Summary: In the realm of indirect taxation, two notable schemes aid in easing business operations. First, the Export with Payment of GST scheme allows exporters to claim refunds on Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) paid, addressing issues of input tax credit accumulation. This process involves filing a shipping bill, Export General Manifest, and accurate GST returns to facilitate the refund. Second, the Authorized Economic Operator (AEO) Scheme benefits businesses involved in international trade by certifying them as secure and compliant. AEO status offers advantages like faster customs clearances, reduced bank guarantees, and enhanced facilitation in mutual recognition agreement countries. The AEO program is optional but provides significant operational benefits, including reduced customs scrutiny and expedited processing of import and export transactions. Both schemes are designed to reduce financial burdens and streamline business operations in the global trade environment.
Indirect Taxation: Beneficial Schemes for Ease of Doing Business
A. Export with Payment of GST
There may be situations at times faced by tax payers in GST regime in form of accumulation of GST Input Tax Credit when there is only Export Sales of Goods which is treated as zero rated Supply under Central Goods and Services Act, 2017 (CGST Act, 2017). As per the CGST Act, Section 2(5) Export of Goods means taking goods out of India to a place Outside India.
Section 16 (1) of Integrated Goods and Services Act, 207 defines Zero Rated Supply as supply of Goods and Services or both namely:
a) Export of Goods and Services or both
b) Supply to SEZ unit.
Section 16(2) – Credit of input tax may be availed for making zero-rated supplies, notwithstanding that such supply may be an exempt supply.
Section 16(3) – A registered person making zero rated supply shall be eligible to claim refund of unutilized input tax credit on supply of goods or services or both, without payment of integrated tax, under bond or Letter of Undertaking, (as per section 54) (in case of non-realization of sale proceeds, return back amount along with the Interest)
Section 16(4) – The Government may, on the recommendation of the Council, and subject to such conditions, safeguards and procedures, by notification, specify-
(i) a class of persons who may make zero rated supply on payment of integrated tax and claim refund of the tax so paid;
(ii) a class of goods or services which may be exported on payment of integrated tax and the supplier of such goods or services may claim the refund of tax so paid.
♦ Why Export with GST?
Registered person paying tax at the time of Inward Supplies is eligible to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) on such supplies except in cases where such ITC is blocked as per section 17(5). ITC availed can be utilized by the registered person against Tax Payable on its Outward Supplies.
Tax on Outward Supplies
Less: Input Tax Credit (ITC)
Net Tax Payable in cash, if any
In case of Export of Goods, as per above provision, No Outward Tax Liability will be generated which will result in accumulation of Input Tax Credit.
To ensure there is no blockage of funds with tax payers, Government has provided with an option of Export of Goods with Payment of GST which is governed by Rule 96 of CGST Rules, 2017.
Note: Rule 96 is only applicable for Export of Goods. For Refund of ITC on Export of Services, application needs to be file in accordance with Section 54.
♦ Procedure for Export with payment of GST (Rule 96)
1. Filing of Shipping Bill for Exports with inclusion of IGST (In case of Exports, place of Supply is place outside India) with the Customs as per applicable GST rate on such goods. There are no other refund application needs to be file, Shipping Bill is treated as a refund application
2. Filing of Export General Manifest The person in charge of the conveyance carrying the export goods duly files an export general manifest for such shipping bill
3. Furnishing a Valid GSTR-1 return including details of such exports done with GST.
Below details should be mentioned properly in Exports table 6A including Shipping Bill and Port Code details which are very much relevant in present case
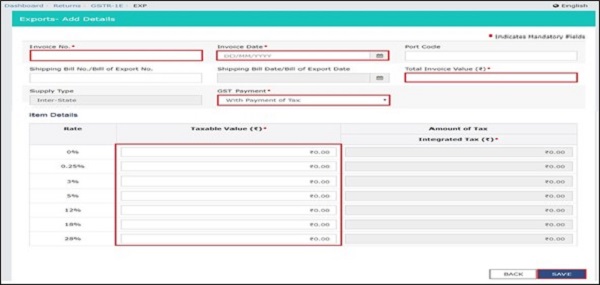
4. The details of the relevant export of goods invoices filed with GST in FORM GSTR-1 shall be transmitted electronically to Customs ICEGATE Portal from GST Portal.
5. Filing of GSTR-3B and discharge of Liability of GST charged in Shipping Bill at the time of Export of Goods either through utilization of Input Tax Credit or payment in Cash (Preferably ITC to liquidate accumulated credit on account of export of goods)
6. Upon the receipt of the information regarding the furnishing of a valid return in FORM GSTR-3B from GST Portal, ICEGATE Portal will validate the details of such invoices with Shipping Bill filed on ICEGATE Portal.
7. Generation of IGST Scroll: Customs officer will generate Scroll once the shipping bill details are validated with the invoices transmitted from GST portal.
User Can check the details of generation of IGST Scroll on the ICEGATE Portal by login into IceGate : e-Commerce Portal of Central Board of Excise and Customs using its log in credentials and check status of scroll putting below details.
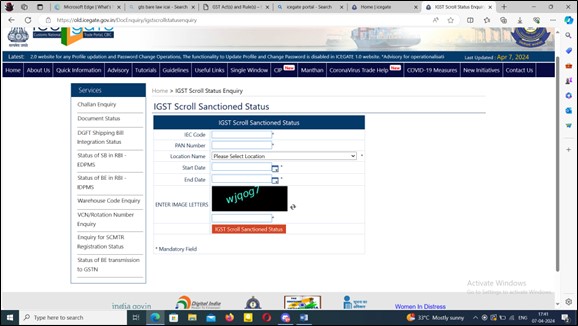
8. Credit of Amount in Bank Account: An amount equal to the integrated tax paid in respect of each shipping bill or bill of export shall be electronically credited to the bank account of the applicant mentioned in his registration particulars and as intimated to the Customs authorities once approved by PAO/PFMS.
♦ Points to be kept in mind while using this arrangement-
1. Accounting Entry after filing of Shipping Bill: Once Shipping Bill is filed, exporter should book GST Refund Receivable entry in the books of Accounts and Create GST Liability as well to be discharge in GSTR-3B of the month in which Shipping Bill is filed
GST Export Refund Receivable A/c Dr.
To IGST Liability A/c
2. Aadhaar Authentication: Registered Tax Payer should undergo Aadhaar Authentication process on the GST Portal for Authorized Signatory and One Director whose name is mentioned in Registration Certificate otherwise Export Invoices will not be transmitted to ICEGATE Portal for Validation.
3. Matching of GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B: Details of Export Invoices reported in GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B in past period should match properly otherwise invoices will not be transmitted to ICEGATE Portal.
4. Accurate Reporting of Export Invoices in GSTR-1- Details such as Invoice No., Shipping Bill no., port code should be same as filed in shipping bill otherwise Invoice will be validated with below errors and scroll will generate only after error is rectified in next return.
| Response Code | Description | Action Required |
| SB000 | Successful | – |
| SB001 | Invalid SB Details | Amend Shipping Bill/GSTR-1 |
| SB002 | EGM not filed for SB | File EGM |
| SB003 | Invalid GSTIN | Check GSTIN status |
| SB004 | GSTR-3B already received | – |
| SB005 | Invalid Invoice Number | Amend GSTR-1 |
| SB006 | Gateway EGM details not available | File EGM and check correctness with SB |
Cases where Export with GST not allowed:
1. When Goods are purchased under Merchant Export i.e. concessional rate of tax of 0.1%.
2. Export of Services- This scheme is only available for Goods.
3. Supply of goods by a registered person against Advance Authorization
4. Supply of capital goods by a registered person against Export Promotion Capital Goods Authorization
5. Supply of goods by a registered person to Export Oriented Unit
6. Supply of gold by a bank or Public Sector Undertaking specified in the notification No. 50/2017-Customs, dated the 30th June, 2017 (as amended) against Advance Authorization
B. Authorized Economic Operator
> Background And Features of AEO Programme:
♦ Who is an authorized economic operator (AEO)?
An AEO is a business entity involved in international movement of goods requiring compliance with provisions of the national Customs law and is approved by or on behalf of national administration in compliance with World Customs Organization (WCO) or equivalent supply chain security standards. The security standards are detailed in World Customs Organization Safe framework of standards [WCO SAFE FoS], which is the basis of the Indian AEO programme.
♦ What is the AEO programme?
The AEO programme enables Customs administration to identify the safe and compliant business entity in order to provide them a higher degree of assured facilitation. This segmentation approach enables Customs resources to focus on less or non-compliant or risky businesses for control. Thus, the aim of AEO programme is to secure the international supply chain by granting recognition to reliable operators and encouraging best practices at all levels in the international supply chain. Through this programme, the Customs shares its responsibility with the businesses, while at the same time rewarding them with a number of additional benefits.
♦ Is AEO mandatory for businesses involved in the supply chain?
The AEO scheme is purely an optional scheme. Applying for AEO status is a business decision de – pending on the role of the business entity in the supply chain and its willingness to acquire the benefit flowing by acquiring AEO status.
♦ What is the aim of the Indian Customs AEO Programme?
The AEO programme has the following objectives:
-
- To provide business entities with an internationally recognized certification;
- To recognize business entities as “secure and reliable” trading partners;
- To incentivize business entities through defined benefits that translate into savings in time and cost;
- Secure supply chain from point of export to import;
- Ability to demonstrate compliance with security standards when contracting to supply overseas importers / exporters;
- Enhanced border clearance privileges in Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA) partner countries;
- Minimal security related disruption to flow of cargo;
- Reduction in dwell time and related costs; and
- Customs advice / assistance if trade faces unexpected issues with Customs of countries with which India has MRAs.
> Benefits of AEO Scheme to Business Entities:
| S. No. | Benefits – AEO | Impact-Financial /Non-Financial |
| 1 | Shorter cargo release time (High level of facilitation) | Non-Financial |
| 2 | Facility of Direct Port Delivery (DPD) of import Containers and Direct Port Entry (DPE) of Export Containers | Non-Financial |
| 3 | Waiver of seal verification/scrutiny of documents | Non-Financial |
| 4 | Out of charge or let export order without any scrutiny by the officers | Non-Financial |
| 5 | Facility of front-line treatment for container scanning | Non-Financial |
| 6 | Facility of deferred payment of duty | Financial |
| 7 | Faster disbursal of drawback amount within 72 hours of EGM submission | Financial |
| 8 | The BEs/SBs selected for Assessment and/or Examination will be processed on priority by the Customs officers | Non-Financial |
| 9 | Facility of self -sealing of export goods would be allowed without the requirement to seek case to case base permission from the authorities | Non-Financial |
| 10 | Faster completion of Special Valuation Branch (‘SVB’) proceedings in case of related party imports and monitoring of such cases for time bound disposal in terms of new guidelines | Non-Financial |
| 11 | Facility to paste MRP stickers in their premises | Non-Financial |
| 12 | Access to consolidated import/export data through ICEGATE from a date that would be communicated separately | Non-Financial |
| 13 | ID cards to be granted to authorized personnel for hassle free entry to Custom Houses, CFSs and ICDs | Non-Financial |
| 14 | Separate space earmarked in Custodian’s premises | Non-Financial |
| 15 | 75% Reduction on bank guarantee | Financial |
| 16 | Investigations, in respect of Customs, Central Excise and Service Tax cases would be completed in six to nine months | Non-Financial |
| 17 | Dispute resolution would be done within six months | Non-Financial |
| 18 | E-mail regarding arrival/ departure of the vessel carrying their consignments | Non-Financial |
| 19 | They will not be subjected to regular transactional Post Clearance Audit, instead of that onsite PCA will be conducted once in three years only | Non-Financial |
| 20 | 24/7 clearances on request at all seaports and airports | Non-Financial |
| 21 | Facility of submitting paperless declarations with no supporting documents in physical form. | Non-Financial |
| 22 | The refund/Rebate of Customs/Central Excise duty and Service Tax would be granted within 45 days of the submission of complete documents | Financial |
| 23 | They will get trade facilitation by a foreign Customs administration with whom India enters a Mutual Recognition Agreement/Arrangement | Non-Financial |
| 24 | Custom Houses will appoint a “Client Relationship Manager” (CRM) at the level of Deputy / Assistant Commissioner who would act as voice of the AEO within Customs in relation to legitimate concerns and issues | Non-Financial |
*Benefits described are of AEO Tier II category
> Tiers in AEO:
There are Three Tier Status in AEO out of which one can be applied by an entity-
| AEO Status | Applicability | Validity |
| Tier1 | Granted only to an importer or to an exporter without physical verification of places/premises. | 3 Years |
| Tier2 | Granted only to an importer or to an exporter after physical verification of premises/places. | 3 Years |
| Tier3 | Granted to (i) an importer or to an exporter who continuously enjoyed the status of AEO-T2 for a period of two years preceding the date of application or (ii) The importer/exporter holding AEO-T2 certificate, and its other business partners namely importers or exporters, Logistics service providers, Custodians/Terminal operators, Customs Brokers and Warehouse operators are holders of AEO-T2or AEO-LO certificate or any other equivalent AEO certificate granted by a foreign Customs. | |
| LO | Granted to economic operators other than importers and exporters, (e.g. Logistics Providers, Custodians or Terminal Operators, Customs Brokers, Warehouse Operators) after physical verification of premises/places. | 5 Years |
> Eligibility for AEO Scheme:
Any business entity that is part of the international supply chain; involved in the cross- border movement of goods and required to fulfill obligations under the Customs law in India, only can apply for AEO status. These may include exporters, importers, logistic providers (e.g. carriers, airlines, freight forwarders, etc.), Custodians or Terminal Operators, Customs House Agents and Warehouse Owners, Port operators, authorized couriers, Stevedores etc. The list is not exhaustive.
> What are the eligibility criteria for a business entity to apply for Indian AEO status?
The eligibility conditions and criteria for granting AEO Status has been listed in the Section 3 of the AEO Circular No. 33/2016 –Customs dated 22nd July, 2016 as amended by Circular No. 3/2018-Customs dated 17th January, 2018. An entity should fulfil the following criteria:
a) Established in India;
b) Business should be involved in Customs related activity;
c) Should have dealt with minimum 25 Customs documents (either Bill of Entry or Shipping Bill) in the last fiscal year;
d) Should have been in business activity for last 3 Financial Years.
> Process of Filing Application:
♦ Application for AEO
The application should be sent to the office of the jurisdictional Chief Commissioner of Customs with copy to AEO Programme Manager, Directorate of International Customs, Directorate of International Customs, 10th Floor, Tower II, Jeevan Bharti Building, Connaught Place, New Delhi – 110001. The jurisdictional Chief Commissioner of Customs is the one from where the Importer/Exporter/Logistic operator is doing majority of business in international supply chain. Application to be filed on website aeoindia.gov.in. The applicant can login to the website and file the AEO- T1 application.
♦ Where to file Application:
With chief Commissioner of Customs at various offices- a) Delhi b) Mumbai Zone-I c) Mumbai Zone-II d) Mumbai Zone-III e) Ahmedabad f) Vishakhapatnam g) Bhubaneswar h) Bangalore i) Chennai j) Hyderabad k) Kolkata l) Tiruchirappalli m) Patna n) Pune, o) Nagpur p) Bhopal
♦ Documents required to be filled for AEO Application:
For Tier1– An Application is required to be filed online on website aeoindia.gov.in in prescribed proforma
Along with a Declaration as indicated in Annexure A- 1, Annexure A-2 to CBEC Circular No. 26/2018 dated 10.08.2018.
For Other Tiers– The application to be filed in accordance with form as specified in the Circular No. 33/2016-Customs containing Ten annexures. However, an applicant is required to fill-in and submit only those annexures which may be applicable to it. Annexures:
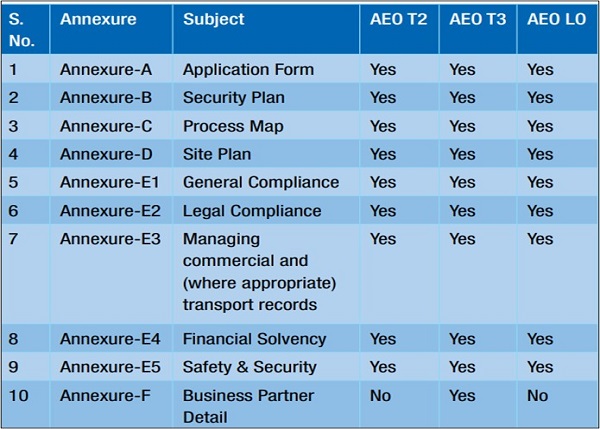
> Circulars issued by CBIC in relation to AEO Scheme
– Circular 33/2016 – Customs (Dated 22.07.2016)
– Circular 3/2018 – Customs (Dated 17.01.2018)
– Circular 26/2018 – Customs (Dated 10.08.2018)
– Circular 51/2018 – Customs (Dated 07.12.2018)
– Circular No. 27/2020 – Customs (Dated 02.06.2020)
(Extension of validity of AEO certification for ease of renewal process)
– Circular No 37/2020 – Customs (Dated 19.08.2020)
– Regarding: Authorised Public Undertakings (APU) Circular for Deferred payment of Customs duty.
– Circular No 54/2020 (Dated 15.12.2020)
– Customs for special facilitation for MSME
– Circular No. 11/2021 (Dated 24.05.2021)
(Extension of validity of AEO Certification)
– Circular No. 13/2021 (Dated 01.07.2021)
(Launch of Version 2.0 of Web-application for Online Filing of AEO T2 & AEO T3 applications)
– Circular No. 18/2021 (Dated 31.07.2021)
(Auto Renewal of AEO T1)





