on leave encashment on the retirement of non-government salaried employees hiked to Rs 25 lakh from Rs 3 lakh.
- A higher limit of Rs 3 crore for TDS on cash withdrawal is to be provided to cooperative societies.
- Next-generation Common IT Return Form to be rolled out for taxpayer convenience.
- Grievance redressal mechanism to be strengthened.
- TDS rate to be reduced from 30 per cent to 20 per cent on the taxable portion of EPF withdrawal in non-PAN cases.
Commodities get Cheaper and Costier:
Cheaper:
- Mobile phones
- TV
- Lab-grown diamonds
- Shrimp feed
- Machinery for lithium-ion batteries
- Raw materials for the EV industry
Costlier:
- Cigarettes
- Silver
- Compounded rubber
- Imitation Jewellery
- Articles made from gold bars
- Imported bicycles and toys
- Imported kitchen electric chimney
- Imitation Jewellery
- Articles made from gold bars
- Imported bicycles and toys
- Imported kitchen electric chimney
- Imported luxury cars and EVs
Indirect Taxes:
- 16% tax hike on certain cigarettes.
- New cooperatives that commence manufacturing till March 2024 to get a lower tax rate of 15%.
- Basic customs duty on crude, glycerine is reduced to 2.5%.
- Import duty on silver bars hiked to align it with gold, and platinum.
- Extend customs duty cut on imports of parts of mobile phones by 1 year.
- To promote TV manufacturing, customs duty on open cells of TV panels is reduced to 2.5%.
- The relief provided on Customs Duty on import of certain parts & inputs like a camera lens.
- Concessional duty on lithium-ion cells for batteries extended for another year.
- The number of basic custom duty rates on goods other than textiles and agriculture is reduced from 21 to 13. As a result, there are minor changes in taxes on some items toys, bicycles, and automobiles.
Saving schemes announcements:
- Maximum deposit limit for Senior Citizen Savings Scheme to be enhanced to Rs 30 lakh from Rs 15 lakh.
- The Monthly Income Scheme limit doubled to Rs 9 lakh and Rs 15 lakh for joint accounts.
- One-time new saving scheme Mahila Samman Saving Certificate for women to be made available for 2 years up to March 2025.
- It will offer a deposit facility of up to Rs 2 lakh in the name of women or girls for the tenure of 2 years fixed interest rate of 7.5 per cent with a partial withdrawal option.
Railways:
- An outlay of Rs 2.4 lakh crore is provided for railways in FY24.
- It’s the highest-ever allocation for Railways and is nearly nine times over FY14 allocations.
- The allocation for track renewal has been increased from Rs 15,388.05 crore in RE 2022-23 to Rs 17,296.84 crore this year.
- The Railways is likely to roll out 75 Vande Bharat trains by August 2023.
- Capex hiked 33%.
- Rs 10 lakh crore capital investment, a steep hike of 33 per cent for the third year in a row, to enhance growth potential and job creation, crowd-in private investments, and provide a cushion against global headwinds.
- Effective capital expenditure of Centre at Rs 13.7 lakh in FY24
- New Infrastructure Finance Secretariat is established to enhance opportunities for private investment in infrastructure.
Defence Budget:
- The Defence Budget is hiked by 13%:
- The defence budget increased to Rs 5.94 lakh crore from last year’s Rs 5.25 lakh crore.
- Rs 1.62 lakh crore is set aside for capital expenditure including purchases of new weapons, aircraft, warships and other military hardware.
- For 2022-23, the budgetary allocation for capital outlay was Rs 1.52 lakh crore.
- The capital budget of the Border Roads Organisation increased to Rs 5,000 crore. Capital outlay for the Indian Air Force was the highest at Rs 57,137.09 crore.
- An amount of Rs 52,804 crore was set aside as the capital outlay for the Indian Navy.
- Capital outlay for the Army has been pegged at Rs 37,241 crore.
- Allocation to Defence Research Development Organisation (DRDO) has been put at Rs 23,264 crore.
Fiscal position:
- Fiscal Deficit targeted to be below 4.5 per cent by 2025-26.
- Fiscal deficit target of 6.4% is retained in the Revised Estimate for FY23; reduced to 5.9% for FY24.
- Gross market borrowing has seen at Rs 15.43 lakh crore in FY24.
- Net market borrowing in FY24 is seen at Rs 11.8 lakh crore.
- FY23 net tax receipts revised estimate stands at Rs 20.9 lakh crore.
- FY23 total expenditure revised estimate stands at Rs 41.9 lakh crore.
- FY23 revised estimate of total receipts other than borrowing at Rs 24.3 lakh crore.
- FY24 net tax receipts are seen at Rs 23.3 lakh crore.
MSME:
- Revamped credit guarantee for MSMEs to take effect from Apr 1, 2023, with the infusion of Rs 9,000 crore in the corpus.
- The scheme would enable additional collateral-free guaranteed credit of Rs 2 lakh crore and also reduce the cost of the credit by about 1 per cent.
Banking:
- Govt moots amendments to Banking Regulation Act to improve governance in banks.
Jobs:
- The government will launch Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0.
- To skill the youth for international opportunities, 30 Skill India International Centres will be set up across different States.
- Direct Benefit Transfer under a pan-India National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme to be rolled out to provide stipend support to 47 lakh youth in three years.
Clean Energy:
- Rs 35,000 crores priority capital for the energy transition.
- The green credit programme will be notified under the Environment Protection Act.
- Battery storage to get viability gap funding.
- Govt to support setting up of battery energy storage of 4,000 MwH.
- National Green Hydrogen mission with an outlay of Rs 19,700 crore will facilitate the transition of the economy to low carbon intensity, reduce dependence on fossil fuel imports and make the country assume technology and market leadership.
Gems and Jewellery:
- To encourage the indigenous production of lab-grown diamonds, a research and development grant is to be provided to one of the IITs for five years.
- Proposal to review customs duty of lab-grown diamonds to be included in Part-B of Budget document.
Aviation & Highways:
- 50 additional airports, helipods, water aero drones, and advanced landing grounds will be revived to improve regional air connectivity.
- Union Budget 2023-24 allocates an enhanced outlay of Rs 2.70 lakh crore for the highways sector.
- Allocation to NHAI increased by 13.90 per cent to Rs 1.62 lakh crore for 2023-24.
Ease of Doing Business:
- Govt to bring another dispute resolution scheme Vivad Se Vishwas-2 to settle commercial disputes.
- PAN as a common identifier for all digital systems of government agencies.
- One-stop solution for reconciliation and updating identity maintained by various agencies to be established using Digi-locker and Aadhaar as foundational identity.
- Central Processing Centre to be set up for faster response to companies filing forms under the Companies Act.
- For business establishments required to have Permanent Account Number, the PAN will be used as a common identifier for all Digital Systems of specified government agencies.
- More than 39,000 compliances have been reduced and over 3,400 legal provisions decriminalised to enhancing t ease of doing business.
- Jan Vishwas Bill to amend 42 Central Acts have been introduced to further trust-based governance.
- Finance Minister announces multiple measures to enhance business activity in GIFT City.
Digital services:
- Scope of services in DigiLocker to be expanded.
- 100 labs for developing applications to use 5G services to be set up in engineering institutions.
- Labs will cover smart classrooms, precision farming, and healthcare applications.
- Phase 3 of E-courts projects to be launched with outlay of Rs 7,000 crore.
- Leading industry players will partner to developing, providing scalable options for health, agriculture and other sector.
Urban Development:
- Govt to spend Rs 10,000 crore per year for urban infra development fund
- Cities to be incentivised to improve creditworthiness for municipal bonds
- All cities and towns will be enabled for 100 per cent transition of sewers and septic tanks.
Health:
- Health sector has been allocated Rs 89,155 crore in the Union Budget.
- Mission to eliminate sickle cell anaemia by 2047.
- A new programme for research in pharmaceuticals will be formulated and the industry will be encouraged to invest in research.
- For the National Tele Mental Health Programme, the budget allocation has been increased from Rs 121 crore to Rs 133.73 crore.
- The budget allocation for autonomous bodies goes up from Rs 10,348.17 crore in 2022-23 to Rs 17,322.55 crore in 2023- 24.
- The allocation for ICMR has been increased from Rs 2,116.73 crore to Rs 2,359.58 crore.
- Out of Rs 89,155 crore, Rs 86,175 crore has been allocated to the Department of Health and Family Welfare, while Rs 2,980 crore to the Department of Health Research.
- budget allocation for the Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana for 2023-2024 is Rs 3,365 crore.
- Among these central sector schemes, the budget allocation for the National Health Mission has been increased from Rs 28,974.29 crore.
- Budget allocation for the AYUSH ministry has been increased from Rs 2,845.75 crore.
- The allocation for the National Digital Health Mission – NHM has been increased from Rs 140 crore to Rs 341.02 crore.
Housing:
- Outlay for PM Awaas Yojana enhanced 66% to over Rs 79,000 crore.
Interest-free loan to states to continue :
- Centre to continue 50-year interest-free loan to state governments for one more year.
Digital Library for Children, Adolescents Will Be Set Up:
- National Digital library will be set up for children and adolescents
- National Book Trust, Children’s Book Trust to replenish non-curricular titles in regional languages, English to digital libraries.
- States to be encouraged to set up physical libraries for them at panchayat and ward levels and provide infrastructure for accessing the National Digital Library resources.
Education:
- Three centres of excellence for artificial intelligence are to be set up in top educational institutions.
- 157 new nursing colleges will be established in colocation with the existing 157 medical colleges established since 2014.
- Eklavaya Model Residential Schools to be set up in the next 3 years. The Centre will recruit 38,800 teachers and support staff for 740 schools serving 3.5 lakh tribal students.
- National Data Governance Policy to be brought out to unleash innovation and research by start-ups and academia.
- Grant for University Grants Commission (UGC) has been increased by Rs 459 crores (9.37 pc).
- Central Universities have increased by 17.66%, Deemed University by 27%, support to IITs has increased by 14%, and NITs, by 10.5% as compared to BE 2022-23.
Agriculture:
- An Agriculture Accelerator Fund will be set up to encourage agri-startups by young entrepreneurs.
- Digital public infrastructure to be developed for the agriculture sector.
- Rs 20 lakh crore agricultural credit targeted at animal husbandry, dairy and fisheries.
- Over the next 3 years, one crore farmers will get assistance to adopt natural farming.
- 10,000 bio-input resource centres will be set up.
- Fisheries: To launch a sub-scheme under PM Mastya Sampada Yojna with an outlay of Rs 6,000 crore to further enable the activities of fishermen.
- To make India a global hub for ‘Shree Anna’, the Indian Institute of Millet Research, Hyderabad will be supported as the Centre of Excellence for sharing best practices, research and technologies at the international level.
- Rs 2,516 crore for the Computerisation of 63,000 credit societies.
- In drought-prone central regions of Karnataka, central assistance of Rs 5,300 crore is to be given to the upper Badra project to provide sustainable micro-irrigation.
- 500 new ‘waste to wealth’ plants under the GOBARdhan (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan) scheme to be established for promoting a circular economy at a total investment of Rs 10,000 crore.
- 5 per cent compressed biogas mandate to be introduced for all organizations marketing natural and biogas.
Tribal Welfare:
- Pradhan Mantri Primitive Vulnerable Tribal Group (PMPVTGS) mission is been launched to improve the socio-economic condition of PMPVTGS.
- Tribals are to get Rs 15,000 crore over the next three years for safe housing, sanitation, drinking water, and electricity.
Space:
- Rs 12,544 crore was allocated to the Department of Space.
- IN-Space receives Rs 95 crore allocation against Rs 21 crore in the Revised Estimate. A large portion of the allocation, Rs 53 crore, has been earmarked for capital expenditure for INSPACe.
- Physical Research Laboratory has received an allocation of Rs 408.69 crore.
Sports:
- Sports gets an allocation of Rs 3,397.32 crore, an increase of Rs 723.97 crore.
- The Rs 3,397.32 crore is the highest sports budget allocation ever in the country.
- ‘Khelo India’ has been allotted Rs 1,045 crore.
- Sports Authority of India gets Rs 785.52 crore for 2023-24.
- National Sports Federations receives a hike of Rs 325 crore.
Seven priorities of the Budget, ‘Saptarishi’:
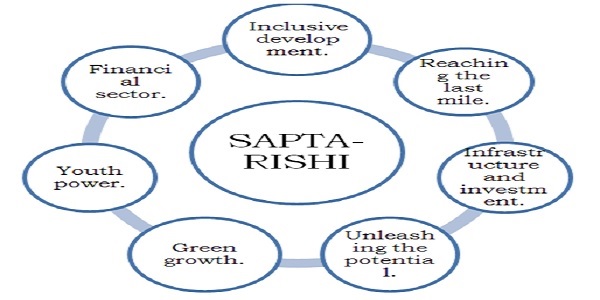
Aims of Budget 2023 to include:
- Facilitating ample opportunities for citizens, especially youth.
- Providing a strong impetus to growth and job creation.
- Strengthening macroeconomic stability.
- To aim for the empowerment of women in Budget 2023.
- To enable women’s self-help groups to reach the next stage of economic empowerment.
- To help self-help groups with raw material supply, branding, and marketing of products.
Tourism:
- Promotion of tourism will be taken up on mission mode with the active participation of states, the convergence of Government programs & public-private partnerships.
- 50 tourist destinations will be selected through challenge mode to be developed as a whole package for domestic and international tourism.
- States will be encouraged to set up a ‘Unity Mall’ in the State capital or the most popular tourist destination in the state for the promotion and sale of ‘One District, One product’ and GI products and other handicrafts.
- The country offers immense attractions for domestic as well as foreign tourists. There is a large potential to be tapped into tourism. The sector holds huge opportunities for jobs and entrepreneurship for youth in particular.
- Tourism infrastructure and amenities are to be facilitated in border villages through the Vibrant Villages Programme.
PM Vishwa Karma Kaushal Samman:
- PM Vishwa Karma Kaushal Samman-package of assistance for traditional artisans and craftspeople has been conceptualised and will enable them to improve the quality, scale & reach of their products, integrating with the MSME value chain.
- Continuing our commitment to food security, we’re implementing from January 1, 2023, a scheme to supply free food grain to all Antyodaya and priority households for one year under PM Garib Kalyan Ann Yojana.
- During the COVID pandemic, we ensured that nobody goes to bed hungry with a scheme to supply free foodgrains to over 80 crore persons for 28 months.
- Our vision for the Amrit Kaal includes a technology-driven and knowledge-based economy, with strong public finances and a robust financial sector. To achieve this ‘janbhagidari’ through ‘sabka saath, sabka prayaas’ is essential, FM said.
- India’s rising global profile is because of several accomplishments – Aadhaar, Cowin, and UPI have contributed to improving India’s global profile. During the pandemic, the government ensured no one went to bed hungry, ” says Finance Minister.
- Finance Minister Says: The government’s efforts since 2014 have ensured for all citizens, a better quality of life and a life of dignity. The per capita income has more than doubled to Rs 1.97 lakh. In these 9 years, the Indian economy has increased in size from being 10th to 5th largest in the world.
- The economy has become a lot more formalised as reflected by the doubling of EPFO membership.
- This is the first Budget in Amritkall, says Finance Minister Niramala Sitharaman.
- Indian economy is on the right track and heading towards a bright future. The Indian economy has increased in size from being 10th to 5th largest in the last nine years.
- The world has recognized India as a bright star, our growth for the current year is estimated at 7%, which is the highest among all major economies, in spite of the massive global slowdown caused by the pandemic and the war.
- In these times of global challenges, India’s G20 presidency gives us a unique opportunity to strengthen India’s role in the world economic order: Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.





