Pallavi Singh
Business risk is defined as the exposure a company or organization has to factors that will lower its profits[1] or lead to its failure. Business risk can arise out of internal as well as external factors to a company.
It is practically impossible for a company to completely shelter itself from any kind of risk at all. The only way is to mitigate the overall risks associated with the business by building a strong risk management strategy. Depending upon the kind of industry, size of company and kind of operations, the type of risk can vary from one company to another.
A company with a higher amount of business risk may decide to adopt a capital structure with a lower debt-ratio to ensure that it can meet its financial obligations at all times. With a low debt ratio, when revenues drop the company may not be able to service its debt which may lead to bankruptcy. On the other hand, when revenues increase, a company with a low debt ratio experiences larger profits and is able to keep up with its obligations.[2]
Risks cannot be characterised in watertight compartments, and one form of risk can fall into other category on case to case basis. However, broadly speaking risks involved in a business are of the following types-
1. Operational Risk– Any risk arising out of day-to-day business activities of the company will fall in operational risk. This risk is more associated with the culture and working of the company. As it reflects man-made procedures and thinking processes, operational risk is more of a human risk due to human error. In areas where there is less human interaction, that are is likely to have lower operational risk.[3]
One of the examples of Operational Risk is Data Breach. Over 50% of all the data breaches reported in Australia were caused by human error.[4] Automating work processes can reduce the human error.
2. Strategic Risk– It is a risk associated with failed business decisions. To achieve business goals, companies face dangers and downfalls. Every internal choice comes with the potential of making the wrong choice also. In addition to it, strategic risk can also come externally because of market demand and the environment in which a product/ service has to compete in the market.
For example, a bank takes on strategic risk by offering credit, but it’s an inherent risk that is directly related to its business goals.[5] Strategic risks occur when businesses fail to meet the market’s needs. To complicate things further, strategic risk isn’t only based on subjective decisions. It can also be caused externally. At the end the responsibility of risk management vests with the board of directors of the company.
3. Reputational Risk– As the name suggests, it is a risk associated with goodwill or name or entity of the business. Reputational Risk are mostly associated with the actions/ inactions of the higher authorities of the company, employees of the company or any associates of the company. The biggest fear of this risk is that its outcome cannot be easily measured. Reputational damage can be in various forms like negative publicity, negative perception of the company due to any unpredictable event etc. It can wipe out billions of dollars in market capitalization and impose sweeping changes to company’s leadership.[6] The biggest drawback with reputational risk is that its unpredictable.
Firms with strong positive reputations are perceived as they are providing more value, which often allows them to charge a premium. Because the market believes that such companies will deliver sustained earnings and future growth, they have higher price-earnings multiples and market values and lower costs of capital. Moreover, in an economy where 70% to 80% of market value comes from hard-to-assess intangible assets such as brand equity, intellectual capital, and goodwill, organizations are especially vulnerable to anything that damages their reputations.[7]
Some companies use the approach of Crisis Management instead of Risk Management, i.e.- having a reactive approach to limit the damage instead of proactive approach to not let the damage occur in the first place. However, like other Risks, it is essential to quantify Reputational Risk also.
4. Financial Risk– This risk is associated with handling of finances. It will also include risks like liquidity and credit risks etc. Companies can not only face the possibility of default on debt they undertake but may also experience failure in an undertaking which causes a financial burden on the business. In some places, financial risk overlaps with operational risk also.
Financial risk can be due to various macroeconomic forces like changes to the market interest rate, and the possibility of default by sectors or large corporations.[8] When company takes any type of debt to grow this creates a financial risk to both the business itself and to any investors or stakeholders invested in the company. Investors can use a number of financial risk ratios to assess a company’s prospects.
Financial Risk like any other risk is inevitable, which means, it is not inherently good or bad up to a certain degree. Calculating a business risk can lead to better, more informed business or investment decisions.[9] There are various tools to calculate financial risk, these include-
A. Fundamental analysis– Process of measuring a security’s intrinsic value by evaluating all aspects of the underlying business including the firm’s assets and its earnings.
B. Technical analysis– Process of evaluating securities through statistics and looks at historical returns, trade volume, share prices, and other performance data.
C. Quantitative analysis– Evaluation of the historical performance of a company using specific financial ratio calculations.
5. Legal & Compliance Risk– Any new legislation, regime, regulations that comes up can decrease or increase your legal risk. It is an organization’s potential exposure to legal penalties, financial forfeiture, and material loss, resulting from its failure to act in accordance with industry laws and regulations, internal policies or prescribed best practices.[10]
Like any other risk, legal risk is also inevitable. It is mandatory for organisations to comply with the law of the land to avoid any potential penalty or any other adverse effect on the company. With increase in a company’s legal risk, exposure to reputational and financial risk also increases manyfold.
Most common reasons of a company’s exposure to legal risks include fraudulent practices, environmental issues, privacy & data security breaches and health and safety issues.
To deal with legal risks companies undertake the process of Compliance Risk Management. While undertaking such process it is essential to look at the regulatory landscape of the industry and the state, however without ignoring the internal processes and procedures set out in company policies. Since, a compliance risk is not codified to one department or one level of the company, it requires a collective approach for successful compliance management.
6. Political Risk (Franchise Risk)- This can vary from changes in the kind of government to a country or area being politically unstable at a particular time. This can also include political instability in another country where the Head Office or Manufacturing Unit is located.
Business Model Risk can also at times fall in this category. Also known as disruption risk in extreme forms.[11] But unlike any other form of risk, this has a wider impact on any business. It is dependent on all aspects of a business model namely- Value Proposition, Supply Chain Management, Customer Segment, Product Identification/ Service Classification, Operations and Competitors etc. This included external as well as internal factors.
Mondelez was charged of using corrupt practices by the SEC. Company upfront agreed to pay 90 crores in the matter. The matter was that Mondelez India was allegedly reported to have paid bribes to government officials for obtaining licenses for a plant in Himachal Pradesh. The company was heavily fined. Mondelez herein was exposed to –
- Reputation risk: as the company was allegedly involved in corrupt practices
- Legal and compliances Risk: if during investigation it would be found that licenses were obtained fraudulently, all licenses would be cancelled thereby halting all the operations
- Financial Risk: Company had to pay hefty penalty and be ready for financial set back if the operations are halted due to fraudulent act of the senior officials of the company.
To Calculate the risks associated with any business analysts use four simple ratios-
1. Contribution margin– Contribution margin ratio is a percentage of total sales; calculated on gross or on per unit basis.
Contribution Margin = Sales Revenue – Variable Cost
Contribution Margin Ratio = Sales Revenue – Variable Cost
Sales Revenue
Percentage of profit margin will tell, on how many per unit sales what profit will the company make.
Contribution margin ratio X per unit sales = increase in profit
It represents the incremental money generated for each product/unit sold after deducting the variable portion of the firm’s costs.[12]
The ratio shows the profit potential of a particular product and what portion of the sales will help to cover the company’s fixed costs. It is of the most essential ratios in break-even analysis. The remaining revenue after covering fixed costs is the profit generated. The higher this margin is, the better it is. The higher your company’s ratio result, the more money it has to cover the company’s fixed costs.[13] If the contribution ratio comes very low relative to its competitors in the market, there is no profit in continuing that product.
2. Operation leverage effect– As the name suggests, it is a leverage calculation on operations of a firm. Operational costs will include fixed and variable costs for production. Ideally, with an increase in sales, there is no change in the cost of fixed assets. But, the variable cost of production will increase accordingly. It means, having a higher fixed cost will have a positive impact on the revenue with every increase in sale.
Operating Leverage ratio is hence a measure of how much income will change given a percentage change in sales volume.
OLE = Contribution Margin Ratio/Operating Margin
A good OLE is above 1. With more fixed assets coming in picture, OLE will rise.
If the OLE is 1, it means that all costs are variable and a X% change in sales volume will mean an exact X% change in income.
3. Financial leverage effect– It is a set of ratios and include equity or debt ratio to calculate the overall load of the company as against the assets it has. In clear terms, the assets can be owned by the shareholders or the creditors. The more the ownership with the stakeholders, more secure the company is. The reason being, less of the assets are loaned or on credit for which less payment of interest needs to be done.
4. Total Leverage effect– It is a combination of both the Financial Leverage Effect (FLE) and Operational Leverage Effect (OLE).
Total Leverage Effect (TLE) = Financial Leverage Effect (FLE) X Operating Leverage Effect (FLE)
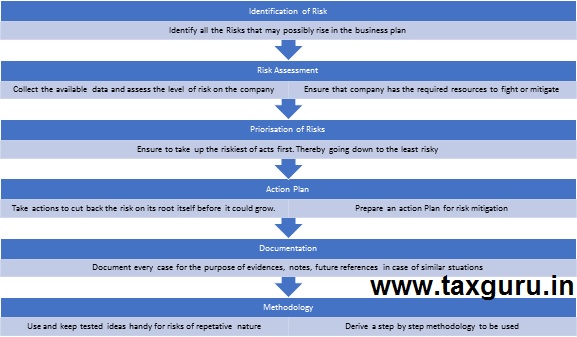
HOW TO MAKE A RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
Preparing a risk management plan is an important task to ensure that company does not go in the state of chaos when any kind of risk hits. Preparation of a risk management plan is a tedious task and requires an extensive study of the entire functioning of not only the company, but the industry as well as the market conditions.
Most companies take professional help for building risk management plans. However, it is important that the directors and senior officials of the company also spend sufficient time with the experts to ensure that there are no loopholes in their risk management plan. As we know, a Risk Management plan is a tailor-made document for the specific company, it is extremely important that company directors and higher management takes more time in framing an effective and functional plan.
An effective risk management plan can not only save a lot of chaos among the employees but can shield the company from huge financial losses and many a times from public embarrassment. Below are a few pointers on how to create an effective risk management plan.
[1] https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/businessrisk.asp, What is Business Risk (Jul. 28, 2020)
[2] Ibid.
[3] Operational Risk Definition (investopedia.com), Operational Risk (Sept 13, 2020)
[4] https://www.readinow.com/blog/top-11-operational-risks, Top 11 Operational Risks for the year, Jul. 31, 2018)
[5] https://www.solvexia.com/blog/strategic-risk-management-5-tips-for-success, Strategic Risk Management: 5 Tips for Success, Jul. 22, 2020
[6] https://www.reputationmanagement.com/blog/reputational-risk/, What is Reputational Risk and how to manage it, Jan. 5, 2021
[7] https://hbr.org/2007/02/reputation-and-its-risks, Reputation and it’s Risks, Feb. 2007
[8] https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/financialrisk.asp, Financial Risk, Mar. 24, 2021
[9] Ibid.
[10] https://searchcompliance.techtarget.com/definition/compliance-risk,
[11] https://www.openriskmanual.org/wiki/Business_Model_Risk, Business Model Risk, Open Risk Manual, Jan 2016
[12] https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/contributionmargin.asp, Contribution margin definition, Dec. 22, 2020
[13] https://www.thebalancesmb.com/contribution-margin-ratio-393478, Defining and Calculating Contribution Margin ratio, Jun. 25, 2019




