Central Government notifies Foreign Trade Policy, 2023 vide Notification No. 1/2023-DGFT | Dated: 31st March, 2023. This Foreign Trade Policy shall come into force with effect from 1st April, 2023.
Government of India
Ministry of Commerce and Industry
Department of Commerce
Directorate General of Foreign Trade
Notification No. 1/2023-DGFT | Dated: 31st March, 2023
S.O. 1565(E).In exercise of powers conferred by Section 5 of the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992 (No.22 of 1992), as amended from time to time, the Central Government hereby notifies the Foreign Trade Policy, 2023. This Foreign Trade Policy shall come into force with effect from 1st April, 2023.
Effect of this Notification: Foreign Trade Policy, 2023, is hereby notified.
(Santosh Kumar Sarangi)
Director General of Foreign Trade
Ex-officio Addl. Secretary to the Govt. of India
[Issued from File No. 01/75/171/00016/AM-23/FTP Cell]
CHAPTER-1
Legal Framework and Trade Facilitation
A. LEGAL FRAMEWORK
1.00 Legal Basis of Foreign Trade Policy
The Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023 is notified by Central Government, in exercise of powers conferred under Section 5 of the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992 (No. 22 of 1992) [FT (D&R) Act], as amended.
1.01 Duration of FTP
The Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023 incorporating provisions relating to export and import of goods and services, shall come into force with effect from 1st April, 2023 and shall continue to be in operation unless otherwise specified or amended. All exports and imports made up to 31.03.2023 shall, accordingly, be governed by the relevant FTP, unless otherwise specified.
1.02 Amendment to FTP
Central Government, in exercise of powers conferred by Section 3 and Section 5 of FT (D&R) Act, 1992, as amended from time to time, reserves the right to make any amendment to the FTP, by means of notification, in public interest.
1.03 Hand Book of Procedures (HBP) and Appendices & Aayat Niryat Forms (ANF)
Director General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) may, by means of a Public Notice, notify Hand Book of Procedures, including Appendices and Aayat Niryat Forms or amendment thereto, if any, laying down the procedure to be followed by an exporter or importer or by any Licensing/Regional Authority or by any other authority for purposes of implementing provisions of FT (D&R) Act, the Rules and the Orders made there under and provisions of FTP.
1.04 Specific provision to prevail over the general
Where a specific provision is spelt out in the FTP/Hand Book of Procedures (HBP), the same shall prevail over the general provision.
1.05 Transitional Arrangements
(a) Any License/ Authorisation/ Certificate/ Scrip/ instrument bestowing financial or fiscal benefit issued before commencement of FTP 2023 shall continue to be valid for the purpose and duration for which it was issued, unless otherwise stipulated.
(b) Item wise Import/Export Policy is delineated in the ITC (HS) Schedule I and Schedule II respectively. The importability/ exportability of a particular item is governed by the policy as on the date of import/ export. The date of import/ export is defined in para 2.17 of HBP 2023. Bill of Lading and Shipping Bill are the key documents for deciding the date of import and export respectively. In case of change of policy from ‘free’ to ‘restricted/prohibited/state trading’ or ‘otherwise regulated’, the import/export already made before the date of such regulation/restriction will not be affected. However, the import through High Sea sales will not be covered under this facility. Further, the import/export on or after the date of such regulation/restriction will be allowed for importer/ exporter who has a commitment through Irrevocable Commercial Letter of Credit (ICLC) before the date of imposition of such restriction/ regulation and shall be limited to the balance quantity, value and period available in the ICLC. For operational listing of such ICLC, the applicant shall have to register the ICLC with jurisdictional RA against computerized receipt within 15 days of imposition of any such restriction/ regulation. Whenever, Government brings out a policy change of a particular item, the change will be applicable prospectively (from the date of Notification) unless otherwise provided for.
B. TRADE FACILITATION AND EASE OF DOING BUSINESS
1.06 National Committee on Trade Facilitation (NCTF)
India has ratified the World Trade Organization’s Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) in April 2016. To facilitate coordination and implementation of the TFA provisions, an inter-ministerial body i.e. National Committee on Trade Facilitation (NCTF) has been constituted.
TFA emanates from the following four pillars:
i. Transparency: focus on improved access to accurate and complete information.
ii. Technology: development and use of digital and detection technologies to ease out trade bottlenecks and improve efficiency.
iii. Simplification of Procedures and Risk based Assessments: simplified, uniform and harmonised procedures with increased adoption of a risk based management approach.
iv. Infrastructure Augmentation: enhancement of infrastructure, particularly the road and rail infrastructure leading to ports and the infrastructure within ports, airports, ICDs, Land Customs Stations is a major enabler for growth in trade that cuts across all stakeholders.
National Trade Facilitation Action Plan aims to achieve : –
Improvement in Ease of Doing Business through reduction in transaction cost and time
- Reduction in cargo release time
- A paperless regulatory environment
- A transparent and predictable legal regime
- Improved investment climate through better infrastructure
1.07 DGFT as a facilitator of exports/ imports
DGFT has a commitment to function as a facilitator of exports and imports. Focus is on good governance, which depends on efficient, transparent and accountable delivery systems. In order to facilitate international trade, DGFT consults various Export Promotion Councils as well as Trade and Industry bodies from time to time.
1.08 Free passage of Export Consignment
Consignments of items meant for exports shall not be withheld/ delayed for any reason by any agency of Central/ State Government. In case of any doubt, authorities concerned may ask for an undertaking from exporter and release such consignment.
1.09 No seizure of export related Stock
No seizure shall be made by any agency so as to disrupt manufacturing activity and delivery schedule of exports. In exceptional cases, concerned agency may seize the stock on the basis of prima facie evidence of serious irregularity. However, such seizure should be lifted within 7 days unless the irregularities are substantiated.
1.10 Export of perishable agricultural Products
To reduce transaction and handling costs, a single window system to facilitate export of perishable agricultural produce is being facilitated through Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA). The detailed procedure is at Appendix 1C.
1.11 Niryat Bandhu – Hand Holding Scheme for new export/ import entrepreneurs
DGFT is implementing the Niryat Bandhu Scheme for mentoring new and potential exporter on the intricacies of foreign trade through counseling, training and outreach programmes including the ‘Districts as Export Hubs’ initiative with ‘industry partners’, ‘knowledge partners’ and other stakeholders to create vibrant District-Product-Market relevant knowledge ecosystem.
1.12 DGFT Online Customer Portal
Export Import related information including Acts, Rules, Policy and Procedures etc. are available online at DGFT portal https://dgft.gov.in/.
1.13 Issue of e-IEC (Electronic-Importer Exporter Code)
Importer Exporter Code (IEC) is mandatory for export/ import from/to India as detailed in paragraph 2.05 of this Policy. DGFT issues Importer Exporter Code in electronic form (e-IEC). For issuance of e-IEC, application can be made on DGFT website (https://dgft.gov.in).
1.14 Online facility for e-RCMC/RC Related Processes
DGFT has created a common digital platform for application of issuance, renewal, amendment and related processes pertaining to Registration Cum Membership Certificate (RCMC)/ Registration Certificate (RC) issued by Registering Authorities in electronic form as per Chapter 2 of HBP.
1.15 Online facility for e-Certificate of Origin (e-CoO)
DGFT has created a common digital platform for issue of Preferential and Non-Preferential Certificate of Origin (e-CoO) by designated agencies. The CoO Certificates are issued in an online environment without any physical interface (https://coo.dgft.gov.in).
A unique number i.e. UDIN (Unique Document Identification Number) and a QR code is endorsed on every e-CoO for validation and authentication by user agencies.
1.16 Online facility to file Quality Control and Trade Disputes (QCTD)
DGFT has created a common digital platform for handling Quality Control and Trade Disputes cases as per Chapter 8 of Foreign Trade Policy where all jurisdictional Indian Mission abroad and Regional Authorities of DGFT have been onboarded to work towards amicable resolution of disputes raised by Indian/Foreigner Importer/Exporter in online environment.
1.17 Electronic record of export proceeds through eBRC & EDPMS
(a) e-BRC (Electronic Bank Realisation Certificate) has enabled DGFT to capture details of realisation of export proceeds directly from the Banks through secured electronic mode. This has facilitated the implementation of various export promotion schemes without any physical interface with the stake holders.
(b) RBI has also developed a comprehensive IT-based system called Export Data Processing and Monitoring System (EDPMS) for monitoring of export of goods and software and facilitating AD banks to report various returns through a single platform. RBI EDPMS data available in DGFT IT System can also be used by exporters on DGFT portal.
1.18 IT Initiatives in DGFT
DGFT has undertaken a number of IT Initiatives to enable a paperless, contactless and transparent environment for availing benefits under the export promotion schemes with a view to improve the ease of doing business. The details of these initiatives have been provided in Para 1.04 of Handbook of Procedures.
1.19 24 X 7 Helpdesk Facility
A dedicated 24 X 7 Helpdesk facility has been put in place to assist the exporters in filing online applications on the DGFT portal and other matters pertaining to Foreign Trade Policy.
1.20 Trade Data and Statistics
Continuous efforts are being made for better collection, compilation and wider dissemination of Trade Data and Statistics to help the policy makers, researchers, exporters and importers to formulate their trade strategy. The trade statistics for merchandise trade is available at –
i. Department of Commerce’s portal at https:// commerce.gov.in & data bank available at https:// tradestat.commerce.gov.in/eidb/default.asp,
ii. DGCI&S portal at http://www.dgciskol.gov.in and
iii. NIRYAT Portal at https://niryat.gov.in.
1.21 Trade Facilitation at Customs
CBIC has undertaken a number of initiatives to facilitate Trade. Some of these are as follows:
i. 24X7 Customs clearance in 20 sea ports and 17 Airports and extended clearance in ICDs as per the needs of the Trade.
ii. Single Window in Customs
iii. E-Sanchit – Enabling Paperless clearance environment
iv. Pan-India Implementation of Faceless e-Assessment in imports.
v. TURANT Customs
vi. Implementation of electronic messages from Document Clearance to Cargo Movement
vii. Paperless Customs initiatives –Preparation and issuance of electronic documents like e-LEO SB, e-Gatepass/e-OOC etc.,
viii. Contactless customs initiatives such as Turant Suvidha Kendras (TKSs).
ix. Release of ICE-DASH–Indian Customs EoDB Monitoring Dashboard
x. Direct Port Delivery (DPD) on imports and Direct Port Entry (DPE) on exports
xi. Compliance Information Portal (CIP)
xii. End to End automated and simplified procedure for Import of certain specified Goods at Concessional Rate of Duty or for specified end use.
For detailed guidelines/procedures visit https://www.cbic. gov.in/ and https://icegate.gov.in/.
1.22 Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) Programme
(a) Based upon WCO’s SAFE Framework of Standards, ‘Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) programme’ has been developed by Indian Customs to enable business involved in the international trade to reap the following benefits:
(i) Secure supply chain from point of export to import;
(ii) Ability to demonstrate compliance with security standards when contracting to supply overseas importers /exporters;
(iii) Enhanced border clearance privileges in Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA) partner countries;
(iv) Minimal disruption to flow of cargo after a security related disruption;
(v) Reduction in dwell time and related costs; and
(vi) Customs advice / assistance if trade faces unexpected issues with Customs of countries with which India have MRA.
(b) The AEO programmes have been implemented by other Customs administrations that give AEO status holders preferential Customs treatment in terms of reduced examination, faster clearances and other benefits. Indian Customs has signed MRA with South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong and US Customs to recognize respective AEO Programmes to enable trade to get benefits on reciprocal basis.
(c) As a step further towards trust-based compliance, Indian Customs has introduced the new/revamped Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) Programme wherein extensive benefits, including greater facilitation and self-certification, have been provided to those entities who have demonstrated internal strong control system and compliance with CBIC.
(d) Under the AEO program of Indian Customs, the MSMEs are also covered.
For detailed guidelines/procedures, visit https://www. aeoindia.gov.in/ and https://www.cbic.gov.in/.
1.23 Towns of Export Excellence (TEE)
(a) Objective: Development and growth of export production centres. A number of towns have emerged as dynamic industrial clusters contributing handsomely to India’s exports. It is necessary to grant recognition to these industrial clusters with a view to maximize their potential and enable them to move up the value chain and also to tap new markets.
(b) Selected towns producing goods of Rs. 750 Crore or more may be notified as TEE based on potential for growth in exports. However, for TEE in Handloom, Handicraft, Agriculture and Fisheries sector, threshold limit would be Rs.150 Crore. The following facilities will be provided to such TEE:
(i) Recognized associations of units will be provided financial assistance under MAI scheme, on priority basis, for export promotion projects for marketing, capacity building and technological services.
(ii) Common Service Providers in these areas shall be entitled for Authorisation under EPCG scheme.
(c) Notified Towns (TEE) are listed in Appendix 1B.
1.24 Duty Free Entitlements to Select Sectors
With a view to expand employment opportunities, certain special focus initiatives for Marine Products and Sports Goods & Toys sectors are required. These sectors are being provided the following duty free entitlements (only basic customs duty is exempted) as per the relevant Customs Notifications:
(a) Marine Sector – Duty free import of specified specialized inputs/ chemicals and flavoring oils not exceeding 1% of FOB value of seafood exports during the preceding financial year.
(b) Sports Goods and Toys – Duty free import of specified inputs not exceeding 3% of FOB value of sports goods exports during the preceding financial year.
For details, refer relevant Customs Notifications in this regard.
1.25 Status Holder Certification
(a) The objective behind certifying certain exporter firms as “Status Holder” is to recognize such exporter firms as business leaders who have excelled in international trade and have successfully contributed to country’s foreign trade. Status Holders are expected to not only contribute towards India’s exports but also provide guidance and handholding to new entrepreneurs.
(b) All exporters of goods, services and technology having an import-export code (IEC) number, on the date of application, shall be eligible for recognition as a status holder based on export performance. An applicant may be categorized as status holder on achieving the threshold export performance in the current and preceding three financial years as indicated in para 1.26 of Foreign Trade Policy. However, for Gems & Jewelry Sector above export performance threshold during the current and preceding two financial years shall be required. The export performance shall be counted on the basis of FOB of export earnings in freely convertible foreign currencies or in Indian Rupees as per para 2.53of the FTP.
(c) For deemed export, FOR value of exports in Indian Rupees shall be converted in USD at the exchange rate notified by CBIC, as applicable on 1st April of each Financial Year.
(d) For granting status, an export performance would be necessary in all the three preceding financial years (and in all the two preceding financial years for Gems & Jewelry Sector).
1.26 Status Holder Categories
| Status Category | Export Performance Threshold In USD Million |
| One Star Export House | 3 |
| Two Star Export House | 15 |
| Three Star Export House | 50 |
| Four Star Export House | 200 |
| Five Star Export House | 800 |
1.27 Grant of Double Weightage
(a) Double Weightage shall be available for grant of One Star Export House Status category only. Such benefit of double weightage shall not be admissible for grant of status recognition of other categories namely Two Star Export House, Three Star Export House, Four Star export House and Five Star Export House. The exports by IEC holders under the following categories shall be granted double weightage for calculation of export performance for grant of status:
i. Micro and Small Enterprises as defined in Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act 2006
ii. Manufacturing units having ISO/BIS Certification
iii. Units located in North Eastern States including Sikkim, and Union Territories of Jammu, Kashmir and Ladakh
iv. Export of fruits and vegetables falling under Chapters 7 and 8 of ITC HS
(b) A merchandise shipment/ service rendered can get double weightage only once in any one of above categories.
1.28 Other Conditions for Grant of Status
(a) Export performance of one IEC holder shall not be permitted to be transferred to another IEC holder. Hence, calculation of exports performance based on disclaimer shall not be allowed.
(b) Exports made on re-export basis shall not be counted for recognition.
(c) Export of items under Authorisation, including SCOMET items, would be included for calculation of export performance.
1.29 Privileges of Status Holders
A Status Holder shall be eligible for privileges as under:
(a) Authorisation and Customs Clearances for both imports and exports may be granted on self-declaration basis;
(b) Input-Output norms may be fixed on priority within 60 days by the Norms Committee; Special scheme in respect of Input Output Norms to be notified by DGFT from time to time, for specified status holder
(c) Exemption from furnishing of Bank Guarantee for Schemes under FTP, unless specified otherwise anywhere in FTP or HBP;
(d) Exemption from compulsory negotiation of documents through banks. Remittance / receipts, however, would be received through banking channels;
(e) Two star and above Export houses shall be permitted to establish Export Warehouses as per Department of Revenue guidelines.
(f) The status holders would be entitled to preferential treatment and priority in handling of their consignments by the concerned agencies.
(g) Manufacturers who are also status holders (Three Star/Four Star/Five Star) will be enabled to self-certify their manufactured goods (as per their IEM/IL/LOI) as originating from India with a view to qualify for preferential treatment under different preferential trading agreements (PTA), Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements (CECA) and Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements (CEPA). Subsequently, the scheme may be extended to remaining Status Holders. Manufacturer exporters who are also Status Holders shall be eligible to self-certify their goods as originating from India as per Para 2.93 (e) of Hand Book of Procedures.
(h) Status holders shall be entitled to export freely exportable items (excluding Gems and Jewelry, Articles of Gold and precious metals) on free of cost basis for export promotion subject to an annual limit of Rupees One Crore or 2% of average annual export realization during preceding three licensing years, whichever is lower. For export of pharma products by pharmaceutical companies, the annual limit would be 2% of the average annual export realisation during preceding three licensing years. In case of supplies of pharmaceutical products, vaccines and lifesaving drugs to health programmes of international agencies such as UN, WHO-PAHO and Government health programmes, the annual limit shall be upto 8% of the average annual export realisation during preceding three licensing years. Such free of cost supplies shall not be entitled to Duty Drawback or any other export incentive under any export promotion scheme.
1.30 Skilling and Mentorship Obligations
(a) To improve the trade ecosystem by enhancing the available skilling opportunities, Status Holders are being made “partners” in providing mentoring and training in international trade. Status Holders will endeavor to provide skill upgradation/ training in international trade as detailed below :
| Status | Number of Trainees per year |
| Two Star Export House | 5 |
| Three Star Export House | 10 |
| Four Star Export House | 20 |
| Five Star Export House | 50 |
(b) A model training program of a minimum duration of 6 weeks would be put up in public domain for guidance.
(c) Detailed eligibility requirements, selection criteria, training curriculum etc will be at the discretion of the Status Holder.
1.31 Inter-Ministerial Committee for MSME Trade related grievances
An inter-ministerial committee to be set up to examine MSME trade related grievances which have policy ramifications. This will expedite decision making with a ‘whole of government approach’.
1.32 Citizen’s Charter
DGFT has in place a Citizen’s Charter, giving time schedules for providing various services to clients. Timeline for disposal of an application is given in Chapter 11 of HBP.
Chapter 2
General Provisions Regarding Imports and Exports
2.00 Objective
The general provisions governing import and export of goods and services are dealt with in this chapter.
2.01 Policy regarding import /Exports of goods
(a) Exports and Imports shall be ‘Free’ except when regulated by way of ‘Prohibition’, ‘Restriction’ or ‘Exclusive trading through State Trading Enterprises (STEs)’ as laid down in Indian Trade Classification (Harmonized System) [ITC (HS)] of Exports and Imports. The list of ‘Prohibited’, ‘Restricted’, and STE items can be viewed under ‘Regulatory Updates’ at https://dgft. gov.in
(b) Further, there are some items which are ‘Free’ for import/export, but subject to conditions stipulated in other Acts or in law for the time being in force.
2.02 Indian Trade Classification (Harmonised System) [ITC (HS)] of Exports and Imports
(a) ITC(HS) is a compilation of codes for all merchandise / goods for export/ import. Goods are classified based on their group or sub-group at 2/4/6/8 digits.
(b) ITC(HS) is aligned at 6-digit level with international Harmonized System goods nomenclature maintained by World Customs Organization (http://www.wcoomd. org). However, India maintains national Harmonized System of goods at 8-digit level notified under First Schedule of the Customs Tariff Act,1975 which may be viewed under ‘Regulatory Updates’ at http://dgft. gov.in and at https://www.cbic.gov.in
(c) The import/export policies for all goods are indicated against each item as per its ITC (HS). Schedule 1 of ITC (HS) lays down the Import Policy regime while Schedule II of ITC(HS) lays down the Export Policy regime.
(d) Except where it is clearly specified, Schedule 1 of ITC (HS), Import Policy is for new goods and not for Second Hand goods. For Second Hand goods, the Import Policy regime is given under Para 2.31 of this FTP.
2.03 Compliance of Imports with Domestic Laws
(a) Domestic Laws/ Rules/ Orders/ Regulations/ technical specifications/ environmental/safety and health norms applicable to domestically produced goods shall apply, mutatis mutandis, to imports, unless specifically exempted.
(b) However, goods to be utilized/ consumed in manufacture of export products may be exempted by DGFT from domestic standards/ quality specifications.
2.04 Authority to specify Procedures
DGFT may, specify Procedures to be followed by an exporter or importer or by any licensing/Regional Authority (RA) or by any other authority for purposes of implementation of the provisions of FT (D&R) Act, the Rules and the Orders made there under and the FTP. Such procedures, or amendments if any, shall be published by means of a Public Notice.
2.05 Importer-Exporter Code (IEC)
An IEC is a 10-character alpha-numeric number allotted to an entity(firm/company/LLP etc.) and is mandatory for undertaking any export/import activities. With a view to maintain the unique identity of an entity, consequent upon introduction / implementation of GST, IEC shall be same as Permanent Account Number(PAN) and shall be separately issued by DGFT based on an online application.
(a) No export or import of goods shall be made by any person without obtaining an IEC unless specifically exempted. For export of services or technology, IEC shall be necessary on the date of rendering services for availing benefits under the Foreign Trade Policy.
(b) Exempt categories and corresponding permanent IECs are given in Para 2.07 of Handbook of Procedures.
(c) Application process for IEC and updation in IEC is completely online and IEC can be generated by the applicant as per the procedure detailed in the Handbook of Procedures.
(d) An IEC holder has to ensure that details in its IEC is updated electronically every year, during the April-June period. In cases where there are no changes in IEC details same also needs to be confirmed online.
(e) An IEC shall be de-activated, if it is not updated within the prescribed period. An IEC so de-activated may be activated, on its successful updation. This would however be without prejudice to any other action taken for violation of any other provisions of the FTP.
(f) An IEC may also be flagged for scrutiny. IEC holder(s) are required to ensure that any risks flagged by the system are timely addressed; failing which the IEC shall be de-activated.
2.06 Mandatory documents for export/ import of goods from/into India
(a) Mandatory documents required for export of goods from India:
1. Bill of Lading/ Airway Bill/ Lorry Receipt/ Railway Receipt/Postal Receipt
2. Commercial Invoice cum Packing List*
3. Shipping Bill/Bill of Export/ Postal Bill of Export
(b) Mandatory documents required for import of goods into India
1. Bill of Lading/Airway Bill/Lorry Receipt/ Railway Receipt/Postal Receipt in form CN-22 or CN 23 as the case may be.
2. Commercial Invoice cum Packing List**
3. Bill of Entry
[Note: *(i) As per CBIC Circulars issued under the Customs Act, 1962 (ii) **Separate Commercial Invoice and Packing List would also be accepted.]
(c) For export or import of specific goods or category of goods, which are subject to any restrictions/ policy conditions or require NOC or product specific compliances under any statute, the regulatory authority concerned may notify additional documents for purposes of export or import.
(d) In specific cases of export or import, the regulatory authority concerned may electronically or in writing seek additional documents or information, as deemed necessary to ensure legal compliance.
2.07 Principles of Restrictions
DGFT may, through a Notification, impose ‘Prohibition’ or ‘Restriction’:
(a) on export of foodstuffs or other essential products for preventing or relieving critical shortages;
(b) on imports and exports necessary for the application of standards or regulations for the classification, grading or marketing of commodities in international trade;
(c) on imports of fisheries product, imported in any form, for enforcement of governmental measures to restrict production of the domestic product or for certain other purposes;
(d) on import to safeguard country’s external financial position and to ensure a level of reserves;
(e) on imports to promote establishment of a particular industry;
(f) for preventing sudden increases in imports from causing serious injury to domestic producers or to relieve producers who have suffered such injury;
(g) for protection of public morals or to maintain public order;
(h) for protection of human, animal or plant life or health;
(i) relating to the importations or exportations of gold or silver;
(j) necessary to secure compliance with laws and regulations including those relating to the protection of patents, trademarks and copyrights, and the prevention of deceptive practices;
(k) relating to the products of prison labour;
(l) for the protection of national treasures of artistic, historic or archaeological value;
(m) for the conservation of exhaustible natural resources;
(n) for ensuring essential quantities for the domestic processing industry;
(o) essential to the acquisition or distribution of products in general or local short supply;
(p) for the protection of country’s essential security interests
i. relating to fissionable materials or the materials from which they are derived;
ii. relating to the traffic in arms, ammunition and implements of war;
iii. taken in time of war or other emergency in international relations; or
(q) in pursuance of country’s obligations under the United Nations Charter for the maintenance of international peace and security
2.08 Export/Import of Restricted Goods/ Services
Any goods /service, the export or import of which is ‘Restricted’ may be exported or imported only in accordance with an Authorisation / Permission or in accordance with the Procedures prescribed in a Notification / Public Notice issued in this regard.
2.09 Actual User Condition
Goods which are importable freely without any ‘Restriction’ may be imported by any person. However, if such imports require an Authorisation, Actual User alone may import such good(s) unless Actual User condition is specifically dispensed with by DGFT.
2.10 Terms and Conditions of an Authorisation
Every Authorisation shall, inter alia, include either all or some of the following terms and conditions (as applicable in terms of the para under which the Authorisation has been issued), in addition to such other conditions as may be specified:
(a) Description, quantity and value of goods;
(b) Actual User condition (as defined in Chapter 11);
(c) Export Obligation;
(d) Minimum Value addition to be achieved;
(e) Minimum export/import price;
(f) Bank guarantee/ Legal undertaking / Bond with Customs Authority/RA (as in para 2.35 of FTP).
(g) Validity period of import/export as specified in Handbook of Procedures.
2.11 Application Fee
(a) Application for IEC/Authorisation/License/Scrips/ Registration must be accompanied by application fees as indicated in the Appendix 2K of Appendices and Aayat Niryat Forms. Fees must be paid online through any of the channels as notified under Appendix 2K, unless provided otherwise.
(b) Application fee is nothing but the fee for processing of the application. Therefore, the fee once received will not be refunded except in the circumstances and in a manner laid down in Appendix 2K.
2.12 Clearance of Goods from Customs against Authorisation
Goods already imported / shipped / arrived, in advance, but not cleared from Customs may also be cleared against an Authorisation issued subsequently. However, such goods already imported/shipped/arrived, in advance are first warehoused against Bill of Entry for Warehousing and then cleared for home consumption against an Authorisation issued subsequently. This facility will however be not available to ‘Restricted’ items or items traded through STEs, unless specifically allowed by DGFT.
2.13 Authorisation – not a Right
No person can claim an Authorisation as a right and DGFT or RA shall have power to refuse to grant or renew the same in accordance with provisions of FT (D&R) Act, Rules made there under and FTP.
2.14 Penal action and placing of an entity in Denied Entity List (DEL)
(a) If an Authorisation holder violates any condition of such Authorisation or fails to fulfill export obligation or fails to deposit the requisite amount within the period specified in demand notice issued by Department of Revenue and /or DGFT, he shall be liable for action in accordance with FT (D&R) Act, the Rules and Orders made there under, FTP and any other law for time being in force.
(b) With a view to raising ethical standards and for ease of doing business, DGFT has provided for self-certification system under various schemes. In such cases, applicants shall undertake self-certification with sufficient care and caution in filling up information/ particulars. Any information/particulars subsequently found untrue/incorrect will be liable for action under FT (D&R) Act, 1992 and Rules therein in addition to penal action under any other Act/Order.
(c) A firm may be placed under Denied Entity List (DEL), by the concerned RA, under the provision of Rule 7 of Foreign Trade (Regulation) Rules, 1993. On issuance of such an order, for reasons to be recorded in writing, a firm may be refused grant or renewal of a licence, authorisation, certificate, scrip or any instrument bestowing financial or fiscal benefits. If a firm is placed under DEL, all new licences, authorisations, scrips, certificates, instruments etc. will be blocked from printing/ issue/renewal.
(d) DEL orders may be placed in abeyance, for reasons to be recorded in writing by the concerned RA. DEL order can be placed in abeyance, for a period not more than 60 days at a time.
(e) A firm’s name can be removed from DEL, by the concerned RA for reasons to be recorded in writing, if the firm completes Export Obligation/ pays penalty/ fulfils requirement of Demand Notice(s) issued by the RA/submits documents required by the RA.
2.15 Firm/company under adjudication proceeding before the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
Any firm/company coming under the adjudication proceeding before the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) shall inform the concerned Regional Authority (RA) and NCLT of any outstanding export obligations/liabilities under any of the schemes under FTP. The total outstanding duty saved amount/dues along with interest, and any penalty imposed under FT (D&R) Act, or any other dues, shall be counted as part of the dues to the government against the said firm/company.
Prohibitions on Trade (Country, Organisations, Groups, Individuals etc. and Product Specific):
2.16 Prohibition on Import and Export of ‘Arms and related material’ from / to Iraq
Notwithstanding the policy on Arms and related materials in Chapter 93 of ITC(HS), the import/export of Arms and related material from/to Iraq is ‘Prohibited’. However, export of Arms and related material to Government of Iraq shall be permitted subject to ‘No Objection Certificate’ from the Department of Defence Production.
2.17 Prohibition on Trade with the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant [ISIL, also known as Daesh], Al Nusrah Front [ANF] and other individuals, groups, undertakings and entities associated with Al Qaida
In compliance with United Nations Security Council Resolution No. 2199 [2015], trade in oil and refined oil products, modular refineries and related materials, besides items of cultural (including antiquities), scientific and religious importance is prohibited with the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant [ISIL], Al Nusrah Front [ANF] and other individuals, groups, undertakings and entities associated, directly or indirectly, with Al Qaida.
2.18 Prohibition on direct or indirect import and export from/to DPRK
Direct or Indirect export and import of items, whether or not originating in Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) to/from DPRK is detailed in Appendix – I of this Chapter.
2.19 Direct or Indirect Export/Import to/ from Iran
(a) Direct or indirect export to Iran or import from Iran of any item, material, equipment, goods and technology mentioned in the following documents would be permitted subject to the provisions contained in Annex-B to the United Nations Security Council Resolution 2231 (2015):
(i) Items listed in INFCIRC/254/Rev.14/Part1 and INFCIRC/254/Rev.11/Part 2 (IAEA Documents) as updated by the UNSC and IAEA from time to time.
(ii) Items listed in S/2015/546 (UN Security Council document) as updated by the Security Council from time to time.
(b) All the UN Security Council Resolutions/Documents and IAEA Documents referred to above are available on the UN Security Council website (https://www. un.org/securitycouncil/) and IAEA website (https:// www.iaea.org/).
2.20 Prohibition on Import of Charcoal from Somalia
Direct or indirect import of charcoal is prohibited from Somalia, irrespective of whether or not such charcoal has originated in Somalia [United Nations Security Council Resolution 2036(2012)]. Importers of Charcoal shall submit a declaration to Customs that the consignment has not originated in Somalia.
Import / Export through State Trading Enterprises:
2.21 State Trading Enterprises (STEs)
(a) State Trading Enterprises (STEs) are governmental and non-governmental enterprises, including marketing boards, which deal with goods for export and /or import. Any good, import or export of which is governed through exclusive or special privilege granted to State Trading Enterprise (STE), may be imported or exported by the concerned STE as per conditions specified in ITC (HS). The list of STEs notified by DGFT is in Appendix-2J.
(b) Such STE(s) shall make any such purchases or sales involving imports or exports solely in accordance with commercial considerations, including price, quality, availability, marketability, transportation and other conditions of purchase or sale in a non-discriminatory manner and shall afford enterprises of other countries adequate opportunity, in accordance with customary business practices, to compete for participation in such purchases or sales.
(c) DGFT may, however, grant an authorisation to any other entity to import or export any of the goods notified for exclusive trading through STEs.
Trade with Specific Countries:
2.22 Trade with Neighbouring Countries
DGFT may issue instructions or frame schemes as may be required to promote and regulate trade and strengthen economic ties with neighbouring countries.
2.23 Transit Facility
Transit of goods through India from/ or to countries adjacent to India shall be enabled and regulated in accordance with strategic and economic interests of India as well as the bilateral treaties between India and those countries. Such arrangements will be subject to conditions and restrictions as may be specified by DGFT in accordance with International Conventions/ Treaties/Agreements.
2.24 Trade with Russia under Debt-Repayment Agreement
In case of trade with Russia under Debt Repayment Agreement, DGFT may issue instructions or frame schemes as may be required, and anything contained in FTP, in so far as it is inconsistent with such instructions or schemes, shall not apply.
Import of Specific Categories of Goods:
2.25 Import of Samples
No Authorisation shall be required for Import of bonafide technical and trade samples of items “restricted” in ITC(HS)
2.26 Import of Gifts
Import of goods, including those purchased from e-commerce portals, through post or courier, where Customs clearance is sought as gifts, is prohibited except for life saving drugs/ medicines and Rakhi (but not gifts related to Rakhi).
Explanation:
1. Rakhi (but not gifts related to Rakhi) will be covered under Section 25(6) of Customs Act, 1962 that reads that “no duty shall be collected if the amount of duty leviable is equal to or less than Rs. 100/-”
2. Import of goods as gifts with payment of full applicable duties is allowed.
2.27 Import through Passenger Baggage
(a) Bona-fide household goods and personal effects may be imported as part of passenger baggage as per limits, terms and conditions thereof in Baggage Rules notified by Ministry of Finance.
(b) Samples of such items that are otherwise freely importable under FTP may also be imported as part of passenger baggage without an Authorisation subject to Baggage Rules as notified by Customs from time to time.
(c) Exporters coming from abroad are also allowed to import drawings, patterns, labels, price tags, buttons, belts, trimming and embellishments required for export, as part of their passenger baggage, without an Authorization subject to value limit as laid down in FTP or as per the relevant Customs notification(s) in this regard.
(d) Any item(s) including Samples or Prototypes of items whose import policy is “restricted” or “prohibited” or is canalised through STEs are not permitted as part of passenger baggage except with a valid authorization/ permission issued by DGFT.
2.28 Re – import of goods repaired abroad
Capital goods, equipment, components, parts and accessories, whether imported or indigenous, except those restricted under ITC (HS) may be sent abroad for repairs, testing, quality improvement or upgradation or standardization of technology and re-imported without an Authorisation.
2.29 Import of goods used in projects abroad
Project contractors after completion of projects abroad, may import without an Authorisation, goods including capital goods used in the project, provided they have been used for at least one year.
2.30 Import of Prototypes
Import of new / second hand prototypes / second hand samples may be allowed on payment of duty without an Authorisation to an Actual User (industrial) engaged in production of or having industrial license / letter of intent for research in item for which prototype is sought for product development or research, as the case may be, upon a self-declaration to that effect, to the satisfaction of Customs authorities.
Import Policy for Second Hand Goods:
2.31 Second Hand Goods
|
Sl.No. |
Categories of Second-Hand Goods | Import Policy |
Conditions, if any |
| I. Second Hand Capital Goods | |||
| I(a) | i. Desktop Computers;
ii. Refurbished/re-conditioned spares of re-furbished parts of Personal Computers/ Laptops; iii. Air Conditioners; iv. Diesel generating sets |
Restricted | Importable against Authorisation |
| I(b) | All electronics and IT Goods notified under the Electronics and IT Goods (Requirements of Compulsory Registration) Order, 2012 as amended from time to time | Restricted | (i) Importable against an authorization subject to conditions laid down under Electronics and IT Goods (Requirements of Compulsory Registration) Order, 2012 as amended from time to time.
(ii) Import of unregistered/ non-compliant notified products as in CRO, 2012 as amended from time to time is “Prohibited” |
| I(c) | Refurbished / re-onditioned spares of Capital Goods | Free | Subject to production of Chartered Engineer certificate to the effect that such spares have at least 80% residual life of original spare |
| I(d) | All other second-hand capital goods {other than (a) (b) & (c) above} | Free | |
| II. | Second Hand Goods other than capital goods | Restricted | Importable against Authorisation |
| III. | Second Hand Goods imported for the purpose of repair/refurbishing / re-conditioning or re-engineering | Free | Subject to condition that waste generated during the repair / refurbishing of imported items is treated as per domestic Laws/ Rules/ Orders/ Regulations/ technical specifications/ Environmental / safety and health norms and the imported item is re-exported back as per the Customs Notification. |
Import Policy for Metallic Waste and Scraps:
2.32 Import of Metallic Waste and Scrap
(a) Import of any form of metallic waste, scrap will be subject to the condition that it will not contain hazardous, toxic waste, radioactive contaminated waste/scrap containing radioactive material, any types of arms, ammunition, mines, shells, live or used cartridge or any other explosive material in any form either used or otherwise as detailed in Para 2.51 of Handbook of Procedures.
(b) The types of metallic waste and scrap which can be imported freely, and the Procedures of import in the shredded form; un-shredded, compressed and loose form is laid down in Para 2.51 of Handbook of Procedures.
2.33 Removal of Scrap/Waste from SEZ
A SEZ unit/Developer/ Co-developer may be allowed to dispose of in DTA any waste or scrap, including any form of metallic waste and scrap, generated during manufacturing or processing activity, without an Authorisation, on payment of applicable Customs Duty.
Other Provisions Related to Imports:
2.34 Import under Lease Financing
No specific permission of DGFT is required for import of lease financed Capital Goods.
2.35 Execution of Legal Undertaking (LUT) / Bank Guarantee (BG)
(a) Wherever any duty-free import is allowed or where otherwise specifically stated, importer shall execute, Legal Undertaking (LUT) / Bank Guarantee (BG) / Bond with the Customs Authority, as prescribed, before clearance of goods.
(b) In case of indigenous sourcing, Authorisation holder shall furnish LUT/BG/Bond to the RA concerned before sourcing material from indigenous supplier/ nominated agency as prescribed in Chapter 2 of Handbook of Procedures.
2.36 Private/Public Bonded Warehouses for Imports
(a) Private/ Public bonded warehouses may be set up in DTA as per rules, regulations and notifications issued under the Customs Act, 1962. Any person may import goods except prohibited items, arms and ammunition, hazardous waste and chemicals and warehouse them in such bonded warehouses.
(b) Such goods may be cleared for home consumption in accordance with provisions of FTP and against Authorisation, wherever required. Customs duty as applicable shall be paid at the time of clearance of such goods.
(c) The clearance of the warehoused goods shall be as per the provisions of the Customs Act, 1962.
2.37 Special provision for Hides Skins and semi-finished goods
Hides, Skins and semi-finished leather may be imported in the Public/ Private Bonded warehouse for the purpose of DTA sale and the unsold items thereof can be re¬exported from such bonded warehouses on payment of the applicable rate of export duty.
2.38 Sale on High Seas
Sale of goods on high seas for import into India may be made subject to FTP or any other law in force.
2.39 Merchanting Trade
Merchanting trade involving shipment of goods from one foreign country to another foreign country without touching Indian ports, involving an Indian intermediary is allowed subject to compliance with RBI guidelines, except for goods/items in the CITES and SCOMET list.
Exports:
2.40 Free Exports
All goods may be exported without any restriction except to the extent that such exports are regulated by ITC(HS) or any other provision of FTP or any other law for the time being in force. DGFT may, however, specify through a Public Notice such terms and conditions according to which any goods, not included in ITC(HS), may be exported without an Authorisation.
2.41 Benefits for Supporting Manufacturers
For any benefit to accrue to the supporting manufacturer (as defined in Para 11.59 of FTP), the names of both supporting manufacturer as well as the merchant exporter must figure in the concerned export documents, especially in Tax Invoice / Shipping Bill / Bill of Export/ Airway Bill.
2.42 Third Party Exports
Third party exports (except Deemed Export) as defined in Chapter 11 shall be allowed under FTP. In such cases, export documents such as shipping bill shall indicate name of both manufacturing exporter/manufacturer and third-party exporter(s). e-Bank Realization Certificate (e-BRC) or export Realizations from RBI’s EDPMS wherever available in DGFT IT Systems, Export Order and Invoice should be in the name of third-party exporter.
Exports of Specific Categories:
2.43 Export of Samples
(a) Exports of bonafide trade and technical samples of General Provisions Regarding Imports and Exports freely exportable item shall be allowed without any limit.
(b) The procedure for Export of Samples and Free of charge goods shall be governed by provisions given in Para 2.63 of Handbook of Procedures.
2.44 Export of Gifts
Goods including edible items, of value not exceeding Rs.5,00,000/- in a licensing year, may be exported as a gift. However, items mentioned as restricted for exports in ITC(HS) shall not be exported as a gift, without an Authorisation.
2.45 Export of Passenger Baggage
(a) Bona-fide personal baggage may be exported either along with passenger or, if unaccompanied, within one year before or after passenger’s departure from India. However, items mentioned as restricted in ITC(HS) shall require an Authorisation. Government of India officials proceeding abroad on official postings shall, however, be permitted to carry along with their personal baggage, food items (free, restricted or prohibited) strictly for their personal consumption. The Provisions of the Para shall be subject to Baggage Rules issued under Customs Act, 1962.
(b) Samples of such items that are otherwise freely exportable under FTP may also be exported as part of passenger baggage without an Authorisation.
2.46 Import for Export
I. (a) Goods imported, in accordance with FTP, may be exported in same or substantially the same form without an Authorisation provided that item to be imported or exported is not in the restricted for import or export in ITC(HS) Schedules.
(b) Goods, including capital goods (both new and second hand), may be imported for export provided:
(i) Importer clears goods under Customs Bond;
(ii) Goods are freely exportable, i.e., are not “Restricted” or “Prohibited” or subject to “exclusive trading through State Trading Enterprises” or any conditionality or requirement as may be required under Schedule 2 of the Export Policy of the ITC (HS);
(iii) Export is against freely convertible currency or as per para 2.52(d)(ii) of FTP.
(c) Goods in (b) above will include ‘Restricted’ goods for import (except ‘Prohibited’ items).
(d) Capital goods, which are freely importable and freely exportable, may be imported for export on execution of LUT/BG with the Customs Authority.
(e) Notwithstanding the above, goods which are freely importable may be re-exported except items as in the Prohibited or SCOMET List of exports, in same or substantially same form even though such goods are under “Restricted list” for export, subject to the following conditions:
(i) Goods are not of Indian Origin;
(ii) Goods imported shall be kept in bonded warehouse under supervision of Customs;
(iii) Goods to be exported have never been cleared for home consumption;
(iv) Export of goods shall be subjected to Section 69 of Customs Act, 1962.
II. (a) Goods imported against payment in freely convertible currency would be permitted for export only against payment in freely convertible currency, unless otherwise notified by DGFT. Goods imported under Para 2.52(d) (i) would be permitted for exports only against payments as per Para 2.52(d)(ii), unless otherwise notified by DGFT.
(b) Export of such goods to the notified countries (presently only Iran) would be permitted against payment in Indian Rupees, subject to minimum 15% value addition.
(c) However, re-export of food, medicine and medical equipment, namely, items covered under ITC(HS) Chapters 2 to 4, 7 to 11, 15 to 21, 23, 30 and items under headings 9018, 9019, 9020, 9021 & 9022 of Chapter-90 of ITC(HS) will not be subject to minimum value addition requirement for export to Iran. Exports of these items to Iran shall, however, be subject to all other conditions of FTP and ITC (HS), as applicable. Bird’s eggs covered under ITC (HS) 0407 & 0408 and Rice covered under ITC (HS) 1006 are not covered
2.47 Export of Replacement Goods
Goods or parts thereof on being exported and found defective/damaged or otherwise unfit for use may be imported for replacement free of charge by the exporter in accordance with the relevant Customs Notification, and such goods shall be allowed for export by Customs authorities, provided that replacement goods are not under the restricted or SCOMET items for exports in ITC(HS). If the export item is ‘Restricted’ or under SCOMET list, the exporter shall require an Authorisation for export of such replacement goods.
2.48 Export of Repaired Goods
Goods or parts thereof, except restricted under ITC (HS), on being exported and found defective, damaged or otherwise unfit for use may be imported for repair and subsequent re-export. Such goods shall be allowed clearance without an Authorisation and in accordance with the relevant customs notification. To that extent the exporter shall return the benefits /incentive availed on the returned goods. If the item is ‘restricted’ for import, the exporter shall require an import license. However, re-export of such defective parts/ spares by the Companies/firms and Original Equipment Manufacturers shall not be mandatory if they are imported exclusively for undertaking root cause analysis, testing and evaluation purpose.
2.49 Export of Spares
Warranty spares (whether indigenous or imported) of plant, equipment, machinery, automobiles or any other goods [except those restricted under ITC (HS)] may be exported along with main equipment or subsequently but within contracted warranty period of such goods, subject to approval of RBI.
2.50 Re-export of imported Goods found defective and unsuitable for use
Imported goods found defective after Customs clearance, or not found as per specifications or requirements may be re-exported back as per Customs Act, 1962.
2.51 Private Bonded Warehouses for Exports
(a) Private bonded warehouses exclusively for exports may be set up in DTA as per terms and conditions of notifications issued by Department of Revenue.
(b) Such warehouses shall be entitled to procure goods from domestic manufacturers for manufacturing and other operations in accordance with Section 65 of the Customs Act, 1962.
Payments and Receipts on Imports / Exports:
2.52 Denomination of Export Contracts
(a) All export contracts and invoices shall be denominated either in freely convertible currency or Indian rupees but export proceeds shall be realized in freely convertible currency.
(b) However, export proceeds against specific exports may also be realized in rupees, provided it is through a freely convertible Vostro account of a non-resident bank situated in any country other than a member country of Asian Clearing Union (ACU) or Nepal or Bhutan. Additionally, rupee payment through Vostro account must be against payment in free foreign currency by buyer in his non-resident bank account. Free foreign exchange remitted by buyer to his non-resident bank (after deducting bank service charges) on account of this transaction would be taken as export realization under export promotion schemes of FTP.
(c) Contracts (for which payments are received through Asian Clearing Union (ACU) shall be denominated in ACU Dollar. However, participants in the ACU may settle their transactions in ACU Dollar or in ACU Euro as per RBI Notifications. Central Government may relax provisions of this paragraph in appropriate cases. Export contracts and invoices can be denominated in Indian rupees against EXIM Bank/Government of India line of credit.
(d) Invoicing, payment and settlement of exports and imports is also permissible in INR subject to compliances as under RBI’s A.P. (DIR Series) Circular No.10 dated 11th July, 2022. Accordingly, settlement of trade transactions in INR shall take place through the Special Rupee Vostro Accounts opened by AD banks in India as permitted under Regulation 7(1) of Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations, 2016, in accordance to the following procedures:
(i) Indian importers undertaking imports through this mechanism shall make payment in INR which shall be credited into the Special Vostro account of the correspondent bank of the partner country, against the invoices for the supply of goods or services from the overseas seller /supplier.
(ii) Indian exporters, undertaking exports of goods and services through this mechanism, shall be paid the export proceeds in INR from the balances in the designated Special Vostro account of the correspondent bank of the partner country.
2.53 Applicability of FTP Schemes for Export Realisations in Indian Rupees
(i) Export proceeds realized in Indian Rupees against exports to Iran are permitted to avail exports benefits / incentives/ fulfilment of Export Obligations under the FTP, at par with export proceeds realized in freely convertible currency, subject to compliance of para 2.19 of the FTP.
(ii) Export proceeds realized in Indian Rupees as per para 2.52(d)(ii) are permitted to avail exports benefits / incentives / fulfilment of Export Obligations under the FTP.
2.54 Non-Realisation of Export Proceeds
(a) If an exporter fails to realize export proceeds within time specified by RBI, he shall, without prejudice to any liability or penalty under any law in force, be liable to return all benefits / incentives availed against such exports and action in accordance with provisions of FT (D&R) Act, Rules and Orders made thereunder and the FTP.
(b) In case an Exporter is unable to realize the export proceeds for reasons beyond his control (force-majeure), he may approach RBI for writing off the unrealized amount as laid down in Para 2.72 of Handbook of Procedures.
(c) The payment realized through insurance cover, would be eligible for benefits under FTP as per Procedures laid down in Para 2.71 of Handbook of Procedures.
2.55 Export Credit Agencies (ECAs)
(i) Export Credit Agencies (ECAs) are policy instruments for Government to support exports. ECAs support exports by insurance, guarantee and also direct lending. Export Credit Agencies (ECAs) like Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India Ltd. (ECGC) provides credit insurance support to exports and export credit lending. Covers issued by ECGC to exporters, protect against losses arising out of payment failures due to insolvency or default of the buyers or due to political risks. Exporters can diversify their markets in addition to protecting existing markets through such covers. ECGC also supports Medium and Long term (MLT) exports including project exports. Exim Bank is the other ECA in the business of lending for MLT exports and fronting the government’s line of credit.
(ii) ECGC indemnifies losses of exporters in export trade due to insolvency or default of the buyer. Additionally, losses due to political risk like war, sudden import restriction, promulgation of law or decree after the shipment has been affected are also covered. Some of the anti- dumping measures or non-tariff barriers introduced after a shipment has been made will come under the purview of the political risk. In such cases exporter’s interest are protected by ECGC.
Export Promotion Councils:
2.56 Recognition of EPCs to function as Registering Authority for issue of RCMC
(a) Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) are organizations of exporters, set up with the objective to promote and develop Indian exports. Each Council is responsible for promotion of a particular group of products/ projects/services as given in Appendix 2T of ANF.
(b) EPCs are also eligible to function as Registering Authorities to issue Registration-cum-Membership Certificate (RCMC) to its members. The criteria for EPCs to be recognized as Registering Authorities for issue of RCMC to its members are detailed in Para 2.78 of the Handbook of Procedures.
2.57 Registration-cum-Membership Certificate (RCMC)
(a) Any person, applying for an Authorisation to import/ export under the FTP (except items listed as ‘Restricted’ items in ITC (HS)) or applying for any other benefit or concession under FTP, shall be required to provide, the RCMC granted by competent authority in accordance with Procedures specified in Handbook of Procedures unless specifically exempted under FTP.
(b) Certificate of Registration as Exporter of Spices (CRES) issued by Spices Board and Certificate of Registration as Exporter of Coir & Coir products issued by the Coir Board shall be treated as Registration-Cum-Membership Certificate (RCMC) for the purposes under this Policy.
2.58 Interpretation of Policy
(a) The decision of DGFT shall be final and binding on all matters relating to interpretation of Policy, or provision in Handbook of Procedures, Appendices and Aayat Niryat Forms or classification of any item for import / export in the ITC (HS).
(b) A Policy Interpretation Committee (PIC) may be constituted to aid and advice DGFT. The composition of the PIC would be as follows:
(i) DGFT: Chairman
(ii) All Additional DGFTs in Headquarters: Members
(iii) All Joint DGFTs in Headquarters looking after Policy matters: Members
(iv) Joint DGFT (PRC/PIC): Member Secretary
(v) Any other person / representative of the concerned Ministry / Department, to be co-opted by the Chairman.
2.59 Exemption from Policy/Procedures
DGFT may in public interest pass such orders or grant such exemption, relaxation or relief, as he may deem fit and proper, on grounds of genuine hardship and adverse impact on trade to any person or class or category of persons from any provision of FTP or any Procedures. While granting such exemption, DGFT may impose such conditions as he may deem fit after consulting the Committees as under:
|
Sl. No. |
Description | Committee |
| (a) | Fixation/modification of product norms under all schemes | Norms Committees |
| (b) | Nexus with Capital Goods (CG) and benefits under EPCG Schemes | EPCG Committee |
| (c) | All other issues | Policy Relaxation Committee (PRC) |
2.60 Personal Hearing by DGFT for Grievance Redressal
(a) Government is committed to easy and speedy redressal of grievances from Trade and Industry. Paragraph 2.59 of FTP provides for relaxation of Policy and Procedures on grounds of genuine hardship and adverse impact on trade. If an importer/exporter is aggrieved by any decision taken by Policy Relaxation Committee (PRC), or a decision/order by any authority in the Directorate General of Foreign Trade, a specific request for Personal Hearing (PH) along with the prescribed application fee as per Appendix-2K has to be made to DGFT. DGFT may consider request for relaxation after consulting concerned Norms Committee, EPCG Committee or Policy Relaxation Committee (PRC) and the decision conveyed in pursuance to the personal hearing shall be final and binding.
(b) The opportunity for Personal Hearing will not apply to a decision/order made in any proceeding, including an adjudication proceeding, whether at the original stage or at the appellate stage, under the relevant provisions of FT (D&R) Act, 1992, as amended from time to time.
2.61 Regularization of EO default and settlement of Customs duty and interest through Settlement Commission
With a view to providing assistance to firms who have defaulted under FTP for reasons beyond their control as also facilitating merger, acquisition and rehabilitation of sick units, it has been decided to empower Settlement Commission in Department of Revenue to decide such cases also with effect from 01.04.2005. However, in cases where the matter is under the purview of the NCLT, Para 2.15 of the FTP shall apply.
Self-Certification of Originating Goods:
2.62 Approved Exporter Scheme for Self-Certification of Certificate of Origin
(i) Currently, Certificates of Origin under various Preferential Trade Agreements [PTA], Free Trade Agreements [FTAs], Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements [CECA] and Comprehensive Economic Partnerships Agreements [CEPA] are issued by designated agencies as per Appendix 2B of Appendices and Aayat Niryat Forms. A new optional system of self-certification is being introduced with a view to reducing transaction cost.
(ii) The Manufacturers who are also Status Holders shall be eligible for Approved Exporter Scheme. Approved Exporters will be entitled to self-certify their manufactured goods as originating from India with a view to qualifying for preferential treatment under different PTAs/FTAs/CECAs/CEPAs which are in operation. Self-certification will be permitted only for the goods that are manufactured as per the Industrial Entrepreneurs Memorandum (IEM) / Industrial License (IL) /Letter of Intent (LOI) issued to manufacturers.
(iii) Status Holders will be recognized by DGFT as Approved Exporters for self-certification based on availability of required infrastructure, capacity and trained manpower as per the details in Para 2.94 of Handbook of Procedures read with Appendix 2F of Appendices & Aayaat Niryat Forms.
(iv) The details of the Scheme, along with the penalty provisions, are provided in Appendix 2F of Appendices and Aayaat Niryat Forms and will come into effect only when India incorporates the scheme into a specific agreement with its partner/s and the same is appropriately notified by DGFT. Further the entities to whom such self-certification will be extended bilaterally under FTA/PTA will be subject to the provisions and conditions of that FTA.
2.63 Certification of Origin of Goods EU-GSP
Exporters can self-certify the Statement on Origin of their goods, as per the self-certification scheme, Certification of Origin of Goods for European Union Generalised System of Preferences (EU-GSP), of the European Union (EU) under the Registered Exporter System (REX) as in Para 2.89(A)(c) of the Handbook of Procedures.
Appendix I (Refer Para 2.18)
Prohibition on direct or indirect import and export from/to Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK)
Prohibition on export:
(A) The direct or indirect supply, sale, transfer or export of the following itemsto Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) is prohibited: –
(i) any battle tanks, armoured combat vehicles, large calibre artillery systems, combat aircraft, attack helicopters, warships, missiles or missile systems as defined for the purpose of the United Nations Register on Conventional Arms, or related material including spare parts;
(ii) all arms and related material, including small arms and light weapons and their related material;
(iii) all items, materials, equipment, goods and technology as set out in the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) and International Atomic Energy
Agency (IAEA) documents, namely,
1. S/2006/853*;
2. S/2006/853/Corr.1;
3. Part B of S/2009/364;
4. Annex III of Resolution 2094 (2013);
5. S/2016/1069;
6. Annex A to INFCIRC/254/Rev.12/Part1 (IAEA document);
7. Annex to INFCIRC/254/Rev.9/Part2 (IAEA document);
8. S/2014/253;
9. S/2016/308;
10. Annex III of Resolution 2321 (2016); and
11. other items, materials, equipment, goods and technology, as determined by the Central Government, which could contribute to DPRK’s nuclear related,ballistic missile-related or other weapons of mass destruction related programmes;
(iv) luxury goods, including undenatured ethyl alcohol [HS Codes 2207 and 2208] and cigars, cheroots, cigarillos and cigarettes, of tobacco or of tobacco substitutes [HS Codes 2402] under Chapter 22 and 24, Schedule 2 ITC (HS) Export Policy 2018, but not limited to, the items specified in Annex IV of Resolution 2094 (2013), Annex IV of Resolution 2270 (2016) and Annex IV of Resolution 2321 (2016);
(v) items as determined by the Central Government, except food or medicine, that could directly contribute to the development of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea’s operational capabilities of its armed forces. This measure is subject to the exemptions set out in paragraph 8 (a) and (b) of Resolution 2270 (2016);
Prohibition on import
(B) The direct or indirect procurement or import from DPRK, of items, whether or not originating in DPRK, covered in sub-paragraphs (A)(i), (A)(ii),(A)(iii) and (A) (v) above is prohibited.
Sectoral prohibitions (export)
(C) The direct or indirect supply, sale, transfer or export of the following items to DPRK is prohibited:
(i) new helicopters and new or used vessels, except as approved in advance bythe Committee on a case-by-case basis;
(ii) aviation fuel, including aviation gasoline, naptha-type jet fuel, kerosene type jet fuel, and kerosene-type rocket fuel. This measure is subject to the provisions of paragraph 31 of Resolution 2270 (2016) and paragraph 20 of Resolution of 2321 (2016);
(iii) condensates and natural gas liquids;
(iv) refined petroleum products. This measure is subject to the limits, exceptions and procedures set out in paragraph 5 of Resolution 2397 (2017);
(v) crude oil. This measure is subject to the limits, exemptions and procedures set out in paragraph 4 of Resolution 2397 (2017);
(vi) all industrial machinery [Chapter 84 and 85 of ITC(HS)], transportation vehicles [Chapter 86 to 89 of ITC(HS)], and iron, steel, and other metals [Chapter 72 to 83 of ITC(HS)]. This measure is subject to the exemptions set out in paragraph 7 of Resolution 2397 (2017);
Sectoral prohibitions (import)
(D) The direct or indirect procurement or import from DPRK, of the following items is prohibited:
(i) coal, iron and iron ore. This measure is subject to the exemptions and procedures set out in paragraph 8 of Resolution 2371 (2017);
(ii) gold, titanium ore, vanadium ore, and rare earth minerals;
(iii) copper, nickel, silver and zinc;
(iv) statues, unless the Committee approves on a case-by-case basis in advance;
(v) seafood (including fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other aquatic invertebrates in all forms). This measure is subject to the exemptions, clarifications and procedures set out in paragraph 9 of Resolution 2371(2017) and paragraph 6 of Resolution 2397 (2017);
(vi) lead and lead ore. This measure is subject to the exemptions and procedures set out in paragraph 10 of Resolution 2371 (2017);
(vii) textiles (including but not limited to fabrics and partially or fully completed apparel products). This measure is subject to the exemptions and procedures set out in paragraph 16 of Resolution 2375 (2017);
(viii) food and agricultural products [Chapters 12, 08, 07 of ITC(HS)], machinery [Chapter 84 of ITC(HS)], electrical equipment [Chapter 85 of ITC(HS)], earth and stone including magnesite and magnesia [Chapter 25 of ITC(HS)], wood [Chapter 44 of ITC(HS)], and vessels [Chapter 89 of ITC(HS)].These measures are subject to the procedures set out in paragraph 6 of Resolution 2397(2017).
Explanation
a) UNSC means the United Nations Security Council;
b) IAEA means the International Atomic Energy Agency;
c) Committee means the Committee of the UNSC set up in terms of paragraph 12 of Resolution 1718 (2006);
d) Resolution, as the case may be, means the UNSC Resolutions under Chapter VII of the Charter of the United Nations on Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, namely, 1718 (2006), 1874 (2009), 2087 (2013),2094 (2013), 2270 (2016), 2231 (2016), 2356 (2017), 2371 (2017),2375 (2017) and 2397(2017).
Chapter 3
Developing Districts as Export Hubs
3.0 Objective
To galvanise districts of the country to become export hubs by identifying products and services with export potential in the district, addressing bottlenecks for exporting these products/services, supporting local exporters/ manufacturers to scale and find potential buyers outside India with the aim of promoting exports, manufacturing & services industry in the District. This is intended to bring greater level of awareness and commitment regarding exports at the district level, build capacity to create new exporters and identify new markets for the focused products and services. This will also empower MSMEs, farmers and small scale industries to get benefit of export opportunities in the overseas markets. This decentralised and focused approach will shift the focus on district led export growth for self-sufficiency and self- reliance by providing global platform to products and services from the districts.
3.1 District Export Promotion Committees – Institutional Mechanism at District Level
Every district has products and services which are being exported, and can be further promoted, along with new products / services, to increase production, grow exports, generate economic activity and achieve the goal of AtmaNirbhar Bharat, Vocal for local and Make in India.
Products/services (GI products, agricultural clusters, toy clusters etc.) with export potential in each District have to be identified and institutional mechanism in the form of District Export Promotion Committees (DEPCs) at the district level is to be created to provide support for export promotion and address the bottlenecks for export growth in the Districts.
Each District shall constitute a District Export Promotion Committee (DEPC) chaired by Collector/DM/DC of the District and co-chaired by designated DGFT Regional Authority with various other stakeholders as its members.
The primary function of the DEPC will be to prepare and implement district specific Export Action Plans in collaboration with all the relevant stakeholders at the Central, State and the District level.
DGFT Regional Authorities will be engaging with all the relevant State and Central agencies to take forward this initiative in each district.
3.2 District Export Action Plans for Each District
The District Export Action Plan (DEAP) may be prepared for each district. 2-3 high potential products/services from the districts may be prioritised and comprehensive plan for their export growth may be prepared. It may include the support required by the local industry in boosting their manufacturing and exports with impetus on supporting the industry from the production stage to the exporting stage. The DEAPs may also include specific quantifiable targets to be achieved in the short term and long term. These plans may outline the interventions that are required to promote the export of identified products and services from the district. Each DEAP may be deliberated by the DEPC and various stakeholders before it is formally adopted by the DEPC of the each District. DEAP of each District, once adopted, may be published in the public domain on a dedicated Portal.
3.3 State/UT Export Promotion Committees
To synergise the efforts of the Department of Commerce/ DGFT and the State/UT governments in promotion of exports from the State, each State shall constitute a State Export Promotion Committee (SEPC) headed by Chief Secretary of the State. The designated Regional Authority of DGFT shall be the co-convener of the committee.
3.4 Nodal DGFT Regional Authority
Districts of the States/UTs have been assigned to the Jurisdictional DGFT Regional Authority and the nodal RA shall be responsible for the Districts under their jurisdiction for all activities related to Districts as Export Hubs initiative in those Districts.
3.5 Online Monitoring of District Export Action Plans
DGFT would develop an online monitoring portal that may be accessed on the DGFT website to enable the States/ DGFT RAs to upload all information related to the products/services with export potential of every District. The portal may also help in monitoring the progress of District Export Action Plan and DEPC meetings in all the Districts. Each DGFT Jurisdictional RA to be primarily responsible for updating the information/progress made in implementing Export Action Plan for each District under their Jurisdiction. The information and reports may also be available in public domain for the benefit of the exporters.
3.6 Export Promotion Activities in Districts
Support in the form of product/sector specific training and development needs of local industries, dissemination of information through outreach activities including buyer-seller meets, trade fairs, workshops etc. may be provided in each District. The training and development needs of District industries may be identified and trainings may be coordinated with other departments. DGFT RAs through DEPCs may facilitate such buyer-seller meets, exhibitions, trade fairs etc. in the District to encourage the industries to showcase their products/services to the world.
3.7 Implementation of District Export Action Plans
The District Export Action Plan notified by the District Export Promotion Committee in each District may include clear identification of products (goods and services) with export potential in the District, institutional/other responsibilities, specifics of policy, regulatory and operational reform, and infrastructure/utilities/logistics interventions required across the entire chain from producer/farm to the export destination, to cover aspects like production, productivity/ competitiveness, improvements required in design, tie up of producers with exporters, aggregation, sorting, testing, certification, packaging, transportation through cold chain or otherwise, import export regulatory formalities, fulfilment of destination countries standards etc. It may also include Identifying bottlenecks/Issues in GI production, registration, marketing and its exports. The plan may also include the support required by the local industry in boosting their manufacturing and exports with impetus on supporting the industry from the production stage to the exporting stage.
Once the plan is formally adopted by the DEPC of the each District, the plan may be implemented by the DEPC by identifying the projects/activities required to be done to promote export growth from the Districts. Convergence of various schemes would be done on priority to build synergy and access the central government and State government scheme funds available for infrastructure development and skill/capacity building activities. Department of Commerce schemes such as Market Access Initiative, Niryat Bandhu scheme etc. may also give priority to district specific needs identified under the District Export Action Plan.
Chapter 4
Duty Exemption / Remission Schemes
4.00 Objective
Schemes under this Chapter enable duty free import of inputs for export production, including replenishment of inputs or duty remission.
4.01 Schemes
(a) Duty Exemption Schemes.
The Duty Exemption schemes consist of the following:
-
- Advance Authorisation (AA) (which will include Advance Authorisation for Annual Requirement).
- Duty Free Import Authorisation (DFIA).
(b) Duty Remission Scheme.
Duty Drawback (DBK) Scheme, administered by Department of Revenue.
(c) Scheme for Rebate on State and Central Taxes and Levies (RoSCTL), as notified by the Ministry of Textiles.
(d) Schemes for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) notified by Department of Commerce and administered by Department of Revenue.
4.02 Applicability of Policy & Procedures
Authorisation under this Chapter shall be issued in accordance with the Policy and Procedures in force on the date of issue of the Authorisation.
4.03 Advance Authorisation
(a) Advance Authorisation is issued to allow duty free import of input, which is physically incorporated in export product (making normal allowance for wastage). In addition, fuel, oil, catalyst which is consumed / utilized in the process of production of export product, may also be allowed.
(b) Advance Authorisation is issued for inputs in relation to resultant product, on the following basis:
(i) As per Standard Input Output Norms (SION) notified (available in Hand Book of Procedures);
OR
(ii) On the basis of self declaration as per paragraph 4.07 of Handbook of Procedures.
OR
(iv) On the basis of Self Ratification Scheme in terms of Para 4.06 of Foreign Trade Policy.
4.04 Advance Authorisation for Spices
Duty free import of spices covered under Chapter-9 of ITC (HS) shall be permitted only for activities like crushing / grinding / sterilization / manufacture of oils or oleoresins. Authorisation shall not be available for simply cleaning, grading, re-packing, etc.
4.04A Special Advance Authorisation Scheme for export of Articles of Apparel and Clothing accessories
Duty free import of fabric under ‘Special Advance Authorisation Scheme for export of Articles of Apparel and Clothing Accessories’ shall be allowed, as per Customs Notification issued for this scheme, for export of items covered under Chapter 61 and 62 of ITC(HS) Classification of Export and Import, subject to the following terms and conditions:
(i) The authorisation shall be issued based on Standard Input Output Norms (SION) or prior fixation of norms by Norms Committee.
(ii) The authorisation may also be issued on the basis of self-declaration as per para 4.07 of HBP. In such cases, adhoc-norms shall be fixed within stipulated time period of 90 days.
(iii) The authorisation shall be issued for the import of relevant fabrics including inter lining only as input. No other input, packing material, fuel, oil and catalyst shall be allowed for import under this authorisation.
(iv) Exporters shall be eligible for All Industry Rate of Duty Drawback, for non fabric inputs, as determined by Central Government for this scheme. For the purpose of value addition norm of Para 4.08 of FTP, the value of any other input used on which benefit of Drawback is claimed or intended to be claimed shall be equal to 22% of the FOB value of export realised. Minimum value addition shall be as per Para 4.09 of FTP.
(v) Where the exporter desires to claim drawback determined and fixed by Jurisdictional Customs Authority (brand rate), he shall follow Para 4.15 of FTP regarding declarations to be made in application for the authorisation and make export under claim for brand rate. In such cases the value addition shall be as per Para 4.08 of FTP. Minimum value addition shall be as per Para 4.09 of FTP.
(vi) Authorisation, and the fabric imported, shall be subject to actual user condition. The same shall be non transferable even after completion of export obligation. However fabric imported may be transferred for job work in terms of provisions of GST Acts under intimation to the Customs authority at the port of registration (excluding the units located in areas eligible for area based exemption from Central Excise Duty). Invalidation of the Authorisation shall not be permitted.
(vii) The fabric imported shall be subject to pre-import condition and it shall be physically incorporated in the export product (making normal allowance for wastage). Only Physical exports shall fulfill the export obligation.
(viii) Provisions of paragraphs 4.02, 4.05(a), 4.13(i), 4.13(ii), 4.14, 4.15, 4.17, 4.19, 4.21(i), 4.21(ii), 4.21(iii), 4.21(iv), 4.22, and 4.23 of Foreign Trade Policy shall be applicable in so far as they are not inconsistent with this scheme.
4.05 Eligible Applicant / Export /Supply
(a) Advance Authorisation can be issued either to a manufacturer exporter or merchant exporter tied to supporting manufacturer.
(b) Advance Authorisation for pharmaceutical products manufactured through Non-Infringing (NI) process (as indicated in paragraph 4.18 of Handbook of Procedures) shall be issued to manufacturer exporter only.
(c) Advance Authorisation shall be issued for:
(i) Physical export (including export to SEZ)
(ii) Intermediate supply; and/or
(iii) Supply of goods to the categories mentioned in paragraph 7.02 (b), (c), (d), (e), (f) and (g) of this FTP.
(iv) Supply of ‘stores’ on board of foreign going vessel / aircraft, subject to condition that there is specific Standard Input Output Norms in respect of item supplied.
4.06 Self-Ratification Scheme
(i) Where there is no SION/valid Adhoc Norms for an export product or where SION has been notified but exporter intends to use additional inputs in the manufacturing process, eligible exporter can apply for an Advance Authorisation under this scheme on self declaration and self ratification basis. The expression “additional inputs” refers not to additionality in terms of quantity/value of an input specified in a norm, but to another additional input. Say, if the inputs specified in the norm are X1 and X2 only, then input Y would represent an additional input. RA may issue Advance Authorisations and such cases need not be referred to Norms Committees for ratification of norms. Application under this scheme shall be made along with a Certificate from Chartered Engineer in the prescribed format.
(ii) A Certificate from a Chartered Engineer who has been not been penalised in the last five years under FT(D&R) Act 1992,Customs Act 1962, Central Excise Act 1944, GST Acts and allied acts and rules made there under shall only be accepted for grant of Authorisation under this scheme.
(iii) Detailed procedure for administering the scheme shall be prescribed in the Handbook of Procedures.
(iv) An exporter (manufacturer or merchant), who holds AEO Certificate under Common Accreditation Programme of CBEC is eligible to opt for this scheme.
(v) A status holder who is a manufacturer cum actual user and holds valid 2-star or above status under para 1.25 of FTP and who has already submitted its application for grant of AEO on CBIC’s AEO portal is also eligible to apply for this scheme subject to following conditions:-
a) Status holder submits copy of numbered and dated acknowledgement of its application for grant of AEO.
b) Status holder undertakes to the DGFT that –
(i) Their application for grant of AEO certification has not yet been rejected;
(ii) There is no case of infringement of Customs and allied laws against the status holder in the current year and last three FYs.
(iii) Status holder has not been issued show cause notice by Customs or GST authorities in the current year and last three FYs.
(iv) Status holder has positive net current assets.
(v) There are no insolvency, bankruptcy or liquidation proceedings taken against the status holder in the current year and last three FYs.
c) If status holder is unable to obtain the AEO certification within 120 days from date of application under this scheme para, the exporter agrees that the facility under this para shall stand withdrawn and he (status holder) will be bound to approach the concerned Norms Committee of DGFT for fixation of norms and to abide by the decision of the said Committee.
d) In case of situation as at (c) above, no further authorisation under this scheme para will be issued.
e) The DGFT may deny authorisation under this scheme para to two star and above status holder based on its risk management principles.
f) Status holder shall be audited by the DGFT as laid down in the Handbook of Procedures.
(vi) The scheme shall not be available for the following export products:
a) All items covered under Chapter-1 to 24 and Chapter-71of ITC(HS) Classification;
b) Biotechnology items and related products; and
c) SCOMET items.
(vii) The scheme shall not be available for the following inputs:
A. All vegetable / edible oils classified under Chapter-15 and all types of oilseeds classified under Chapter-12 of ITC (HS)book;
B. All types of cereals classified under Chapter–10 of ITC (HS) book;
C. Horn, hoof and any other organ of animal;
D. Wild animal products, organs and waste thereof;
E. Honey;
F. All items with basic customs duty of 30% or more;
G. All types of fruits/ nuts/ vegetables classified under Chapter-7 and Chapter-8 of ITC (HS) book;
H. Items covered under heading 2515, 2516, 3301, 3302, 3303, 6801 and 6802 of ITC(HS) Classification;
I. Items covered under Chapter 50 to 63 of ITC(HS) classification.
J. Acetic Anhydride, Ephedrine and Pseudoephedrine;
K. Vitamins;
L. Biotechnology items and related products;
M. Insecticides, Rodenticides, Fungicides, Herbicides, Anti sprouting products, and plant growth regulators, disinfectants and similar products of all forms, types and grades;
N. Waste/Scrap of all types; and
O. Second hand goods.
(viii) Inputs imported shall be subject to pre import condition and they shall be physically incorporated in the export product (making normal allowance for wastage). In case of local procurement under invalidation/ARO, the inputs shall be procured prior to manufacture of export item and shall be physically incorporated in the export product.
(ix) Wherever value of by-products and recoverable wastage generated during manufacturing process is more than 5% of CIF value, corresponding quantity of main input shall be reduced from the entitlement to the extent that value of disallowed quantity is equal to the value of by-products and recoverable wastage generated during manufacturing process.
(x) Concerned Norms Committee may conduct audit of the manufacturer. The frequency and manner of audit shall be prescribed by DGFT in Handbook of Procedures. The manufacturer shall be required to provide the necessary facility to verify the books of account/other documents as required, give information and assistance for timely completion of the audit. Non-availability of production and consumption documents/data shall be treated as misdeclaration and indulgence in fraudulent activities and shall be penalised under FT(D&R) Act, as amended and rules made there under.
(xi) Concerned Norms Committee may initiate special audit, considering the nature and complexity of the case and revenue of government, if he is of the opinion at any stage of scrutiny/enquiry/investigation that the norms have not been claimed correctly or the excess benefit has been availed. Special audit can be conducted even if the manufacturer has already been audited before.
(xii) If the audit results in detection of mis-declaration and/ or instances of claiming of inputs which are not used in manufacturing process or excess quantity of inputs than consumed, demand and recovery actions will be initiated in addition to initiation of action against the authorisation holder, manufacturer and Chartered Engineer in terms of Foreign Trade Development and Regulation Act 1992 and/or Customs Act 1962, as amended and rules made there under.
(xiii) In cases where Chartered Engineer has not exercised due diligence or has willfully become party to mis-declaration action will be initiated under against such person under FT(D&R) Act 1992, as amended and rules made there under. In addition, such cases shall also be referred to ‘The Institute of Engineers India’ for taking action as warranted under the bylaws of the institute.
(xiv) All the provisions applicable for Advance Authorisation Scheme shall be applicable to this scheme also in so far they are not inconsistent with this scheme.
4.07 Advance Authorisation for Annual Requirement and Eligibility Condition
(i) Advance Authorisation for Annual Requirement shall only be issued for items notified in Standard Input Output Norms (SION). And it shall not be available in case of adhoc norms under paragraph 4.03 (b) (ii) of FTP.
(ii) Advance Authorisation for Annual Requirement shall also not be available in respect of SION where any item of input appears in Appendix 4-J.
(iii) Exporters having past export performance (in at least preceding two financial years) shall be entitled for Advance Authorisation for Annual requirement.
(iv) Entitlement in terms of CIF value of imports shall be upto 300% of the FOB value of physical export and / or FOR value of deemed export in preceding financial year or Rs 1 Crore, whichever is higher.
4.08 Value Addition
Value Addition for the purpose of this Chapter (except for Gems and Jewellery sector for which value addition is prescribed in paragraph 4.37 of FTP) shall be:-
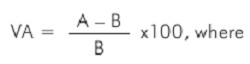 A =FOB value of export realized/FOR value of supply received.
A =FOB value of export realized/FOR value of supply received.
Duty Exemption / Remission Schemes
B =CIF value of inputs covered by Authorisation, plus value of any other input used on which benefit of DBK is claimed or intended to be claimed.
4.09 Minimum Value Addition
(i) Minimum value addition required to be achieved under Advance Authorisation is 15%.
(ii) Export Products where value addition could be less than 15% are given in Appendix 4D.
(iii) Minimum value addition for Gems & Jewellery Sector is given in paragraph 4.60 of Handbook of Procedures.
(iv) In case of Tea, minimum value addition shall be 50%.
(v) In case of spices, minimum value addition shall be 25%.
4.10 Import of Mandatory Spares
Import of mandatory spares which are required to be exported / supplied with the resultant product shall be permitted duty free to the extent of 10% of CIF value of Authorisation.
4.11 Ineligible categories of import on Self Declaration basis
(a) Import of following products shall not be permissible on self-declaration basis:
i. All vegetable / edible oils classified under Chapter- 15 and all types of oilseeds classified under Chapter- 12 of ITC (HS) book;
ii. All types of cereals classified under Chapter–10 of ITC (HS) book;
iii. All Spices other than light black pepper (light berries) having a basic customs duty of more than 30%, classified under Chapter-9 and 12 of ITC (HS)book;
iv. All types of fruits/ vegetables having a basic customs duty of more than 30%, classified under Chapter-7 and Chapter-8 of ITC(HS) book;
v. Horn, Hoof and any other organ of animal;
vi. Honey;
vii. Rough Marble Blocks/Slabs;
viii. Rough Granite;
ix. Vitamins except for use in pharmaceutical industry; and
x. All items with a basic custom duty of more than 30%.
(b) For export of perfumes, perfumery compounds and various feed ingredients containing vitamins, no Authorisation shall be issued by Regional Authority under paragraph 4.07 of Handbook of Procedures and applicants shall be required to apply under paragraph 4.06 of Hand Book of Procedures to the Norms Committee.
(c) Where export and/or import of biotechnology items and related products are involved, Authorisation under paragraph 4.07 of Handbook of Procedures shall be issued by Regional Authority only on submission of a “No Objection Certificate” from Department of Biotechnology.
4.12 Accounting of Input
(i) Wherever SION permits use of either (a) a generic input or (b) alternative input, unless the name of the specific input together with quantity [which has been used in manufacturing the export product] gets indicated / endorsed in the relevant shipping bill and these inputs, so endorsed, within quantity specified and match the description in the relevant bill of entry, the concerned Authorisation will not be redeemed. In other words, the name/description of the input used (or to be used) in the Authorisation must match exactly with the name/description endorsed in the shipping bill.
(ii) In addition, if in any SION, a single quantity has been indicated against a number of inputs (more than one input), then quantities of such inputs to be permitted for import shall be in proportion to the quantity of these inputs actually used/consumed in production, within overall quantity against such group of inputs. Proportion of these inputs actually used/consumed in production of export product shall be clearly indicated in shipping bills.
(iii) At the time of discharge of export obligation (issue of EODC) or at the time of redemption, Regional Authority shall allow only those inputs which have been specifically indicated in the shipping bill together with quantity.
(iv) The above provisions will also be applicable for supplies to SEZs and supplies made under Deemed exports. Details as given above will have to be indicated in the relevant Bill of Export, ARE-3, Central
4.13 Pre-import condition in certain cases
i. DGFT may, by Notification, impose pre-import condition for inputs under this Chapter.
ii. Import items subject to pre-import condition are listed in Appendix 4-J or will be as indicated in Standard Input Output Norms (SION).
4.14 Details of Duties exempted
Imports under Advance Authorisation are exempted from payment of Basic Customs Duty, Additional Customs Duty, Education Cess, Anti- dumping Duty, Countervailing Duty, Safeguard Duty, Transition Product Specific Safeguard Duty, wherever applicable. Import against supplies covered under paragraph 7.02 (c) & (f) of FTP will not be exempted from payment of applicable Anti-dumping Duty, Countervailing Duty, Safeguard Duty and Transition Product Specific Safeguard Duty, if any. However, imports under Advance Authorisation for physical as well as deemed exports are also exempt from whole of the Integrated Tax and Compensation Cess leviable under sub-section (7) and sub-section (9) respectively, of section 3 of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 (51 of 1975).
4.15 Admissibility of Drawback
Drawback as per rate determined and fixed by Customs authority in terms of DoR Rules shall be available for duty paid imported or indigenous inputs (not specified in the norms) used in the export product. For this purpose, applicant shall indicate clearly details of duty paid input in the application for Advance Authorisation. As per details mentioned in the application, Regional Authority shall also clearly endorse details of such duty paid inputs in the condition sheet of the Advance Authorisation.
4.16 Actual User Condition for Advance Authorisation
i. Advance Authorisation and / or material imported under Advance Authorisation shall be subject to ‘Actual User’ condition. The same shall not be transferable even after completion of export obligation. However, Authorisation holder will have option to dispose of product manufactured out of duty free input once export obligation is completed.
ii. In case where CENVAT/input tax credit facility on input has been availed for the exported goods, even after completion of export obligation, the goods imported against such Advance Authorisation shall be utilized only in the manufacture of dutiable goods whether within the same factory or outside (by a supporting manufacturer). For this, the Authorisation holder shall produce a certificate from Chartered Accountant at the time of filing application for Export Obligation Discharge Certificate to Regional Authority concerned. An AEO having valid certificate has the option to produce self declaration to this effect.
iii. Waste / Scrap arising out of manufacturing process, as allowed, can be disposed off on payment of applicable duty even before fulfillment of export obligation.
4.17 Validity Period for Import and its Extension
Validity period for import under Advance Authorisation shall be as prescribed in Handbook of Procedures.
4.18 Importability / Exportability of items that are Prohibited/ Restricted / STE
i. No export or import of an item shall be allowed under Advance Authorisation / DFIA if the item is prohibited for exports or imports respectively. Export of a prohibited item may be allowed under Advance Authorisation provided it is separately so notified, subject to the conditions given therein.
ii. Items reserved for imports by STEs cannot be imported against Advance Authorisation / DFIA. However, those items can be procured from STEs against ARO or Invalidation letter. STEs are also allowed to sell goods on High Sea Sale basis to holders of Advance Authorisation / DFIA holder. STEs are also permitted to issue “No Objection Certificate (NOC)” for import by Advance Authorisation / DFIA holder and may charge a reasonable fee subject to a maximum of ₹5000 from the applicant.
iii. Items reserved for export by STE can be exported under Advance Authorisation / DFIA only after obtaining a ‘No Objection Certificate’ from the concerned STE.
iv. Import of restricted items shall be allowed under Advance Authorisation/DFIA unless specifically disallowed.
v. Export of restricted / SCOMET items however, shall be Duty Exemption / Remission Schemes subject to all conditionalities or requirements of export authorisation or permission, as may be required, under Schedule 2 of ITC (HS).
4.19 Free of Cost Supply by Foreign Buyer
Advance Authorisation shall also be available where some or all inputs are supplied free of cost to exporter by foreign buyer. In such cases, notional value of free of cost input shall be added in the CIF value of import and FOB value of export for the purpose of computation of value addition. However, realization of export proceeds will be equivalent to an amount excluding notional value of such input.
4.20 Domestic Sourcing of Inputs
i. Holder of an Advance Authorisation / Duty Free Import Authorisation can procure inputs from indigenous supplier/ State Trading Enterprise/EOU/EHTP/BTP/ STP in lieu of direct import. Such procurement can be against Advance Release Order (ARO), or Invalidation Letter.
ii. When domestic supplier intends to obtain duty free material for inputs through Advance Authorisation for supplying resultant product to another Advance Authorisation / DFIA /EPCG Authorisation, Regional Authority shall issue Invalidation Letter.
iii. Regional Authority shall issue Advance Release Order if the domestic supplier intends to seek refund of duties exempted through Deemed Exports mechanism as per provisions under Chapter-7 of FTP.
iv. Regional Authority may issue Advance Release Order or Invalidation Letter at the time of issue of Authorisation simultaneously or subsequently.
v. Advance Authorisation holder under DTA can procure inputs from / SEZ units against Certificate of supply till EDI message system between SEZ and Customs is enabled.
vi. Validity of Advance Release Order / Invalidation Letter shall be co- terminous with validity of Authorisation.
4.21 Currency for Realisation of Export Proceeds.
i. Export proceeds shall be realized in freely convertible currency or in Indian Rupees as per para 2.53 of FTP, except otherwise specified. Provisions regarding realisation and non-realisation of export proceeds are given in paragraph 2.52, 2.53 and 2.54 of FTP.
ii. Export to SEZ Units shall be taken into account for discharge of export obligation provided payment is realised from Foreign Currency Account of the SEZ unit.
iii. Export to SEZ Developers / Co-developers can also be taken into account for discharge of export obligation even if payment is realised in Indian Rupees.
iv. Authorisation holder needs to file Bill of Export for export to SEZ unit/ developer / co-developer in accordance with the procedures given in SEZ Rules, 2006.
4.22 Export Obligation Period and its Extension
Period for fulfillment of export obligation and its extension under Advance Authorisation shall be as prescribed in Handbook of Procedures.
4.23 Re-import of exported goods under Duty Exemption/ Remission Scheme
Goods exported under Advance Authorisation/ Duty Free Import Authorisation may be re-imported in same or substantially same form subject to such conditions as may be specified by Department of Revenue. Authorisation holder shall also inform about such re- importation to the Regional Authority which had issued the Authorisation within one month from date of re-import.
DUTY FREE IMPORT AUTHORISATION SCHEME (DFIA)
4.24 DFIA Scheme
(a) Duty Free Import Authorisation is issued to allow duty free import of inputs. In addition, import of oil and catalyst which is consumed/ utilised in the process of production of export product, may also be allowed.
(b) Provisions of paragraphs 4.12, 4.18, 4.20, 4.21 and 4.23 of FTP shall be applicable to DFIA also.
(c) Import of Tyre under DFIA scheme is not allowed.
4.25 Duties Exempted
i. Duty Free Import Authorisation shall be exempted only from payment of Basic Customs Duty (BCD).
ii. Drawback as per rate determined and fixed by Customs authority shall be available for duty paid inputs, whether imported or indigenous, used in the export product. However, in case such drawback is claimed for inputs not specified in SION, the applicant should have indicated clearly details of such duty paid inputs also in the application for Duty Free Import Authorisation, and as per the details mentioned in the application, the Regional Authority should also have clearly endorsed details of such duty paid inputs in the condition sheet of the Duty Free Import Authorisation.
4.26 Eligibility
i. Duty Free Import Authorisation shall be issued on post export basis for products for which Standard Input Output Norms have been notified.
ii. Merchant Exporter shall be required to mention name and address of supporting manufacturer of the export product on the export document viz. Shipping Bill/ Bill of Export / Tax Invoice for export prescribed under the GST rules.
iii. Application is to be filed with concerned Regional Authority before effecting export under Duty Free Import Authorisation.
iv. No Duty Free Import Authorisation shall be issued for an input which is subjected to pre-import condition or where SION prescribes ‘Actual User’ condition or Appendix-4J prescribes pre import condition for such an input.
4.27 Minimum Value Addition
Minimum value addition of 20% shall be required to be achieved.
4.28 Validity &Transferability of DFIA
(i) Applicant shall file online application to Regional Authority concerned before starting export under DFIA.
(ii) Export shall be completed within 12 months from the date of online filing of application and generation of file number.
(iii) While doing export/supply, applicant shall indicate file number on the export /supply documents viz. Shipping Bill / Bill of Export / Tax invoice for supply prescribed under GST rules.
(iv) In terms of Para 4.12 of FTP, Wherever SION permits use of either (a) a generic input or (b) alternative input, the specific input together with quantity [which has been used in manufacturing the export product] should be indicated / endorsed in the relevant Shipping Bill/ Bill of Export / Tax invoice for supply prescribed under GST rules. Only such inputs may be permitted for import in the authorisation in proportion to the quantity of these inputs actually used/consumed in production, within overall quantity against such generic input/alternative input.
(v) In addition, if in any SION, a single quantity has been indicated against a number of inputs (more than one input), then quantities of such inputs to be permitted for import shall be in proportion to the quantity of these inputs actually used/consumed in production and declared in Shipping Bill / Bill of Export / Tax invoice for supply prescribed under GST rules within overall quantity against such group of inputs. Proportion of these inputs actually used/consumed in production of export product shall be clearly indicated in Shipping Bill / Bill of Export / Tax invoice for supply prescribed under GST rules.
(iv) Separate DFIA shall be issued for each SION.
(v) Exports under DFIA shall be made from any port listed in Para 4.35 of Handbook of Procedures. However, separate application shall be made for EDI and non-EDI ports. In case export is made from a non-EDI port, separate application shall be made for each non-EDI port.
(vi) Regional Authority shall issue transferable DFIA with a validity of 12 months from the date of issue. No further revalidation shall be granted by Regional Authority.
4.29 Sensitive Items under Duty Free Import Authorisation
(a) In respect of following inputs, exporter shall be required to provide declaration with regard to technical characteristics, quality and specification in Shipping Bill:
“Alloy steel including Stainless Steel, Copper Alloy, Synthetic Rubber, Bearings, Solvent, Perfumes/ Essential Oil/ Aromatic Chemicals, Surfactants, Relevant Fabrics, Marble, Articles made of Polypropylene, Articles made of Paper and Paper Board, Insecticides, Lead Ingots, Zinc Ingots, Citric Acid, Relevant Glass fibre reinforcement (Glass fibre, Chopped / Stranded Mat, Roving Woven Surfacing Mat), Relevant Synthetic Resin (unsaturated Polyester Resin, Epoxy Resin, Vinyl Ester Resin, Hydroxy Ethyl Cellulose), Lining Material”.
(b) While issuing Duty Free Import Authorisation, Regional Authority shall mention technical characteristics, quality and specification in respect of above inputs in the Authorisation.
SCHEMES FOR EXPORTERS OF GEMS AND JEWELLERY
4.30 Import of Input
Exporters of Gems and Jewellery can import / procure duty free (excluding Integrated Tax and Compensation Cess leviable under Section 3(7) and 3(9) of Customs Tariff Act) input for manufacture of export product.
4.31 Items of Export
(i) “Gold jewellery, including partly processed jewellery, and articles including medallions and coins (excluding legal tender coins), whether plain or studded, containing gold of 8 carats and above up to a maximum limit of 22 carats.
Gold religious idols (only gods and goddess) of 8 carats and above (up to 24 carats) subject to the following conditions:
i) Exports would be subject to 100% examination by the Approved Government Valuer.
ii) Foreign remittance has to be realized within a period of 3 months from the date of export.
iii) Exporters must submit confirmed export order before effecting export.
iv) Distinction must be made between a religious idol and simply moulded gold article/idol.
v) Exports may be allowed only be actual manufactures of such idols.
The findings like posts, push backs, locks which help in collating the jewellery pieces together, containing gold of 3 carats and above up to a maximum limit of 22 carats.
(ii) Silver jewellery including partly processed jewellery, silverware, silver strips and articles including medallions and coins (excluding legal tender coins and any engineering goods) containing more than 50% silver by weight;
(iii) Platinum jewellery including partly processed jewellery
4.32 Schemes
The schemes are as follows:
(i) Advance Procurement/ Replenishment of Precious Metals from Nominated Agencies;
(ii) Replenishment Authorisation for Gems;
(iii) Replenishment Authorisation for Consumables;
(iv) Advance Authorisation for Precious Metals.
4.33 Advance Procurement/ Replenishment of Precious Metals from Nominated Agencies
(i) Exporter of gold / silver / platinum jewellery and articles thereof including mountings and findings may obtain gold/ silver / platinum as an input for export product from Nominated Agency, in advance or as replenishment after export in accordance with the procedure specified in this behalf. Replenishment of gold/silver/platinum will be subject to Customs notification No. 57/2000-Customs dated 08.05.2000, as amended.
(ii) The export would be subject to wastage norms and minimum value addition as prescribed in paragraph 4.59 and 4.60 respectively in the Handbook of Procedures.
4.34 Replenishment Authorisation for Gems
(i) Exporter may obtain Replenishment Authorisation for Gems from Regional Authority in accordance with procedure specified in Handbook of Procedures as per the replenishment rate prescribed in Appendix 4F. Replenishment Authorisation for Gems shall be freely transferable.
(ii) Replenishment Authorisation for Gems may be issued against export including that made against supply by Nominated Agency (paragraph 4.40 of FTP) and against supply by foreign buyer (paragraph 4.44 of FTP).
(iii) In the case of studded gold/silver/platinum jewellery and articles thereof, the value of Gem Replenishment Authorisation shall be on the remaining FOB value of exports after deducting the value of gold/ silver/ platinum including admissible wastage. The scale of replenishment and the item of import will be as prescribed in Appendix 4G.
4.35 Replenishment Authorisation for Consumables
(i) Replenishment Authorisation for duty free (excluding Integrated Tax and Compensation Cess leviable under Section 3(7) and 3(9) of Customs Tariff Act) import of Consumables, Tools and other items namely, Tags and labels, Security censor on card, Staple wire, Poly bag (as notified by Customs) for Jewellery made out of precious metals (other than Gold & Platinum) equal to 2% and for Cut and Polished Diamonds and Jewellery made out of Gold and Platinum equal to 1% of FOB value of exports of the preceding year, may be issued on production of Chartered Accountant Certificate indicating the export performance. However, in case of Rhodium finished Silver jewellery, entitlement will be 3% of FOB value of exports of such jewellery. This Authorisation shall be non- transferable and subject to actual user condition.
(ii) Application for import of consumables as given above shall be filed online to the concerned Regional Authority in ANF 4H.
4.36 Advance Authorisation for Precious Metals
(a) Advance Authorisation shall be granted on pre-import basis with ‘Actual User’ condition for duty free (excluding Integrated Tax and Compensation Cess leviable under Section 3(7) and 3(9) of Customs Tariff Act) import of:
(i) Gold of fineness not less than 0.995 and mountings, sockets, frames and findings of 8 carats and above;
(ii) Silver of fineness not less than 0.995 and mountings, sockets, frames and findings containing more than 50% silver by weight;
(iii) Platinum of fineness not less than 0.900 and mountings, sockets, frames and findings containing more than 50% platinum by weight.
(b) Advance Authorisation shall carry an export obligation which shall be fulfilled as per procedure indicated in Chapter 4 of Handbook of Procedures.
(c) Value Addition shall be as per paragraph 4.37 of FTP and 4.60 of Handbook of Procedures.
(d) Advance Authorisation Scheme is not available where the item of export is ‘Gold Medallions and Coins’ or ‘Gold jewellery/articles manufactured by fully mechanized process’.
4.37 Value Addition
Minimum Value Addition norms for gems and jewellery sector are given in paragraph 4.60 of Handbook of Procedures. It would be calculated as under:
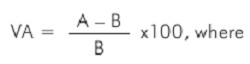 A = FOB value of the export realised/ FOR value of supply received.
A = FOB value of the export realised/ FOR value of supply received.
B= Value of inputs (including domestically procured) such as gold/silver/platinum content in export product plus admissible wastage along with value of other items such as gemstone etc. Wherever gold has been obtained on loan basis, value shall also include interest paid in free foreign exchange to foreign supplier.
4.38 Wastage Norms
Wastage or manufacturing loss for gold/silver/platinum jewellery shall be admissible as per paragraph 4.59 of Handbook of Procedures.
4.39 DFIA not available
Duty Free Import Authorisation scheme shall not be available for Gems and Jewellery sector.
4.40 Nominated Agencies
(i) Exporters may obtain gold / silver / platinum from Nominated Agency. Exporter in EOU and units in SEZ would be governed by the respective provisions of Chapter-6 of FTP / SEZ Rules, respectively.
(ii) Nominated Agencies are The Handicraft and Handlooms Exports Corporation of India Ltd, MSTC Ltd., and Diamond India Limited.
(iii) Reserve Bank of India can authorize any bank as Nominated Agency.
(iv) Procedure for import of precious metal by Nominated Agencies shall be as per the provisions laid down in HBP. The procedure for import of precious metals by the Gems & Jewellery units operating under EOU & SEZ schemes will be as per the applicable schemes.
The monitoring mechanism for the Nominated Agencies (other than banks authorised by RBI) shall be as per para 4.93 of HBP.
(v) A bank authorised by Reserve Bank of India is allowed export of gold scrap for refining and import standard gold bars as per Reserve Bank of India guidelines.
4.41 Import of Diamonds for Certification / Grading & Re-export
Following agencies are permitted to import diamonds to their laboratories without any import duty, for the purpose of certification / grading reports, with a condition that the same should be re-exported with the certification/grading reports, as per the procedure laid down in Hand Book of Procedures:
(1) Gemological Institute of America (GIA), Mumbai, Maharashtra.
(2) Indian Diamond Institute, Surat, Gujarat, India.
(3) De Beers India Private Ltd., Surat, Gujarat, India.
(4) HRD Diamond Institute Private Limited, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
(5) International Gemological Institute (India) Pvt. Ltd., Bandra Kurla Complex, Mumbai,
(6) Gemological Science International (GSI) Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
4.42 Export of Cut & Polished Diamonds for Certification/ Grading & Re-import
List of authorized laboratories for certification / grading of diamonds of 0.25 carat and above are given in paragraph 4.73 of Handbook of Procedures.
4.43 Export of Cut & Polished Diamonds with Re-import Facility at Zero Duty
An exporter (with annual export turnover of Rs 5 crores for each of the last three years) or the authorized offices/ agencies in India of laboratories mentioned under paragraph 4.73 of Hand Book of Procedures may export cut & polished diamonds (each of 0.25 carat or above) to any of the agencies/laboratories mentioned under paragraph 4.73 of Handbook of Procedures with re-import facility at zero duty within 3 months from the date of export. Such facility of re- import at zero duty will be subject to guidelines issued by Central Board of Customs & Excise, Department of Revenue.
4.44 Export against Supply by Foreign Buyer
(i) Where export orders are placed on nominated agencies / status holder / exporters of three years standing having an annual average turnover of Rupees five crores during preceding three financial years, foreign buyer may supply in advance and free of charge, gold/silver/ platinum, alloys, findings and mountings of gold / silver / platinum for manufacture and export.
(ii) Such supplies can also be in advance and may involve semi- finished jewellery including findings / mountings / components for repairs / re-make and export subject to minimum value addition as prescribed under paragraph 4.60 of Handbook of Procedures. In such cases of export, wastage norms as per paragraph 4.59 of Handbook of Procedures shall apply.
(iii) Exports may be made by nominated agencies directly or through their associates or by status holder / exporter. Import and Export of findings shall be on net to net basis.
4.45 Export Promotion Tours/ Export of Branded Jewellery
(i) Nominated Agencies and their associates, with approval of Department of Commerce and with approval of Gem & Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC), may export gold / silver / platinum jewellery and articles thereof for exhibitions abroad.
(ii) Personal carriage of gold / silver / platinum jewellery, precious, semi-precious stones, beads and articles and export of branded jewellery is also permitted, subject to conditions as in Handbook of Procedures.
4.46 Personal Carriage of Export /Import Parcels
Personal carriage of gems and jewellery export parcels by foreign bound passengers and import parcels by an Indian importer/foreign national may be permitted as per the Handbook of Procedures.
4.47 Export by Post
Export of jewellery through Foreign Post Office including via Speed Post is allowed. The jewellery parcel shall not exceed 20 kgs by weight.
4.48 Private / Public Bonded Warehouse
Private / Public Bonded Warehouses may be set up in SEZ/ DTA for import and re-export of cut and polished diamonds, cut and polished coloured gemstones, uncut & unset precious & semi- precious stones, subject to achievement of minimum value addition of 5% by DTA units.
4.49 Special Notified Zone (SNZ)
Import, auction/sale and re-export of rough diamonds by entities, as notified vide RBI Notification 116 of 1st April, 2014, as amended from time to time, on consignment or outright basis, will be permitted in Special Notified Zone (SNZ) administered by the operator of SNZ, under supervision of Customs. The procedure of import, auction/ sale and re- export of rough diamonds (unsold) would be as specified by CBIC.
4.50 Diamond & Jewellery Dollar Accounts
(a) Firms and companies dealing in purchase / sale of rough or cut and polished diamonds / precious metal jewellery plain, minakari and / or studded with / without diamond and / or other stones with a track record of at least three years in import or export of diamonds / coloured gemstones / diamond and coloured gemstones studded jewellery / plain gold jewellery and having an average annual turnover of Rs. 3 crore or above during preceding three licensing years may also carry out their business through designated Diamond Dollar Accounts(DDA).
(b) Dollars in such accounts available from bank finance and / or export proceeds shall be used only for:
(i) Import / purchase of rough diamonds from overseas/ local sources;
(ii) Purchase of cut and polished diamonds, coloured gemstones and plain gold jewellery from local sources;
(vii) Import / purchase of gold from overseas / nominated agencies and repayment of dollar loans from the bank; and
(iii) Transfer to Rupee Account of exporter. Details of this DDA Scheme are given in Handbook of Procedures.
(c) A non DDA holder is also permitted to supply cut and polished diamonds to DDA holder, receive payment in dollars and convert the same into Rupees within 7 days. Cut and polished diamonds and coloured gemstones so supplied by non-DDA holder will also be counted towards discharge of his export obligation and/ or entitle him to replenishment Authorisation.
4.51 Export of cut & polished precious and semi-precious stones for treatment and re-import
Gems and Jewellery exporters shall be allowed to export cut and polished precious and semi-precious stones for the treatment and re- import as per customs rules and regulations. In case of re-export, the exporter shall be entitled for duty drawback as per rules.
4.52 Re-import of rejected Jewellery
Gems & Jewellery exporters shall be allowed to re-import rejected precious metal jewellery as per paragraph 4.90 of Handbook of Procedures.
4.53 Export and import on consignment basis
Gems & Jewellery exporters shall be allowed to export and import diamond, gemstones & jewellery on consignment basis as per Handbook of Procedures and Customs Rules and Regulations.
SCHEME FOR REMISSION OF DUTIES AND TAXES ON EXPORTED PRODUCTS
4.54 Scheme Objective and Operating Principles
i. The Scheme’s objective is to refund, currently un-refunded:
a. Duties/ taxes / levies, at the Central, State and local level, borne on the exported product, including prior stage cumulative indirect taxes on goods and services used in the production of the exported product and
b. Such indirect Duties/ taxes / levies in respect of distribution of exported product.
ii. The rebate under the Scheme shall not be available in respect of duties and taxes already exempted or remitted or credited.
iii. The determination of ceiling rates under the Scheme will be done by a Committee in the Department of Revenue/Drawback Division with suitable representation of the DoC/DGFT, line ministries and experts, on the sectors prioritized by Department of Commerce and Department of Revenue.
iv. The overall budget/outlay for the RoDTEP Scheme would be finalized by the Ministry of Finance in consultation with Department of Commerce (DoC), taking into account all relevant factors.
v. The Scheme will operate in a Budgetary framework for each financial year and necessary calibrations and revisions shall be made to the Scheme benefits, as and when required, so that the projected remissions for each financial year are managed within the approved Budget of the Scheme. No provision for remission of arrears or contingent liabilities is permissible under the Scheme to be carried over to the next financial year.
vi. The sequence of introduction of the Scheme across sectors, prioritization of the sectors to be covered, degree of benefit to be given on various items within the rates recommended by the Committee and within a ceiling as may be prescribed, on the per item/total overall benefit amount permissible, within the overall budget/ outlay finalized, will be decided and notified by the Department of Commerce (DoC) in consultation with Department of Revenue.
vii. Under the Scheme, a rebate would be granted to eligible exporters at a notified rate as a percentage of FOB value with a value cap per unit of the exported product, wherever required, on export of items which are categorized under the notified 8 digit HS Code. However, for certain export items, a fixed quantum of rebate amount per unit may also be notified. Rates of rebate / value cap per unit under RoDTEP will be notified in Appendix 4R. In addition to necessary changes which may be brought in view of budget control measures as mentioned above, efforts would be made to review the RoDTEP rates on an annual basis and to notify them well in advance before the beginning of a financial year.
viii. The rebate allowed is subject to the receipt of sale proceeds within time allowed under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 failing which such rebate shall be deemed never to have been allowed. The rebate would not be dependent on the realization of export proceeds at the time of issue of rebate. However, adequate safeguards to avoid any misuse on account of non-realization and other systemic improvements as in operation under Drawback Scheme, IGST and other GST refunds relating to exports would also be applicable for claims made under the RoDTEP Scheme.
ix. Mechanism of Issuance of Rebate: Scheme would be implemented through end to end digitization of issuance of rebate amount in the form of a transferable duty credit/electronic scrip (e-scrip), which will be maintained in an electronic ledger by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC). Necessary rules and procedure regarding grant of RoDTEP claim under the Scheme and implementation issues including manner of application, time period for application and other matters including export realization, export documentation, sampling procedures, record keeping etc. would be notified by the CBIC, Department of Revenue on an IT enabled platform with a view to end to end digitization. Necessary provisions for recovery of rebate amount where foreign exchange is not realized, suspension/withholding of RoDTEP in case of frauds and misuse, as well as imposition of penalty will also be built suitably by CBIC.
x. The Scheme will take effect for exports from 1st January 2021. However for exports made by categories under Para 4.55 (x), (xi) and (xii), the implementation date will be decided later as per provisions of Para 4.55B.
4.55 Ineligible Supplies/ Items/Categories under the Scheme
The following categories of exports/ exporters shall not be eligible for rebate under RoDTEP Scheme:
i. Export of imported goods covered under paragraph 2.46 of FTP.
ii. Exports through trans-shipment, meaning thereby exports that are originating in third country but trans¬shipped through India.
iii. Export products which are subject to Minimum export price or export duty.
iv. Products which are restricted for export under Schedule-2 of Export Policy in ITC (HS).
v. Products which are prohibited for export under Schedule-2 of Export Policy in ITC (HS).
vi. Deemed Exports.
vii. Supplies of products manufactured by DTA units to SEZ/FTWZ units.
viii. Products manufactured in EHTP and BTP.
ix. Products manufactured partly or wholly in a warehouse under section 65 of the Customs Act, 1962 (52 of 1962).
x. Products manufactured or exported in discharge of export obligation against an Advance Authorisation or Duty Free Import Authorization or Special Advance Authorisation issued under a duty exemption scheme of relevant Foreign Trade Policy.
xi. Products manufactured or exported by a unit licensed as hundred per cent Export Oriented Unit (EOU) in terms of the provisions of the Foreign Trade Policy.
xii. Products manufactured or exported by any of the units situated in Free Trade Zones or Export Processing Zones or Special Economic Zones.
xiii. Products manufactured or exported availing the benefit of the Notification No. 32/1997-Customs dated 1st April, 1997.
xiv. Exports for which electronic documentation in ICEGATE EDI has not been generated/ Exports from non-EDI ports.
xv. Goods which have been taken into use after manufacture.
4.55 A Government, however, reserves the right to modify any of the categories as mentioned above for inclusion or exclusion under the scope of RoDTEP, at a later date.
4.55 B Inclusion of exports made by categories mentioned in para 4.55 (x), (xi) and (xii) above and RoDTEP rates for export items under such categories would be decided based on the recommendations of the RoDTEP Committee.
4.56 Nature of Rebate
The e-scrips would be used only for payment of duty of Customs leviable under the First Schedule to the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 viz. Basic Customs Duty.
4.57 Monitoring, Audit and Risk Management System:
For the purposes of audit and verification, the exporter would be required to keep records substantiating claims made under the Scheme. A monitoring and audit mechanism with an IT based Risk Management System (RMS) would be put in place by the CBIC, Department of Revenue to physically verify the records of the exporters on sample basis. Sample cases for physical verification will be drawn objectively by the RMS, based on risk and other relevant parameters.
4.57A For a broad level monitoring, an Output
Outcome framework will be maintained and monitored at regular intervals.
4.58 Residual Issues
Residual issues related to the Scheme arising subsequently shall be considered by an Inter-Ministerial Committee, named as “RODTEP Policy Committee (RPC)” chaired by DGFT (comprising members of Department of Commerce and Department of Revenue), whose decisions would be binding.
4.59 The Appendix 4R containing the eligible RoDTEP export items, rates and per unit value caps, wherever applicable is available at the DGFT portal www.dgft.gov.in under the link ‘Regulatory Updates >RoDTEP’.
Chapter 5
Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) Scheme
5.00 Objective
The objective of the EPCG Scheme is to facilitate import of capital goods for producing quality goods and services and enhance India’s manufacturing competitiveness.
5.01 EPCG Scheme
(a) EPCG Scheme allows import of capital goods (except those specified in negative list in Appendix 5 F) for pre-production, production and post-production at zero customs duty. Capital goods imported under EPCG Authorisation for physical exports are also exempt from IGST and Compensation Cess, leviable thereon under the subsection (7) and subsection (9) respectively, of section 3 of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 (51 of 1975), as provided in the notification issued by Department of Revenue. Alternatively, the Authorisation holder may also procure Capital Goods from indigenous sources in accordance with provisions of paragraph 5.07 of FTP. Capital goods for the purpose of the EPCG scheme shall include:
(i) Capital Goods as defined in Chapter 11 including in CKD/SKD condition thereof;
(ii) Computer systems and software which are a part of the Capital Goods being imported;
(iii) Spares, moulds, dies, jigs, fixtures, tools & refractories; and
(iv) Catalysts for initial charge plus one subsequent charge.
(b) Import under EPCG Scheme shall be subject to an Export Obligation (EO) equivalent to 6 times of duties, taxes and cess saved on capital goods, to be fulfilled in 6 years reckoned from date of issue of Authorisation.
(c) Import/procurement under EPCG scheme shall also be subjected to Average Export Obligation (AEO) as given in para 5.04(c) of FTP.
(d) Authorisation shall be valid for import for 24 months from the date of issue of Authorisation. Revalidation of EPCG Authorisation shall not be permitted.
(e) In case Integrated Tax and Compensation Cess are paid in cash on imports under EPCG, incidence of the said Integrated Tax and Compensation Cess would not be taken for computation of net duty saved provided Input Tax Credit is not availed.
(f) Import of items which are restricted for import shall be permitted under EPCG Scheme only after approval from Exim Facilitation Committee (EFC) at DGFT Headquarters.
(g) If the goods proposed to be exported under EPCG Authorisation are restricted for export, the EPCG Authorisation shall be issued only after approval for issuance of Export Authorisation from Exim Facilitation Committee (EFC) at DGFT Headquarters.
5.02 Coverage
(a) EPCG scheme covers manufacturer exporters with or without supporting manufacturer(s), merchant exporters tied to supporting manufacturer(s) and service providers. Name of supporting manufacturer(s) shall be endorsed on the EPCG Authorisation before installation of the capital goods in the factory / premises of the supporting manufacturer(s). In case of any change in supporting manufacturer(s), the RA shall intimate such change to jurisdictional Customs Authority of existing as well as changed supporting manufacturer(s) and the Customs at port of registration of Authorisation.
(b) Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) Scheme also covers a service provider who is certified as a Common Service Provider (CSP) by the DGFT – HQs, Department of Commerce in a Town of Export Excellence or Prime Minister Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel Parks (PM MITRA) subject to provisions of Foreign Trade Policy/Handbook of Procedures with the following conditions:
(i) Common utility services like providing Electricity, Water, Gas, Sanitation, Sewerage, Telecommunication, Transportation etc. shall not considered for benefit of CSP;
(ii) Export by users of the common service shall be counted towards fulfillment of EO of the CSP provided the EPCG Authorisation details of the CSP is mentioned in the respective Shipping bills and concerned RA must be informed about the details of the users prior to such export;
(iii) Such export will not count towards fulfillment of specific export obligation in respect of other EPCG Authorisations of the user;
(iv) Authorisation holder shall be required to submit Bank Guarantee (BG) which shall be equivalent to the duty saved. BG can be given by CSP or by any one of the users or a combination thereof, at the option of the CSP; and
(v) Capital goods shall be installed within a Town of Export Excellence or PM MITRA.
5.03 Actual User Condition
Imported capital goods shall be subject to Actual User condition till export obligation is completed and Export Obligation Discharge Certificate (EODC) is granted.
5.04 Export obligation
Following conditions shall apply to the fulfillment of Export obligation:-
(a) Export obligation shall be fulfilled by the Authorisation holderthrough export of goods which are manufactured by him or his supporting manufacturer / services rendered by him, for which the EPCG authorisation has been granted.
(b) For export of goods, EPCG Authorisation holder may export either directly or through third party(ies).
(c) EO under the scheme shall be, over and above, the average level of exports achieved by the applicant in the preceding three licensing years for the same and similar products within the overall EO period including extended period, if any; except for categories mentioned in paragraph 5.12(a). Such average would be the arithmetic mean of export performance in the preceding three licensing years for same and similar products. The Average Export Obligation (AEO) shall be fulfilled every financial year, till export obligation is completed. Exports/supplies made over and above AEO shall only be considered for fulfillment of Export Obligation.
(d) In case of indigenous sourcing of Capital Goods, specific EO shall be 25% less than the EO stipulated in Para 5.01. There shall be no change in average EO imposed, if any, as stipulated in Para 5.04(c).
(e) Exports under Advance Authorisation, DFIA, Duty Drawback, RoSCTL and RoDTEP Schemes would also be eligible for fulfilment of EO under EPCG Scheme.
(f) Export obligation may be fulfilled both by physical exports as well as deemed exports. Deemed export supplies shall also be eligible for benefits available under paragraph 7.03 of FTP.
(g) Exports made from DTA units shall only be counted for calculation and/or fulfillment of AEO and/or EO.
(h) EO can also be fulfilled by the supply of ITA-I items to DTA, provided realization is in free foreign exchange.
(i) Royalty payments received by the Authorisation holder in freely convertible currency and foreign exchange received for R&D services shall also be counted for discharge under EPCG.
(j) Payment received in rupee terms for such Services as notified in Appendix 5D shall also be counted towards discharge of export obligation under the EPCG scheme.
(k) Export proceeds realized in Indian Rupees as per para 2.52(d)(ii) are also counted towards fulfillment of export obligation.
(l) Only one benefit specified in paras 5.04(d), 5.09, 5.10 and 5.11 shall be admissible.
(m) Extension of EO period shall be permitted as prescribed in Handbook of Procedures.
5.05 Provision for companies admitted under the provisions of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016
A company holding EPCG authorizations and having been admitted under the provisions of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016 for commencement of insolvency proceedings and in respect of whom the resolution plan has been approved under Section 31 of IBC 2016 by Adjudicating Authority may be permitted to relief, concessions and waivers in accordance with the resolution plan approved/ finalised by Adjudicating Authority/Appellate Authorities as the case may be.
5.06 LUT/Bond/BG in case of Agro units
LUT/Bond or 15% BG, as applicable, may be furnished for EPCG Authorisation granted to units in Agri-Export Zones provided EPCG Authorisation is taken for export of primary agricultural product(s) notified or their value added variants.
5.07 Indigenous Sourcing of Capital Goods and benefits to Domestic Supplier
A person holding an EPCG Authorisation may source capital goods from a domestic manufacturer either through Invalidation Letter or through Advance Release Order. Such domestic manufacturer shall be eligible for deemed export benefits under paragraph 7.03 of FTP, and as may be provided under GST Rules under the category of deemed exports. Such domestic sourcing shall also be permitted from EOUs and these supplies shall be counted for purpose of fulfillment of positive NFE by said EOU as provided in Para 6.08 (a) of FTP.
5.08 Calculation of Export Obligation
In case of direct imports, EO shall be reckoned with reference to actual duty /Taxes/Cess saved amount. In case of domestic sourcing, EO shall be reckoned with reference to notional Customs duty /Taxes/Cess saved on FOR value as indicated in ARO / Invalidation letter.
5.09 Incentive for early EO fulfillment
With a view to accelerating exports, in cases where Authorisation holder has fulfilled 75% or more of specific export obligation and 100% of Average Export Obligation till date, if any, in half or less than half the original export obligation period specified, remaining export obligation shall be condoned and the Authorisation redeemed by RA concerned.
5.10 Reduced EO for Green Technology Products
For exporters of Green Technology Products, Specific EO shall be 75% of EO as stipulated in Para 5.01(b). There shall be no change in average EO imposed, if any, as stipulated in Para 5.04(c). The list of Green Technology Products is given in Para 5.26 of HBP.
5.11 Reduced EO for North East Region and UTs of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
For manufacturing units located in Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh, specific EO shall be 25% of the EO, as stipulated in Para 5.01(b). There shall be no change in average EO imposed, if any, as stipulated in Para 5.04(c).
5.12 Exemption from maintenance of average export obligation
(a) In case of export of goods relating to the following, the EPCG Authorisation holder shall not be required to maintain average export obligation.
(i) Handicrafts, (ii) Handlooms, (iii) Industries covered under Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) (iv) Agriculture (v) Aquaculture (including Fisheries),Pisciculture, (vi) Animal husbandry and Dairying, (vii) Floriculture & Horticulture, (viii) Poultry, (ix) Viticulture, (x) Sericulture, (xi) Carpets, (xii) Coir, and (xiii) Jute
(b) However, this exemption from maintenance of average export obligation shall not be allowed for import of fishing trawlers, boats, ships and other similar items.
(c) Goods, excepting tools imported under EPCG scheme by sectors specified in sub-paragraph (a) above, shall not be allowed to be transferred for a period of five years from date of imports even in cases where export obligation has been fulfilled.
5.13 Transitional Arrangements:
Authorisations issued during various policy periods viz., 2002-07, 2004-09, 2009-14, 2015-20 issued prior to 05.12.2017 and 2015-20 RE 2017 shall be governed by corresponding Foreign Trade Policy provisions and Handbook of Procedures, unless otherwise specifically stated.
Chapter 6
Export Oriented Units (EOUs), Electronics Hardware Technology Parks (EHTPs), Software Technology Parks (STPs) and Bio-Technology Parks (BTPs)
6.00 Introduction and Objective
(a) Units undertaking to export their entire production of goods and services(except permissible sales in DTA), may be set up under the Export Oriented Unit (EOU) Scheme, Electronics Hardware Technology Park (EHTP) Scheme, Software Technology Park(STP) Scheme or Bio-Technology Park (BTP) Scheme for manufacture of goods, including repair, re-making, reconditioning, re- engineering, rendering of services, development of software, agriculture including agro-processing, aquaculture, animal husbandry, bio-technology, floriculture, horticulture, pisciculture, viticulture, poultry and sericulture. Trading units are not covered under these schemes.
(b) Objectives of these schemes are to promote exports, enhance foreign exchange earnings, attract investment for export production and employment generation.
6.01 Export and Import of Goods
(a) An EOU / EHTP / STP / BTP unit may export all kinds of goods and services except items that are prohibited in ITC (HS). However export of gold jewellery, including partly processed jewellery, whether plain or studded, and articles, containing gold of 8 carats and above up to a maximum limit of 22 carats only shall be permitted. The export of findings like posts, push backs, locks which help in collating the jewellery pieces together, containing gold of 3 carats and above up to a maximum limit of 22 carats only shall be allowed.
(b) Export of Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies (SCOMET) shall be subject to fulfillment of conditions contained in the Chapter 10 of the FTP (new Chapter for SCOMET). In respect of an EOU, permission to export prohibited item(s) may be considered by BOA on a case to case basis, provided the input(s) used for the export item(s) is/are imported and there is no procurement of such inputs from DTA.
(c) Procurement and supply of export promotion material like brochure/literature, pamphlets, hoardings, catalogues, posters etc. upto a maximum value limit of 1.5% of FOB value of previous year’s exports shall also be allowed.
(d) (i) An EOU / EHTP/ STP/ BTP unit may import and / or procure, from DTA or bonded warehouses in DTA / international exhibition held in India, all types of goods, including capital goods, required for its activities, provided they are not prohibited items of import in the ITC (HS) subject to conditions given at para (ii) & (iii) below. Any permission required for import under any other law shall be applicable. Units shall also be permitted to import goods including capital goods required for approved activity, free of cost or on loan / lease from clients. Import of capital goods will be on a self-certification basis. Goods imported by a unit shall be with actual user condition and shall be utilized for export production.
(ii) The imports and/ or procurement from bonded warehouse in DTA or from international exhibition held in India shall be without payment of duty of customs leviable thereon under the First Schedule to the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 and additional duty, if any, leviable thereon under Section 3(1), 3(3) and 3(5) of the said Customs Tariff Act. Such imports and/ or procurements shall be made without payment of integrated tax and compensation cess leviable thereon under section 3(7) and 3(9) of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 as per notification issued by the Department of Revenue.
(iii) The procurement of goods covered under GST from DTA would be on payment of applicable GST and compensation cess. The refund of GST paid on such supply from DTA to EOU would be available to the supplier subject to such conditions and documentations as specified under GST rules and notifications issued there under. EOUs can also procure excisable goods falling under the Fourth Schedule of Central Excise Act, 1944 from DTA without payment of applicable duty of excise.
(e) State Trading regime shall not apply to EOU manufacturing units. However, in respect of Chrome Ore/Chrome concentrate, State Trading Regime as stipulated in export policy of these items will be applicable to EOUs.
(f) EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP units may import/procure from DTA, with or without payment of duties/taxes as provided at Para 6.01 (d) (ii) and 6.01(d) (iii) above, certain specified goods for creating a central facility. Software EOU/DTA units may use such facility for export of software.
(g) An EOU engaged in agriculture, animal husbandry, aquaculture, floriculture, horticulture, pisciculture, viticulture, poultry or sericulture may be permitted to remove specified goods in connection with its activities for use outside the premises of the unit.
(h) Gems and jewellery EOUs may source gold / silver / platinum through nominated agencies on loan / outright purchase basis. Units obtaining gold / silver / platinum from nominated agencies, either on loan basis or outright purchase basis shall export gold / silver / platinum within 90 days from date of release of such metals by the nominated agencies.
(i) EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP units, other than service units, may export to Russian Federation in Indian Rupees against repayment of State Credit/ Escrow Rupee Account of buyer subject to RBI clearance, if any.
(j) Procurement and export of spares / components, upto 5% of FOB value of exports, may be allowed to same consignee / buyer of the export article, subject to the condition that it shall not count for NFE and direct tax benefits.
(k) Development Commissioner /Designated Officer in EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP units may allow, on a case to case basis, EOU / EHTP / STP/ BTP units in sectors other than Gems & Jewellery, for consolidation of goods related to manufactured articles and export thereof along with manufactured article. Such goods may be allowed to be imported / procured from DTA by EOU with or without payment of duty and/ or taxes as provided at Para 6.01(d) (ii) and (iii) above, as the case may be to the extent of 5% FOB value of such manufactured articles exported by the unit in preceding financial year. Details of procured / imported goods and articles manufactured by the EOU will be listed separately in the export documents. In such cases, value of procured / imported goods will not be taken into account for calculation of NFE and DTA sale entitlement. Such procured / imported goods Export Oriented Units (EOUs), Electronics Hardware Technology Parks (EHTPs), Software Technology Parks (STPs) and Bio-Technology Parks (BTPs) shall not be allowed to be sold in DTA. Development Commissioner /Designated Officer may also specify any other conditions.
6.02 Second hand Capital Goods
Second hand capital goods, without any age limit, may also be imported with or without payment of duty/ taxes as provided under Para 6.01(d)(ii) above.
6.03 Leasing of Capital Goods
(a) An EOU / EHTP/STP/BTP unit may, on the basis of a firm contract between parties, source capital goods from a domestic / foreign leasing company with or without payment of duties/taxes as provided at Para 6.01 (d) (ii) and (iii) above, as the case may be in such a case, EOU / EHTP/STP/BTP unit and domestic / foreign leasing company shall jointly file documents to enable import/ procurement of capital goods.
(b) An EOU/ EHTP/STP/BTP unit may sell capital goods and lease back the same from a Non Banking Financial Company (NBFC), subject to the following conditions:
(i) The unit should obtain permission from the jurisdictional Deputy/Assistant Commissioner of Customs for entering into transaction of ‘Sale and Lease Back of Assets’, and submit full details of the goods to be sold and leased back and the details of NBFC;
(ii) The goods sold and leased back shall not be removed from the unit’s premises;
(iii) The unit should be NFE positive at the time when it enters into sale and lease back transaction with NBFC;
(iv) A joint undertaking by the unit and NBFC should be given to pay duty on goods in case of violation or contravention of any provision of the notification under which these goods were imported or procured, read with Customs Act, 1962 or Central Excise Act, 1944, and that the lien on the goods shall remain with the Customs Department, which will have first charge over the said goods for recovery of sum due from the unit to Government under provision of Section 142(b) of the Customs Act, 1962 read with the Customs (Attachment of Property of Defaulters for Recovery of Govt. Dues) Rules, 1995.
6.04 Net Foreign Exchange Earnings
EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP unit shall be a positive net foreign exchange earner. In addition sector specific provision of Appendix 6B of Appendices & ANFs, where a higher value addition and other conditions are given, shall be required to be followed. NFE Earnings shall be calculated cumulatively in blocks of five years, starting from commencement of production. Whenever a unit is unable to achieve NFE due to prohibition / restriction imposed on export of any product mentioned in LoP, the five year block period for calculation of NFE earnings may be suitably extended by BoA. Further, wherever a unit is unable to achieve NFE due to adverse market condition or any grounds of genuine hardship having adverse impact on functioning of the unit, the five year block period for calculation of NFE earnings may be extended by BoA for a period of upto one year, on a case to case basis. The method of calculation of NFE in detail is given in para 6.10 of current Handbook of Procedures.
6.05 Applications & Approvals/Letter of Permission / Letter of Intent and Legal Undertaking
(a) (i) Application for setting up an EOU shall be considered by Unit Approval Committee (UAC)/ Board of Approval (BoA) as the case may be, as detailed in the Hand Book of Procedure. The powers of DC are defined in para 6.34 of HBP.
(ii) In case of units under EHTP / STP schemes, necessary approval / permission under relevant paras of this Chapter shall be granted by officer designated by Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology, instead of DC, and by Inter- Ministerial Standing Committee (IMSC) instead of BOA.
(iii) Bio-Technology Parks (BTP) would be notified by DGFT on recommendations of Department of Biotechnology. In case of units in BTP, necessary approval / permission under relevant provisions of this chapter will be granted by designated officer of Department of Biotechnology.
(iv) On approval, a Letter of Permission (LoP) / Letter of Intent (LoI) shall be issued by DC / Designated officer to EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP unit. The validity of LoP/LoI shall be given in the Hand Book of Procedures.
(b) LoP / LoI issued to EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP units by concerned authority, subject to compliance of provision in Para 6.01 above, would be construed as an Authorisation for all purposes.
(c) Unit shall execute an LUT with DC concerned. Failure to ensure positive NFE or to abide by any of the terms and conditions of LoP / LoI / IL / LUT shall render the unit liable to penal action under provisions of the FT (D&R) Act, as amended, and Rules and Orders made thereunder, without prejudice to action under any other law / rules and cancellation or revocation of LoP / LoI / IL.
6.06 Investment Criteria
Only projects having a minimum investment of Rs.1 Crore in plant & machinery shall be considered for establishment as EOUs. However, this shall not apply to existing units, units in EHTP / STP/ BTP, and EOUs in Handicrafts/Agriculture/ Floriculture/Aquaculture/Animal Husbandry/Information Technology, Services, Brass Hardware and Handmade jewellery sectors. BoA may allow establishment of EOUs with a lower investment criteria.
6.07 DTA Sale of Finished Products/Rejects/ Waste/Scrap/Remnants and By- products
Entire production of EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP units shall be exported. However, the following are allowed as exceptions subject to the conditions specified.
(a) (i) Units, other than those of gems and jewellery may sell finished goods manufactured by them as specified in LoP (including by-products, rejects, waste and scraps arising in the course of production, manufacture, processing or packaging of such goods) which are freely importable under FTP in DTA, subject to fulfillment of positive NFE, on payment of excise duty, if applicable, and/ or payment of GST and compensation cess along with reversal of duties of Custom leviable under First Schedule to the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 availed as exemption, if any on the inputs utilized for the purpose of manufacturing of such finished goods (including by-products, rejects, waste and scraps arising in the course of production, manufacture, processing or packaging of such goods). No DTA sale shall be permissible in respect of, pepper & pepper products, marble and such other items as may notified from time to time. This reversal of Customs Duty would be as per prevailing SION norms or norms fixed by Norms Committee (where no SION norms are fixed).
(ii) Such DTA sale shall also not be permissible to units engaged in activities of packaging / labeling / segregation / refrigeration / compacting / micronisation / pulverization / granulation / conversion of monohydrate form of chemical to anhydrous form or vice-versa.
(iii) Sales made to a unit in SEZ shall also be taken into account for purpose of arriving at FOB value of export by EOU provided payment for such sales are made from Foreign Currency Account of SEZ unit. Sale to DTA would also be subject to mandatory requirement of registration of pharmaceutical products (including bulk drugs).
(iv) An amount equal to Anti Dumping duty under section 9A of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 leviable at the time of import, shall be payable on the goods used for the purpose of manufacture or processing of the goods cleared into DTA from the unit.
(v) Such DTA sale shall also be subject to refund of any benefits under Chapter 7 of FTP availed by the EOU/supplier as per FTP, on the goods used for manufacture of the goods cleared into the DTA.
(b) For services, including software units, sale in DTA in any mode, including on line data communication, shall also be permissible up to 50% of FOB value of exports and /or 50% of foreign exchange earned, where payment of such services is received in foreign exchange. However, sale in DTA in respect of services classified under Chapter Heading 9988 and 9989 under GST, but covered in LOP/para 11.31 of FTP as manufacturing of goods, will continue to be covered under para 6.07(a) above. At the time of DTA clearance, applicable GST and compensation cess as per GST classification would apply.
(c) Gems and jewellery units may sell upto 10% of FOB value of exports of the preceding year in DTA, subject to fulfillment of positive NFE. The unit shall pay applicable GST and compensation cess along with reversal of duties of Customs leviable under First Schedule of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 availed as exemption, on inputs used in such jewellery.
(d) Unless specifically prohibited in LoP, rejects may be Export Oriented Units (EOUs), Electronics Hardware Technology Parks (EHTPs), Software Technology Parks (STPs) and Bio-Technology Parks (BTPs) sold in DTA on payment of excise duty, if applicable, and/or payment of GST and compensation cess along with reversal of duties of Customs leviable under First Schedule of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 availed as exemption on inputs on prior intimation to Customs authorities. Sale of rejects upto 5% of FOB value of exports shall not be subject to achievement of NFE.
(e) Scrap / waste / remnants arising out of production process or in connection therewith may be sold in DTA, as per SION notified under Duty Exemption Scheme, on payment of applicable duties and/ or taxes and compensation cess. Such sales of scrap / waste / remnants shall not be subject to achievement of positive NFE. In respect of items not covered by norms, DC may fix ad- hoc norms for a period of six months and within this period, norms should be fixed by Norms Committee. Ad-hoc norms will continue till such time norms are fixed by Norms Committee. Scrap / waste / remnants may also be exported.
(f) There shall be no duties / taxes on scrap / waste / remnants, in case same are destroyed with permission of Customs authorities. The expression “no duties/ taxes” shall not include applicable taxes and cess under the GST laws.
(g) By-products included in LoP may also be sold in DTA subject to achievement of positive NFE, on payment of excise duty, if applicable, and/or payment of GST and compensation cess along with reversal of duties of Custom leviable under First Schedule to the Customs Tariff Act, 1975, if availed on inputs.
(h) In case of units manufacturing electronics hardware and software, NFE and DTA sale entitlement shall be reckoned separately for hardware and software.
(i) In case of new EOUs, advance DTA sale will be allowed not exceeding 50% of its estimated exports for first year, except pharmaceutical units where this will be based on its estimated exports for first two years.
(j) Procurement of spares / components, up to 2% of the value of manufactured articles, cleared into DTA, during the preceding year, may be allowed for supply to the same consignee / buyer for the purpose of after-sale-service. The same can be cleared in DTA on payment of applicable GST and compensation cess along with reversal of duties of Customs leviable under First Schedule of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 availed as exemption if any.
6.08 Other Supplies counted for fulfilment of NFE
Following supplies effected from EOU / EHTP / STP / BTP units will be counted for fulfillment of positive NFE. Such supplies shall not include “marble”, except if such supply of marble is an inter unit supply as provided at Sub-Para(c) below:
(a) Supplies effected in DTA to holders of Advance Authorization / Advance Authorization for annual requirement / DFIA under duty exemption / remission scheme / EPCG scheme. However, printing sector EOUs (or any other sector that may be notified in HBP), can’t supply goods, where basic customs duty and CVD is nil or exempted otherwise, to holders of Advance Authorization / Advance Authorization for annual requirement.
(b) Supplies effected in DTA against foreign exchange remittance received from overseas.
(c) Supplies to other EOU / EHTP / STP / BTP / SEZ units, provided that such goods are permissible for procurement in terms of Para 6.01 of FTP.
(d) Supplies made to bonded warehouses set up under FTP and / or under section 65 of Customs Act and free trade and warehousing zones, where payment is received in foreign exchange.
(e) Supplies of goods and services to such organizations which are entitled for duty free import of such items in terms of general exemption notification issued by MoF, as may be provided in HBP.
(f) Supplies of Information Technology Agreement (ITA-1) items and notified zero duty telecom / electronics items.
(g) Supplies of items like tags, labels, printed bags, stickers, belts, buttons or hangers to DTA unit for export.
(h) Supply of LPG produced in an EOU refinery to Public Sector domestic oil companies for being supplied to household domestic consumers at subsidized prices under the Public Distribution System (PDS) Kerosene and Domestic LPG Subsidy Scheme, 2002, as notified by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas vide notification No. E-20029/18/2001-PP dated 28.01.2003 (hereinafter referred to as PDS Scheme) subject to the following conditions:-
(i) Only supply of such quantity of LPG would be eligible for which Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas declines permission for export and requires the LPG to be cleared in DTA; and
(ii) The Ministry of Finance by a notification has permitted duty free imports of LPG for supply under the aforesaid PDS Scheme.
6.09 Export through others
An EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP unit may export goods manufactured! software developed by it through another exporter or any other EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP/SEZ unit subject to conditions mentioned in Para 6.19 of HBP.
6.10 Entitlement for Supplies from the DTA
(a) Supplies from DTA to EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP units for use in their manufacture for exports will be eligible for “benefits under Chapter 7 of FTP”. DTA supplier shall be eligible for relevant entitlements under chapter 7 of FTP, besides discharge of export obligation, if any, on the supplier. The refund of GST paid on such supply from DTA to EOU would be available to the supplier subject to such conditions and documentations as specified under GST rules and notifications issued there under.
(b) Suppliers of precious and semi-precious stones, synthetic stones and processed pearls from DTA to EOU shall be eligible for grant of Replenishment Authorizations at rates and for items mentioned in HBP.
(c) In addition, EOU!EHTP!STP!BTP units shall be entitled to following :-
(i) Reimbursement of Central Sales Tax (CST) on goods manufactured in India, wherever applicable. Simple interest @ 6% per annum will be payable on delay in refund of CST, if the case is not settled within 30 days of receipt of complete application (as in Para 11.10 of HBP).
(ii) Exemption from payment of Central Excise Duty on goods, falling in Fourth Schedule of Central Excise Act, procured from DTA on such goods manufactured in India.
6.11 Other Entitlements
Other entitlements of EOU!EHTP!STP!BTP units are as under:
(a) Exemption from industrial licensing for manufacture of items reserved for micro and small enterprises.
(b) Export proceeds will be realized within nine months.
(c) Units will be allowed to retain 100% of its export earnings in the EEFC account.
(d) Unit will not be required to furnish bank guarantee at the time of import or going for job work in DTA, where:
(i) the unit has turnover of Rs. 5 crore or above; and
(ii) the unit is in existence for at least three years; and
(iii) the unit has achieved positive NFE/ export obligation wherever applicable; and has not been issued a show cause notice or a confirmed demand, during the preceding 3 years, on grounds other than procedural violations, under the penal provision of the Customs Act, CGST/SGST/UTGST//IGST Acts, the Central Excise Act, the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992, the Foreign Exchange Management Act, the Finance Act, 1994 covering Service Tax or any allied Acts or the rules made thereunder, on account of fraud/collusion/willful mis-statement/suppression of facts or contravention of any of the provisions thereof.
(e) Unit will also not be required to furnish bank guarantee at the time of import or going for job work in DTA, if it has achieved necessary certification as an Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) and has not been issued a show cause notice or a confirmed demand, during the preceding 3 years, on grounds other than procedural violations, under the penal provision of the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992 and the Foreign Exchange Management Act.
(f) 100% FDI investment permitted through automatic route similar to SEZ units.
(g) The Units Approval Committee may consider on a case-to-case basis request for sharing of infrastructural facilities among EOUs and it shall forward its recommendation to the Board of Approval for its consideration. While accepting such proposals, the NFE obligations of the units shall not be altered. Such facilities will be available to units in EHTP ! STP after getting approval from IMSC. However, sharing of facilities between EOUs and SEZ Units shall not be permitted.
6.12 Inter Unit Transfer
(a) Transfer of manufactured goods from one EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP unit to another EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP Export Oriented Units (EOUs), Electronics Hardware Technology Parks (EHTPs), Software Technology Parks (STPs) and Bio-Technology Parks (BTPs) unit is allowed on payment of applicable GST and compensation cess with prior intimation to concerned Development Commissioners of the transferor and transferee units as well as concerned Customs authorities, as per following procedure for movement of goods:
i. The supplier unit shall endorse on usual commercial documents, such as, tax invoice and delivery challan, the amount of duties of Custom leviable under First Schedule to the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 availed as exemption on inputs used in the manufacture of such finished goods (including by- products, rejects, waste and scraps arising in the course of production, manufacture, processing or packaging of such goods) supplied to another unit. The recipient unit shall pay such endorsed Customs duty besides his own liability of reversal of Customs duty as provided in Para 6.07 above, before clearance of such finished goods in DTA and as provided under DoR notifications/ circulars/ guidelines in this regard.
ii. Upon receipt of goods, the recipient unit shall submit endorsed copies of tax invoice to their jurisdictional Customs authority as well as to the jurisdictional Customs authorities of the supplier unit.
(b) Capital goods may be transferred or given on loan to other EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP/SEZ units, with prior intimation to concerned DC and Customs authorities on payment of applicable GST and compensation cess. Such transferred goods may also be returned by the second unit to the original unit in case of rejection or for any reason on payment of applicable GST and compensation cess.
(c) Goods supplied by one unit of EOU/EHTP/STP/ BTP to another unit shall be treated as imported goods for second unit for payment of duty, on DTA sale by second unit.
(d) In respect of a group of EOUs/EHTPs/STPs/BTP units which source inputs centrally in order to obtain bulk discount and / or reduce cost of transportation and other logistics cost and / or to maintain effective supply chain, inter unit transfer of goods and services may be permitted on a case-to-case basis by the Unit Approval Committee. In case inputs so sourced are imported and then transferred to another unit, then value of the goods so transferred shall be taken as inflow for the unit transferring these goods and as outflow for the unit receiving these goods, for the purpose of calculation of NFE.
6.13 Sub–Contracting
(a) (i) EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP units, including gems and jewellery units, may be on the basis of annual permission from Customs authorities, sub¬contract production processes to DTA through job work which may also involve change of form or nature of goods, through job work by units in DTA.
(ii) These units may sub–contract upto 50% of overall production of previous year in value terms in DTA with permission of Customs authorities.
(d) (i) EOU may, with annual permission from Customs authorities, under take job work for export, on behalf of DTA exporter, provided that goods are exported directly from EOU and export document shall jointly be in name of DTA/ EOU. For such exports, DTA units will be entitled for refund of duty paid on inputs by way of brand rate of duty drawback. However, such brand rate of drawback shall be as per Customs and Central Excise Duties Drawback Rules, 2017 and shall be limited to Customs duties and Central Excise Duties (in respect of eligible items covered under Schedule IV of Central Excise Act, 1944).
(ii) Import of goods for execution of export order placed on EOU by foreign supplier on job work basis, would be allowed with or without payment of duties and/or taxes as provided under Para 6.01(d)(ii) above subject to condition that no DTA clearance shall be allowed.
(iii) Sub-contracting of both production and production processes may also be under taken without any limit through other EOU/EHTP/STP/ BTP/SEZ units, on the basis of records maintained in unit.
(iv) EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP units may sub-contract part of production process abroad and send intermediate products abroad as mentioned in LoP. No permission would be required when goods are sought to be exported from sub-contractor premises abroad. When goods are sought to be brought back, prior intimation to concerned DC and Customs authorities shall be given.
(c) Scrap/waste/remnants generated through job work may either be cleared from job worker’s premises on payment of applicable duty and/or taxes, as provided under Para 6.07 above on transaction value or destroyed in presence of Customs authority or returned to unit. Destruction shall not apply to gold, silver, platinum, diamond, precious and semi-precious stones.
(d) Sub-contracting/ exchange by gems and jewellery EOUs through other EOUs or SEZ units or units in DTA, shall be as per procedure indicated in HBP.
6.14 Sale of Unutilized Material and Capital Goods
(a) In case an EOU / EHTP/ STP/BTP unit is unable to utilize goods and services imported or procured from DTA, it may be:
(i) Transferred to another EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP/ SEZ unit; or
(ii) Disposed of in DTA with intimation to Customs authorities on payment of applicable duties and/ or taxes and compensation cess. In addition, exemption of duties of Customs leviable under First Schedule of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 availed, if any on the goods , at the time of import will also be payable. This sale would be further subject to compliance of applicable import conditions such as requirement of import Authorisation; or
(iii) Exported.
(iv) Such transfer from EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP unit to another such unit would be treated as import for receiving unit.
(b) Capital goods and spares that have become obsolete/ surplus, may be exported or transferred to SEZ unit, transferred to another EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP/on payment of applicable GST and compensation cess or disposed of in DTA on payment of applicable GST and compensation cess and duties of Customs leviable under First Schedule of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975. Benefit of depreciation will be available in case of disposal in DTA only when the unit has achieved positive NFE taking into consideration the depreciation allowed. No duty shall be payable other than the applicable taxes under GST laws incase capital goods, raw material consumables, spares, goods manufactured, processed or packaged, and scrap/ waste/remnants /rejects are destroyed within unit after intimation to Customs authorities or destroyed outside unit with permission of Customs authorities. Destruction as stated above shall not apply to gold, silver, platinum, diamond, precious and semi¬precious stones.
(c) In case of textile sector, disposal of left over material/ fabrics upto 2% of CIF value or quantity of import, whichever is lower, on payment of duty on transaction value, may be allowed, subject to certification of Central Excise/Customs officers that these are left over items.
(d) Disposal of used packing material will be allowed on payment of duty on transaction value.
6.15 Reconditioning/Repair and Re-engineering
(a) EOUs shall be set up with approval of UAC to carry out reconditioning, repair, remaking, testing, calibration, quality improvement, upgradation of technology and re-engineering activities for export in foreign currency. Provisions of paragraphs 6.07, 6.08, 6.09, 6.12, 6.13 of FTP and para 6.29(a), (b), (c) and (d) of HBP shall not, however, apply to such activities.
(b) EHTP/STP/BTP units shall be set up with approval of IMSC to carry out reconditioning, repair, remaking, testing, calibration, quality improvement, upgradation of technology and re-engineering activities for export in foreign currency. Provisions of paragraphs 6.07, 6.08, 6.09, 6.12, 6.13of FTP and para 6.29(a), (b), (a) and (d) of HBP shall not, however, apply to such activities.
6.16 Replacement / Repair of Imported / Indigenous Goods
(a) General provisions of FTP relating to export /import of replacement/repair of goods would also apply equally to EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP units. Cases not covered by these provisions shall be considered on merits by DC.
(b) Goods sold in DTA and not accepted for any reasons, may be brought back for repair/replacement, under intimation to concerned jurisdictional customs authorities.
(c) Goods or parts thereof, on being imported / indigenously procured and found defective or otherwise unfit for use or which have been damaged or become defective subsequently, may be returned against refund of purchase value/ against replacement or destruction. In the event of replacement, goods may be received from foreign suppliers or their authorized agents in India or indigenous suppliers. The unit can take free of cost replacement (duty paid) from the authorized agents in India of foreign suppliers, provided the defective part is re–exported or destroyed. However, destruction shall not apply to precious and semi-precious stones and precious metals.
6.17 Exit from the Scheme
(a) With approval of DC/Designated officer of EHTP/ STP/BTP, an EOU/EHTP/STP/BTP unit may opt out of scheme. Such exit shall be subject to payment of applicable Excise and Customs duties and on payment of applicable IGST/ CGST/ SGST/ UTGST and compensation cess, if any, and industrial policy in force.
(b) If unit has not achieved obligations, it shall also be liable to penalty at the time of exit.
(c) In the event of a gems and jewellery unit ceasing its operation, gold and other precious metals, alloys, gems and other materials available for manufacture of jewellery, shall be handed over to an agency nominated by DoC, at price to be determined by that agency.
(d) An EOU / EHTP / STP / BTP unit may also be permitted by DC to exit from the scheme at any time on payment of applicable duties and taxes and compensation cess on capital goods under the prevailing EPCG Scheme for DTA Units. This will be subject to fulfillment of positive NFE criteria under EOU scheme, eligibility criteria under EPCG scheme and standard conditions indicated in HBP.
(e) Unit proposing to exit out of the scheme shall intimate DC of EOU/Designated officer of EHTP/STP/BTP and Customs authorities in writing. Unit shall assess duty liability arising out of exit and submit details of such assessment to Customs authorities. Customs authorities shall confirm duty liabilities on priority basis, subject to the condition that the unit has achieved positive NFE, taking into consideration the depreciation allowed. After payment of duty and clearance of all dues, unit shall obtain “No Dues Certificate” from Customs authorities. On the basis of “No Dues Certificate” so issued by the Customs authorities, unit shall apply to DC/Designated officer for final exit. In case there is no proceeding pending under FT(D&R) Act, as amended, DC/Designated officer shall issue final exit order within a period of 7 working days. Between “No Dues Certificate” issued by Customs authorities and final exit order by DC/Designated officer, unit shall not be entitled to claim any exemption for procurement of capital goods or inputs. However, unit can claim Advance Authorization / DFIA/ Duty Drawback as per its eligibility. In case the duty calculations and dues are disputed and take a long time, a BG / Bond / Installment processes backed by BG shall be provided for expediting the exit process.
(f) In cases where a unit is initially established as DTA unit with machines procured from abroad after payment of applicable import duty, or from domestic market after payment of excise duty/GST, and unit is subsequently converted to EOU, in such cases removal of such capital goods to DTA after exit would be without payment of duty. Similarly, in cases where a DTA unit imported capital goods under EPCG Scheme and after completely fulfilling export obligation gets converted into EOU, unit would not be charged customs duty on capital goods at the time of removal of such capital goods in DTA upon exit.
(g) An EOU / EHTP / STP / BTP unit may also be permitted by DC to exit under Advance Authorisation as one time option. This will be subject to fulfillment of positive NFE criteria.
(h) A simplified procedure may be provided to fast track the De-bonding/ Exit of the STP / EHTP Unit which has not availed any duty benefit on procurement of raw material, capital goods etc.
6.18 Conversion
(a) Existing DTA units may also apply for conversion into an EOU / EHTP / STP/ BTP unit.
(b) Existing EHTP / STP units may also apply for conversion / merger to EOU unit and vice-versa. In such cases, units will avail exemptions in duties and taxes as applicable.
(c) Applications for conversion into an EOU / EHTP / STP / BTP unit from existing DTA units, having an investment of Rs. 50 crores and above in plant and machinery or exporting Rs. 50 crores and above annually, shall be placed before BOA for a decision.
6.19 Monitoring of NFE
Performance of EOU/EHTP/STP/ BTP units shall be monitored by Units Approval Committee as per guidelines in HBP.
6.20 Export through Exhibitions/ Export Promotion Tours/ Showrooms Abroad /Duty Free Shops
EOU / EHTP / STP / BTP are permitted to:
(i) Export goods for holding/participating in Exhibitions abroad with permission of DC /Designated officer.
(ii) Personal carriage of gold / silver / platinum jewellery, precious, semi-precious stones, beads and articles.
(iii) Export goods for display / sale in permitted shops set up abroad.
(iv) Display / sell in permitted shops set up abroad, or in showrooms of their distributors / agents.
(v) Set up showrooms / retail outlets at International Airports.
6.21 Personal Carriage of Import / Export Parcels including through Foreign Bound Passengers
Import/ export through personal carriage of gems and jewellery items may be undertaken as per Customs procedure. However, export proceeds shall be realized through normal banking channel. Import/ export through personal carriage by units, other than gems and jewellery units, shall be allowed provided goods are not in commercial quantity. An authorized person of Gems & Jewellery EOU may also import gold in primary form, upto 10 Kgs in a financial year through personal carriage, as per guidelines prescribed by RBI and DoR.
6.22 Export /Import by Post/ Courier
Goods including free samples, may be exported/imported by air freight or through foreign post office or through courier, as per Customs procedure.
6.23 Administration of EOU / EHTP / STP / BTP units and Powers of DC/Designated Officer of EOU/EHTP/STP/SEZ
Details of administration of EOUs / EHTP / STP / BTP units and powers of DC/Designated Officer are given in HBP.
Chapter 7
Deemed Exports
7.00 Objective
To provide a level-playing field to domestic manufacturers and to promote Make in India, in certain specified cases, as may be decided by the Government from time to time.
7.01 Deemed Exports
(i) “Deemed Exports” for the purpose of this FTP refer to those transactions in which goods supplied do not leave country, and payment for such supplies is received either in Indian rupees or in free foreign exchange. Supply of goods as specified in Paragraph 7.02 below shall be regarded as “Deemed Exports” provided goods are manufactured in India.
(ii) “Deemed Exports” for the purpose of GST would include only the supplies notified under Section 147 of the CGST/SGST Act, on the recommendations of the GST Council. The benefits of GST and conditions applicable for such benefits would be as specified by the GST Council and as per relevant rules and notification.
7.02 Categories of Supply
Supply of goods under following categories (a) to (c) by a manufacturer and under categories (d) to (g) by main / sub-contractors shall be regarded as ‘Deemed Exports’:
A. Supply by manufacturer:
(a) Supply of goods against Advance Authorisation / Advance Authorisation for annual requirement / DFIA.
(b) Supply of goods to EOU / STP / EHTP / BTP.
(c) Supply of capital goods against EPCG Authorisation.
B. Supply by main / sub-contractor(s):
(d) (i) Supply of goods to projects financed by multilateral or bilateral Agencies / Funds as notified by Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), MoF, where legal agreements provide for tender evaluation without including customs duty.
(ii) Supply and installation of goods and equipment (single responsibility of turnkey contracts) to projects financed by multilateral or bilateral Agencies/Funds as notified by Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), MoF, for which bids have been invited and evaluated on the basis of Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) prices for goods manufactured abroad.
(iii) Supplies covered in this paragraph shall be under International Competitive Bidding (ICB) in accordance with procedures of those Agencies / Funds.
(iv) A list of agencies, covered under this paragraph, for deemed export benefits, is given in Appendix-7A.
(e) (i) Supply of goods to any project or for any purpose in respect of which the Ministry of Finance by Customs Notification No. 50/2017-Customs dated 30.6.2017, as amended from time to time, permits import of such goods at zero basic customs duty subject to conditions mentioned therein. Benefits of deemed exports shall be available only if the supply is made under procedure of ICB.
(i) Supply of goods required for setting up of any mega power project, as specified in the list 31 at Sl. No. 598 of Department of Revenue Notification No. 50/2017-Customs dated 30.6.2017, as amended from time to time and subject to conditions mentioned therein, shall be eligible for deemed export benefits provided such mega power project conforms to the threshold generation capacity specified in the above said Notification.
(ii) For mega power projects, ICB condition would not be mandatory if the requisite quantum of power has been tied up through tariff based competitive bidding or if the project has been awarded through tariff based competitive bidding.
(f) Supply of goods to United Nations or International organization for their official use or supplied to the projects financed by the said United Nations or an International organization approved by Government of India in pursuance of Section 3 of United Nations (Privileges and Immunities Act), 1947. List of such organization and conditions applicable to such supplies is given in the Customs Notification No. 84/97-Customs dated 11.11.1997, as amended from time to time. A list of Agencies, covered under this paragraph, is given in Appendix-7B.
(g) Supply of goods to nuclear power projects provided:
i) Such goods are required for setting up of any Nuclear Power Project as specified in the list 32 at Sl. No. 602, Customs notification No. 50/2017-Customs dated 30.6.2017, as amended from time to time and subject to conditions mentioned therein.
ii) The project should have a capacity of 440 MW or more.
iii) A certificate to the effect is required to be issued by an officer not below the rank of Joint Secretary to Government of India, in Department of Atomic Energy.
iv) Tender is invited through National competitive bidding (NCB) or through ICB.
7.03 Benefits for Deemed Exports
Deemed exports shall be eligible for any / all of following benefits in respect of manufacture and supply of goods, qualifying as deemed exports, subject to terms and conditions as given in HBP and ANF-7A:
(a) Advance Authorisation / Advance Authorisation for annual requirement / DFIA.
(b) Deemed Export Drawback.
(c) Refund of terminal excise duty for excisable goods mentioned in Schedule 4 of Central Excise Act, 1944 provided the supply is eligible under that category of deemed exports and there is no exemption.
7.04 Benefits to the Supplier /Recipient
|
Categories of supplies as per Para 7.02 |
Benefits on supplies, as given in Para 7.03 above, whichever is applicable. | ||
| Para 7.03 (a) Advance Authorisation | Para 7.03 (b) Duty Drawback | Para 7.03 (c) Terminal Excise Duty |
|
| (a) | Yes (for intermediate supplies against an invalidation letter) | Yes (against ARO) | Yes |
| (b) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (c) | Yes | Yes | NA |
| (d) | Yes | Yes | NA |
| (e) | Yes | Yes | NA |
| (f) | Yes | Yes | NA |
| (g) | Yes | Yes | NA |
7.05 Conditions for refund of Terminal Excise Duty
Supply of goods will be eligible for refund of terminal excise duty as per Para 7.03 (c) of FTP, provided recipient of goods does not avail CENVAT credit/rebate on such goods.
7.06 Conditions for refund of Deemed Export drawback
Supplies will be eligible for deemed export drawback as per para 7.03 (b) of FTP, as under:
Refund of drawback on the inputs used in manufacture and supply under the said category can be claimed on ‘All Industry Rate’ of Duty Drawback Schedule notified by Department of Revenue from time to time provided no CENVAT credit has been availed by supplier of goods on excisable inputs or on ‘Brand Rate Basis’ upon submission of documents evidencing actual payment of basic custom duties.
7.07 Common conditions for deemed export benefits
(i) Supplies shall be made directly to entities listed in the Para 7.02. Third party supply shall not be eligible for benefits/exemption.
(ii) In all cases, supplies shall be made directly to the designated Projects / Agencies/ Units/ Advance Authorisation/ EPCG Authorisation holder. Sub-contractors may, however, make supplies to main contractor instead of supplying directly to designated Projects/ Agencies. Payments in such cases shall be made to sub-contractor by main-contractor and not by project Authority.
(iii) Supply of domestically manufactured goods by an Indian Subcontractor to any Indian or foreign main contractor, directly at the designated project’s/ Agency’s site, shall also be eligible for deemed export benefit provided name of sub- contractor is indicated either originally or subsequently (but before the date of supply of such goods) in the main contract. In such cases payment shall be made directly to sub-contractor by the Project Authority.
(iv) Steel manufacturers supplying steel against Advance Authorization under Para 7.02 (a), through their Service Centers/ Distributors/ Dealers/ Stock yards, shall also be eligible to claim duty drawback provided such supplies are made in accordance with Ministry of Steel O.M. No. S-21016/3/2020-TRADE-TAX-Part(1) dated 27.5.2020 read with O.M. dated 24.6.2020, as amended from time to time. However, the invoice against such supplies would be raised by the manufacturer on the Advance Authorization holder. Delivery of such supplies can be made through their Service Centers/ Distributors/ Dealers/ Stock yards, who in turn will raise the tax invoice on the steel manufacturer bearing a cross reference for such supplies.
7.08 Benefits on specified supplies
(i) Deemed export benefits shall be available for supplies of “Cement” under Para 7.02(d) only.
(ii) Deemed export benefit shall be available on supply of “Steel”:
(a) As an inputs to Advance Authorisation/ Annual Advance Authorisation/DFIA holder/ an EOU.
(b) To multilateral/ bilateral funded Agencies as per sub-para 7.02(d).
(iii) Deemed export benefit shall be available on supply of “Fuel” (in respect of eligible fuel items covered under Schedule 4 of Central Excise Act, 1944) provided supplies are made to:
(a) EOUs.
(b) Advance Authorisation holder / Annual Advance Authorisation holder.
7.09 Liability of Interest
Incomplete/deficient application is liable to be rejected. However, simple interest @ 6% per annum will be payable on delay in refund of duty drawback and terminal excise duty under the scheme, provided the claim is not settled within 30 days from the date of issue of final Approval Letter by RA.
7.10 Risk Management and Internal Audit mechanism
(a) A Risk Management system shall be in operation, wherein every month, Computer system in DGFT headquarters, on random basis, will select 10% of cases, for each RA, where benefit(s) under this Chapter has/have already been granted. Such cases shall be scrutinized by an internal Audit team, headed by a Joint DGFT, in the office of respective Zonal Addl. DGFT. The team will be responsible to audit claims of not only for its own office but also the claims of all RAs falling under the jurisdiction of the Zone.
(b) The respective RA may also, either on the basis of report from Internal Audit/ External Audit Agency(ies) or suo-motu, re-assess any case, where any erroneous/ in-eligible payment has been made/claimed. RA will take necessary action for recovery of payment along with interest at the rate of 15% per annum on the recoverable amount.
7.11 Penal Action
In case, claim is filed by submitting mis-declaration/ mis-representation of facts, then in addition to effecting recovery under Para 7.10(b) above, the applicant shall be liable for penal action under the provisions of FT(D&R) Act, Rules and orders made there under.
Chapter 8
Quality Complaints and Trade Disputes
8.00 Objective
Exporters need to project a good image of the country abroad to promote exports. Maintaining an enduring relationship with foreign buyers is of utmost importance, and complaints or trade disputes, whenever they arise, need to be settled amicably as soon as possible. Importers too may have grievances as well.
In an endeavour to resolve such complaints or trade disputes and to create confidence in the business environment of the country, a mechanism is being laid down to address such complaints and disputes in an amicable way.
Complaints/Disputes between two or more Indian entities are not covered under this mechanism. Similarly, complaints/disputes between two or more foreign entities are also not covered.
8.01 Quality Complaints/ Trade disputes
The following type of complaints may be considered:
(a) Complaints received from foreign buyers in respect of quality of goods or services or technology supplied by exporters from India;
(b) Complaints of importers against foreign suppliers in respect of quality of the goods or services or technology supplied; and
(c) Complaints of unethical commercial dealings categorized mainly as non-supply/ partial supply of goods or services or technology after confirmation of order; supplying goods or services or technology other than the ones as agreed upon; non- payment; non¬adherence to delivery schedules, etc.
8.02 Obligation on the part of importer/ exporter
(a) Rule 11 of the Foreign Trade (Regulation) Rules, 1993, requires that on the importation into, or exportation out of, any customs ports of any goods or services or technology, whether liable to duty or not, the owner of such goods or services or technology shall in the Bill of Entry or the Shipping Bill or any other documents prescribed under the Customs Act, 1962 (52 of 1962), state the value, quality and description of such goods or services or technology to the best of his knowledge and belief and in case of exportation of goods or services or technology, certify that the quality and specification of the goods or services or technology as stated in those documents, are in accordance with the terms of the export contract entered into with the buyer or consignee in pursuance of which the goods or services or technology are being exported and shall subscribe a declaration of the truth of such statement at the foot of such Bill of Entry or Shipping Bill or any other documents. Violation of this provision renders the exporter liable for penal action;
(b) Certain export commodities have been notified for Compulsory Quality Control & Pre-shipment Inspection prior to their export. Penal action can be taken under the Export (Quality Control & Inspection) Act, 1963 as amended in 1984, against exporters who do not conform to these standards and/ or provisions of the Act as laid down for such products.
8.03 Provisions in FT (D&R) Act, 1992, as amended & FT (Regulation) Rules, 1993, as amended for necessary action against erring exporters/ importers
Action against erring exporters/importers can be taken under the Foreign Trade (Development and Regulation) Act, 1992, as amended and under Foreign Trade (Regulation) Rules, 1993, as amended, as follows:-
a) Section 8 of the Act empowers the Director General of Foreign Trade or any other officer authorized by him to suspend or cancel the Importer Exporter Code Number for the reasons as given therein;
b) Section 9 (2) of the Act empowers the Director General of Foreign Trade or an officer authorised by him to refuse to grant or renew a license, certificate, scrip or any other instrument bestowing financial or fiscal benefit granted under the Act;
c) Section 9(4) of the Act empowers the Director General of Foreign Trade or the officer authorized by him to suspend or cancel any License, certificate, scrip or any instrument bestowing financial or fiscal benefit granted under the Act;
d) Section 11(2) of the Act provides for imposition of fiscal penalty in cases where a person makes or abets or attempts to make any import or export in contravention of any provision of the Act, any Rules or Orders made there under or the Foreign Trade Policy.
8.04 Mechanism for handling of Complaints/ Disputes
(a) Committee on Quality complaints and Trade Disputes (CQCTD)
To deal effectively with the increasing number of complaints and disputes, a ‘Committee on Quality Complaints and Trade Disputes’ (CQCTD) will be constituted in the Regional Authorities (RAs) of DGFT. Names of RAs, where CQCTD has been constituted and jurisdiction of CQCTD is given in Chapter 8 of the Handbook of Procedures .
(b) Composition of the CQCTD
The CQCTD would be constituted under the Chairpersonship of the Head of Office. The constitution of CQCTD is given in Chapter 8 of the Hand Book of Procedures.
(c) Functions of CQCTD
The Committee (CQCTD) will be responsible for enquiring and investigating into all Quality related complaints and other trade related complaints falling under the jurisdiction of the respective RAs. It will take prompt and effective steps to redress and resolve the grievances of the importers/ exporters and overseas buyers/ sellers preferably within three months of receipt of the complaint. Wherever required, the Committee (CQCTD) may take the assistance of the Export Promotion Councils/FIEO/Commodity Boards or any other agency as considered appropriate for settlement of these disputes. CQCTD will hold its meetings at regular intervals and at least four in a year given the pendency of complaints/disputes.
8.05 Proceedings under CQCTD
CQCTD proceedings are conciliatory in nature and the aggrieved party, whether the foreign entity or the Indian entity, is free to pursue any legal recourse against the other erring party.
8.06 Procedures to deal with complaints and trade disputes
The procedure for making an application for such complaints or trade disputes and the procedure to deal with such quality complaints and disputes is given in the Handbook of Procedures.
8.07 Corrective Measures
a) The Committee at RA level can authorize the Export Inspection Agency or any technical authority to assess whether there has been any technical failure of not meeting the standards, manufacturing/ design defects, etc. for which complaints have been received;
b) Initially, efforts will be made to settle the complaint/ dispute amicably. In case the matter is not settled amicably, action may be taken against the erring Indian entity in terms of the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992, as amended, and the Foreign Trade (Regulation) Rules, 1993, as amended;
c) Complaints against foreign entities would be taken up for settlement by the respective ‘Foreign Trade Division’ in the Department of Commerce, Vanijya Bhavan, New Delhi through Indian Missions abroad. Indian Missions Abroad will take up the complaints against the foreign entities with authorities concerned;
d) In case, the Indian Missions abroad are satisfied about the malafide of any foreign entity, they shall send such information to DGFT for circulation amongst the EPCs/Commodity Boards, ECGC and other regulatory authorities.
A Case Officer will be assigned for monitoring purposes in the designated Regional Authorities for resolving complaints and trade disputes in a time bound manner.
8.09 Nodal Officer
Director General of Foreign Trade would appoint an officer, not below the rank of Joint Director General, in the Headquarters, to function as the ‘Nodal Officer’ for monitoring the trade disputes and coordinating with Regional Authorities of DGFT, Foreign Trade Divisions of Department of Commerce, Indian Missions and other agencies.
Chapter 9
Promoting Cross Border Trade in Digital Economy
9.00 Objective
The objective of this chapter is to provide a framework for cross-border trade of goods and services from India in the digital economy and the promotion of e-Commerce and other emerging channels of exports from India.
9.01 E-Commerce Exports of Goods
Export of goods where selling is through the internet on an e-Commerce platform, the payment for which shall be done through international credit or debit cards, or other authorised electronic payment channels and as specified by the RBI from time to time.
9.02 E-Commerce Exports of Services
Exports of services where selling is through the internet on an e-Commerce platform, the payment for which shall be done through international credit or debit cards, or other authorised electronic payment channels and as specified by the RBI from time to time.
9.03 E-Commerce Platform
E-Commerce platform is an electronic platform, including a web-portal, that enables the commercial process of buying and selling through the internet.
9.04 E-Commerce Export Logistics Provider
Any service provider who provides logistics services towards exports of goods or services for e-Commerce Exports.
9.05 Export through Courier Service/Post
Exports through a registered courier service/Foreign Post Office is permitted as per Notification(s) issued under Customs Act, 1962. However, exportability of such items shall be regulated in accordance with FTP/Export Policy in ITC(HS) as notified. The value limit for exports through courier service shall be Rs. 10,00,000 per consignment.
9.06 Import through courier service/Post
i. Imports through a registered courier service or Post are permitted as per Notification(s) issued under the Customs Act, 1962. However, importability of such items shall be regulated in accordance with FTP and the ITC(HS) based Import Policy as notified.
ii. Exports by courier mode of precious Metal Jewellery governments/Central government. Request for approval of an ECEH proposed shall be submitted to the notified committee to be constituted by DGFT.
ii. Existing facility with the required infrastructure may also apply to be designated as ECEH.
A. PROMOTION OF E-COMMERCE EXPORTS
9.07 Handholding and outreach to promote e-Commerce Exports
i. The Niryat Bandhu Scheme (NBS) as defined under Chapter 1 of the Policy shall have a component for the promotion of e-Commerce and other emerging channels of exports. Under the given NBS component, DGFT shall organise outreach activities/workshops in partnership with Customs Authorities, Department of Post, ‘Industry Partners’ and ‘Knowledge Partners’ for promotion of e-Commerce exports. Besides outreach/ workshops, specific focus may be on creation of electronic content as well.
ii. In addition to increasing awareness on e-Commerce related rules and processes, actions may be undertaken under the said NBS component for capacity building and skill development for promotion of e-Commerce exports, in partnership with Customs Authorities, Department of Post, ‘Industry Partners’ or the ‘Knowledge Partners’.
B. E-COMMERCE EXPORT HUBS (ECEHs)
9.08 Objective of E-Commerce Export Hubs
The objective is to establish designated areas as E-Commerce Export Hubs (hereafter called “ECEH”), which would act as a centre for favourable business infrastructure and facilities for Cross Border E-Commerce activities.
9.09 Creation of ECEH
i. The ECEH shall ordinarily be setup through private initiative. It may also be setup in Public-Private-Partnership (PPP) mode in partnership with the State
9.10 Nature of ECEH Operations
i. ECEH will function to achieve agglomeration benefits for e-commerce exporters. The ECEH may provide for storage (including cold storage facilities), packaging, labelling, certification & testing and other common facilities for the purposes of export.
ii. The ECEH shall also provide for dedicated logistics infrastructure for connecting to and leveraging the services of the nearest Logistics hub(s).
iii. All goods, including SCOMET and Restricted goods (subject to suitable compliance of regulations and conditions) and except goods which are prohibited or otherwise disallowed, may be handled at ECEH.
iv. Capital goods brought to a ECEH shall be utilized only for activities as mentioned at (i) above on payment of the duties and taxes, as applicable, in terms of extant laws.
9.11 Entitlement under ECEHs
i. ECEH may be provided financial assistance under MAI scheme, for e-Commerce export promotion projects for marketing, capacity building and technological services such as imaging, cataloguing, product video creation of e-Commerce Goods.
C. PROMOTION OF E-COMMERCE EXPORTS THROUGH POSTAL ROUTE
9.12 Dak Niryat Kendras
Dak Ghar Niryat Kendras shall be operationalised throughout the country to work in a hub-and-spoke model with Foreign Post Offices (FPOs) to facilitate cross-border e-Commerce and to enable artisans, weavers, craftsmen, MSMEs in the hinterland and land-locked regions to reach international markets.
Chapter 10
SCOMET: Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies
10.00 Objective
The general provisions governing the export of dual use items, munitions and nuclear related items, including software and technology viz. SCOMET, are dealt with in this Chapter.
10.01 Brief Background
India is a signatory to international conventions on disarmament and non-proliferation, viz. the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) and Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention (BWC). The United Nations Security Council Resolution 1540 obliges all countries to prohibit access of weapons and mass destruction and their delivery systems to non-state actors (in particular for terrorist purposes); and prescribed measures and controls on weapons of mass destruction, their delivery systems and related materials, equipment and technology. India is also a member of the major multilateral export control regimes, viz. the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), Wassenaar Arrangement (WA) and Australia Group (AG); and has harmonized its guidelines and control lists with that of the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG). In consonance with the guidelines and control lists of these international conventions and obligations as well as multilateral export control regimes, India has regulated the exports of dual use items, nuclear related items, including software and technology.
In respect of controls on export of specified goods, services and technology, the Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Act, 2005 (21 of 2005) shall apply to exports, transfers, re-transfers, brought in transit, trans-shipment of, and brokering in specified goods, technology or services. These provisions have been incorporated in Chapter IVA of Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992, as amended in 2010.
10.02 SCOMET List
Export of dual-use items, including software and technologies, having potential civilian / industrial applications as well as use in weapons of mass destruction is regulated. It is either prohibited or is permitted under an Authorization unless specifically exempted.
SCOMET is an acronym for Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies. Accordingly, the SCOMET list is our National Export Control List of dual use items munitions and nuclear related items, including software and technology and is aligned to the control lists of the all the multilateral export control regimes and conventions. The SCOMET List has been notified under Appendix 3 to Schedule 2 of ITC (HS) Classification of Export and Import Items, which is available on the website of DGFT.
10.03 Classification of SCOMET categories and Licensing jurisdiction
The SCOMET List is divided into nine categories of items from Category 0 to Category 8. However, Category 7 is presently ‘Reserved’ and has not been populated. The broad classification of different categories under SCOMET List and their jurisdictional licensing authorities are tabulated as under:
Table: SCOMET Categories and Licensing Jurisdiction
|
SCOMET |
SCOMET items | Jurisdictional Licensing Authority |
Remark |
| 0 | Nuclear materials, nuclear-related other materials, equipment and technology | Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) | Including items mentioned in Note 2 of CIN of SCOMET List |
| 1 | Toxic chemical agents and other chemicals | Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) | |
| 2 | Micro-organisms, Toxins | DGFT | |
| 3 | Materials, Materials Processing Equipment and related Technologies | DGFT | |
| 4 | Nuclear-related other equipment and technology, not controlled under Category ‘0’ | DGFT | |
| 5 | Aerospace systems, equipment, including production and test equipment, and related Technology and specially designed components and accessories thereof. | DGFT | |
| 6 | Munitions List | Department of Defence Production (DDP) /Ministry of Defence | Excluding those covered under Note 2 and 3 of CIN and Sub-category 6A007, 6A008 |
| 7 | ‘Reserved’ | DGFT | |
| 8 | Special Materials and Related Equipment, Material Processing, Electronics, Computers, Telecommunications, Information Security, Sensors and Lasers, Navigation and Avionics, Marine, Aerospace and Propulsion. |
DGFT |
CIN : Commodity Identification Note of SCOMET List
Note: DGFT to be licensing authority for above specified categories/sub-categories and any other sub-category as may be specified.
10.04 Export of SCOMET Items
Procedure for grant of export authorization for SCOMET items in respect of Categories 1 to 5 and 8, is specified under Chapter 10 of Hand Book of Procedures (HBP).Export of SCOMET items under Category 0 and Note 2 of the Commodity Identification Note (CIN) of SCOMET will be permitted against an authorization issued by the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) as per the guidelines for Nuclear Transfers (Exports) and Notification of schedule of Prescribed Substances, Prescribed Equipment and Technology” issued under Atomic Energy Act 1962 and Atomic Energy (Working of Mines, Minerals and Handling of Prescribed Substance) Rules 1984.Export of SCOMET items under Category 6 (Munitions List) [except those covered under Note 2 and 3 of CIN and items under Category 6A007, 6A008], irrespective of end use of the items, whether military or civil will be permitted against an authorization to be issued by Department of Defence Production (DDP)/ Ministry of Defence under the extant guidelines /Standing Operating Procedure (SOP) issued by the DDP, time to time.
10.05 Additional controls on Non-SCOMET items for dual use (Catch-all controls)
Export of items not in the SCOMET List may also be regulated under provisions of the Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Act,2005.If the exporter has been notified in writing by DGFT or he knows or has reason to believe that an item not covered in the SCOMET list has a potential risk of use in or diversion to weapons of mass destruction (WMD) or in their missile system or military end use (including by terrorists and non-state actors), the export of such an item may be denied or permitted subject to the grant of a license, as per the procedure provided for SCOMET items in Para 10.05 and 10.06 of HBP.
10.06 Supply of SCOMET Items from DTA to SEZ/EOU and outside the country
Export authorisation is not required for supply of SCOMET items from DTA to SEZ /EoU. However, all supplies of SCOMET items from DTA to SEZ/EOU will be reported to the Development Commissioner (DC) of the respective SEZ/EoU by the supplier in the prescribed performa within one week of the supplies getting effected. Export Authorisation is, however, required if the SCOMET items are to be physically exported outside the country from SEZ/ EOU, i.e. to another country (Rule 26 of the SEZ Rules, 2006 may be referred).
10.07 Export of imported SCOMET items
Imported goods covered under the SCOMET list are not permitted for export, even from the Customs bonded ware house, without an export authorization, unless specifically exempted.
10.08 Different types of export authoriza¬tions for SCOMET items
(i) Direct export to ultimate end user: Export to the ultimate end users abroad after due verification process;
(ii) Export for repeat orders of same SCOMET items: Repeat export of items of same technical specifications which have earlier been allowed for export to the same countries/entities after due verification process;
(iii) Export for Stock and Sale purpose: Export of items initially to the stockist abroad and then from the stockist to the ultimate end users in the same country or approved countries;
(iv) Export of spare parts under SCOMET under Stock and Sale: Export of spare parts along with main item/ equipment under stock and sale;
(v) Export for/after repair / replacement of defective SCOMET items: Export authorizations for repair/ replacement of imported items on being found defective and export authorization after repair of indigenous/third party items imported for repair;
(vi) Temporary export of SCOMET items: Export authorization for demo/display/exhibition/tenders/ RFP/RFQ/NIT abroad or for return abroad after demo/ display/ exhibition/ tenders/ RFP/ RFQ/ NIT etc. in India;
(vii) Export of imported items to the same foreign entity or to its OEM: Export of imported items to its foreign supplier or its OEM on obsolescence of technology, dead on arrival, cancellation of order, calibration, testing, etc.;
(viii) Global Authorization for Intra-Company Transfers (GAICT) of SCOMET Items including Software/ Technology :Only one time authorization will be required, for export and/or re-export of SCOMET items including software and technology under SCOMET Category 8 (except items listed in Appendix 10M), where the export is an Intra-company transfer from the Indian parent company (applicant exporter) to its foreign subsidiary company or from the Indian subsidiary of foreign company (applicant exporter) to its foreign parent/another subsidiary of foreign parent company and; based on a Master Service Agreement / Contract between the Indian parent company/Indian subsidiary of foreign company and foreign subsidiary of Indian company/foreign parent company of Indian subsidiary for carrying out certain services but not limited to design, encryption, research, development, delivery, validation, calibration, testing, related services, etc. in specified countries for the one time validity of 3 years subject to the post export reporting of all the exports done under the authorisation.
(ix) General Authorization for export of Chemicals and related equipments(GAEC) except software and technology : Export of chemicals (Excluding Software and Technology) listed in 1C,1D, 3D001 and 3D004 sub-categories is allowed to Australian Group(AG) countries and those listed in 1E sub-category allowed for export to State Parties to the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) on the basis of a onetime General authorization for export of Chemicals and related equipments (GAEC) issued by DGFT with one time validity of 5 years subject to the post export reporting of all the exports done under the authorisation.
(x) General Authorization for export after repair in India(GAER): Export of imported SCOMET items to the same entity abroad after repair in India will be allowed on the basis of a one-time General authorization for Export after Repair in India (GAER) issued by DGFT subject to post reporting on quarterly basis and other conditions as specified in para 10.12(D) of the Hand Book of Procedures.
10.09 Issue, amendment and revalidation of SCOMET authorizations
Export authorization for SCOMET items will be issued centrally by the DGFT (HQrs). Amendments, including revalidation, etc. on such authorization will also be done by the DGFT (HQrs) only. The procedure for Revalidation is prescribed in Para 10.20 of Handbook of Procedures.
10.10 Outreach Programmes on SCOMET and Export Control Framework
DGFT in association with Administrative Ministries/ Departments and Trade Associations will organize Industry Outreach Programmes on regular basis for effective awareness among the exporters/importers dealing with trade and manufacture, in particular, of SCOMET items. Institutional mechanism will be adopted to organize sector specific / region specific outreach programmes with focus on MSMEs and Startups.
10.11 Voluntary Self Disclosure of export of dual use items
DGFT recognizes that there may be occasions where responsible exporters, occasionally did not comply with the export control provisions of the FTDR Act, WMD Act, Customs Act, or any regulation, order, license, or other authorization on export controls issued by DGFT. DGFT encourages voluntary self disclosures of failure to comply with the export control provisions, and supports raising awareness among exporters to avoid any incidents of non¬compliance while taking strict action under FTDR Act for violation of SCOMET policy in cases other than voluntary self disclosure.
Chapter 11
Definitions
For purpose of FTP, unless context otherwise requires, the following words and expressions shall have the following meanings attached to them:-
11.01 “Accessory” or “Attachment” means apart, sub-assembly or assembly that contributes to efficiency or effectiveness of a piece of equipment without changing its basic functions.
11.02 “Act” means Foreign Trade (Development and Regulation) Act, 1992 (No.22 of 1992) [FT (D&R) Act] as amended from time to time.
11.03 “Actual User” is a person (either natural & legal) who is authorized to use imported goods in his/ its own premise which has a definitive postal address.
(a) “Actual User (Industrial)” is a person (either natural & legal) who utilizes imported goods for manufacturing in his own industrial unit or manufacturing for his own use in another unit including a jobbing unit which has a definitive postal address.
(b) “Actual User (Non-Industrial)” is a person (either natural & legal) who utilizes the imported goods for his own use in.
(i) any commercial establishment, carrying on any business, trade or profession, which has a definitive postal address; or
(ii) any laboratory, Scientific or Research and Development(R&D) institution, university or other educational institution or hospital which has a definitive postal address; or
(iii) Any service industry which has a definitive postal address.
11.04 “AEZ” means Agricultural Export Zones notified by DGFT in Appendix 2V of Appendices and Aayat Niryat Forms.
11.05 “Appeal” is an application filed under section 15 of the Act and includes such applications preferred by DGFT officials in government interest against decision by designated adjudicating/ appellate authorities.
11.06 “Applicant” means person on whose behalf an application is made and shall, wherever context so requires, includes person signing the application.
11.07 “Authorisation” means permission as included in Section 2(g) of the Act to import or export as per provisions of FTP.
11.08 “Capital Goods” means any plant, machinery, equipment or accessories required for manufacture or production, either directly or indirectly, of goods or for rendering services, including those required for replacement, modernisation, technological up-gradation or expansion. It includes packaging machinery and equipment, refrigeration equipment, power generating sets, machine tools, equipment and instruments for testing, research and development, quality and pollution control.
Capital goods may be for use in manufacturing, mining, agriculture, aquaculture, animal husbandry, floriculture, horticulture, pisciculture, poultry, sericulture and viticulture as well as for use in services sector.
11.09 “Competent Authority” means an authority competent to exercise any power or to discharge any duty or function under the Act or the Rules and Orders made there under or under FTP.
11.10 “Component” means one of the parts of a sub-assembly or assembly of which a manufactured product is made up and into which it may be resolved. A component includes an accessory or attachment to another component.
11.11 “Consumables” means any item, which participates in or is required for a manufacturing process, but does not necessarily form part of end-product. Items, which are substantially or totally consumed during a manufacturing process, will be deemed to be consumables.
11.12 “Consumer Goods” means any consumption goods, which can directly satisfy human needs without further processing and includes consumer durables and accessories thereof.
11.13 “Counter Trade” means any arrangement under which exports/imports from /to India are balanced either by direct imports/exports from importing/exporting country or through a third country under a Trade Agreement or otherwise.
Exports/Imports under Counter Trade may be carried out through Escrow Account, Buy Back arrangements, Barter trade or any similar arrangement. Balancing of exports and imports could wholly or partly be in cash, goods and/or services.
11.14 “Developer” means a person or body of persons, company, firm and such other private or government undertaking, who develops, builds, designs, organises, promotes, finances, operates, maintains or manages a part or whole of infrastructure and other facilities in SEZ as approved by Central Government and also includes a co- developer.
11.15 “Development Commissioner” means Development Commissioner of SEZ.
11.16 “Domestic Tariff Area (DTA)” means area within India which is outside SEZs and EOU/ EHTP/ STP/BTP.
11.17 “e-commerce” means buying and selling of goods through the internet on an e-commerce platform, the payment for which shall be done through international credit or debit cards, or other authorised electronic payment channels and as specified by the Reserve Bank of India from time to time.
11.18 “EOU” means Export Oriented Unit for which a letter of permit has been issued by Development Commissioner.
11.19 “Excisable goods” means any goods produced or manufactured in India and subject to duty of excise under Central Excise and Salt Act 1944(1of 1944).
11.20 “Export” is as defined in FT (D&R) Act, 1992, as amended from time to time.
11.21 “Exporter” means a person who exports or intends to export and holds an IEC number, unless otherwise specifically exempted.
11.22 “Export Obligation” means obligation to export product or products covered by Authorisation or permission in terms of quantity, value or both, as may be prescribed or specified by Regional or competent authority.
11.23 “Free” as appearing in context of import/export policy for items means goods which do not need any ‘Authorisation’/ License or permission for being imported into the country or exported out.
11.24 “FTP” means the Foreign Trade Policy, which specifies policy for exports and imports under Section 5 of the Act.
11.25 “Import” is as defined in FT (D&R) Act, 1992 as amended from time to time.
11.26 “Importer” means a person who imports or intends to import and holds an IEC number, unless otherwise specifically exempted.
11.27 ITC (HS) refers to Indian Trade Classification (Harmonized System) at 8 digits.
11.28 “Jobbing” means processing or working upon of raw materials or semi-finished goods supplied to job worker, so as to complete a part of process resulting in manufacture or finishing of an article or any operation which is essential for aforesaid process.
11.29 “Licensing Year” means period beginning on the 1st April of a year and ending on the 31st March of the following year.
11.30 “Managed Hotel” means hotels managed by a three star or above hotel/ hotel chain under an operating management contract for duration of at least three years between operating hotel/ hotel chain and hotel being managed. Management contract must necessarily cover the entire gamut of operations/management of managed hotel.
11.31 “Manufacture” means to make, produce, fabricate, assemble, process or bring into existence, by hand or by machine, a new product having a distinctive name, character or use and shall include processes such as refrigeration, re-packing, polishing, labeling, Re-conditioning repair, remaking, refurbishing, testing, calibration, re-engineering.
Manufacture, for the purpose of FTP, shall also include agriculture, aquaculture, animal husbandry, floriculture, horticulture, pisciculture, poultry, sericulture, viticulture and mining.
11.32 “Manufacturer Exporter” means a person who exports goods manufactured by him or intends to export such goods.
11.33 “Merchant Exporter” means a person engaged in trading activity and exporting or in tending to export goods.
11.34 “NC” means the Norms Committee in the Directorate General of Foreign Trade for approval of adhoc input –output norms in cases where SION does not exist and recommend SION to be notified in DGFT.
11.35 “Notification” means a notification published in Official Gazette.
11.36 “Order” means an Order made by Central
11.37 “Part” means an element of a sub-assembly or assembly not normally useful by itself, and not amenable to furtherdisassemblyfor maintenance purposes. Apart may be a component, spare or an accessory.
11.38 “Person” means both natural and legal and includes an individual, firm, society, company, corporation or any other legal person including the DGFT officials.
11.39 “Policy” means Foreign Trade Policy, 2023 as amended from time to time.
11.40 “Prescribed” means prescribed under the Act or the Rules or Orders made there under or under FTP.
11.41 “Prohibited” indicates the import/export policy of an item, as appearing in ITC (HS) or elsewhere, whose import or export is not permitted.
11.42 “Public Notice” means a notice published under provisions of paragraph 1.03 and 2.04 of FTP.
11.43 “Project Exports” refers to export of engineering goods on deferred payment terms and execution of turnkey projects and civil construction contracts abroad collectively.
Project Exports would encompass
(i) Civil construction contracts;
(ii) Turnkey Engineering contracts including supply of Capital Goods on deferred payment terms;
(iii) Process and Engineering Consultancy Services; and
(iv) Project Construction items (excluding Steel and Cement).
11.44 “Quota” means the quantity of goods of a specific kind that is permitted to be imported without restriction or imposition of additional Duties
11.45 “Raw material” means input(s) needed for manufacturing of goods. These inputs may either be in a raw/natural/unrefined/unmanufactured or manufactured state.
11.46 “Regional Authority” means authority competent to grant an Authorisation under the Act/Order.
11.47 “Registration-Cum-Membership Certificate” (RCMC) means certificate of registration and membership granted by an Export Promotion Council/Commodity Board/Development Authority or other competent authority as prescribed in FTP or HBP.
11.48 “Restricted” is a term indicating the import or export policy of an item, which can be imported into the country or exported outside, only after obtaining an Authorisation from the offices of DGFT.
11.49 “Rules” means Rules made by Central Government under Section 19 of the FT (D&R) Act.
11.50 “SCOMET” is the nomenclature for dual use items of Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies (SCOMET). Export of dual-use items and technologies under India’s FTP is regulated. It is either prohibited or is permitted under an Authorisation.
11.51 “Services” include all tradable services covered under General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) and earning free foreign exchange.
11.52 “Service Provider” means a person providing:
(i) Supply of a ‘service’ from India to any other country; (Mode1- Cross border trade)
(ii) Supply of a ‘service’ from India to service consumer(s)of any other country in India; (Mode 2-Consumption abroad)
(iii) Supply of a ‘service’ from India through commercial presence in any other country. (Mode 3 – Commercial Presence.)
(iv) Supply of a ‘service’ from India through the presence of natural persons in any other country (Mode 4- Presence of natural persons.)
11.53 “Ships” means all types of vessels used for seaborne trade or coastal trade, and shall include second hand vessels.
11.54 “SION” means Standard Input Output Norms notified by DGFT.
11.55 “Spares” means a part or a sub-assembly or assembly for substitution that is ready to replace an identical or similar part or sub- assembly or assembly. Spares include a component or an accessory.
11.56 “Specified” means specified by or under the provisions of this Policy through Notification/ Public Notice.
11.57 “Status holder” means an exporter recognized for export performance by an RA as per para 1.25 of the FTP.
11.58 “Stores” means goods for use in a vessel or aircraft and includes fuel and spares and other articles of equipment, whether or not for immediate fitting.
11.59 (a) “Supporting Manufacturer” is one who manufactures goods/products or any part/accessories/components of a good/ product for a merchant exporter or a manufacturer exporter under a specific Authorisation.
(b) “Supporting Manufacturer” for the EPCG Scheme shall be one in whose premises/ factory Capital Goods imported/ procured under EPCG Authorisation is installed.
11.60 State Trading Enterprises (STEs), for the purpose of this FTP, are those entities which are granted exclusive right/privileges export and /or import as per Para 2.20 (a) of FTP.
11.61 “Third-party exports” means exports made by an exporter or manufacturer on behalf of another exporter(s). In such cases, export documents such as shipping bills shall indicate names of both manufacturer exporter/manufacturer and third party exporter(s). Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC), Self Declaration Form (SDF), export order and invoice should be in the name of third party exporter.
11.62 “Transaction Value” is as defined in Customs Valuation Rules of Department of Revenue.
11.63 “Wild Animal” means any wild animal as defined in Section2 (36) of Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.




