Page Contents
- The Indian MSME Sector
- What’s MSME : What are Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises ? How MSMEs are classified?
- The New Turnover based Classification of MSMEs
- Measures to Improve MSME Capacity and Competency
- Decisions Taken @ 32nd GST Council meeting dated 10.01.2019
- 1. Higher exemption threshold limit for supplier of goods:
- 2. Increase in Turnover Limit for the Existing Composition Scheme for Goods :
- 3. Higher Recommended Threshold Limit only for Providers of Goods & Restaurants
- 4. Compliance simplification under composition scheme
- 5. Free Accounting and Billing Software
- MSME Ministry for Setting up Governing Council to Boost Exports
- A tech-enabled online portal shall be developed
- Export Promotion Council Established for MSME Sector
- Mudra Bank Loan Yojana
The Indian MSME Sector
The Indian MSME sector is the backbone of the national economic structure and has unremittingly acted as the bulwark for the Indian economy, providing it resilience to ward off global economic shocks and adversities.
With around 63.4 million units throughout the geographical expanse of the country, MSMEs contribute around 6.11% of the manufacturing GDP and 24.63% of the GDP from service activities as well as 33.4% of India’s manufacturing output.
MSMEs contribute to 95% of the enterprises in the country. According to 2015-2016 data, there are around 63 million enterprises in India, of which majority are micro and small segments. They have been able to provide employment to around 120 million persons and contribute around 45% of the overall exports from India.
The sector has consistently maintained a growth rate of over 10%.
About 20% of the MSMEs are based out of rural areas, which indicates the deployment of significant rural workforce in the MSME sector and is an exhibit to the importance of these enterprises in promoting sustainable and inclusive development as well as generating large scale employment, especially in the rural areas.
What’s MSME : What are Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises ? How MSMEs are classified?
The government has given a new turnover based classification of MSMEs in February 2018. As per this new classification, the MSMEs are categorized in term of business turnover.
This is in place of the previous classification based on investment made in plant and machineries if they are operating in the manufacturing sector and investment in equipment for service sector companies.
As per the new classification, the same turnover based criteria have been applied for all type of MSMEs including those operating in the services sector.
Though the primary responsibility of promotion and development of MSMEs is of the State Governments, the center has passed an Act in 2006 to empower the sector and also has formed a Ministry (Ministry of MSMEs).
It was the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act which was notified in 2006 that defined the three tier of micro, small and medium enterprises and set investment limits.
The new turnover criteria will better suit with the GST Network (GSTN) and other formats of segregating the MSMEs.
The New Turnover based Classification of MSMEs
The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006 was amended to define units producing goods and rendering services in terms of annual turnover as follows:
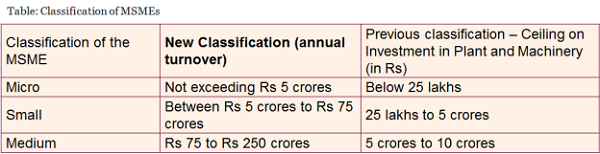
Under the previous classification a separate methodology was adopted for service sector.
Now the classification was made similar to the goods MSMEs as the general turnover-based criteria was made applicable to service sector also.
Measures to Improve MSME Capacity and Competency
To improve its capacity and competency, Government of India has taken many initiatives to eliminate the hindrances and ease the developmental ecosystem of MSMEs. This is to encourage the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises to compete in the domestic as well as international markets.
> Mandatory procurement by PSUs have increased from 20% to 25% and there is 3% reservation for women.
> Technology is the key aspect to drive this sector globally, and said government has set up tech-centers around the country. In addition, 141 cluster development programs have been conducted to train artisans and manufacturers.
> The government has started the ZED Certification Scheme (zero manufacturing defect and zero environmental impact) that guarantees the resultant product being of high quality.
> Technology plays an important role in influencing quality of product, towards which, 20 large and 100 small technology-centres (with expertise in both block chain and artificial intelligence) have been established across the country and 15 more are under construction.
> Identified 15 different locations all over the world for trade promotion services. This will also help in facilitating compliance to international standards.
Decisions Taken @ 32nd GST Council meeting dated 10.01.2019
Higher Threshold Limit for GST Registration
1. Higher exemption threshold limit for supplier of goods:
a. two threshold limits for exemption from registration and payment of GST for supplier of goods:
– Rs. 40 lakhs, and
– Rs. 20 lakhs.
States would have an option to decide about one of the limits within a weeks’ time;
b. threshold limit for exemption for service providers would continue to be as follows:
– Rs. 20 lakhs, and
– Rs. 10 lakhs in case of Special category States.
Comments
Earlier the Threshold Limit is Rs 20 Lakhs (Rs 10 Lakhs in case of Special Category States)
Higher Exemption Threshold Limit for Supplier of Goods only. For Service Provider the earlier Threshold Limits shall Continue.
Effective Date : 1st of April, 2019.
State wise separate registration limit, if decided, will be a departure from uniform applicability across nation.
No Clarity on when the Supplier is Providing both Goods & Services
2. Increase in Turnover Limit for the Existing Composition Scheme for Goods :
The limit of annual turnover in the preceding financial year for availing composition scheme for goods shall be increased to Rs 1.5 crore.
Special category States would decide, within one week, about the composition limit in their respective States.
Comments
Earlier the Threshold Limit is Rs 1 Cr (Rs 75 Lakhs in case of Special Category States)
There was Long pending due for such Recommendation
Effective Date : 1st of April, 2019.
3. Higher Recommended Threshold Limit only for Providers of Goods & Restaurants
Not Applicable for Service Providers
Composition Scheme for Services:
A composition scheme shall be made available for suppliers of services (or mixed suppliers) with a tax rate of 6% (3% CGST + 3% SGST) having an annual turnover in preceding financial year up to Rs 50 lakhs.
The said scheme shall be applicable to both service providers as well as suppliers of goods and services, who are not eligible for the presently available composition scheme for goods.
Comments
Earlier Services (Excepts Food & Beverage Services) are not allowed under Composition Scheme
Effective Date : 1st of April, 2019.
The said scheme shall be applicable to both service providers as well as suppliers of goods and services, who are not eligible for the presently available composition scheme for goods
Manufacturers of Demerit Items like Ice Cream, Tobacco Products & Pan Masala are now Eligible for this Scheme
4. Compliance simplification under composition scheme
The compliance under composition scheme shall be simplified as now they would need to file one annual return but payment of taxes would remain quarterly(along with a simple declaration).
Comments
As of now Every Composition Dealer shall File Quarterly Return GSTR 4 by 18th of the Month following the Quarter.
Now it is Proposed to Simplify by allowing Filling on Annual Basis.
However, payment of taxes would remain quarterly (along with a simple declaration).
Effective Date : 1st of April, 2019.
In due Course Govt Shall Notify Proposed Format for Tax Payment
5. Free Accounting and Billing Software
Software for Accounting and Billing shall be provided to small taxpayers by GSTN.
Comments
This will be a Great Relief to MSME, as they are Struggling to File Returns
This will also Expected to Improve Compliance
MSME Ministry for Setting up Governing Council to Boost Exports
The ministry has recommended a detailed analysis of various trade agreements, including FTAs and bilateral and multilateral trade agreements, to identify areas of concern for MSMEs.
The MSME Ministry has proposed to establish a governing council to ensure efficient delivery of all export-related interventions as part of its action plan to boost shipments from micro, small and medium enterprises.
The ministry has recommended a detailed analysis of various trade agreements, including FTAs and bilateral and multilateral trade agreements, to identify areas of concern for MSMEs in the strategic action plan titled ‘Unlocking the Potential of MSME Exports’.
It said a study will be conducted of special economic zones and export promotion zones in the country to reassess their role and objectives as these are an essential constituent of Foreign Trade Policy and it is important to harness their potential.
A tech-enabled online portal shall be developed
Moreover, a tech-enabled online portal shall be developed featuring country-wise list of global products and services in demand and information on how to enter specific foreign markets. It will also have details on loans and credit offered by various financial institutions.
A formal platform may also be created by the ministry to ensure that it is involved in all bilateral and multilateral trade negotiations which have an impact on the enterprises.
The governing council shall be chaired by Secretary, MSME and co-chaired by Development Commissioner in MSME Ministry. It shall comprise senior officials and members from MSME Ministry, Commerce Ministry, MSME Export Promotion Councils, Export Development Authorities, Commodity Boards, etc., the MSME Ministry said.
National Resource Centre for MSME Exporters will engage with various international agencies
As part of the action plan, National Resource Centre for MSME Exporters will engage with various international agencies including UN organisations to promote procurement from Indian MSMEs and further enhance their capabilities.
A guide or handbook shall also be developed to help the export community to understand the processes involved in export business, access the potential markets etc. The guide shall consists of practical information which will be useful for exporters.
Export Promotion Council Established for MSME Sector
Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) has recently established an Export Promotion Cell with an aim to create a sustainable ecosystem for entire MSME development.The benefits likely to accrue to the MSMEs are:
1. Evaluate readiness of MSMEs to export their products and services
2. Recognize areas where improvements are required in order to be able to export effectively and efficiently
3. Integration of MSME into global value chain. This was stated by Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises,Giriraj Singh in theLok Sabha today, while replying to a question.
The MSME Minister further said that the current status of exports from the MSME sector as per the information received from Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics (DGCIS), the value of MSME related products is USD 147,390.08 million and share of MSME related products in the country’s exports was 48.56% during 2017-18.
To ensure efficient and effective delivery of all MSME export related interventions, the Ministry proposed to formulate a governing council that will be chaired by Secretary, M/o MSME and Co-chaired by Development Commissioner, M/o MSME. The council will comprise of senior officials and members from M/o MSME, Commerce, MSME Export Promotion Councils, Export Development Authorities, Commodity Boards, and other bodies.
An action plan is also proposed to be put in place to achieve the following objectives:
> Target of USD 100 billion of exports from India by 2020
> Evaluate readiness of MSMEs to export their products and services
> Recognize areas where improvements are required in order to be able to export effectively and efficiently
> Integration of MSMEs into Global Value Chain.
Mudra Bank Loan Yojana
Key Features for Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana:
> Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana– The Indian government has come with loan scheme and named as Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana and it is also called as Mudra Loan Yojana. Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana is the Indian government scheme to “Fund the unfunded”.
> Indian government supports the micro or small business as well as start-ups. Micro-unit development and refinance agency popularly called as Mudra
> Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojanais the refinancing agency and not a direct financial institution
> Mudra is the common platform where financial institutions like RRBs, banks, MFIs, NBFCs will meet the applicants to set up their micro-enterprises.
> Under this scheme there can be sole proprietors, manufacturers, partnership firms, machinery business and more can be considered.
Types of Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana loans
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana – PMMY has issued 3 types of loans for applicants. The loan types are listed below:
> Shishu: This Shishu loan is issued for the people who required lesser funds. Applicant will get loan up to Rs 50,000 under this stage
> Kishor: Kishor loan is the issue for the people who are already started their business and want some funds to improve their business. The applicant will get loan between Rs 50,000 to Rs 5 Lakh.
> Tarun: In this stage, an applicant will get highest loan amount and required eligible conditions. The applicant will get the loan above Rs 5 Lakh and up to Rs 10 lakh.
Under this scheme which type of firms can apply?
Any type of firm either it individual or partnership comes under the purview of being NCSBS (non corporate small business segments) can avail of this scheme. This NCSBS can be in urban and rural areas.
> A manufacturing Unit
> An artisan
> A service sector unit
> A food service/food processing unit
> Fruit or vegetable vendor
> A shopkeeper
> Small industrial unit
> A truck operator
> Under the Mahila Uddyami Scheme, a woman entrepreneur can also avail of the scheme. It is part of MUDRA Yojana, the woman can also apply for Loan under all loan categories like Shishu, Kishor, and Tarun.
Mudra Bank Loan Yojana Interest rates
> Interest rates won’t be fixed as well as it depends on the type of business and bank. Each bank will have their criteria. The Indian government may give some subsidy on the interest rates but the particular percentage is still not declared. Mudra loan interest rates are between 10% to 18%.
> Mudra bank loan application form – mudra loan online apply :
> Sponsored Links
> Apply for Pradhan Mantri Mudra Bank Loan Yojana with mudra loan application form online. Download mudra loan application form and apply for Pradhan Mantri Mudra Loan Yojana
How to apply Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana:
Sponsored Links: Visit below Link
http://www.mudraloanyojana.com/apply-pradhan-mantri-mudra-yojana-online/
Here are the steps to apply the Mudra Bank loan Yojana for all categories (Shishu, Kishor, and Tarun)
> Applicants need to visit the private or commercial bank nearest to his/her location
> Submit your business idea with the loan application form
> Along with the form you need to submit the some required documents (as mentioned above)
> All formalities follow as per the bank instructions
> After document verification, your loan will be sanctioned and made available to loan seeker.
Mudra Loan card
This Mudra loan card acts as the credit card with the pre-approved loan amount. It also acts as the debit cards and allows ATM withdrawals.
The Mudra card will work with Rupay platform and can be used or point of sales This card will allow users to:
> Can be used as credit card to avail the Overdraft facility
> Swipe the card at PoS
> Withdraw cash from ATMs
PPT can be viewed @:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_zAejfsApes&t=74s
Disclaimer : The views and opinions; thoughts and assumptions; analysis and conclusions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect any legal standing.
Author : SN Panigrahi, GST Consultant, Practitioner, Corporate Trainer & Author
Can be reached @ snpanigrahi1963@gmail.com





