The following clarifications are issued through the GST Central Tax circulars (Circular No. 76 to 80 of 2018 and 84 to 85 of 2019) (explained below) and will be effective from the date of applicability of actual provision for which clarification is issued: –
Page Contents
- A. Circular No. 76/50/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
- 1. Taxability on supply of used vehicles, seized & confiscated goods, old & used goods, waste & scrap by Government departments-
- 2. Applicability of penalty u/s 73 (11) of the CGST Act in case GSTR-3B is filed after due date-
- 3. Rate of Tax applicable for the issuance of Supplementary Invoice, Debit note or Credit note in case of revision in the prices of goods & services after 01st Jul 2017-
- 4. Clarification regarding the persons notified by the government for the applicability of TDS provisions in GST-
- 5. Inclusion of TCS collected as per Income Tax Act, 1961 in taxable value of supply as per GST-
- 6. Who will be considered as the owner of goods detained or seized/confiscated as per GST-
- B. Circular No. 77/51/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
- C. Circular No. 78/52/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
- D. Circular No. 79/53/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
- 1. Option of online submission of all the documents for applying GST refund-
- 2. Refund of Accumulated ITC on A/c of Inverted Duty Structure-
- 4. Clarification regarding Refund applications that have been generated on the portal but not physically received in the jurisdictional tax offices-
- 5. Process for Application of Refund for Compensation Cess (not claimed earlier in GST return) on A/c of Export with LUT/Bond-
- 7. Issue related to the refund of cess not availed in the GST return of the relevant period-
- 8. Refund of ITC of GST paid on invoices of earlier tax period but availed in the subsequent tax period-
- 9.Clarification regarding the eligibility of inputs for being included in “Net ITC” for the calculation of GST refund-
- 10. Clarification on the refund of accumulated ITC of input services and capital goods on A/c of inverted duty structure-
- E. Circular No. 80/54/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
- F. Circular No. 84/03/2019 – Central Tax Dated: – 01st January, 2019
- G. Circular No. 85/04/2019 – Central Tax Dated: – 01st January, 2019
A. Circular No. 76/50/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
1. Taxability on supply of used vehicles, seized & confiscated goods, old & used goods, waste & scrap by Government departments-
| Recipient of supply
|
Taxability |
| A Registered Person | Tax would be payable by that registered recipient on RCM (Reverse charge) basis. |
| An Unregistered Person | The respective Govt. departments (i.e. CG, SG, UT or a local authority) shall be liable to get GST registration *subject to provisions of Sec. 22 (Persons liable for registration) and Sec. 24 (Compulsory registration in certain cases) of CGST Act, and pay GST on such supply by charging from Unregistered person. |
* It means that in case of above supply to Unregistered Person, respective Government department will take GST registration only if that department is liable to be registered as per the provisions of Sec. 22 & 24 of CGST Act.
2. Applicability of penalty u/s 73 (11) of the CGST Act in case GSTR-3B is filed after due date-
– The penalty u/s 73 (11) of CGST Act can be imposed only when the provisions of Section 73 are invoked. A SCN (Show cause notice) is required to be issued for the same by the proper officer.
– The provisions of Section 73 are not invoked in case of late filing of GSTR-3B with payment of proper tax & applicable interest.
– Hence, the penalty u/s 73 (11) of CGST Act can not be imposed in this case.
– It is further clarified that since late payment of tax is a violation of the provisions of CGST Act, a general penalty u/s 125 of the CGST Act may be imposed after following the due process of law.
3. Rate of Tax applicable for the issuance of Supplementary Invoice, Debit note or Credit note in case of revision in the prices of goods & services after 01st Jul 2017-
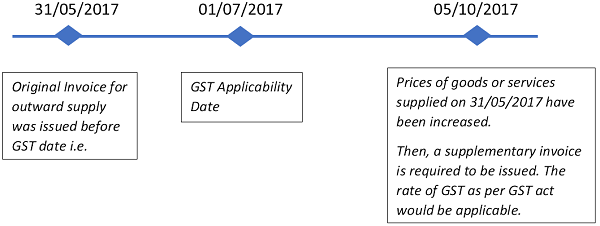
As explained above, in case a debit/credit note is required to be issued after 01st July 2017 in respect of the outward supplies done before GST, the rate of GST would be applicable for the issuance of such debit/credit note.
4. Clarification regarding the persons notified by the government for the applicability of TDS provisions in GST-
As per the provisions of Section 51(1) of CGST Act, 2017, some persons have been specified for the applicability of TDS provisions in clause (a), (b), (c) & (d).
In clause (d), Government has notified additional category of persons, on whom the TDS provisions would be applicable, those are as follows: –
(a) an authority or a board or any other body, –
(I) set up by an Act of Parliament or a State Legislature; or
(II) established by any Government,
*with fifty-one per cent. or more participation by way of equity or control, to carry out any function;
(b) Society established by the Central Government or the State Government or a Local Authority under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 (21 of 1860);
(c) public sector undertakings.
*Clarification: – This long-written line is applicable to both the points i.e. (I) and (II) of clause (a). It means that the condition of 51% or more equity with the Government must be fulfilled for being covered in clause (a).
5. Inclusion of TCS collected as per Income Tax Act, 1961 in taxable value of supply as per GST-
It is clarified that taxable value in GST shall include: –
– The TCS amount collected by the supplier under Income Tax Act, 1961.
For Example: –
– Value of sale of goods is Rs. 2,00,000/-
– The TCS @ 1% i.e. Rs. 2000/- is to be collected as per Income Tax Act
– Then the total taxable value would be Rs. 2,02,000/-
– GST @ 18% would be calculated on Rs. 2,02,000/-
– Amount of GST would be Rs. 36,360/-
6. Who will be considered as the owner of goods detained or seized/confiscated as per GST-

B. Circular No. 77/51/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
1. Effective date of withdrawal from the composition scheme by Taxpayer-
– In case, a Composition dealer has applied for the withdrawal from composition scheme,
– the effective date of such withdrawal shall be the date indicated by the dealer in intimation/application filed in the form CMP-04
*But that date can not be prior to the commencement of FY in which withdrawal application is filed.
For Example: – CMP-04 is filed on 23/04/2018 (FY 2018-19). The date to be indicated in CMP-04 for the withdrawal, can not be before 01/04/2018.
– A person has availed the composition scheme,
– After some period, it has found by tax authorities that he has *contravened the provisions of the GST act regarding the eligibility of composition scheme i.e. violated the eligibility
– There will be a withdrawal of composition scheme by the tax authorities.
– The effective date of such withdrawal shall be the date: –
- Including any old date,
- as determined by the Tax Authorities but not before the date of *contravention of the eligibility by Taxpayer.
– An order will be issued after proceedings have been completed against Taxpayer.
– Registered person shall be liable to pay tax as Regular Dealer from the date of Issue of Order.
– That dealer shall be entitled to take input tax credit on the stock or capital goods left on the date immediately preceding the date of issue of Order.
For Example: – Date of issue of order: – 28/03/2018, ITC would be calculated on the stock as on 27/03/2018.
C. Circular No. 78/52/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
1. Clarification on export of services in GST by outsourcing-
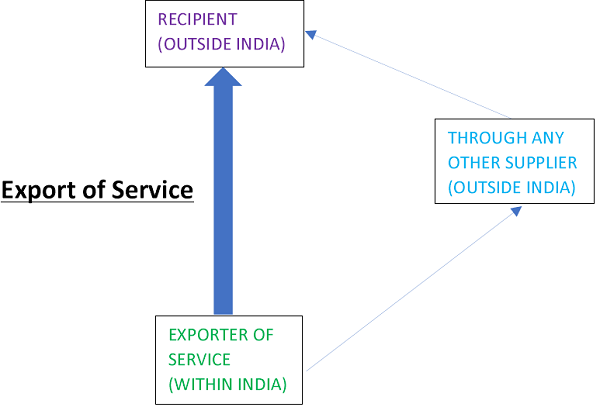
– As per the above diagram, a person of India is exporting the services outside India with the help of another supplier outside India e. by outsourcing (whether full portion or part portion of the service); and
– the payment of outsourced part of service was done by the Recipient (Outside India) directly to Supplier (Outside India) and the balanced consideration was received in convertible foreign exchange by the Supplier (Within India) for the direct portion of service, or the full payment was received by the Supplier (Within India) from the Recipient (Outside India) even then,
– the full amount of contract will be considered as the export of service subject to the following conditions: –
- IGST is paid by the Supplier (Within India) under RCM (Reverse charge mechanism) on the value of that outsourced portion (Since that will be an import of serviceby person (Within India) from Supplier (Outside India); and
- RBI has allowed by general instruction or by specific approval that a part of the consideration for such export can be retained outside India.
Example: ABC Ltd. India has received an order for supply of services amounting to $ 5,00,000/- to a US based client. ABC Ltd. India is unable to supply the entire services from India and asks XYZ Ltd. Mexico (who is not merely an establishment of a distinct person viz. ABC Ltd. India, in accordance with the Explanation 1 in Section 8 of the IGST Act) to supply a part of the services (say 40% of the total contract value). ABC Ltd. India shall be the exporter of services for the entire value if the invoice for the entire amount is raised by ABC Ltd. India. The services provided by XYZ Ltd. Mexico to the US based client shall be import of services by ABC Ltd. India and it would be liable to pay integrated tax on the same under reverse charge and also be eligible to take input tax credit of the integrated tax so paid.
Further, if the provisions contained in section 2(6) of the IGST Act are not fulfilled with respect to the realization of convertible foreign exchange, say only 60% of the consideration is received in India and the remaining amount is directly paid by the US based client to XYZ Ltd. Mexico, even in such a scenario, 100% of the total contract value shall be taken as consideration for the export of services by ABC Ltd. India provided integrated tax on import of services has been paid on the part of the services provided by XYZ Ltd Mexico directly to the US based client and RBI (by general instruction or by specific approval) has allowed that a part of the consideration for such exports can be retained outside India. In other words, in such cases, the export benefit will be available for the total realization of convertible foreign exchange by ABC Ltd. India and XYZ Ltd. Mexico.
D. Circular No. 79/53/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
1. Option of online submission of all the documents for applying GST refund-
– Government has now allowed the online submissionof all the documents related to the GST refund on common portal with RFD-01A. It means that no manual submission of the refund application with physical documents is required.
– It is an option for the Taxpayer, manually submission of GST refund can also be done.
– In case of online submission of all the documents: –
- As soon as ARN is generated, the refund application & all the documents shall be transferred to the proper jurisdictional officer.
- But acknowledgment and DM (Deficiency Memo) if any will be issued manually only.
2. Refund of Accumulated ITC on A/c of Inverted Duty Structure-
– What officers were doing in the same case?
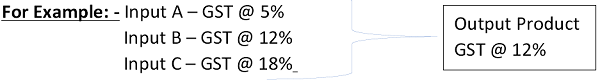
The above-mentioned case belongs to the Inverted Duty Structure. Department officers were denying the refund of Accumulated ITC of Input A & B, since GST rate of Tax for these inputs is less than or equal to the GST rate of output supply.
Clarification: – The Accumulated ITC on Input A & B will also be included for the calculation of maximum refund amount. Since, the definition of “Net ITC” includes the same as per rule 89(5) of the CGST Rules.
3. Duration for the GST Refund by department-
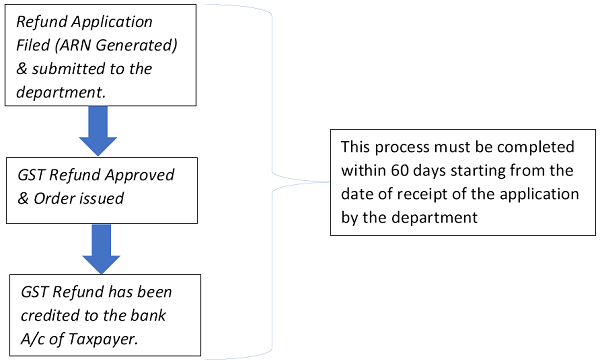 – If DM (Deficiency Memo) is issued, 60 days will be counted from the date of submission of fresh refund application (ARN).
– If DM (Deficiency Memo) is issued, 60 days will be counted from the date of submission of fresh refund application (ARN).
– If GST refund is not credited to the bank A/c of the Taxpayer within 60 days as mentioned above, interest @ 6% p.a. on the refund amount will be paid.
- Period of Interest: –From the date immediately after the expiry of 60 days period (as per the above procedure) to the date on which the refund amount was actually credited to the bank a/c of the Taxpayer.
For Example: –
Date of submission of the application (ARN): – 15/05/2018
Refund credited in the Bank A/c: – 28/07/2018
The last date up to which GST refund must be credited to the Bank A/c is 13/07/2018 (i.e. 60 days from the date 15/05/2018)
Hence, the interest would be calculated for the period of (14/07/2018 to 28/07/2018) i.e. for 15 days.
4. Clarification regarding Refund applications that have been generated on the portal but not physically received in the jurisdictional tax offices-
For the refund applications *(except those relating to the refund of excess balance in Electronic Cash ledger): –
i. Amount of refund (less than Rs. 1,000/- per head) should be rejected and recredited in Electronic Credit Ledger.
ii. Other applications of refund, which are not received within 60 days from the date of ARN generation-
– Intimation (mail) will be sent to such Taxpayers to physically submit the documents within 15 days of the date of the mail.
– And if not submitted within the above-mentioned period of 15 days, the refund application shall be rejected and recredited to the Electronic Credit Ledger of the Taxpayer.
For the refund applications generated on the common portal before the issuance of this circular in relation to the excess balance in Electronic Cash Ledger: –
i. The amount of refund applied shall be re-credited to Electronic Cash Ledger provided that no GST liability is pending in liability register.
ii. The said amount shall be re-credited even though GSTR-3B return, as the case may be for the relevant period has not been filed.
5. Process for Application of Refund for Compensation Cess (not claimed earlier in GST return) on A/c of Export with LUT/Bond-
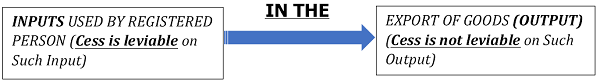
– For the period July 2017 to May 2018, no ITC of cess was claimed in the GST returns. Only the ITC of CGST, SGST & IGST was claimed & refund was applied for the same in the respective months.
– Vide Circular No. 45/19/2018-GST dated 30.05.2018, it was clarified that refund of accumulated ITC of compensation cesson account of export made under LUT/Bond, is available even if cess is not leviable on exported product.
– After this circular, the registered person decides to start exporting under bond/LUT without payment of tax. They also availed the old ITC of cess (not claimed earlier) for the period of July 2017 to May 2018in the GST return of July 2018.
– The registered person then goes on to file refund claim for ITC accumulated on account of exports for the month of July, 2018 and includes the said accumulated ITC of Cessin that refund amount.
Clarification: – As per this circular, in the cases as mentioned above, refund of cess is to be *re-computed on monthly basis for the period of July 2017 to May 2018 as if the same was available in the respective months.
* Meaning of re-computed as per GST Act: –
Refund of Cess shall be re-computed as per the following formula-
Refund Amount of Cess = Net ITC of Cess X (Value of Export of goods & services) / (Adjusted Total Turnover)
i. If the aggregate of recomputed value (e.g. For July 2017 to May 2018 as per above) is less than or equal to the eligible refund of Cess computed for the month in which it was actually claimed (e.g. July 2018 as per above), then the aggregate of the recomputed refund of compensation cess of the respective months would be allowed.
ii.If the inputs used in the “export with payment of Tax”e. without LUT/Bond, refund for that part of recomputed value of cesswould not be allowed. It means for taking refund of Input Cess, the export must be done with LUT/Bond.
This process would be applicable for application for refund of compensation cess (not claimed earlier) in respect of the past period.
6. Issue related to the refund of accumulated Input Tax Credit of Compensation Cess: –

Now refund is filed for the accumulated ITC of Cess paid on coal.
Question-: Can the said refund claim be rejected on the ground that coal is used for the generation of electricity which is an intermediate product and not the final product which is exported and since electricity is exempt from GST, the ITC of the tax paid on coal for generation of electricity is not available?
Answer-: There is no distinction between intermediate goods or services and final goods or services under GST. Since coal is an input used in the production of aluminium, even indirectly through the captive generation of electricity and electricity is directly connected with the business of the registered person. Hence, input tax credit in relation to the same cannot be denied. (Hence refund of accumulated Cess in this case will be allowed).
Description of the issue-
– A registered person avails the ITC of Compensation Cess (e.g. Rs. 100/-)paid on the purchase of coal every month,
– At the same time, he reverses a certain proportion (e.g. Rs. 50/-) of the ITC of cess so availed on purchases of coal which are used in making zero rated outward supplies.
– Both these details are entered in the FORM GSTR-3B filed for the month as a result of which an amount of Rs. 50/- only is credited in the electronic credit ledger.
– *The reversed amount (i.e. Rs. 50/-) is then shown as a ‘cost’ in the books of accounts of the registered person.
– Assuming the Total Turnover is Rs. 5,00,000/- and Export Turnover is Rs. 1,00,000/-
Question-: What would be the amount of refund of unutilized ITC on A/c of zero-rated supplies, as allowed by the proper officer?
Answer-: ITC which is reversed cannot be considered as ‘availed’ in the relevant period. Therefore, the same cannot be part of refund of unutilized ITC on account of zero-rated supplies.
Hence the refund amount would be calculated as follows: –
Net ITC unutilized = Rs. 50/- only (which is not reversed)
Maximum Refund Amount = 50 x 1,00,000/5,00,000
= Rs. 10/-
However, if that reversed part (i.e. Rs. 50/-) is reclaimed in the later tax period (till the due date of GST return of Sep month of the next FY), it can be refunded in the ratio of Export Turnover to Total turnover of that tax period as per the same procedure as explained above.
*For getting the refund of that reversed part in the later tax period, the accounting entry showing that ITC as cost must also be reversed.
8. Refund of ITC of GST paid on invoices of earlier tax period but availed in the subsequent tax period-
– Goods purchased against a Tax invoice which is issued in Aug 2017,
– but ITC on that invoice was availed in the GST return of Sep 2017,
– that ITC can not be excluded from the calculation of the refund amount for the month of Sep 2017.
Net ITC means input availed during the relevant period but only till the due date of GST return of Sep month of the next FY.
Relevant period means the period for which the refund claim has been filed.
In the above case, the relevant period would be Sep 2017. Input will be deemed to have been availed when it is shown in GSTR-3B, and was reflected in the Electronic Credit Ledger. Hence, that ITC would be included in the refund calculation for the month of Sep 2017.
9.Clarification regarding the eligibility of inputs for being included in “Net ITC” for the calculation of GST refund-
Question 1-: Whether the following items are considered as “Inputs” to be included in “Net ITC for the calculation of GST refund?
– ITC on stores & spares
– ITC on packing materials
– ITC on materials purchased for machinery repairs
– ITC on printing & stationery items
Question 2-: Whether ITC on stores & spares (recognized as revenue expenditure) is allowed to be included in “Net ITC” for the calculation of GST refund?
Clarification: – First of all, eligibility of ITC has nothing to do with that whether that input is used in manufacturing or sale of final product.
The ITC of GST will be allowed to a registered person subject to the following conditions: –
I. The registered person uses or intents to use such inputs for the purpose of his/her business; and
II. There is no specific restriction on the availment of such ITC in GST Act
III. There is no specific restriction on such inputs u/s 17(5) i.e. blocked credit
Answer 1-: ITC on such inputs shall be allowed & be included in “Net ITC” as long as these inputs are used for the purpose of the business and/or for effecting taxable supplies, including zero-rated supplies, and the ITC for such inputs is not restricted under section 17(5) i.e. blocked credit of the CGST Act.
Answer 2-: In case the expenditure on stores & spares are recognized as revenue expenditure, such stores & spares cannot be held to be capital goods. Since it is not covered in the definition of “Capital goods” as defined in section 2(19) of the CGST Act.
Hence, ITC availed on stores & spares charged to revenue shall be included in “Net ITC” for the calculation of GST refund.
10. Clarification on the refund of accumulated ITC of input services and capital goods on A/c of inverted duty structure-
Section 2(59) of the CGST Act defines inputs as any goods other than capital goods used or intended to be used by a supplier in the course or furtherance of business.
As per section 54(3) of the CGST Act, only refund of accumulated ITC of inputs is allowed on A/c of inverted duty structure.
Clarification-: Since inputs do not include services or capital goods, the refund of accumulated ITC of input services and capital goods on A/c of inverted duty structure shall not be allowed.
“Inverted duty structure” means the rate of tax on inputs being higher than the rate of tax on output supplies (other than nil rated or fully exempt supplies)
For Example: – Inputs (GST @ 18%) > Output (GST @ 12%)
E. Circular No. 80/54/2018 – Central Tax Dated: – 31st December, 2018
This circular is about the clarifications issued by Government regarding the HSN Code & rate of GST on some items.
| Sr. No. | Name of Item | HSN Code | Rate of GST | Remarks |
| 1. | Chhatua or Sattu | 1106 | NIL Rate | Unbranded |
| 5% | Branded | |||
| 2. | Fish meal and other raw materials used for making cattle/poultry/aquatic feed | 2301 | 5% | – |
| 3. | Animal Feed Supplements/feed additives from drugs | 2309 | As per heading | Specific use as food supplement for animals and not capable of any general use |
| 2936 | As per heading | Vitamins, provitamins are supplied in a form in which they are capable of general use i.e could be used for further processing instead of being ready to use | ||
| 4. | Liquefied Petroleum Gas for Domestic Use (With effect from 25.01.2018) | 2711 | 5% | LPG supplied in bulk, whether by a refiner/ fractionator to an OMC or by one OMC to another for bottling and further supply for domestic use will fall under this code |
| 5. | Polypropylene Woven and Non-Woven Bags and PP Woven and Non-Woven Bags laminated with BOPP | 3923 | 18% | Non-laminated woven bags would be classified as per their constituting materials. |
| 6. | Wood logs for pulping | 4403 | 18% | Wood logs or any kind of wood in the rough/timber, including the wood in rough/log/timber used for pulping falls under this code |
| 7. | Bagasse based laminated particle board | Chapter 44 or any other chapter | 12% (Fixed) | Bagasse board [whether plain or laminated] falling under chapter 44 will attract concessional GST rate of 12%. |
| 8. | Embroidered fabric sold in three piece for lady suits (fabric for suit, salwar and dupatta) | Chapter 50 to 55 and 60 | 5% | Chapter will be classified as per the constituent meterials of fabric |
| 9. | GST on Supply of “Waste to Energy Plant” (WTEP) | Chapter 84, 85 and 94 | 5% | 5% rate only on the following renewable energy devices & parts for their manufacture: (a) Bio-gas plant (b) Solar power based devices (c) Solar power generating system (d) Wind mills, Wind Operated Electricity Generator (WOEG) (e) Waste to energy plants / devices (f) Solar lantern / solar lamp (g) Ocean waves/tidal waves energy devices/plant (h) Photo voltaic cells, whether or not assembled in modules or made up into panels |
| This concession would be available only to such machinery, equipment etc., which fall under Chapter 84, 85 and 94 and used in the initial setting up of renewable energy plants and devices including WTEP | ||||
| This entry does not cover goods falling under other chapters, say a transport vehicle falling under Chapter 87 that may be used for movement of waste to WTEP. | ||||
| Supplier needs to satisfy himself with the requisite document from a buyer such as supply contracts/order for WTEP from the concerned authorities before supplying goods claiming concession under said entry 234. | ||||
| 10. | Turbo Charger for railways | 8414 | 18% | Turbo charger is specifically classified under chapter HS code 8414 80 30. It continues to remain classified under this code irrespective of its use by Railways. |
| 11. | Applicability of GST on supply of cranes, rigs, tools & Spares and other machinery when moved from one state to another by a person on his account for their use for supply of service | ⇒⇒⇒⇒⇒⇒⇒ | This would not be a supply and not be liable to GST subject to the following conditions: – | |
| (a) Inter-state movement of goods for provision of service on own account by a service provider | ||||
| (b) No transfer of title in such goods or transfer of goods to the distinct person by way of stock transfer is involved | ||||
| (c) Such movement is not intended for further supply of such goods. | ||||
F. Circular No. 84/03/2019 – Central Tax Dated: – 01st January, 2019

Wrong SAC code was being used for the above service and that wrong SAC code is 998912 @ 12% GST.
As per the explanatory notes-:
SAC – 998386 @ 18% GST (Photographic and video graphic processing services) includes–
I. Developing of negatives and the printing of pictures for others according to customer specification,
II. Colour printing of images from film or digital media,
III. Slide & negative duplicates, reprints etc.
IV. Developing of film for both amateur photographers and commercial clients,
V. Preparing of photographic slides,
VI. Copying of films,
VII. Conversion of photographs and films to other media.
SAC – 998912 @ 12% GST (Printing & reproduction services of recorded media on a fee or contract basis) excludes–
I. Colour printing of images from film or digital media (SAC – 998386)
II. Audio and video production services (SAC – 999613)
G. Circular No. 85/04/2019 – Central Tax Dated: – 01st January, 2019

However, such supply of food and beverages by: –
– Any person other than the educational institution based on a contractual agreement with such educational institution
Shall be liable to GST @ 5% SAC – 9963 (Supply of Food & beverages services)




